Professional Documents
Culture Documents
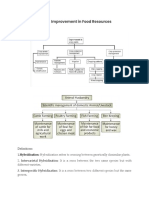
CH 13 Improvement in Food Resources
Uploaded by
PRAVEEN KUMARCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH 13 Improvement in Food Resources
Uploaded by
PRAVEEN KUMARCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER – 15
FOOD PRODUCTION
I.VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Which one is not a source of carbohydrate?
a)Rice b)Millets c)Sorghum d)Gram
2. Which one of the following species of honey bee is an Italian species?
a) Apis dorsata b) Apis florae c) Apis cerana indica d) Apis mellifera
3. To solve the food problem following is of the country, which among the necessary?
a) Increased production and storage of food grains b) Easy access of people to the food grain
c) People should have money to purchase the grains d) All of the above
4. What is a GM crop? Name any one such crop which is grown in India.
Ans: GM crops are the crops which are developed by introducing a new gene from any other
source e.g. bacteria or any other organism. Bt cotton is an example of GM crop which is made
insect-resistant by introducing gene from the bacteria.
5. Define hybridization.
Ans: Hybridization is a process by which only desired type and number of pollen grains are used
for fertilization and reproduction.
6. Define mixed cropping.
Ans: Mixed cropping is a cropping technique in which different types of crops are cultivated
together on the same field or land so that nutrient requirements are shared. This reduces risk
and gives some insurance against the failure of one of the crops.
II.SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Why is organic matter important for crop production?
Ans: Organic matter is very much important for enhancement in food production. Organic matter
is added in the form of manures to the crop. The organic matter enriches the soil with nutrients
and replenish the general deficiency of nutrients in the soil. It also water and for aeration of soil.
For example, the organic matter present in the manures increases the water holding capacity in
sandy soils and drainage in clayey soil. It also avoids water logging in clayey soils. The organic
matter also provides food for soil organisms (decomposers, such as bacteria, fungi, etc.) which in
turn help in making nutrients available to plants.
2. Cultivation practices and crop yield are related to environmental condition. Explain.
Ans: Cultivation practices and crops yield are related to environmental condition. Various crops
require different climatic conditions, temperature and photoperiod, for their growth and
completion of life cycle. On the basis of seasonal variations, crops in India can be classified into
three main groups:
*Rabi crop: It is a winter season crop grown from November to April.
*Kharif crop: It is a rainy season crop grown from June to October.
*Zaid crop: It is a summer season crop grown from April to June.
3. ln agricultural practices, higher input gives higher yield. Discuss how?
Ans:In agricultural practices, higher inputs give higher yield. Higher inputs in the form of sowing
of seeds of improved variety, application of better manures and fertiliser, proper spraying of
pesticides and weedicides, improved threshing and harvesting of crops leads to increase in crop
productivity. This also means the higher money inputs to raise the yield. Financial condition of
farmers allow them to take up different farming practices and technologies. The farmer’s
purchasing capacity for input decides cropping system and production practices.
4. Differentiate between compost and vermi- compost?
Ans:Compost: It is prepared from farm and town refuse such as vegetable and animal refuse,
faecal matter of human beings, weeds, straw, rice husks, forest litter, etc. It is a biological process
in which both aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms decompose the organic matter.
It takes about 3 to 6 months for decomposition of organic refuse.
Vermicompost: It is the degradation of organic waste through the consumption by earthworms.
It takes about 1-2 months to prepare a vermicompost.
III.LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Discuss the role of hybridisation in crop improvement.
Ans:The crossing between genetically dissimilar plants to produce a new kind (hybrid) is called
hybridisation. Crossing may be between two different varieties (intervarietal), between two different
species (interspecific) and between different genera (intergeneric).Cross-breeding of two varieties of
plants is carried out to obtain an improved variety of plants which will combine in it both the desired
characteristics of parent crop plants. For example, the new improved variety of crop plants, thus obtained
will give high yield of food grains and it will be disease resistant too. This process of cross breeding of
different plants to obtain a new improved variety of crops is called hybridisation.
Selection and hybridisation are often combined in breeding. In India crops are grown in diverse types of
soil and different climatic conditions by poor to progressive farmers. Keeping in mind climatic factors,
input application, disease and pest resistance, quality and adaptability etc. a large number of varieties
have been developed by hybridisation. Such varieties are high- yielding, resistant to diseases and pests,
have better quality and early to late maturing time.
