Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ABDOMEN
Uploaded by
khayceemeade20 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageThe gastrointestinal tract is a hollow tube that begins at the mouth and ends at the anus. It consists of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and accessory organs like the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas. The liver metabolizes nutrients, detoxifies blood, and synthesizes proteins, while the gallbladder stores and releases bile to help digest fats. The pancreas releases enzymes and insulin to aid in digestion and regulate blood sugar. Together, these organs work to break down food, absorb nutrients, and eliminate waste from the body.
Original Description:
Abdomen trans 1st year
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe gastrointestinal tract is a hollow tube that begins at the mouth and ends at the anus. It consists of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and accessory organs like the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas. The liver metabolizes nutrients, detoxifies blood, and synthesizes proteins, while the gallbladder stores and releases bile to help digest fats. The pancreas releases enzymes and insulin to aid in digestion and regulate blood sugar. Together, these organs work to break down food, absorb nutrients, and eliminate waste from the body.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageABDOMEN
Uploaded by
khayceemeade2The gastrointestinal tract is a hollow tube that begins at the mouth and ends at the anus. It consists of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and accessory organs like the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas. The liver metabolizes nutrients, detoxifies blood, and synthesizes proteins, while the gallbladder stores and releases bile to help digest fats. The pancreas releases enzymes and insulin to aid in digestion and regulate blood sugar. Together, these organs work to break down food, absorb nutrients, and eliminate waste from the body.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
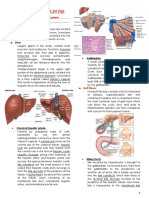
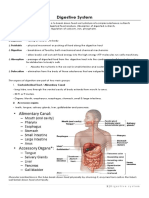
ABDOMEN ACCESSORY GI ORGANS N VESSELS
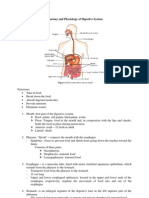
GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT A. LIVER
- Weighs only 3lbs in adult
- Hollow tube that begins at mouth n ends at anus - Metabolizes carbohydrates, fats, proteins
- Consists of smooth muscle alternating w/ blood vessels n - Detoxifies blood
nerve tissue - Converts ammonia to urea for excretion
- Specialized circular n longitudinal fibers contract > - Synthesizes plasma proteins, nonessential amino acids,
peristalsis: propels food thru GI tract vitamins, and essential nutrients
- Peristalsis: involuntary contraction n relaxation of - Secretes bile (greenish fluid that helps digest fats and
longitudinal n circular muscle throughout digestive tract absorbs fatty acids, cholesterol, lipids that give stool color)
PARTS OF THE DIGESTIVE TRACT B. GALLBLADDER
- Stores bile from liver till bile empties the duodenum
A. MOUTH C. BILE DUCTS
- Begins digestion thru chewing, salivating, swallowing - Hepatic ducts: drain bile from liver
B. TONGUE - Cystic ducts: drain bile from GB
- Provides sense of taste - Common bile duct: receives bile from hepatic n cystic
C. PAROTID, SUBLINGUAL & SUBMANDIBULAR GLANDS ducts n empties bile to duodenum
- Produces saliva D. PANCREAS
D. EPIGLOTTIS - Releases insulin n glycogen into bloodstream n produces
- Keeps food n fluid from being aspirated into airway by enzymes that aid in digestion
closing over the larynx when food is swallowed - Consists of head, body, tail
E. PHARYNX - 6-8’’ 15-20.5 cm in length
- Consists of nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx E. VESSELS
- Passage of food from mouth to esophagus - the abdominal aorta supplies blood to GI tract
