Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biochem
Uploaded by
Bayriel Dudeq Opok0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views18 pagesOriginal Title
biochem
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views18 pagesBiochem
Uploaded by
Bayriel Dudeq OpokCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
RL10703
Biochemistry for Livestock
Production
Lecture 13
Cellular respiration: Oxidative
Phosphorylation
Dr Wan Ahmad Izuddin Wan Ibrahim
PhD and MSc (Animal Nutrition), BAgr (Animal Science) UPM
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAH
BERTEKAD CEMERLANG
Overall view of cellular respiration
• Glycolysis, Krebs (citric acid) cycle and oxidative phosphorylation.
• Lecture 13: Oxidative phosphorylation
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAH
BERTEKAD CEMERLANG
Mitochondria structure
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAH
BERTEKAD CEMERLANG
Mitochondria structure | Zoom in!
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAH
BERTEKAD CEMERLANG
Let’s recap Krebs cycle
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAH
BERTEKAD CEMERLANG
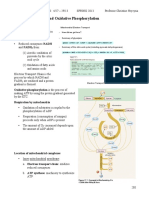
Oxidative phosphorylation
• NADH and FADH2 (by Krebs cycle) supplies the materials for the
next phase: oxidative phosphorylation.
• Oxidative phosphorylation uses an electron transport chain, which
is a series of mitochondrial membrane protein that sit in the inner
membrane.
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAH
BERTEKAD CEMERLANG
Oxidative phosphorylation | Inner membrane
• There are two parts of oxidative phosphorylation
• Electron transport chain (ETC)
• Chemiosmosis
• There are several important key steps in oxidative phosphorylation
1. Delivery of electrons by NADH and FADH
2. Electron transfer and proton pumping Electron transport
chain
3. Splitting of oxygen to form water
4. Gradient-driven synthesis of ATP. Chemiosmosis
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAH
BERTEKAD CEMERLANG
Oxidative phosphorylation | Inner membrane
• There are several types of membrane protein involves in oxidative
phosphorylation
• Complex I, II, III and IV - Involved in electron transport chain.
• Complex V (ATP synthase) – Involved in chemiosmosis
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAH
BERTEKAD CEMERLANG
Oxidative phosphorylation | Electron transport
chain (ETC)
• The concept of electron transport chain:
• transfer of electrons from one membrane proteins to another
(from membrane protein complex I to IV).
• We will see the step by steps on how the electron transfer from
one membrane protein to another.
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAH
BERTEKAD CEMERLANG
Oxidative phosphorylation | Electron transport
chain (ETC)
1. DELIVERY OF ELECTRON BY NADH AND FADH
• NADH and FADH2 give up its electron to membrane protein complex.
• NADH to complex I (NADH à NAD+)
• FADH2 to complex II (FADH2 à FAD)
2. ELECTRON TRANSFER AND PROTON PUMP
• Once NADH feeds electron into complex I, the complex I become
supercharged and start a series of reactions transferring the electron from
complex I to another complex.
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAH
BERTEKAD CEMERLANG
Oxidative phosphorylation | Electron transport
chain (ETC)
2. ELECTRON TRANSFER AND PROTON PUMP
• Supercharged membrane protein complex able to pump the proton (H+)
from mitochondrial matrix to intermembrane space.
• It creates proton gradient.
• Accumulation of proton (H+) at the intermembrane space will induce
another protein complex, the ATP synthase.
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAH
BERTEKAD CEMERLANG
Oxidative phosphorylation | Electron transport
chain (ETC)
3. SPLITTING OF OXYGEN TO FORM WATER
• At the end of electron transport chain, electrons are transferred to
molecular oxygen, which split in half and takes up H+ to form water.
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAH
BERTEKAD CEMERLANG
Oxidative phosphorylation | Chemiosmosis
4. GRADIENT-DRIVEN SYNTHESIS OF ATP
• As H+ ions flow down their gradient and back into the
mitochondrial matrix, they pass through an enzyme called ATP
synthase (the only route).
• Flow of protons (H+) synthesize the ATP from ADP.
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAH
BERTEKAD CEMERLANG
Oxidative phosphorylation | Chemiosmosis
• This process is called chemiosmosis
• The proton power the ATP synthase to phosphorylate ADP to ATP.
• NADH and FADH2 generated from a single molecule of glucose
can produce around 30 - 32 ATP from oxidative phosphorylation.