2. Write the modes by which insects affect the crop yield.
Ans: Insects affect the crop yields in both useful and harmful ways. Harmful insects attack the plants and
are called insect pests. Insect pests are of following types :
Chewing insects: Insect pests of this category cut the roots, stem and leaves with the help of their
chewing mouth parts. They chew and swallow the pieces of plant parts. E.g., grasshoppers, caterpillars,
locusts etc.
Sucking insects: These insects puncture the plant parts and suck the cell sap with the help of their
needle like hollow beaks. E.g., leaf hoppers, aphids, bugs, etc.
Internal feeders: These insects bore into stem and fruits. They live inside the plant parts and harm the
crop yield. E.g., weevils, borers, etc.
Every year Insect pests cause a significant damage to the crops and thereby reduce the productivity.
Various methods like use of chemical pesticides, natural insecticides like neem, nicotine etc. and various
biological methods are employed to control the pest infestation and reduce the damage done by them.
Useful insects are those which assist in pollination thus, ensure fruit formation and those which feed on
harmful) insect pests. E.g., lady bird beetle feeds on aphids thus controls this pest.
You might also like
- Heirloom Gardening and Biodiversity_ Cultivating a Time : Honored Legacy for a Sustainable FutureFrom EverandHeirloom Gardening and Biodiversity_ Cultivating a Time : Honored Legacy for a Sustainable FutureNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources-NotesDocument9 pagesImprovement in Food Resources-Notesapi-285274293No ratings yet
- IX SC - CH 15 - Q & A - Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument6 pagesIX SC - CH 15 - Q & A - Improvement in Food Resourcesgbshse.techNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Biology Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument13 pagesCBSE Class 9 Biology Improvement in Food ResourcesChander Bhan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Improve Food Resources Through Crop VarietyDocument5 pagesImprove Food Resources Through Crop VarietyAnn VargheseNo ratings yet
- Module - 1/4 Class IX Prepared By-Punam Jyoti Lakra School - AECS TuramdihDocument16 pagesModule - 1/4 Class IX Prepared By-Punam Jyoti Lakra School - AECS TuramdihDanica S.JNo ratings yet
- 15 Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument10 pages15 Improvement in Food Resourcestara tuitionNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument5 pagesImprovement in Food ResourcesJ.S CommercialNo ratings yet
- Question Bank BioDocument19 pagesQuestion Bank BioMr Sony MathewNo ratings yet
- IX-15-Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument14 pagesIX-15-Improvement in Food Resourcesvaishnav.shrot777No ratings yet
- Use of Microbes in AgricultureDocument4 pagesUse of Microbes in AgricultureAran MuthNo ratings yet
- Page No: 204: Chapter 15 - Improvement in Food Resources in Text QuestionsDocument7 pagesPage No: 204: Chapter 15 - Improvement in Food Resources in Text Questionsmadhurreet jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 15: Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument14 pagesChapter - 15: Improvement in Food Resourcesanmolmuskan2020No ratings yet
- RELEVANCE OF BIOLOGY TO AGRICULTUREDocument14 pagesRELEVANCE OF BIOLOGY TO AGRICULTUREAlex JuniorNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument20 pagesImprovement in Food ResourcesSarvagya ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Biology Study MaterialDocument74 pagesBiology Study MaterialSatish KumarNo ratings yet
- Improvement of Food ResourcesDocument6 pagesImprovement of Food ResourcesSanvi SinghNo ratings yet
- Sarthak Arora: - IX - C:-S.R.D.A.V. Public Scool: Made by ClassDocument15 pagesSarthak Arora: - IX - C:-S.R.D.A.V. Public Scool: Made by ClassNaman Gaur100% (1)
- Improvement in Food Resources-NotesDocument9 pagesImprovement in Food Resources-NotesHemang NityantNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources Class 9 NotesDocument8 pagesImprovement in Food Resources Class 9 NotesANAYA SHARANNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources Important Questions 2022-23Document20 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources Important Questions 2022-23abhishek singhNo ratings yet
