Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organic Compounds (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acid)
Organic Compounds (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acid)
Uploaded by
Ishi Balbin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesOrganic compounds contain carbon and other elements like hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, or phosphorus. There are four main types of organic compounds: carbohydrates made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and used as energy sources; lipids made of similar elements and used for storing energy; proteins made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen and consisting of amino acid chains used for cellular structure and functions; and nucleic acids made of additional elements and used to direct and store genetic information.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentOrganic compounds contain carbon and other elements like hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, or phosphorus. There are four main types of organic compounds: carbohydrates made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and used as energy sources; lipids made of similar elements and used for storing energy; proteins made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen and consisting of amino acid chains used for cellular structure and functions; and nucleic acids made of additional elements and used to direct and store genetic information.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesOrganic Compounds (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acid)
Organic Compounds (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic Acid)
Uploaded by
Ishi BalbinOrganic compounds contain carbon and other elements like hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, or phosphorus. There are four main types of organic compounds: carbohydrates made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and used as energy sources; lipids made of similar elements and used for storing energy; proteins made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen and consisting of amino acid chains used for cellular structure and functions; and nucleic acids made of additional elements and used to direct and store genetic information.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
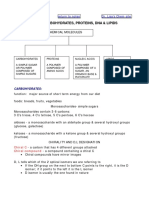
LECTURE 9: ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
In chemistry, the term ORGANIC describes
chemical compounds that contain Carbon and
other elements such as Hydrogen, Oxygen,
Nitrogen, Sulfur, or Phosphorus.
THE FOUR TYPES OF ORGANIC
COMPOUND
1. CARBOHYDRATES
It is made up elements such as C, H, O,
where H:O = 2:1
Example: Glucose (C H O )
6 12 6
Uses: energy source, cell structure, &
stored energy in plants (starch).
Classification:
Monosaccharide – glucose, fructose
Disaccharide – maltose, sucrose
Polysaccharide – starch, glycogen,
cellulose
2. LIPIDS
It is made up elements such as C, H, O,
where H:O > 2:1
Example: fats, oils, waxes, cheese
Uses: storing energy, components of cell
membranes, signaling, waterproof covering.
Classification:
Triglycerides – fats, oils, waxes
Steroids – tablets, syrups, inhalers
Phospholipids – soybean, canola seed,
sunflower
3. PROTEINS
It is made up elements such as C, H, O, and
N. It consists of chains of amino acids called
peptides.
Example: hemoglobin in our blood, insulin,
collagen, myoglobin
Uses: cellular structure, controls substances
in and out of cell, fights diseases.
4. NUCLEIC ACID
It is made up
elements such as C,
H, O, N and P. The
building blocks of
nucleic acids are
called nucleotides. It
is composed of phosphate group attached to a
sugar and nitrogenous base.
Uses: direct and store information for
reproduction and cellular growth
Classification:
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) – single strand
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) – double-
helix strand
You might also like
- Sources of CarbohydratesDocument17 pagesSources of Carbohydratesjcee2008No ratings yet
- Bot-403 Cell Biology, Genetics and Evolution 4 (3-1)Document38 pagesBot-403 Cell Biology, Genetics and Evolution 4 (3-1)Abdul Rehman100% (1)
- Monosaccharide Disaccharide PolysaccharideDocument3 pagesMonosaccharide Disaccharide PolysaccharideRhissan Bongalosa AcebucheNo ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument6 pagesBiological MacromoleculesThalia Diosenne ArabesNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Quarter 1 Week 4 Discussion 1Document26 pagesPhysical Science Quarter 1 Week 4 Discussion 1CrimstonNo ratings yet
- Physical Science - Biological MacromoleculesDocument18 pagesPhysical Science - Biological MacromoleculesToni GraceNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument10 pagesCarbohydratestomdas2011No ratings yet
- Submitted To: Meenakshi Ma'am Submitted By: Kunal Singh Shekhawat, Kuldeep Singh RathoreDocument67 pagesSubmitted To: Meenakshi Ma'am Submitted By: Kunal Singh Shekhawat, Kuldeep Singh RathoreKunal Singh Shekhawat100% (1)
- Biomolecules (2022)Document51 pagesBiomolecules (2022)Raymon Inolino IletoNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument57 pagesBio MoleculesRandelNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Carbon Compounds: Unit 3: BiochemistryDocument21 pages3.1 Carbon Compounds: Unit 3: Biochemistryapi-520057338No ratings yet
