Professional Documents
Culture Documents
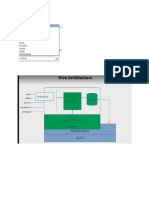
Hive Code
Uploaded by
Abdul KhaliqOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hive Code
Uploaded by
Abdul KhaliqCopyright:
Available Formats
Hive Illustration : Basics
To get started with the hive shell,
hive
To check what is present in the HDFS,
hadoop fs – ls
To create a directory in the current path (let’s say the name is ‘foo’),
hadoop fs - mkdir foo
To create a database, in the hive shell (let’s say the name is ‘vin_emp’),
create database vin_emp;
To see existing databases,
show databases;
To start using the database,
use vin_emp;
To check the tables present in the database,
show tables;
To come out of the hive shell,
quit;
to list contents of the current working directory,
ls
To create a directory,
mkdir myhivedata
To navigate into that data,
cd myhivedata
To check the present working directory
pwd
To check the contents of a file (name of the file is employees.txt),
cat employees.txt
To create a table within the hive shell,
create table emp_global(id int,name string,city string,continent string)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ‘ , ‘
stored as textfile ;
To check the tables,
show tables ;
To query the table,
select * from emp_global ;
To load data into the table,
load local inpath ‘employees.txt’ into table emp_global;
To drop all tables inside a database,
drop database vin_emp cascade,
To know the schema of the table,
describe emp_global ;
To drop a table,
drop table emp_global ;
Hive Illustration : External tables in hive
To create a database in a certain desired location,
create database vin_emp_loc location ‘/user/cloudera/myhivedata’ ;
To copy a file from local file system to hdfs location,
hadoop fs – put empglobal.csv empdata
To see the contents of the file,
hadoop df – cat empdata/empglobal.csv
Hive Illustration : Loading different file formats
How to know what the table type is, whether internal or external,
describe extended emp_global ;
To load the data into orc table,
insert into table emp_global_orc select * from emp_global ;
Create a table whose schema is exactly like an existing table,
create table emp_global_seq LIKE emp_global_orc stored as sequencefile ;
Hive Illustration : Loading data into Hive tables
Create table only if another table of the same name doesn’t exist and an input multiple
values in a single column using an array,
create table if not exists sibling_data (
name string, age int, country string, siblings array<string> )
row format delimited
fields terminated by ‘ , ‘
collection items terminated by ‘#’
lines terminated by ‘\n’
sorted as textfile ;
To create table with multiple inputs of different data type in a single column,
create table auto_details(company string, model string, fuel string,
basic_specs struct<vehicle_type : string, doors : int, gears : int>,
engine_specs struct<cc : int, bhp : double>)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ‘ , ‘
collection items terminated by ‘#’ ;
Hive Illustration : Simple Operations on Hive tables
To rename an existing table,
alter table auto_details rename to auto_table ;
To change the name of any column,
alter table auto_details change fuel fuel_type string ;
To add a new column to an existing table,
alter table auto_details add columns (milage double) ;
To drop columns,(mention columns which need to remain inside the brackets after “replace”
keyword)
alter table auto_details replace (company string, model string, fuel_type string) ;
Hive Illustration : Query Operations on Hive tables
To create a table inside a desired pre-existing database, without navigating into the
database first
create table if not exists company.empdata (
empid int,
empname string,
salary double,
designation string,
department string,,
salary double,
designation string,
department string,
age int)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ‘ , ‘
lines terminated by ‘\n’
tblproperties(‘skip.header.line.count’ = ‘1’) ;
To select all columns and only those rows which satisfy a certain condition,