- Science UT 1Document99 pagesScience UT 1chitra sabarinathanNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources... Chapter .. Home Work QuestionsDocument6 pagesImprovement in Food Resources... Chapter .. Home Work Questionsthe pantherNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes of Improvement in Food Resources Class 9Document11 pagesRevision Notes of Improvement in Food Resources Class 9Mayank ShiniNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources Class 9 NotesDocument8 pagesImprovement in Food Resources Class 9 NotesRubeena VargheseNo ratings yet
- Nutritious Foods from Cereals, Pulses, Fruits and VegetablesDocument6 pagesNutritious Foods from Cereals, Pulses, Fruits and Vegetablesapoorv saxenaNo ratings yet
- 15 Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument24 pages15 Improvement in Food Resourcesjohn neil basasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 SIPDocument4 pagesChapter 1 SIPCarlos GeronaNo ratings yet
- Improve food resources through scientific practicesDocument11 pagesImprove food resources through scientific practicesminakshi kalraNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources-NotesDocument6 pagesImprovement in Food Resources-Notesyatharthdange131No ratings yet
- Transgenic BT Cotton PDFDocument18 pagesTransgenic BT Cotton PDFnurul9535No ratings yet
- Biology - Chapter 15 Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument3 pagesBiology - Chapter 15 Improvement in Food ResourcesShailaja MestryNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Zonal PlantDocument6 pagesClass 8 Zonal PlantRitesh SNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resource - Mat PDFDocument13 pagesImprovement in Food Resource - Mat PDFAyushman TripathyNo ratings yet
- St. Theresa - Sr.Sec - School: Crop Protection and ManagementDocument13 pagesSt. Theresa - Sr.Sec - School: Crop Protection and ManagementqwertyuiNo ratings yet
- Class 8 - Science - Crop Production and ManagementDocument7 pagesClass 8 - Science - Crop Production and ManagementAyaan KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Ypvpgwl15ypvpgwl15-Study Material-202005110828pm028364-Science 1-1Document5 pagesYpvpgwl15ypvpgwl15-Study Material-202005110828pm028364-Science 1-1AnantNo ratings yet
- Project Report On BiofertilizerDocument9 pagesProject Report On BiofertilizerEIRI Board of Consultants and Publishers100% (1)
- Fathima ShireenDocument27 pagesFathima ShireenMuhsina HananNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 15, Improvement in Food Resources Part IDocument10 pagesChapter - 15, Improvement in Food Resources Part IMonika Mehan100% (14)
- Untitled DocumentDocument26 pagesUntitled Documentkartikmishra89299No ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes Ch15 Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument12 pages09 Science Notes Ch15 Improvement in Food ResourcesDhiraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- A Exercise 8Document7 pagesA Exercise 8Khent TermoorNo ratings yet
- PBG 301 First Half NotesDocument79 pagesPBG 301 First Half NotesUnknownAuthorNo ratings yet
- Science Notes 8Document41 pagesScience Notes 8adarsh bhushanNo ratings yet
- Anic FarmingDocument8 pagesAnic FarmingAbdullah Al MamunNo ratings yet
- IPM Control MethodsDocument13 pagesIPM Control Methodscristian ricopertoNo ratings yet
- Crop Protection PPTDocument14 pagesCrop Protection PPTqwertyuiNo ratings yet
- Non-Conventional Farming Cont'dDocument3 pagesNon-Conventional Farming Cont'dDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Answer Book VIII ScienceDocument59 pagesAnswer Book VIII Sciencecfhss70% (33)
- Ganesh Project (Of) 2Document31 pagesGanesh Project (Of) 2Banty Chandresh DixitNo ratings yet
- Food Production and ManagementDocument6 pagesFood Production and ManagementAamirNo ratings yet
- Ch-15 Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument9 pagesCh-15 Improvement in Food ResourcesAakankshaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Intext QuesionsDocument5 pagesChapter 15 - Intext QuesionsShailaja MestryNo ratings yet
- Controls of Insect PestsDocument17 pagesControls of Insect PestsDitto V DavisNo ratings yet
- Diy BiodiversityDocument5 pagesDiy BiodiversityRoger MillerNo ratings yet
- Indigenous MicroorganismsDocument42 pagesIndigenous MicroorganismsJaylord Agpuldo100% (1)
- Noraina Thesis ProposalDocument18 pagesNoraina Thesis ProposalMAE ANN TOLENTINONo ratings yet