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAH
BERTEKAD CEMERLANG
Oxidative phosphorylation | Chemiosmosis
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAH
BERTEKAD CEMERLANG
Oxidative phosphorylation | Summary
• 30 - 32 ATP molecules are generated from the electron transport
chain
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAH
BERTEKAD CEMERLANG
Cellular respiration | Summary
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAH
BERTEKAD CEMERLANG
THANK YOU
FOR YOUR ATTENTION
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA SABAH
BERTEKAD CEMERLANG
You might also like
- Electron Transport Chain andDocument25 pagesElectron Transport Chain andLovely Joy Aranda CurammengNo ratings yet
- Oxidative Phosphorylation-WPS OfficeDocument30 pagesOxidative Phosphorylation-WPS OfficeZoyaNo ratings yet
- Electron TransportDocument17 pagesElectron TransportKofi Fofie-AsieduNo ratings yet
- 20 Electron TransportDocument41 pages20 Electron TransportGian BanaresNo ratings yet
- Oxidative Phosphorylation and The Electron Transport Chain (ETC)Document16 pagesOxidative Phosphorylation and The Electron Transport Chain (ETC)glenn johnstonNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation: Paul D. Adams - University of ArkansasDocument43 pagesElectron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation: Paul D. Adams - University of ArkansasKrishly Ann Medina SalazarNo ratings yet
- 1 Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument10 pages1 Oxidative PhosphorylationRoland ToroNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport and Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument38 pagesElectron Transport and Oxidative PhosphorylationSyedaNaveenBatoolNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainetcDocument19 pagesElectron Transport Chainetcpk kaleenaNo ratings yet
- Microbial Physiology Unit 2 Bacterial RespirationDocument37 pagesMicrobial Physiology Unit 2 Bacterial RespirationsankarNo ratings yet
- Etc (Electron Transport Chain)Document24 pagesEtc (Electron Transport Chain)Dark_KiroNo ratings yet
- Oxidative Phosphorylation385184939Document14 pagesOxidative Phosphorylation385184939mohamedamine.abdelhadiNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport Chain: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument16 pagesElectron Transport Chain: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchJennie KimNo ratings yet
- University of Central Punjab: Assignment No. 01 Subject TopicDocument7 pagesUniversity of Central Punjab: Assignment No. 01 Subject TopicAli ImranNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics: Mahpara Gondal Pharm D Ms Pharmaceutical Chemistry Rashid Latif College of PharmacyDocument30 pagesBioenergetics: Mahpara Gondal Pharm D Ms Pharmaceutical Chemistry Rashid Latif College of PharmacyShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainDocument11 pagesElectron Transport ChainSoofia SharifNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument14 pagesBiologyHarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- ETCDocument8 pagesETCRy L.No ratings yet
- Tema 6quim Al17-18Document39 pagesTema 6quim Al17-18noelia100997No ratings yet
- NutCultCatab IIDocument28 pagesNutCultCatab IIDuane HallNo ratings yet
- Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument18 pagesOxidative Phosphorylationjason misticaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Chain & Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument57 pagesRespiratory Chain & Oxidative PhosphorylationHanifa AffianiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6: Part 1 Oxidative Phosphorylation and ETC: Produced by Samira Aili Presented by Alvaro GarciaDocument23 pagesLecture 6: Part 1 Oxidative Phosphorylation and ETC: Produced by Samira Aili Presented by Alvaro Garciakristal elias100% (1)
- Oxidative Phosphorylation - Biology (Article) - Khan AcademyDocument16 pagesOxidative Phosphorylation - Biology (Article) - Khan Academydeepali_nih9585No ratings yet
- Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument40 pagesOxidative PhosphorylationIram AnwarNo ratings yet
- Lehninger ElectronTransportDocument20 pagesLehninger ElectronTransportZahid AliNo ratings yet
