Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Spinal Cord Lesions
Uploaded by
luismpereaunamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Spinal Cord Lesions
Uploaded by
luismpereaunamCopyright:
Available Formats
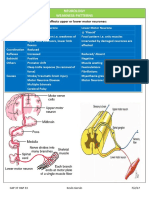
SPINAL CORD LESIONS
Poliomyelitis
Syringomyelia Damage to anterior motor horn due to poliovirus
Cystic degeneration of the spinal cord infection (feco-oral transmission, infects
Arises with trauma or in association with oropharynx and small bowel: fever, sore throat,
Arnold- Chiari malformation abdominal pain with nausea and vomiting).
Usually occurs at C8- T1 When it spreads to the CNS via blood →
Sensory loss of pain and temp anterior motor horn.
Sparing of fine touch and position sense in Presents with lower motor neuron signs
the upper extremities (UE)
Img.: Flaccid paralysis with muscle atrophy,
weakness with decreased tone, impaired
reflexes, negative Babinsky
Werdnig- Hoffmann disease
Inherited degeneration of anterior motor
horn; autosomal recessive
Presents as “floppy baby”
Death occurs within a few years after birth
Same symptoms as previous disease
Img.: Pain and temp crosses in anterior
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
white commisure (3 independent neurons).
Degenerative disorder of upper and lower
In syringomyelia, the anterior white commisure
motor neurons (corticospianl tracts)
is knocked up → P/T on both sides (from C8 to
Anterior motor horn involvement leads to
T1). Dorsal column (fine touch and position
LMN signs
sense) isn’t altered.
Lateral corticospinal tract involvement leads
If the syrinx expands → knocks up anterior horn
to UMN signs.
→ LMN disorder → muscle weakness with
Atrophy and weakness of hands is an early
atrophy, decreased tone impaired reflexes
sign
*If it knocks the lateral horn (hipothalamus-
Can resemble syringomyelia bc syringo
spianl tract carries sympathetic input to face) →
involves C8-T1 so it would affect UE
lateral horn in T1: Horner syndrome → ptosis,
(including hands) & also damage to anterior
myosis, anhidrosis.
horns (atrophy and weakness of hands)
BUT… in syringo: loss of P/T (not in ALS).
Most cases are sporadic
Arises in middle- aged adults
Zinc- copper superoxide dismutase
mutation is present in some familial cases
Img.: SOD removes free radicals by converting
superoxide to hydrogen peroxide. → free
radicals damage neurons
Friedreich Ataxia
Degenerative disorder of cerebellum and
spinal cord tracts
Presents as ataxia (cerebellum) with loss of
vibratory sense and propioception, muscle
weakness in lower extremities, and loss of
DTR.
A.Recessive; unstable trinucleotide repeat
(GAA) in frataxin gene (frataxin gene →
mitochondrial Fe regulation → increases risk of
producing free radicals by the Fenton reaction.
