Professional Documents
Culture Documents
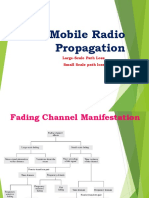
Large Scale Vs Small Scale Fading
Uploaded by
Mohammed BotOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Large Scale Vs Small Scale Fading
Uploaded by
Mohammed BotCopyright:
Available Formats
In the context of wireless communication, the terms "large scale" and "small scale" refer to
different aspects of signal propagation and channel characteristics.
1. Large-Scale Fading (Path Loss):
Definition: Large-scale fading, also known as path loss, refers to the
attenuation of the signal strength over long distances. It is associated with
the average power loss as the signal travels from the transmitter to the
receiver.
Factors: Large-scale fading is influenced by factors such as distance,
obstacles, and the environment. The free space path loss formula is an
example of large-scale fading.
Large-scale fading is deterministic and can be predicted based on the distance and
the environment. Antenna height and the presence of obstacles play a significant
role in large-scale fading.
2. Small-Scale Fading:
Definition: Small-scale fading refers to the rapid variations in the received
signal strength due to the constructive and destructive interference of
multiple signal paths (multipath propagation). It occurs over short distances
and is often characterized by rapid fluctuations in signal amplitude and
phase.
Factors: Small-scale fading is influenced by factors such as reflections,
diffractions, and scattering. As the signal travels, it encounters multiple paths
with varying lengths, causing constructive or destructive interference.
Small-scale fading is typically modeled using statistical approaches, such as Rayleigh
fading (for non-line-of-sight scenarios) or Rician fading (for line-of-sight scenarios
with multipath components).
In summary, large-scale fading deals with the average signal attenuation over long
distances and is often predictable based on distance and environmental factors. Small-
scale fading deals with the rapid fluctuations in signal strength over short distances due to
multipath propagation, and its behavior is often modeled statistically. Both large-scale and
small-scale fading are critical considerations in the design and optimization of wireless
communication systems.
You might also like
- GROUP3Document11 pagesGROUP3makangara22No ratings yet
- Characteristics of fading channels: Types of fading and their effectsDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of fading channels: Types of fading and their effectsAzim War100% (1)
- ShadowingDocument1 pageShadowingMohammed BotNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Wireless Fading ChannelsDocument15 pagesCharacteristics of Wireless Fading ChannelsKasini venthan manikandanathanNo ratings yet
- LF - bt1006 - E01 - 0 Lte Ofdm Principle 32Document29 pagesLF - bt1006 - E01 - 0 Lte Ofdm Principle 32Camilo Bazan HerediaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Part 1Document40 pagesChapter 3 Part 1Behailu AsmareNo ratings yet
- Tendai B Chingwena. 2206assDocument7 pagesTendai B Chingwena. 2206assBright Tendai ChingwenaNo ratings yet
- Unit II Possible Questions With AnswersDocument19 pagesUnit II Possible Questions With AnswersNithish.V.J.No ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Introduction To Channel ModelingDocument7 pagesChapter Two: Introduction To Channel Modelinggashawbeza tayeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document4 pagesAssignment 2hamza shahbazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4MIMODocument15 pagesChapter 4MIMOSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Small Scale FadingDocument43 pagesChapter Two Small Scale FadingGuta MekesaNo ratings yet
- Mobile Radio Propagation EffectsDocument42 pagesMobile Radio Propagation EffectsShakeel HashmiNo ratings yet
- Modelling of WCDMA Base Station Signal in Multipath EnvironmentDocument7 pagesModelling of WCDMA Base Station Signal in Multipath EnvironmentInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Channel Hazards and Remedies for Mobile CommunicationsDocument9 pagesChannel Hazards and Remedies for Mobile Communicationsavenger hulkNo ratings yet
- MADEFELUDocument10 pagesMADEFELUBirhanu BangaNo ratings yet
- Fading Details in CelPlannerDocument15 pagesFading Details in CelPlannerCristine KorowajczukNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 MANET NotesDocument24 pagesUnit 1 MANET NotesSrie Teja N150232No ratings yet
- Fading Types in Wireless Communications Systems: S.Popa, N. Draghiciu, R. ReizDocument6 pagesFading Types in Wireless Communications Systems: S.Popa, N. Draghiciu, R. ReizHasan ShehzadNo ratings yet
- Adhoc and Sensor Networks CharacteristicsDocument25 pagesAdhoc and Sensor Networks CharacteristicsMohammed AkilNo ratings yet
- 6.LTE OFDM Principle-32Document31 pages6.LTE OFDM Principle-32Asad MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communication ConceptsDocument8 pagesMobile Communication ConceptssauravNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Tuorial Co5Document14 pages5.3 Tuorial Co5HarreniNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication FundamentalsDocument9 pagesWireless Communication FundamentalsRavi TejaNo ratings yet