- Fosforilasi OksidatifDocument82 pagesFosforilasi OksidatifSanti WilujengNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainDocument3 pagesElectron Transport ChainEmma MelNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation: Refer To: Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry (Chapter 19)Document43 pagesElectron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation: Refer To: Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry (Chapter 19)Yousef KhallafNo ratings yet
- Etc N Oxid PhoshphorylationDocument74 pagesEtc N Oxid Phoshphorylationhassanainshahi13No ratings yet
- Electron Transport Chain - WikipediaDocument53 pagesElectron Transport Chain - WikipediaLsaurusNo ratings yet
- 2023 2024 b3502 Lecture 16 Carbohydrate+Metabolism+Cont Electron+Transport+Chain+and+Oxidative+PhosphorylationDocument14 pages2023 2024 b3502 Lecture 16 Carbohydrate+Metabolism+Cont Electron+Transport+Chain+and+Oxidative+Phosphorylationpitsolerato60No ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument16 pagesBiology ProjectSoumya Ranjan PradhanNo ratings yet
- Biological Oxidation ETCDocument37 pagesBiological Oxidation ETCsanofazal786No ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainDocument18 pagesElectron Transport ChainArlyn Pasion BungbongaNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport Chai1Document6 pagesElectron Transport Chai1shanto.tn98No ratings yet
- Electron Transport and Clinical CorrelationDocument52 pagesElectron Transport and Clinical CorrelationReborn Paredes100% (2)
- Regulation of Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument14 pagesRegulation of Oxidative Phosphorylationmaaz629No ratings yet
- Electron Transport ch14Document21 pagesElectron Transport ch14tania.delafuenteNo ratings yet
- AtthapuDocument21 pagesAtthapuPrashanth PuttapagaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Electron Transport and Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument14 pagesChapter 20 Electron Transport and Oxidative PhosphorylationRaabia Ansari100% (1)
- The Electron Transport Chain Consists of Four Protein ComplexesDocument4 pagesThe Electron Transport Chain Consists of Four Protein ComplexesMD. Humayun KobirNo ratings yet
- ELECTRON-TRANSPORT-CHAIN-STRYERDocument47 pagesELECTRON-TRANSPORT-CHAIN-STRYERAngelikaOdimerNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport and Chemiosmosis-5thDocument68 pagesElectron Transport and Chemiosmosis-5tholawandeilo123No ratings yet
- Biological Oxidation: DR Nazakat Hussain Assistant ProfessorDocument32 pagesBiological Oxidation: DR Nazakat Hussain Assistant ProfessorMuhammad JamalNo ratings yet
- CHO L5, L6 Metabolisim 2nd NutriDocument48 pagesCHO L5, L6 Metabolisim 2nd NutriLeena KhaledNo ratings yet
- 2 Lec. Biochemistry (4th)Document25 pages2 Lec. Biochemistry (4th)Doctor SonuNo ratings yet
- Cell RespirationDocument49 pagesCell RespirationJanine CambaNo ratings yet
- 4.1. Third Stage Metabolism - Electron Transport ChainDocument20 pages4.1. Third Stage Metabolism - Electron Transport ChainJames ChabuNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics Part 3Document36 pagesBioenergetics Part 3CM Nursing DepartmentNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainDocument15 pagesElectron Transport ChainKimber ManiulitNo ratings yet
- 5 BioenergeticsDocument37 pages5 BioenergeticsYashfa YasinNo ratings yet
- Plant Physiology Week 4Document68 pagesPlant Physiology Week 4PENELOPE LAWAGANNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument55 pagesCellular RespirationFuad sabsebNo ratings yet
- 3 Lec. Biochemistry (4th)Document18 pages3 Lec. Biochemistry (4th)Doctor SonuNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport Chain ExplainedDocument9 pagesElectron Transport Chain Explainedmaria genioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument35 pagesLecture 6 Oxidative PhosphorylationBiology BảoNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport and Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument34 pagesElectron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylationapi-321453350No ratings yet
- In Relation To Lsm2101 Lec 2Document11 pagesIn Relation To Lsm2101 Lec 2jojolim18No ratings yet