Presents in early childhood
Associated with hypertrophic
cardiomyopathy
You might also like
- Neurology XXXXDocument13 pagesNeurology XXXXAmeer AslamNo ratings yet
- 38 SchoonoverDocument41 pages38 SchoonoverEmma ElliotNo ratings yet
- Clinicals of NeuroanatomyDocument9 pagesClinicals of Neuroanatomyaneeqahmed99No ratings yet
- Disease/syndrome Inciting Incident Structures Affected PoliomyelitisDocument12 pagesDisease/syndrome Inciting Incident Structures Affected PoliomyelitismrhemmatNo ratings yet
- Motor Neuron Disease: Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)Document2 pagesMotor Neuron Disease: Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)james cordenNo ratings yet
- Neurology LocalizationDocument6 pagesNeurology LocalizationPramod ThapaNo ratings yet
- Amyotrophic Lateral SclerosisDocument8 pagesAmyotrophic Lateral SclerosisSangguniang Kabataan Brgy. 36-ANo ratings yet
- NBME CMS Forms NotesDocument4 pagesNBME CMS Forms NotesJack Guccione100% (7)
- Umnl & LMNLDocument13 pagesUmnl & LMNLTammy BoudNo ratings yet
- Neuro LesionsDocument7 pagesNeuro Lesionskep1313100% (5)
- GuillainDocument4 pagesGuillainanime listNo ratings yet
- Child With Weak MusclesDocument5 pagesChild With Weak MusclesStephen AttardNo ratings yet
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesAmyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: PathophysiologyJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- NMJ Disorders: Differentiation: Myasthenia Gravis (MG) Id. PathophysiologyDocument1 pageNMJ Disorders: Differentiation: Myasthenia Gravis (MG) Id. PathophysiologyPixy StxNo ratings yet
- Neurology - Weakness PatternsDocument2 pagesNeurology - Weakness PatternsAnisah AliNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy ClinicalsDocument9 pagesNeuroanatomy ClinicalsMuhammad Nabeel AbbasNo ratings yet
- D.D of Wasting in Small Ms of The HandDocument3 pagesD.D of Wasting in Small Ms of The HandMohamed SharafNo ratings yet
- Sensory System - PathwaysDocument25 pagesSensory System - PathwaysHamid Hussain HamidNo ratings yet
- 2nd SG Book NotesDocument4 pages2nd SG Book NotesLeah DeeNo ratings yet
- Disease Destroys Manifestations: Spinothalamic Tract (STT) ContralateralDocument3 pagesDisease Destroys Manifestations: Spinothalamic Tract (STT) ContralateralRenata V CNo ratings yet
- Week 4-Pni Ue LeDocument115 pagesWeek 4-Pni Ue LeJAZH EDREY LOZANONo ratings yet
- Dermatomal Sensory Manifestations in Opalski SyndromeDocument2 pagesDermatomal Sensory Manifestations in Opalski SyndromeAndresPinedaMNo ratings yet
- Revalida Review NotesDocument14 pagesRevalida Review NotesBryan Lloyd RayatNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Neuropathy AidaDocument36 pagesPeripheral Neuropathy AidaAdlina ArifinNo ratings yet
- Etiology: Molecular Mimicry - Myelin-ReactiveDocument2 pagesEtiology: Molecular Mimicry - Myelin-ReactiveJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- 신경과 novel episode IDocument33 pages신경과 novel episode I김정우No ratings yet
- Neuro Short Case SummaryDocument14 pagesNeuro Short Case Summaryquojo041No ratings yet
- Insula Anterior Cingulate Cortex: Amygdala, Hypothalamus, Periaqueductal Grey, Basal GangliaDocument8 pagesInsula Anterior Cingulate Cortex: Amygdala, Hypothalamus, Periaqueductal Grey, Basal GangliaKunal KatyayanNo ratings yet
- Neurology Passmedicine & Onexamination Notes 2016Document158 pagesNeurology Passmedicine & Onexamination Notes 2016Muhammad Haneef100% (2)
- Spinal Cord DiseaseDocument77 pagesSpinal Cord Diseasemirabel IvanaliNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience I - Neurologic History Taking and Examination (POBLETE)Document9 pagesNeuroscience I - Neurologic History Taking and Examination (POBLETE)Johanna Hamnia PobleteNo ratings yet
- Sensory DisturbancesDocument4 pagesSensory DisturbancesNicNo ratings yet
- How To Localize Neurological LesionDocument25 pagesHow To Localize Neurological LesionBeenish IqbalNo ratings yet