select * from empdata where department = “HR” ;
To select all columns and only those rows which satisfy more than one condition,
select * from empdata where department =”HR” and salary > 25000 ;
To select only desired columns and only those rows which satisfy more than one condition,
select empname, age from empdata where department =”HR” and salary > 25000 ;
To select all columns and sort the rows based on a desired column,
select * from empdata order by salary ;
To select all columns and sort the rows based on a desired column in descending order,
select * from empdata order by salary desc ;
To count the total number of rows in the dataset,
select count(*) from empdata ;
To use ‘groupby’ to count number of rows based in each category of a certain column,
select department, count(*) from empdata group by department ;
To select all column but only those rows which do not have null value in a desired column,
select * from empdata where salary is not null ;
To select rows by matching a substring with a desired column value,
select * from empdata where designation rlike “Manager” or rlike “manager” or “Lead” ;
To find the average of a desired numerical column, grouped by a categorical column,
select department, avg(salary) from empdata group by department;
Hive Illustration : Querying complex structures
To enable join operations in the hive shell,
SET hive.auto.conveert.join = False;
To perform a join operation,
select emp.empname, emp.salary from emp_epf pf join empdata emp on (pf.empid = emp.empid) ;
To perform a left outer join operation,
select emp.empname, emp.salary from emp_epf pf left outer join empdata emp on (pf.empid =
emp.empid) ;
To perform a right outer join operation,
select emp.empname, emp.salary from emp_epf pf right outer join empdata emp on (pf.empid =
emp.empid) ;
To perform a full outer join operation,
select emp.empname, emp.salary from emp_epf pf full outer join empdata emp on (pf.empid =
emp.empid) ;
Hive Illustration : Views
To create view,
create view if not exists high_sal as select * from empdata where salary > 50000 ;
To query data from view,
select * from high_sal ;
To see if view is created,
show tables ;
To see the table type, (virtual or Managed),
describe formatted high_sal ;
To create a table, partitioned by a desired column,
create table emp_global_part(id int, name string, city string, country string)
portioned by (continent string)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ‘ , ‘
stored as textfile ;
You might also like
- HivepptDocument29 pagesHivepptkavithaNo ratings yet
- BignoteDocument4 pagesBignotedavidNo ratings yet
- InterDocument8 pagesInterAnonymous rt8iK9pbNo ratings yet
- Hari Hive AssignmentDocument4 pagesHari Hive AssignmentHari SampathiraoNo ratings yet
- Python Data CleaningDocument20 pagesPython Data CleaningBeni Djohan100% (1)
- Hive TutorialDocument25 pagesHive TutorialSankalp JangamNo ratings yet
- Big DataDocument25 pagesBig DataAnu GraphicsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Overview: Two Things in BackendDocument21 pagesLecture 1 Overview: Two Things in Backendwec11011No ratings yet
- Hive OverviewDocument28 pagesHive OverviewParag GuptaNo ratings yet
- Oracle SQL 2Document6 pagesOracle SQL 2Srikanth gsNo ratings yet
- Advanced Table Functionalities in OAF!Document5 pagesAdvanced Table Functionalities in OAF!Vijay KishanNo ratings yet
- MYSQLDocument6 pagesMYSQLLigo PastiNo ratings yet
- Apache Hive: An IntroductionDocument51 pagesApache Hive: An IntroductionSaeed MeethalNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3: Hive: Aim: To Understand Data Processing Tool - Hive and HQL (Hive Query Language)Document11 pagesExperiment 3: Hive: Aim: To Understand Data Processing Tool - Hive and HQL (Hive Query Language)Ňąŕëşh ķümãŕ SNo ratings yet
- I Want To Display 1 To 10 Numbers Using One Select StatementDocument20 pagesI Want To Display 1 To 10 Numbers Using One Select StatementSelvaraj VNo ratings yet
- BDA Assignment I and IIDocument8 pagesBDA Assignment I and IIAshok Mane ManeNo ratings yet