- Chemistry - 2Document173 pagesChemistry - 2utkarshgourfake8No ratings yet
- Edexcel IAL Biology A Level 12: Core PracticalDocument5 pagesEdexcel IAL Biology A Level 12: Core Practicalrifu91No ratings yet
- Mixture and Alligation Last 5 Year Best Questions by Gagan PratapDocument8 pagesMixture and Alligation Last 5 Year Best Questions by Gagan Pratapprashant.1196tyagiNo ratings yet
- Amine Expert Company PDFDocument2 pagesAmine Expert Company PDFWajid NizamiNo ratings yet
- Makin (2019) PDSNDocument11 pagesMakin (2019) PDSNFabricio CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Effect of Beeswax Content On Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose-Based Edible FilmDocument7 pagesEffect of Beeswax Content On Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose-Based Edible Filmcarranclan077No ratings yet
- 9.8 Iron Extraction Steel Making Set 4 QP MsDocument8 pages9.8 Iron Extraction Steel Making Set 4 QP MsdawsontangxyNo ratings yet
- UV-Visible Systems - Operational Qualification - Col23 PDFDocument10 pagesUV-Visible Systems - Operational Qualification - Col23 PDFIsabelle PlourdeNo ratings yet
- Tribromoisocyanuric Acid As A Green Reagent For Benzylic Bromination of AlkylarenesDocument3 pagesTribromoisocyanuric Acid As A Green Reagent For Benzylic Bromination of AlkylarenesjavasoloNo ratings yet
- Hydroxymethylfurfural From Fructose WO20130538Document14 pagesHydroxymethylfurfural From Fructose WO20130538ramcatNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction Lab (11Document7 pagesRate of Reaction Lab (11Sara Alexander100% (3)
- Case Study:Iron Pillar Near Qutub Minar: Ji .'1, FJF,) .'1, (Document1 pageCase Study:Iron Pillar Near Qutub Minar: Ji .'1, FJF,) .'1, (Maina SharmaNo ratings yet
- Use of Industrial Waste - (Red Mud) in The Production of Self Compacting ConcreteDocument8 pagesUse of Industrial Waste - (Red Mud) in The Production of Self Compacting ConcreteIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Aci 548.3R-03Document40 pagesAci 548.3R-03jerryNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 01 - ThermochemistryDocument78 pagesSheet - 01 - ThermochemistrySushant VermaNo ratings yet
- Denge Kimya Ve Tekstil Tic A.S - Chemchecksummary - 28!08!2023Document50 pagesDenge Kimya Ve Tekstil Tic A.S - Chemchecksummary - 28!08!2023syed adnan naqviNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Bonding: Where To Find Hydrogen Bonds?Document28 pagesHydrogen Bonding: Where To Find Hydrogen Bonds?Rahul DhimanNo ratings yet
- Solving Problems Regarding Vapor-Liquid EquilibriumDocument19 pagesSolving Problems Regarding Vapor-Liquid EquilibriumblessaNo ratings yet
- MSDS - TDS Hyaluronic AcidDocument3 pagesMSDS - TDS Hyaluronic AcidDominique WNo ratings yet
- La Flotación de Esfalerita Mía Relaves Como Remediación MétodoDocument11 pagesLa Flotación de Esfalerita Mía Relaves Como Remediación MétodokristallNo ratings yet
- M.Sc. (Part-II) (Chemistry) (For Colleges) - 18.082020Document120 pagesM.Sc. (Part-II) (Chemistry) (For Colleges) - 18.082020KuNdAn DeOrENo ratings yet
- NACOL - NAFOL Fatty AlcoholDocument20 pagesNACOL - NAFOL Fatty AlcoholAlexander100% (1)
- Crystals: Anti-Solvent Crystallization Strategies For Highly Efficient Perovskite Solar CellsDocument21 pagesCrystals: Anti-Solvent Crystallization Strategies For Highly Efficient Perovskite Solar CellsGianluca J BravettiNo ratings yet
- Flogard MS6209Document1 pageFlogard MS6209Arunkumar ChandaranNo ratings yet
- Aiats Schedule For Class Xii (CF + Oym) 2021-22Document2 pagesAiats Schedule For Class Xii (CF + Oym) 2021-22Lian M ShineNo ratings yet
- Act 2 Gas Law Avogadro's and Idealgas LawDocument5 pagesAct 2 Gas Law Avogadro's and Idealgas LawMark TomoNo ratings yet
- CLO2 Sensor 110 - MWC Instruction Manual MCD7 - MPES7 - MOZ7 - MWP7 PDFDocument27 pagesCLO2 Sensor 110 - MWC Instruction Manual MCD7 - MPES7 - MOZ7 - MWP7 PDFSergio HernandezNo ratings yet
- 2019 Cisile Exhibitor ListDocument5 pages2019 Cisile Exhibitor ListKanagarajan UmapathiNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Consumabili Elga 2017Document150 pagesCatalogo Consumabili Elga 2017Eraldo MigliavaccaNo ratings yet