- Assists in swallowing - gastric n splenic veins drain absorbed nutrients into portal
- Secretes mucus, aids digestion vein of liver
F. ESOPHAGUS
- Hollow, muscular tube that’s approx.. 10’’ (25.5 cm) ASSESSMENT OF THE ABDOMEN
- Moves food from pharynx to stomach using peristalsis - INSPECTION, AUSCULTATION, PERCUSSION, PALPATION
G. STOMACH - Start at the RLQ>RUQ>LUQ>LLQ
- Dilated, saclike lies obliquely in left upper quadrant - Auscultate first cause when you palpate first it may change
- Contains 2 important sphincters: the sound of the bowel sounds; peristalsis
- cardiac sphincter: protects entrance to stomach -
- pyloric sphincter: guards the exit -
- stores food n mixes it w/ gastric juice
- passes chyme into small intestine for further digestion n
absorption
H. RUGAE
- Accordion-like folds in stomach lining
- Allow stomach to expand
I. SMALL INTESTINE
- Duodenum, jejenum, ileum
- Loc of carbohydrate, fat, protein breakdown
- Absorbs end product of digestion
J. VERMIFORM APPENDIX
- Fingerlike projection that’s attached to cecum
K. LARGE INTESTINE
- Consists of the cecum; ascending, transverse, descending,
sigmoid colons; rectum n anus
- Absorbs excess water n electrolytes
- Stores food residue
- Eliminates waste products in form of feces
You might also like
- Digestive SystemDocument43 pagesDigestive SystemDaniella100% (2)
- Chromosomal DisordersDocument4 pagesChromosomal DisordersYoussry JaranillaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument117 pagesDigestive SystemKBDNo ratings yet
- Computed Tomography of The Cardiovascular System PDFDocument536 pagesComputed Tomography of The Cardiovascular System PDFdrAlbertoVVNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Anaphy Lec Digestive System 2nd PartDocument6 pagesReviewer Anaphy Lec Digestive System 2nd PartAubrey Gale MendozaNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Study GuideDocument34 pagesNCLEX Study GuideCaren Reyes100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Digestive SystemAngelica JavierNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal PDFDocument70 pagesGastrointestinal PDFCarol FuentesNo ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument44 pagesThe Digestive SystemJoy NatividadNo ratings yet
- Digestive System - MefloresDocument117 pagesDigestive System - MefloresJohnMichaelDominguezNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing The Gastro-Intestinal System Nurse Licensure Examination Review By: John Mark B. Pocsidio, RN, Usrn, MSNDocument22 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing The Gastro-Intestinal System Nurse Licensure Examination Review By: John Mark B. Pocsidio, RN, Usrn, MSNjm_pocsidio8213No ratings yet
- Digestive System NotesDocument5 pagesDigestive System NotesRavenApigoNo ratings yet
- Presentation On The Digestive SystemDocument48 pagesPresentation On The Digestive SystemOsman Saidu Sesay0% (1)
- Nursing Test 1 (NP III)Document10 pagesNursing Test 1 (NP III)Paul Nathan Betita100% (2)
- 182 Anatomy Digestive SystemDocument15 pages182 Anatomy Digestive SystemDAPHNE CLAIRE L. SARINONo ratings yet
- Lectire-Hypoxia 2020Document21 pagesLectire-Hypoxia 2020Bol Dhalbeny Malual100% (1)
- MS GitDocument34 pagesMS GitShayesra-Radina Laja SahibadNo ratings yet
- 182 Anatomy Digestive SystemDocument15 pages182 Anatomy Digestive SystemFrencee Rein Caleo100% (1)
- Digestive SystemDocument16 pagesDigestive SystemamirehmoNo ratings yet
- Metabolism (Ncm-216)Document10 pagesMetabolism (Ncm-216)Sofronio OmboyNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Five Basic ActivitiesDocument5 pagesDigestive System: Five Basic ActivitiesCrystal MaidenNo ratings yet
- Sci - Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesSci - Digestive SystemClaude de alger ObeliaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument11 pagesDigestive SystemShiela Mae SagayoNo ratings yet