- Back Spine ConditionsDocument2 pagesBack Spine ConditionsNinjaNo ratings yet
- Where Da Lesion atDocument5 pagesWhere Da Lesion atDeeWallyNo ratings yet
- Plenary Discussion 21DDocument40 pagesPlenary Discussion 21DBima Akdrian AdbertaNo ratings yet
- Neuropsychology DetailsDocument15 pagesNeuropsychology DetailswillemrikhofspamNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument27 pagesStrokeJASON KO CHIA SHENGNo ratings yet
- In The Name of God, Most Gracious, Most MercifulDocument48 pagesIn The Name of God, Most Gracious, Most MercifulMohammad Sadiq AzamNo ratings yet
- COURSE TASK 6 - Degenerative Table SummaryDocument2 pagesCOURSE TASK 6 - Degenerative Table SummaryJordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- NeurologyDocument23 pagesNeurologyAhmad Naufal Basri100% (3)
- Cerebral Cortex and Speech NajeebDocument27 pagesCerebral Cortex and Speech NajeebchawkatNo ratings yet
- Neurology: Apprauching and Localizing Neurological LesionDocument53 pagesNeurology: Apprauching and Localizing Neurological LesionMahad IbrahemNo ratings yet
- Therefore "Weakness" DOES NOT Help To Establish Whether It Is UMN or LMN lesion-FOLLOWING Pattern of Signs Help Us To EstablishDocument66 pagesTherefore "Weakness" DOES NOT Help To Establish Whether It Is UMN or LMN lesion-FOLLOWING Pattern of Signs Help Us To EstablishBaishakhi ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal DisordersDocument9 pagesMusculoskeletal DisordersBloom DhillonNo ratings yet
- Motor Neuron DiseasesDocument103 pagesMotor Neuron DiseasesJamil AhmadNo ratings yet
- Clinical Aspects of UMN LMNDocument24 pagesClinical Aspects of UMN LMNKelly YeowNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Injury: General Medical BackgroundDocument8 pagesSpinal Cord Injury: General Medical BackgroundWynne Cirera100% (3)
- NeuroscienceDocument5 pagesNeuroscienceChing MacarubboNo ratings yet
- NeuroTracts - Ascending, Descending, UMN, LMNDocument5 pagesNeuroTracts - Ascending, Descending, UMN, LMNBrandi Allen HensonNo ratings yet
- Localization of sensory 肖争1 -student-2020Document49 pagesLocalization of sensory 肖争1 -student-2020mirabel IvanaliNo ratings yet
- Neuro Cns OcclusionsDocument1 pageNeuro Cns OcclusionsFaye Stephanie CantagoNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument24 pagesThe Nervous SystemKiara GovenderNo ratings yet
- HemiplegiaDocument30 pagesHemiplegiasarguss14100% (1)
- Res 113Document197 pagesRes 113Belinda ELISHANo ratings yet
- Neurology and Special Senses ' Neurology and Special Senses ' Section IiiDocument20 pagesNeurology and Special Senses ' Neurology and Special Senses ' Section IiiLuis Jose VelazquezNo ratings yet
- Flash Notes Radio GagaDocument28 pagesFlash Notes Radio GagaschxzerrydawnNo ratings yet
- Stroke SindromDocument13 pagesStroke SindromEvi Andriani LestariNo ratings yet
- StrokeDocument17 pagesStrokeRama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Neurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IIFrom EverandNeurology Multiple Choice Questions With Explanations: Volume IIRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Diabetic Gastroparesis: Pathophysiology, Evaluation and ManagementDocument10 pagesDiabetic Gastroparesis: Pathophysiology, Evaluation and ManagementboomNo ratings yet
- Amniotic Fluid and Placenta AbnormalitiesDocument60 pagesAmniotic Fluid and Placenta AbnormalitiesMonique BorresNo ratings yet
- Mech-5-20-JSA - Activity For Erection of ScaffoldingDocument10 pagesMech-5-20-JSA - Activity For Erection of ScaffoldingNasrullah JanNo ratings yet
- Visual Mnemonics Medicine 2e 40 Medical Mnemonics 41 40 Oct 16 2019 41 40 1700212737 41 40 Independently Published 41Document146 pagesVisual Mnemonics Medicine 2e 40 Medical Mnemonics 41 40 Oct 16 2019 41 40 1700212737 41 40 Independently Published 41El Farouk100% (1)
