Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Oxidative Phosphorylation385184939
Uploaded by
mohamedamine.abdelhadi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views14 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views14 pagesOxidative Phosphorylation385184939
Uploaded by
mohamedamine.abdelhadiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
Oxidative Phosphorylation
dr. Sri Wahyuni, M.Sc.
Biochemistry Department
Faculty of Medicine Universitas
Malikussaleh
INTRODUCTION
• Oxidative phosphorylation is the process in
which ATP is formed as a result of the transfer
of electrons from NADH or FADH2 to O2 by a
series of electron carriers.
• This process, which takes place in
mitochondria, is the major source of ATP in
aerobic organisms
• Oxidative phosphorylation is conceptually
simple and mechanistically complex
• Oxidative phosphorylation is the culmination of a series of
energy transformations that are called cellular respiration
• First, carbon fuels are oxidized in the citric acid cycle to yield
electrons with high transfer potential → this electron-motive
force is converted into a proton-motive force and → the
proton-motive force is converted into phosphoryl transfer
potential.
• The conversion of electron-motive force → proton-motive
force is carried out by three electron-driven proton pumps
NADH-Q oxidoreductase, Q-cytochrome c oxidoreductase, and
cytochrome c oxidase
• The final phase of oxidative phosphorylation is carried out by
ATP synthase, an ATP-synthesizing assembly that is driven by
the flow of protons back into the mitochondrial matrix.
Essence of Oxidative Phosphorylation
• Oxidation and ATP
synthesis are coupled
by transmembrane
proton fluxes.
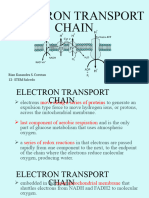
Diagram of a Mitochondrion
• Oxidative
phosphorylation takes
place in the inner
mitochondrial
membrane, in contrast
with most of the
reactions of the citric
acid cycle and fatty acid
oxidation, which take
place in the matrix
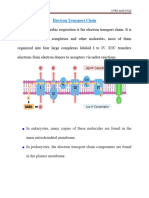
The Respiratory Chain Consists of Four Complexes: Three Proton Pumps and a
Physical Link to the Citric Acid Cycle
The respiratory chain is one of the pathways involved in
oxidative phosphorylation
It catalyzes the steps by which electrons are transported from
NADH+H+ or reduced
ubiquinone (QH2) tomolecular oxygen
Most of the energy released is used to establish a proton
gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane, which is
then ultimately used to synthesize ATP with the help of ATP
synthase.
Components of the respiratory chain
• The electron transport chain consists of:
ü3 protein complexes (complexes I, III, and IV),
which are integrated into the
innermitochondrial membrane, and
ü2 mobile carrier molecules— ubiquinone
(coenzyme Q) and cytochrome c
• Oxidative
phosphorylation takes
place in the inner
mitochondrial
membrane, in contrast
with most of the
reactions of the citric
acid cycle and fatty acid
oxidation, which take
place in the matrix
You might also like
- Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument40 pagesOxidative PhosphorylationIram AnwarNo ratings yet
- 20 Electron TransportDocument41 pages20 Electron TransportGian BanaresNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport Chain andDocument25 pagesElectron Transport Chain andLovely Joy Aranda CurammengNo ratings yet
- Biological Oxidation ETCDocument37 pagesBiological Oxidation ETCsanofazal786No ratings yet
- Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation: Paul D. Adams - University of ArkansasDocument43 pagesElectron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation: Paul D. Adams - University of ArkansasKrishly Ann Medina SalazarNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation: Refer To: Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry (Chapter 19)Document43 pagesElectron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation: Refer To: Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry (Chapter 19)Yousef KhallafNo ratings yet
- Electron TransportDocument17 pagesElectron TransportKofi Fofie-AsieduNo ratings yet
- Microbial Physiology Unit 2 Bacterial RespirationDocument37 pagesMicrobial Physiology Unit 2 Bacterial RespirationsankarNo ratings yet
- BiochemDocument18 pagesBiochemBayriel Dudeq OpokNo ratings yet
- NutCultCatab IIDocument28 pagesNutCultCatab IIDuane HallNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument14 pagesRegulation of Oxidative Phosphorylationmaaz629No ratings yet
- Electron Transport and Clinical CorrelationDocument52 pagesElectron Transport and Clinical CorrelationReborn Paredes100% (2)