- Agricultural AssignmentDocument5 pagesAgricultural AssignmentKeiann Renae SimonNo ratings yet
- Organic and Inorganic Landscape ElementsDocument29 pagesOrganic and Inorganic Landscape ElementsAli ZainalNo ratings yet
- Contoh Kurva S AddendumDocument3 pagesContoh Kurva S AddendumAnjar Satria NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Soil Cohesion and Friction Angle ValuesDocument6 pagesSoil Cohesion and Friction Angle ValuesHarish Kumar Mahavar0% (1)
- Lee and Poulos - 1990 - Axial Response Analysis of PilesDocument16 pagesLee and Poulos - 1990 - Axial Response Analysis of PilesRsiggyNo ratings yet
- Strength Optimization Models For A Multi-Variant Binder Concrete Using Osadebe's Optimized MixesDocument14 pagesStrength Optimization Models For A Multi-Variant Binder Concrete Using Osadebe's Optimized MixesIJAERS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Marijuana Grower's HandbookDocument69 pagesMarijuana Grower's HandbookrevengemrkNo ratings yet
- Types of Rigid Pavements: Jointed Plain Concrete Pavement (JPCP), Jointed Reinforced Concrete Pavement (JRCP), Continuously Reinforced Concrete Pavement (CRCPDocument48 pagesTypes of Rigid Pavements: Jointed Plain Concrete Pavement (JPCP), Jointed Reinforced Concrete Pavement (JRCP), Continuously Reinforced Concrete Pavement (CRCPashoknrNo ratings yet
- Effects of PH On The Leaching Mechanisms of Elements From y Ash Mixed SoilsDocument16 pagesEffects of PH On The Leaching Mechanisms of Elements From y Ash Mixed SoilsArvindKumarNo ratings yet
- Mektan 1Document39 pagesMektan 1ErychrystNo ratings yet
- Western Indonesia Roads Project Density & Moisture Content Test ResultsDocument2 pagesWestern Indonesia Roads Project Density & Moisture Content Test ResultsivanNo ratings yet
- Terra Viva: Staying AliveDocument13 pagesTerra Viva: Staying AliveChelsea Green PublishingNo ratings yet
- G.F. ReportDocument3 pagesG.F. ReportIsra Bint zahedNo ratings yet
- Agric Science G 8 9Document61 pagesAgric Science G 8 9Mwansa Nkandu100% (1)
- Seaweeds ExtractDocument6 pagesSeaweeds ExtractWahid SandagNo ratings yet
- Qualities of Successful EntrepreneursDocument13 pagesQualities of Successful EntrepreneursHF ManigbasNo ratings yet
- Unsaturated Soil Mechanics in Engineering Practice-2 (A1 4pages)Document6 pagesUnsaturated Soil Mechanics in Engineering Practice-2 (A1 4pages)logarwallNo ratings yet
- Organic Farming-Kunfan Chuskit (761) PPTDocument40 pagesOrganic Farming-Kunfan Chuskit (761) PPTKunfan Chuskit100% (1)
- Optimization and Stress Analysis of Underground Oil Pipelines in High and Steep Slope AreasDocument7 pagesOptimization and Stress Analysis of Underground Oil Pipelines in High and Steep Slope AreasdakidofdaboomNo ratings yet
- Solar Panels CleaningDocument13 pagesSolar Panels CleaningEdu Daryl Maceren100% (1)
- A Case Study of Slope Failure in Central Trinidad Due To Water Pipe LeakageDocument6 pagesA Case Study of Slope Failure in Central Trinidad Due To Water Pipe Leakageneil beeraspatNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical Cycles ExplainedDocument25 pagesBiogeochemical Cycles ExplainedAlokfriNo ratings yet
- Water Lab Report AnalysisDocument18 pagesWater Lab Report AnalysisElilragiGanasanNo ratings yet
- Soil Texture Analysis Using Laser Diffraction TechniquesDocument6 pagesSoil Texture Analysis Using Laser Diffraction TechniquesZaharul Luthfi ZakiyahNo ratings yet
- The Amazing Race PPTX NewDocument19 pagesThe Amazing Race PPTX Newapi-297841438No ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Living in The Environment 19th Edition Miller Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Living in The Environment 19th Edition Miller Solutions Manual PDFemicant.pintosfe9soe100% (10)
- Case StudY - ManagementDocument12 pagesCase StudY - ManagementSeph De Castro BrabanteNo ratings yet
- Engineering Soil Classification Systems GuideDocument51 pagesEngineering Soil Classification Systems GuideEARL JOHN REYESNo ratings yet
- ResumeDocument49 pagesResumeAtikDwiOktavianiNo ratings yet
- Pegging and Leveling A Section of Road 2. What Type of Instrument Is Useful For Setting Out The Road 3. Soil Compaction and StabilizationDocument24 pagesPegging and Leveling A Section of Road 2. What Type of Instrument Is Useful For Setting Out The Road 3. Soil Compaction and StabilizationRujhat ZakhoyNo ratings yet