- Scie - 10 M 6 Q4Document4 pagesScie - 10 M 6 Q4ainahNo ratings yet
- Dicussion Forum: Carbohydrates ProteinsDocument3 pagesDicussion Forum: Carbohydrates ProteinsKim Angelo del CastilloNo ratings yet
- What Is A CarbohydrateDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Carbohydrateai4138769No ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument36 pagesBiological MacromoleculesArthur LaurelNo ratings yet
- Organic CompoundsDocument16 pagesOrganic Compoundsjezzaniexyane28No ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument22 pagesBiological Macromoleculesharrymirabs19No ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument62 pagesBiological MacromoleculesTeresita OlegarioNo ratings yet
- Biochemical MoleculesDocument4 pagesBiochemical MoleculesValeria OlmedoNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates and LipidsDocument11 pagesCarbohydrates and LipidsCarlene OretaNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 BiomoleculesDocument3 pagesGrade 12 BiomoleculesLeopoldo Domingo, Jr.No ratings yet
- Biomolecules Activity SheetDocument5 pagesBiomolecules Activity SheetVanessa QuinolNo ratings yet
- Unit 13Document65 pagesUnit 13amna.qadri60No ratings yet
- Anatomy at PhysiologyDocument17 pagesAnatomy at Physiologyagentlara28No ratings yet
- Chemistry Assignment: BiomoleculesDocument28 pagesChemistry Assignment: BiomoleculesShruthi GNo ratings yet
- Biological MacroDocument49 pagesBiological MacroChristine De San JoseNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Molecules of LifeDocument20 pagesBiochemistry: Molecules of Lifeapi-464344582No ratings yet
- Macromolecules: Self-Preparation Biology Assessment TestDocument36 pagesMacromolecules: Self-Preparation Biology Assessment Testmay ann dimaanoNo ratings yet
- Biological Macromolecules PDFDocument31 pagesBiological Macromolecules PDFAngeline CortezNo ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument26 pagesBiological MacromoleculesZairra Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument2 pagesBIOMOLECULESLynette BantayanNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument75 pagesBiomoleculesHumms B Lyka Jenny Alterado BangugNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument11 pagesBiomoleculesHarrish SandeevNo ratings yet
- Marites PPT Demo Final....Document52 pagesMarites PPT Demo Final....Marites B. MartinNo ratings yet
- Scie - 10 M 6 Q4Document4 pagesScie - 10 M 6 Q4ainahNo ratings yet
- Biomolcules (Week 3) (AutoRecovered)Document6 pagesBiomolcules (Week 3) (AutoRecovered)JoshRobertD.ObaobNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument27 pagesBio MoleculesAceres John HenryNo ratings yet
- I. Monosaccharides (Simple Sugars) :: Aldoses KetosesDocument9 pagesI. Monosaccharides (Simple Sugars) :: Aldoses KetosesdenisseNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Chemistry AssignmentDocument25 pagesBiomolecules Chemistry Assignmentxelivo8277No ratings yet
- BiochemicalsDocument8 pagesBiochemicalsAlthea Lynn B. CallantaNo ratings yet
- BBC1 K14 K15 KarbohidratDocument31 pagesBBC1 K14 K15 Karbohidratbrigita charvioNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Chemistry Lecture HandoutsDocument28 pagesCarbohydrate Chemistry Lecture Handoutsnasreenshaker0No ratings yet
- Lecture Molecular Biology IDocument26 pagesLecture Molecular Biology ImartinmulingeNo ratings yet
- Week 3 A BiochemistryDocument27 pagesWeek 3 A BiochemistryRinaldo Paulus BolangNo ratings yet
- MoleculesDocument60 pagesMoleculesCharlize Jeneah MedinaNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument58 pagesBio Moleculescheryl tayasNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument7 pagesBio MoleculesJatt PandherNo ratings yet
- SMB1102Document164 pagesSMB1102supremesiddharth0No ratings yet
- LipidsDocument29 pagesLipidszubairahmed27272No ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument54 pagesBiomoleculeslevi0417No ratings yet
- Chemistry Course LH and ESDocument22 pagesChemistry Course LH and ESkhaledshekh133No ratings yet
- Eglamour SlidesCarnivalDocument36 pagesEglamour SlidesCarnivalmunnu2461No ratings yet
- Biochemistery Mid TermDocument159 pagesBiochemistery Mid TermPh. Omar yasirNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument34 pagesBio MoleculeshaimahmampaocutieNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 11 - Week 4 - Quarter 3Document45 pagesPhysical Science 11 - Week 4 - Quarter 3santihera878No ratings yet
- Genbio3 Stem11bDocument72 pagesGenbio3 Stem11bKyle BajandeNo ratings yet
- Lecture Research BiochemDocument16 pagesLecture Research BiochemDianne MaeNo ratings yet
- Life Substances (Macromolecules)Document20 pagesLife Substances (Macromolecules)vkil YNo ratings yet
- Notes On Lipids and Nucleic Acids-Df 19-1Document21 pagesNotes On Lipids and Nucleic Acids-Df 19-1Albert MweembaNo ratings yet
- Polar Lipids: Biology, Chemistry, and TechnologyFrom EverandPolar Lipids: Biology, Chemistry, and TechnologyMoghis U. AhmadNo ratings yet
- Structural Characteristics of CarbonDocument2 pagesStructural Characteristics of CarbonIshi BalbinNo ratings yet
- Seismic WavesDocument2 pagesSeismic WavesIshi BalbinNo ratings yet
- Organic Compounds ActivityDocument2 pagesOrganic Compounds ActivityIshi BalbinNo ratings yet
- Types of Strike Slip FaultDocument1 pageTypes of Strike Slip FaultIshi BalbinNo ratings yet