- Bioenergetics: Mahpara Gondal Pharm D Ms Pharmaceutical Chemistry Rashid Latif College of PharmacyDocument30 pagesBioenergetics: Mahpara Gondal Pharm D Ms Pharmaceutical Chemistry Rashid Latif College of PharmacyShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- 3 Lec. Biochemistry (4th)Document18 pages3 Lec. Biochemistry (4th)Doctor SonuNo ratings yet
- Biological OxidationDocument35 pagesBiological Oxidationjou joNo ratings yet
- 5 BioenergeticsDocument37 pages5 BioenergeticsYashfa YasinNo ratings yet
- Oxidative Phosphorylation and The Electron Transport Chain (ETC)Document16 pagesOxidative Phosphorylation and The Electron Transport Chain (ETC)glenn johnstonNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainetcDocument19 pagesElectron Transport Chainetcpk kaleenaNo ratings yet
- University of Central Punjab: Assignment No. 01 Subject TopicDocument7 pagesUniversity of Central Punjab: Assignment No. 01 Subject TopicAli ImranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Electron Transport and Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument14 pagesChapter 20 Electron Transport and Oxidative PhosphorylationRaabia Ansari100% (1)
- Lehninger ElectronTransportDocument20 pagesLehninger ElectronTransportZahid AliNo ratings yet
- 1 Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument10 pages1 Oxidative PhosphorylationRoland ToroNo ratings yet
- Respiration Lecture 2-3Document49 pagesRespiration Lecture 2-3Mr. Faraz KhanNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport and Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument38 pagesElectron Transport and Oxidative PhosphorylationSyedaNaveenBatoolNo ratings yet
- Etc (Electron Transport Chain)Document24 pagesEtc (Electron Transport Chain)Dark_KiroNo ratings yet
- Cell RespirationDocument49 pagesCell RespirationJanine CambaNo ratings yet
- Tema 6quim Al17-18Document39 pagesTema 6quim Al17-18noelia100997No ratings yet
- Lec. 1 Respiratory ChainDocument6 pagesLec. 1 Respiratory ChainhawraaNo ratings yet
- MCB201 L-TWO (General Microbiology I)Document16 pagesMCB201 L-TWO (General Microbiology I)omotolaNo ratings yet
- CHO L5, L6 Metabolisim 2nd NutriDocument48 pagesCHO L5, L6 Metabolisim 2nd NutriLeena KhaledNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Bio Topic 5Document6 pagesEdexcel Bio Topic 5quesntinmoorsNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainDocument15 pagesElectron Transport ChainKimber ManiulitNo ratings yet
- (Bio3lec4) ETCDocument36 pages(Bio3lec4) ETCHerpy OtterNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainDocument33 pagesElectron Transport ChainAfaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- STPM BIOLOGY RespirationDocument14 pagesSTPM BIOLOGY Respirationwkwhui75% (4)
- Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical EnergyDocument37 pagesCellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical EnergyEdward GanggangNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport Chai1Document6 pagesElectron Transport Chai1shanto.tn98No ratings yet
- Ch. 9 Biological OxidationDocument71 pagesCh. 9 Biological OxidationKrishna KanthNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument55 pagesCellular RespirationFuad sabsebNo ratings yet
- Biology Guided NotesDocument2 pagesBiology Guided NotesDanny BayerNo ratings yet
- Electron TransportDocument8 pagesElectron Transportเทพนิมิตร สมภักดีNo ratings yet
- Chemiosmosis: By: Albolote & GelilangDocument15 pagesChemiosmosis: By: Albolote & GelilangQuenard Medillo GalesNo ratings yet
- ELECTRON-TRANSPORT-CHAIN-STRYERDocument47 pagesELECTRON-TRANSPORT-CHAIN-STRYERAngelikaOdimerNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport Channel & Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument55 pagesElectron Transport Channel & Oxidative PhosphorylationShahabNo ratings yet
- Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument18 pagesOxidative PhosphorylationNeel JhalaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 NMJ10103 Answer SchemeDocument5 pagesTutorial 2 NMJ10103 Answer SchemeWendy LohNo ratings yet
- Chemiosmosis ReportDocument23 pagesChemiosmosis ReportArlyn Pasion BungbongaNo ratings yet
- Portal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksDocument4 pagesPortal For CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and TricksSHRAVYA K REDDYNo ratings yet
- Plant Physiology Week 4Document68 pagesPlant Physiology Week 4PENELOPE LAWAGANNo ratings yet
- 20 (Lloyd)Document3 pages20 (Lloyd)CJ PorrasNo ratings yet
- Oxidative Metabolism 1Document24 pagesOxidative Metabolism 1Frolian MichaelNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument43 pagesPhotosynthesisOussema Ben KasdallahNo ratings yet