- Contemporary Clinical Immunology and Serology Pearson Clinical Laboratory ScienceDocument61 pagesContemporary Clinical Immunology and Serology Pearson Clinical Laboratory Sciencehazel.farley831100% (44)
- Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) : Prof Deepthi SamarageDocument20 pagesJuvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) : Prof Deepthi SamarageTrishenth FonsekaNo ratings yet
- Unit VIII PRESUMPTIVE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF PREGNANCYDocument5 pagesUnit VIII PRESUMPTIVE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF PREGNANCYNancy100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY ClonazepamDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY ClonazepamP BNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Master Tung PDFDocument25 pagesSyllabus Master Tung PDFkamran ahmadNo ratings yet
- Juvenile Polyposis Syndrome - UpToDateDocument13 pagesJuvenile Polyposis Syndrome - UpToDateHartemes RosarioNo ratings yet
- Qa & QC Biological Assay: Pigitalis Rabbinsulin Tubocurrabit Glucatgon Corats Vamarat Oxytochic Paradog SheeparinDocument19 pagesQa & QC Biological Assay: Pigitalis Rabbinsulin Tubocurrabit Glucatgon Corats Vamarat Oxytochic Paradog Sheeparinlorenjoy19No ratings yet
- Case Study Renal DiseaseDocument33 pagesCase Study Renal DiseaseJewel BrondaNo ratings yet
- Surgical ComplicationsDocument7 pagesSurgical Complicationsrjh1895No ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument2 pagesAnemiaLazeh MeNo ratings yet
- Oxygen AdministrationDocument25 pagesOxygen Administrationkirutheka nithilaaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Application of EpidemiologyDocument33 pagesUnit 7 Application of EpidemiologySamantha Adduru100% (1)
- Dark Winter: Operation Dark Winter Was The Code Name For A Senior-Level Bio-Terrorist AttackDocument5 pagesDark Winter: Operation Dark Winter Was The Code Name For A Senior-Level Bio-Terrorist AttackJosephNo ratings yet
- Pranic Healing For Partially Blind-A Case Study: Srikanth N Jois, Nagendra K PrasadDocument5 pagesPranic Healing For Partially Blind-A Case Study: Srikanth N Jois, Nagendra K PrasadMagdalena BozinoskaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Guideline BIRDEM 2021.pdf Version 1Document92 pagesAntibiotic Guideline BIRDEM 2021.pdf Version 1Imran Khan100% (6)
- Drug Index Updated2 2Document104 pagesDrug Index Updated2 2docaliNo ratings yet
- 20-21 - M - ENG - Part - 1 - PDFDocument34 pages20-21 - M - ENG - Part - 1 - PDFPulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Theroleofpain Classificationsystemsin Painmanagement: Patty Montgomery Orr,, Bettina Cobb Shank,, Amy Conner BlackDocument12 pagesTheroleofpain Classificationsystemsin Painmanagement: Patty Montgomery Orr,, Bettina Cobb Shank,, Amy Conner Blackneurologi standart4No ratings yet
- A3 Mortality 2023-1Document39 pagesA3 Mortality 2023-1marvie barbosaNo ratings yet
- Occupational Health Assignment Question OUMDocument8 pagesOccupational Health Assignment Question OUMRaz IsmailNo ratings yet
- THYROID YunitaDocument81 pagesTHYROID YunitaPandu KusumawardhanyNo ratings yet
- Texas A&M Hazard Reduction & Recovery CenterDocument63 pagesTexas A&M Hazard Reduction & Recovery CenterLeigh AshtonNo ratings yet
- Letter: "Kambô" Frog (Phyllomedusa Bicolor) : Use in Folk Medicine and Potential Health RisksDocument2 pagesLetter: "Kambô" Frog (Phyllomedusa Bicolor) : Use in Folk Medicine and Potential Health RisksEdilene Coffaci de LimaNo ratings yet
- Economic ZoologyDocument14 pagesEconomic ZoologyHira AroojNo ratings yet
- Health Law Renaissance Law College NotesDocument37 pagesHealth Law Renaissance Law College NotesGowtham SolicitorNo ratings yet
- Exercise Physiology Theory and Application To Fitness and Performance Eleventh Edition Scott K Powers Full ChapterDocument68 pagesExercise Physiology Theory and Application To Fitness and Performance Eleventh Edition Scott K Powers Full Chapterhoward.mcguirl514100% (3)