- Digestive TermsDocument2 pagesDigestive TermsTorio Kristine Anne P.No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PresentationDocument82 pagesChapter 9 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PresentationMary Jane LubricoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesAnaphy Digestive Systemheyraheyra70No ratings yet
- Q4 Week 3 Human Digestive System - PPTX 4thDocument47 pagesQ4 Week 3 Human Digestive System - PPTX 4thdenveralbarico143No ratings yet
- Exam 2 NotesDocument36 pagesExam 2 NotesClara PianaltoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document28 pagesChapter 1Miden AlbanoNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive System ProcessDocument7 pagesHuman Digestive System ProcessdatoysybilrussmirNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument16 pagesAnaphy ReviewerBr1nfoNo ratings yet
- NUTRIDIETDocument4 pagesNUTRIDIETyasmingapaz30No ratings yet
- Digestive System 1Document11 pagesDigestive System 1Louise Mica LeeNo ratings yet
- DigestiveDocument74 pagesDigestiveLeah Magbago RemolisanNo ratings yet
- Digestive System AnatomyDocument15 pagesDigestive System AnatomyDanielle Abatay HipulanNo ratings yet
- Ch.14 Human NutritionDocument11 pagesCh.14 Human Nutritionprachi98601No ratings yet
- دمج شباتر البالغين .....Document511 pagesدمج شباتر البالغين .....Abdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Process of DigestionDocument4 pagesProcess of DigestionKennard LIONGNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Kaikiyi Sykay Pacheco BEED1Document3 pagesDigestive System Kaikiyi Sykay Pacheco BEED1Kaikiyi Sykay PachecoNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Presented By: Areeba Aqil 15-B.ED-14 B.Ed Iv Semester GC-9755Document15 pagesDigestive System: Presented By: Areeba Aqil 15-B.ED-14 B.Ed Iv Semester GC-9755Uzma SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesChapter 6 - Digestive SystemIbby HooriyaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesDigestive SystemadeNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System: AnatomyDocument7 pagesGastrointestinal System: AnatomyMYKRISTIE JHO MENDEZNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology TerminologiesDocument7 pagesHuman Physiology TerminologiesKrisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- GastrointestinalDocument39 pagesGastrointestinalالمسوول الاعلاميNo ratings yet
- General Zoology LabDocument3 pagesGeneral Zoology Labgerlyn duranNo ratings yet
- Patho - Digestive SystemDocument17 pagesPatho - Digestive SystemLinda XueNo ratings yet
- Jawaban Tugas Biology Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesJawaban Tugas Biology Digestive Systemaulia nurfadillahNo ratings yet
- GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM 1 Ngan 2Document14 pagesGASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM 1 Ngan 2Stephen Jil BocoNo ratings yet
- Digestion & Absorption NotesDocument15 pagesDigestion & Absorption NotesKankana BiswasNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument19 pagesDigestive SystemMariel BugnaNo ratings yet
- General Biology: 1. Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology: 1. Digestive SystemJuno Merdien GarciaNo ratings yet
- Module 14 AbdomenDocument22 pagesModule 14 Abdomenjohn maikeilNo ratings yet
- FenieDocument32 pagesFenieLilacx ButterflyNo ratings yet
- 3 - Nutrition (I) - The Digestive SystemDocument36 pages3 - Nutrition (I) - The Digestive SystemValery GvNo ratings yet
- L - 6 Life Processes - Heterotrophic NutritionDocument7 pagesL - 6 Life Processes - Heterotrophic NutritionNotImmortalNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Physiology: Department of Physiology CHS, UniosunDocument59 pagesGastrointestinal Physiology: Department of Physiology CHS, UniosunTeeNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System Powerpoint 1227698045024899 8Document44 pagesThe Digestive System Powerpoint 1227698045024899 8Julia Rae Delos Santos100% (1)