- Informatics Practices Review of MysqlDocument16 pagesInformatics Practices Review of MysqlsauravnarukaNo ratings yet
- Dishaa - Database NotesDocument36 pagesDishaa - Database Notesrohan.gNo ratings yet
- 4 Stacks PDFDocument23 pages4 Stacks PDFbaessienNo ratings yet
- PowerShell Training PrimerDocument29 pagesPowerShell Training PrimerLoriLevy100% (1)
- COMP322: Assignment 2 - Winter 2010: Due at 11:59pm EST, 3 Mar 2010Document3 pagesCOMP322: Assignment 2 - Winter 2010: Due at 11:59pm EST, 3 Mar 2010Yam AradaNo ratings yet
- Building A WebsiteDocument5 pagesBuilding A Websitewww.uchihamadara2019No ratings yet
- PostgreSQL CHEAT SHEETDocument8 pagesPostgreSQL CHEAT SHEETHarshNo ratings yet
- Apche HiveDocument66 pagesApche HiveVijay CrisNo ratings yet
- A View Is Also Called Virtual Table Stored Query Window Create View Viewname As Query (With Check Option) (With Read Only)Document35 pagesA View Is Also Called Virtual Table Stored Query Window Create View Viewname As Query (With Check Option) (With Read Only)chowdareiamNo ratings yet
- Lab BDH Sample SolutionDocument2 pagesLab BDH Sample Solutionsun_jojoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Oracle Insert, Delete, Update - DMLDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Oracle Insert, Delete, Update - DMLAli Sheikh AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document32 pagesLecture 4NodirNo ratings yet
- Lab ProgramsDocument2 pagesLab Programsrahulshastri0126No ratings yet
- Datatypes in HiveDocument31 pagesDatatypes in HiveMytheesh WaranNo ratings yet
- SQL IntroDocument31 pagesSQL IntroPratik MahoreyNo ratings yet
- Constraints and DDLDocument23 pagesConstraints and DDLGAME DEV MONISH. RNo ratings yet
- Stacks in Data StructureDocument40 pagesStacks in Data StructureKaran RoyNo ratings yet
- Fy Sem2 Notes Unit1Document21 pagesFy Sem2 Notes Unit1sachin koreNo ratings yet
- Dbms Manual PDocument26 pagesDbms Manual PDeepak kumarNo ratings yet
- Institute of Engineering and ManagementDocument30 pagesInstitute of Engineering and ManagementAbhishek DasNo ratings yet
- Jan Jacobus Spies - Form 4 Unit 2 Arrays Learner WorkbookDocument11 pagesJan Jacobus Spies - Form 4 Unit 2 Arrays Learner Workbookjeanspies18No ratings yet
- Data Base (SQL) : Creating TablesDocument24 pagesData Base (SQL) : Creating TablesShaji kahoutNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1+2Document16 pagesChapter 1+2Thiều Nhat AnhNo ratings yet
- ABAP Internal Table DeclarationDocument21 pagesABAP Internal Table Declarationharish_inNo ratings yet
- Hbase PDFDocument8 pagesHbase PDFchandra reddyNo ratings yet
- SAP HANA Import & Export StatementsDocument13 pagesSAP HANA Import & Export StatementsamruthaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Tables and Worksheet Databases: Figure 9-13: This Table Shows Sales by Month and by RegionDocument5 pagesChapter 9: Tables and Worksheet Databases: Figure 9-13: This Table Shows Sales by Month and by Regionxdpablo328No ratings yet
- Database Lab Manuals From Sorting To AvgDocument17 pagesDatabase Lab Manuals From Sorting To AvgHajra AnwarNo ratings yet
- Coding Workshop: Implement A Table Component: The TablelistboxDocument11 pagesCoding Workshop: Implement A Table Component: The TablelistboxSayyam Ch0% (1)
- Data AcquisitionDocument2 pagesData Acquisitionapi-286344277No ratings yet
- Unit-4 Pig HiveDocument40 pagesUnit-4 Pig HiveSivaNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Relational Database Management System (RDBMS)Document15 pagesUnit - I Relational Database Management System (RDBMS)Zacharia VincentNo ratings yet
- SQL - PHP: TutorialDocument27 pagesSQL - PHP: TutorialFaiz Syed MohammedNo ratings yet
- PL SQL PracticalDocument14 pagesPL SQL Practical321&No ratings yet
- Rules of PrecedenceDocument40 pagesRules of Precedencearistu01No ratings yet
- EIM ProcessDocument11 pagesEIM ProcesskittusiebelNo ratings yet