- Propagation Measurements and Models For Wireless Communications ChannelsDocument8 pagesPropagation Measurements and Models For Wireless Communications ChannelsSawsan SaadNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Spread Spectrum System (Direct Sequence) Over Fading Channel Models - and Multi-Carrier CDMADocument18 pagesPerformance Analysis of Spread Spectrum System (Direct Sequence) Over Fading Channel Models - and Multi-Carrier CDMAMounesh PanchalNo ratings yet
- 1st Half - Module 4Document87 pages1st Half - Module 4SampNo ratings yet
- Mobile Radio Environment and Signal DisturbanceDocument49 pagesMobile Radio Environment and Signal DisturbanceNaresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Simple Analysisof BERPerformancefor BPSKand MQAMOver Fading ChannelDocument9 pagesSimple Analysisof BERPerformancefor BPSKand MQAMOver Fading ChannelLê Ngọc UyênNo ratings yet
- Vehicle To Vehicle RF Propagation MeasurementsDocument14 pagesVehicle To Vehicle RF Propagation MeasurementsWesal RefatNo ratings yet
- Channel Models For Wireless Communication SystemsDocument2 pagesChannel Models For Wireless Communication Systemsmohammed algmatyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document38 pagesLecture 5Haris ShoukatNo ratings yet
- Ps2 Mobile CommunicationDocument10 pagesPs2 Mobile Communicationchikku090700No ratings yet
- Statistical Modeling and Characterization of Fading ChannelsDocument13 pagesStatistical Modeling and Characterization of Fading ChannelsAhmad KhalifehNo ratings yet
- Digital Communications: Design For The Real WorldDocument19 pagesDigital Communications: Design For The Real WorldShunyi LiuNo ratings yet
- Lec 8 FadingDocument30 pagesLec 8 FadingDuy LeNo ratings yet
- Rappaport - 3er CapDocument70 pagesRappaport - 3er CapStevenArroyave100% (1)
- A Survey of Various Propagation Models For Mobile CommunicationsDocument32 pagesA Survey of Various Propagation Models For Mobile CommunicationsAnonymous 7yvOCCG100% (1)
- Unit 2Document37 pagesUnit 2Rakesh MenonNo ratings yet
- IEEE journal explores channel modeling for satellite communicationsDocument10 pagesIEEE journal explores channel modeling for satellite communicationsHiba AltahirNo ratings yet
- Microwave Path Design ConsiderationsDocument6 pagesMicrowave Path Design Considerationssayys1390No ratings yet
- WCN Notes-MergedDocument173 pagesWCN Notes-MergedYamini BollineniNo ratings yet
- P d) p P dB) =10 log P P: r t.G .G - λ L t rDocument10 pagesP d) p P dB) =10 log P P: r t.G .G - λ L t rTrifa QadirNo ratings yet
- Modul 2 - LargeScaleFading - WCSDocument74 pagesModul 2 - LargeScaleFading - WCSRamsel BataraNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument48 pagesUnit IManochandar ThenralmanoharanNo ratings yet
- Wireless Mobile Communication Unit 3Document28 pagesWireless Mobile Communication Unit 3Siva KumarNo ratings yet
- WC Module 2Document151 pagesWC Module 2rushildhamandeNo ratings yet
- Mobile Radio PropagationDocument6 pagesMobile Radio PropagationteshomeNo ratings yet
- Wireless Channel CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesWireless Channel Characteristicsbenny_1811No ratings yet
- RF PlanningDocument29 pagesRF Planningmohas92No ratings yet
- Wireless LocalizationDocument137 pagesWireless LocalizationNicoli LourençoNo ratings yet
- Cellular Networks Signal LossesDocument4 pagesCellular Networks Signal LossesDoncollins MuneneNo ratings yet
- Propagation Fundamentals and Literature SearchDocument24 pagesPropagation Fundamentals and Literature SearchkoncypikeNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communications HandbookDocument40 pagesMobile Communications HandbookSai RamNo ratings yet
- Link Budget Design and Doppler ShiftDocument5 pagesLink Budget Design and Doppler ShiftDr.S.ThenappanNo ratings yet
- FADING Unit 2Document8 pagesFADING Unit 2TisthaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1: Introduction of Wireless NetworksDocument23 pagesUnit - 1: Introduction of Wireless NetworksRashmi BhadoriyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Introduction of Wireless Channel PDFDocument83 pagesUnit 1 - Introduction of Wireless Channel PDFAman MugutNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Mobile Radio Propagation Small-Scale Fading and MultipathDocument43 pagesChapter 4: Mobile Radio Propagation Small-Scale Fading and MultipathAnonymous H6bzpSwYtNo ratings yet
- Limited Noise SystemsDocument2 pagesLimited Noise SystemsMohammed BotNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 NMDocument4 pagesLab 3 NMMohammed BotNo ratings yet
- MIT-BIH Arrhythmia Database Directory (Tables) PDFDocument1 pageMIT-BIH Arrhythmia Database Directory (Tables) PDFMohammed BotNo ratings yet
- Data StructureDocument6 pagesData StructureMohammed BotNo ratings yet
- Lab 01 PLCDocument5 pagesLab 01 PLCMohammed BotNo ratings yet
- Midterm2 313 SolutionDocument4 pagesMidterm2 313 SolutionMohammed BotNo ratings yet