- Gastrointestina L Tract: (Digestive System)Document56 pagesGastrointestina L Tract: (Digestive System)Josephine AcioNo ratings yet
- Digestive System ReviewDocument2 pagesDigestive System ReviewSherriena LeangNo ratings yet
- Speaking EnglishDocument4 pagesSpeaking EnglishwybcxkNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Digestive-SystemDocument38 pagesLecture 1 Digestive-SystemJhona NaragNo ratings yet
- Digestive System 2021Document29 pagesDigestive System 2021fashion20trendsNo ratings yet
- Low Molecular Weight Heparins (LMWH) : I. Mechanism of ActionDocument7 pagesLow Molecular Weight Heparins (LMWH) : I. Mechanism of ActionIniya RajendranNo ratings yet
- Management of Pneumonia in Critically Ill Patients: Catia Cillóniz, Antoni Torres, Michael S NiedermanDocument24 pagesManagement of Pneumonia in Critically Ill Patients: Catia Cillóniz, Antoni Torres, Michael S NiedermanMarvin Josue Bustamante GutierrezNo ratings yet
- AACE Clinical Case ReportsDocument4 pagesAACE Clinical Case ReportsShuaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) : Topic OutlineDocument5 pagesElectrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) : Topic OutlineDan Dan ManaoisNo ratings yet
- GASTRECTOMYDocument3 pagesGASTRECTOMYMaria Ydela MeradoresNo ratings yet
- Isosorbide DinitrateDocument1 pageIsosorbide Dinitrate202110439No ratings yet
- 12 Clin Path Exocrine and Endocrine Functions of The PancreasDocument13 pages12 Clin Path Exocrine and Endocrine Functions of The PancreasJolaine ValloNo ratings yet
- CardioplegiaDocument1 pageCardioplegiaapi-594434664No ratings yet
- Тopic 2. Review of individual body partsDocument13 pagesТopic 2. Review of individual body partslayla kambalaNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Fitness and Wellness A Comprehensive Lifestyle Approach 10th Edition Corbin Test BankDocument9 pagesConcepts of Fitness and Wellness A Comprehensive Lifestyle Approach 10th Edition Corbin Test Bankdominiccosimawye100% (31)
- 1 s2.0 S0085253822010171 MainDocument15 pages1 s2.0 S0085253822010171 MainJack JackNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09 - Aortic StenosisDocument9 pagesChapter 09 - Aortic StenosisAndrada CatrinoiuNo ratings yet
- 37 1Document3 pages37 1MoneymakerNo ratings yet
- ps420 Umeng0100Document42 pagesps420 Umeng0100Herry PrayNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Ischemic StrokeDocument9 pagesTreatment of Ischemic Strokeka 66No ratings yet
- Drug-Study NCPDocument5 pagesDrug-Study NCPMURILLO, FRANK JOMARI C.No ratings yet
- BISOPROLOLDocument4 pagesBISOPROLOLHY Hong YiNo ratings yet
- A Drug Study On: Furosemide TabletDocument7 pagesA Drug Study On: Furosemide TabletRaijenne VersolaNo ratings yet
- Development of Midbrain and HindbrainDocument58 pagesDevelopment of Midbrain and HindbrainBramwell K. MiteiNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Encephalopathy Blok NeurologiDocument19 pagesMetabolic Encephalopathy Blok NeurologiKarlos Sihaloho IINo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology: Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentDocument63 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology: Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentJoana Mae BascoNo ratings yet
- (2019) - Nandrolone Decanoate Relieves Joint Pain in Hypogonadal Men Men: A Novel Prospective Pilot Study and Review of The LiteratureDocument9 pages(2019) - Nandrolone Decanoate Relieves Joint Pain in Hypogonadal Men Men: A Novel Prospective Pilot Study and Review of The LiteratureGuilherme LealNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Edema by DR Gireesh Kumar K PDocument16 pagesPulmonary Edema by DR Gireesh Kumar K PAETCM Emergency medicineNo ratings yet
- Pharma Nca1 Notes MidtermDocument8 pagesPharma Nca1 Notes MidtermAICEL A. ABILNo ratings yet
- 03 Cardiovascular System Examination FinalDocument49 pages03 Cardiovascular System Examination FinalYared TJNo ratings yet