- Database Management System by Harshit Bansal (18BCS3805 - CSE IBM BDA - 1)Document5 pagesDatabase Management System by Harshit Bansal (18BCS3805 - CSE IBM BDA - 1)harshitNo ratings yet
- Lab 7Document13 pagesLab 7hassan IQNo ratings yet
- Abap UdemyDocument22 pagesAbap UdemySunil kumarNo ratings yet
- SQL StatementDocument9 pagesSQL Statementshweta_delhiite2526No ratings yet
- Import Set 2Document12 pagesImport Set 2akash dahiphaleNo ratings yet
- 数据库原理与实践 Database Systems-Principle and PracticeDocument182 pages数据库原理与实践 Database Systems-Principle and Practicerajesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Create SnapshotDocument8 pagesCreate SnapshotShiva Mca0% (1)
- DoctrineDocument24 pagesDoctrineshambalicNo ratings yet
- A Language School Database ModelDocument13 pagesA Language School Database ModelNoor Mast AfridiNo ratings yet
- The Relational Database Model: Database Systems: Design, Implementation, and Management, Fifth Edition, Rob and CoronelDocument35 pagesThe Relational Database Model: Database Systems: Design, Implementation, and Management, Fifth Edition, Rob and CoronelJorge ResurreccionNo ratings yet
- Oracle Database 19c OverviewDocument40 pagesOracle Database 19c OverviewGiovedy MarmolejoNo ratings yet
- 2VAA000812R0001 en S Engineering Composer Harmony Version 5.1 Primary Interface User ManualDocument223 pages2VAA000812R0001 en S Engineering Composer Harmony Version 5.1 Primary Interface User ManualJim Sumire Salazar100% (2)
- Empty Table KeyDocument2 pagesEmpty Table Keyraky0369No ratings yet
- SAP Query ManualDocument94 pagesSAP Query ManualAnupam SarkarNo ratings yet
- Joins: Normalize DataDocument17 pagesJoins: Normalize Datacool_spNo ratings yet
- SAP ABAP Internal TableDocument8 pagesSAP ABAP Internal TableAnjan KumarNo ratings yet
- SQL QueDocument78 pagesSQL QueMILINDNo ratings yet
- DBMS UNIT 2 SQL CommandsDocument92 pagesDBMS UNIT 2 SQL CommandsDrastiNo ratings yet
- Chapter12 AnsDocument6 pagesChapter12 AnsBlasta45No ratings yet
- Product Version: Boost Up Your Certification ScoreDocument40 pagesProduct Version: Boost Up Your Certification ScoreGayathri SNo ratings yet
- Spotfire Interview QuestionsDocument3 pagesSpotfire Interview QuestionsmitunvNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis Oracle Logical Standby Data Guard Configuration and ScriptsDocument13 pagesDiagnosis Oracle Logical Standby Data Guard Configuration and ScriptsIrfan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Asm502 Ind Assignment Access Dec2022Document22 pagesAsm502 Ind Assignment Access Dec2022NORFATIN NABILA BT MOHD FADZILNo ratings yet
- Interview Questionson Oracle SCMAOLFormsDocument33 pagesInterview Questionson Oracle SCMAOLFormsprabhuwweNo ratings yet
- SQL UdemyDocument34 pagesSQL UdemySandeep Chowdary MuthineniNo ratings yet
- NormalizationDocument4 pagesNormalizationmeenahilNo ratings yet
- PDI2000 LabsDocument281 pagesPDI2000 LabsBhaskar ReddyNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument373 pagesDBMSTushar PatelNo ratings yet
- SQL Interview QuestionDocument22 pagesSQL Interview Questionrenakumari100% (3)
- Sqldatagrid Symbol User'S Guide: ArchestraDocument36 pagesSqldatagrid Symbol User'S Guide: ArchestraAde SuryaNo ratings yet
- PostgreSQL For BeginnersDocument142 pagesPostgreSQL For BeginnersRubén Ruíz100% (3)
- Database Programming With PL/SQL 5-2: Practice Activities: Using Explicit Cursor AttributesDocument2 pagesDatabase Programming With PL/SQL 5-2: Practice Activities: Using Explicit Cursor AttributesBogdan BicaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 09, SQLite DatabasesDocument23 pagesLecture 09, SQLite DatabasesM. Talha NadeemNo ratings yet
- EOM ChecklistDocument4 pagesEOM ChecklistVinothkumar RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- PracticeExam DataEngineerAssociateDocument23 pagesPracticeExam DataEngineerAssociateDivya KhatriNo ratings yet