- 4.1. Third Stage Metabolism - Electron Transport ChainDocument20 pages4.1. Third Stage Metabolism - Electron Transport ChainJames ChabuNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainDocument8 pagesElectron Transport ChainMituSamadderNo ratings yet
- 2021 Learning Material in MC 2 Chapter 7Document5 pages2021 Learning Material in MC 2 Chapter 7Domusthones TuplanoNo ratings yet
- Electron Transport ChainDocument18 pagesElectron Transport ChainArlyn Pasion BungbongaNo ratings yet
- Title: Electron Transport System (Aerobic)Document4 pagesTitle: Electron Transport System (Aerobic)GISRemoteSensingNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 2: ChloroplastsDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis 2: ChloroplastsBonny Ya SakeusNo ratings yet
- Microbial Energy ConservationDocument30 pagesMicrobial Energy ConservationSantos, Kimberly R.No ratings yet
- Human Metabolism MapDocument1 pageHuman Metabolism MapPkern83% (6)
- Electron Transport ChainDocument35 pagesElectron Transport ChainNusrat JahanNo ratings yet
- I. Specific Catabolic PathwaysDocument17 pagesI. Specific Catabolic PathwaysMary Rose Bobis VicenteNo ratings yet
- Marks Basic Medical Biochemistry A Clinical ApproachDocument61 pagesMarks Basic Medical Biochemistry A Clinical Approachwillie.kostyla455100% (43)
- Cellular Respiration - Fermentation Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesCellular Respiration - Fermentation Review WorksheeterikabeltranNo ratings yet
- 2.1. Factors Affecting PhotosynthesisDocument12 pages2.1. Factors Affecting PhotosynthesisGabriel Alejandro Garcia OrregoNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration in Animals Plants Notes-2022-2023Document17 pagesCellular Respiration in Animals Plants Notes-2022-2023MARIA ISABILLE DUALLO MUSONGNo ratings yet
- Bio 4212examDocument5 pagesBio 4212examAsheNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 4 Moses Miller - Overview of Enzyme KineticsDocument5 pagesWorksheet 4 Moses Miller - Overview of Enzyme Kineticsscience departmentNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10-Integration of MetabolismDocument4 pagesChapter 10-Integration of MetabolismJenelyn Lanang DiariosNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Metabolism: Santosh YadavDocument36 pagesBacterial Metabolism: Santosh YadavAurora ÇizmjaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of CVSDocument311 pagesBiochemistry of CVSAsne ManNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 4.1-4.3Document6 pagesStudy Guide 4.1-4.3Bekani SanchezNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Carbohydrates Part 2Document53 pagesUnit 2 - Carbohydrates Part 2Avril Ros ReyesNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Unit TwoDocument158 pagesBiology Notes Unit TwoBlohsh KeenenNo ratings yet
- Cell RespirationDocument19 pagesCell RespirationPauline FrascaNo ratings yet
- How Cells Harvest Chemical EnergyDocument75 pagesHow Cells Harvest Chemical EnergylinNo ratings yet
- Pemberdayaan Masyarakat Dalam Pencegahan Dan Penanganan Asam Urat Pada LansiaDocument7 pagesPemberdayaan Masyarakat Dalam Pencegahan Dan Penanganan Asam Urat Pada LansiaLutfi VaniaNo ratings yet
- Review Inhibitory Metabolites PDFDocument13 pagesReview Inhibitory Metabolites PDFManika KargetiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Kmk22004 Industrial MicrobiologyDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 Kmk22004 Industrial Microbiologyaliaanis386No ratings yet
- Worksheet: Cellular Respiration & Cell EnergyDocument4 pagesWorksheet: Cellular Respiration & Cell Energyclaryl alexaNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1 BIS2A Section KeyDocument6 pagesMidterm 1 BIS2A Section KeyKevinZamudioNo ratings yet
- 3 Glikolisis 9Document17 pages3 Glikolisis 9Rafi Ahmad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 17 - Nutrition, Metabolism, & Body Temperature Regulation)Document17 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 17 - Nutrition, Metabolism, & Body Temperature Regulation)Eliezer NuenayNo ratings yet
- Lipid MetabolismDocument17 pagesLipid MetabolismMiran El-MaghrabiNo ratings yet
- 22 PhotosynthesisDocument12 pages22 Photosynthesisvickytang22072002No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - Shobhit NirwanDocument21 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher Plants - Shobhit NirwanVraj M Barot100% (1)
- Cellular Respiration Model SHODocument4 pagesCellular Respiration Model SHODeana Amira MontgomeryNo ratings yet
- SCHOOL COPY Gen Bio 1 - Q2 Module 4Document20 pagesSCHOOL COPY Gen Bio 1 - Q2 Module 4PLS help me get 1k subsNo ratings yet