- Dark Data: Why What You Don’t Know MattersFrom EverandDark Data: Why What You Don’t Know MattersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Fusion Strategy: How Real-Time Data and AI Will Power the Industrial FutureFrom EverandFusion Strategy: How Real-Time Data and AI Will Power the Industrial FutureNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Basics: A Non-Technical Introduction in 25 StepsFrom EverandBlockchain Basics: A Non-Technical Introduction in 25 StepsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (24)
- Business Intelligence Strategy and Big Data Analytics: A General Management PerspectiveFrom EverandBusiness Intelligence Strategy and Big Data Analytics: A General Management PerspectiveRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Grokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleFrom EverandGrokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (16)
- Starting Database Administration: Oracle DBAFrom EverandStarting Database Administration: Oracle DBARating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- SQL QuickStart Guide: The Simplified Beginner's Guide to Managing, Analyzing, and Manipulating Data With SQLFrom EverandSQL QuickStart Guide: The Simplified Beginner's Guide to Managing, Analyzing, and Manipulating Data With SQLRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (46)
- THE STEP BY STEP GUIDE FOR SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION OF DATA LAKE-LAKEHOUSE-DATA WAREHOUSE: "THE STEP BY STEP GUIDE FOR SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION OF DATA LAKE-LAKEHOUSE-DATA WAREHOUSE"From EverandTHE STEP BY STEP GUIDE FOR SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION OF DATA LAKE-LAKEHOUSE-DATA WAREHOUSE: "THE STEP BY STEP GUIDE FOR SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION OF DATA LAKE-LAKEHOUSE-DATA WAREHOUSE"Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Big Data and Analytics: The key concepts and practical applications of big data analytics (English Edition)From EverandBig Data and Analytics: The key concepts and practical applications of big data analytics (English Edition)No ratings yet
- Joe Celko's SQL for Smarties: Advanced SQL ProgrammingFrom EverandJoe Celko's SQL for Smarties: Advanced SQL ProgrammingRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Cloud Computing Playbook: 10 In 1 Practical Cloud Design With Azure, Aws And TerraformFrom EverandCloud Computing Playbook: 10 In 1 Practical Cloud Design With Azure, Aws And TerraformNo ratings yet
- DB2 9 System Administration for z/OS: Certification Study Guide: Exam 737From EverandDB2 9 System Administration for z/OS: Certification Study Guide: Exam 737Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Mastering Amazon Relational Database Service for MySQL: Building and configuring MySQL instances (English Edition)From EverandMastering Amazon Relational Database Service for MySQL: Building and configuring MySQL instances (English Edition)No ratings yet
- High-Performance Oracle: Proven Methods for Achieving Optimum Performance and AvailabilityFrom EverandHigh-Performance Oracle: Proven Methods for Achieving Optimum Performance and AvailabilityNo ratings yet
- Optimizing DAX: Improving DAX performance in Microsoft Power BI and Analysis ServicesFrom EverandOptimizing DAX: Improving DAX performance in Microsoft Power BI and Analysis ServicesNo ratings yet
- Modelling Business Information: Entity relationship and class modelling for Business AnalystsFrom EverandModelling Business Information: Entity relationship and class modelling for Business AnalystsNo ratings yet
- Web Dragons: Inside the Myths of Search Engine TechnologyFrom EverandWeb Dragons: Inside the Myths of Search Engine TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- DATABASE From the conceptual model to the final application in Access, Visual Basic, Pascal, Html and Php: Inside, examples of applications created with Access, Visual Studio, Lazarus and WampFrom EverandDATABASE From the conceptual model to the final application in Access, Visual Basic, Pascal, Html and Php: Inside, examples of applications created with Access, Visual Studio, Lazarus and WampNo ratings yet