Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Thyroid Gland Is A Small
Uploaded by
Ameyrh SHehabOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Thyroid Gland Is A Small
Uploaded by
Ameyrh SHehabCopyright:
Available Formats
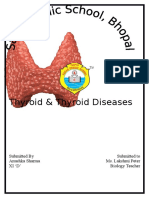
The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of the
neck. It plays a crucial role in the body's metabolism and produces hormones
that regulate various bodily functions. Here is a brief overview of how the
thyroid gland functions:
1. Hormone production: The thyroid gland produces two main hormones
called thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones contain
iodine and are essential for the regulation of metabolism, growth, and
development.
2. Hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis: The production of thyroid
hormones is regulated by a feedback loop involving the hypothalamus,
pituitary gland, and thyroid gland. The hypothalamus releases
thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which stimulates the pituitary
gland to secrete thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH, in turn,
stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release T3 and T4.
3. Iodine uptake: The thyroid gland requires iodine to produce thyroid
hormones. Iodine is obtained through the diet and is actively taken up
by the thyroid gland from the bloodstream.
4. Thyroid hormone synthesis: Within the thyroid gland, iodine is
combined with an amino acid called tyrosine to create T3 and T4. T4 is
the main hormone produced by the thyroid, but it is converted into the
more active form, T3, in various tissues throughout the body.
5. Hormone release: Once synthesized, T3 and T4 are stored in the thyroid
follicles. When stimulated by TSH, they are released into the
bloodstream to reach target tissues throughout the body.
6. Feedback regulation: The levels of T3 and T4 in the bloodstream are
continuously monitored by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. If the
levels are too low, the hypothalamus and pituitary gland increase the
production and release of TRH and TSH, respectively, to stimulate the
thyroid gland. Conversely, if the levels are too high, the production of
TRH and TSH is decreased to reduce thyroid hormone production.
Overall, the thyroid gland plays a vital role in maintaining the body's metabolic
rate, growth, and development by producing and regulating thyroid
hormones.
You might also like
- Thyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedFrom EverandThyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Anatomy & Physiology of Thyroid GlandDocument5 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Thyroid GlandJohnpaul DelapenaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!From EverandThyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- All About ThyroidDocument1 pageAll About ThyroidSky Rain Haven OpsimarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Thyroid Gland: To The TracheaDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Thyroid Gland: To The TracheaDuchess Ciedelle Abano ManatadNo ratings yet
- Physio Essay 15Document3 pagesPhysio Essay 15Zoya LiaquatNo ratings yet
- 15.thyroid GlandDocument3 pages15.thyroid GlandNektarios TsakalosNo ratings yet
- Thyroid HormonesDocument7 pagesThyroid HormonesAbdullah EssaNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination Animal HormonesDocument46 pagesControl and Coordination Animal HormonesgolaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument5 pagesThyroid GlandJhaloe Papa FawwazNo ratings yet
- Hypothyroidism PathophysiologyDocument1 pageHypothyroidism PathophysiologyCleo Joyce C. CristalNo ratings yet
- Hashimoto's Thyroiditis InfographicDocument2 pagesHashimoto's Thyroiditis InfographicPetraNo ratings yet
- Physiology - Final Endocrine #2 Sunday 26 /12/2010 Dr. Mohammad Ja'afar By:Israa Qudah & Sura Al-HamiDocument9 pagesPhysiology - Final Endocrine #2 Sunday 26 /12/2010 Dr. Mohammad Ja'afar By:Israa Qudah & Sura Al-HamiisraaqudahNo ratings yet
- ThyroidDocument84 pagesThyroidMeLissa Pearl GuillermoNo ratings yet
- HypothyroidismDocument7 pagesHypothyroidismGkdhdhdgdgidNo ratings yet
- Week 11 Endocrinology Part 2 3Document12 pagesWeek 11 Endocrinology Part 2 3Toff GoyenecheaNo ratings yet
- Wa0000.Document10 pagesWa0000.parabharshita2709No ratings yet
- Exp 03Document5 pagesExp 03NaitikNo ratings yet
- Thyroid HormonDocument13 pagesThyroid HormonWira SentanuNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Endocrinology (Week-2)Document8 pagesMetabolic Endocrinology (Week-2)wasimsafdarNo ratings yet
- Week 13 Endocrine 2 1 PPDocument57 pagesWeek 13 Endocrine 2 1 PPJoy KNo ratings yet
- HormonesDocument23 pagesHormonesKU ExergonicNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Thyroid Gland: "Name: Huma R.No: ZG-07 Bs Zoology-VII" Thyroid GlandDocument5 pagesAnatomy of The Thyroid Gland: "Name: Huma R.No: ZG-07 Bs Zoology-VII" Thyroid GlandHuma r.no:7 Bs zoology Vll100% (1)
- 3.thyroid Hormones and DisordersDocument46 pages3.thyroid Hormones and DisorderssinayupeNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Metabolic HormonesDocument4 pagesThyroid Metabolic HormonesHala RezaNo ratings yet
- Thyroid SummaryDocument2 pagesThyroid Summarydrsean ananiaNo ratings yet
- What Are Thyroid DisordersDocument1 pageWhat Are Thyroid Disordersfatima chrystelle nuñalNo ratings yet
- What Are Thyroid DisordersDocument2 pagesWhat Are Thyroid DisordersChellaMarieNo ratings yet
- 0a27thyroid Function TestDocument35 pages0a27thyroid Function TestAshokvardhan Chowdary Nandigam67% (3)
- (MS) Trans 2 - Thyroid and Parathyroid DisordersDocument5 pages(MS) Trans 2 - Thyroid and Parathyroid DisordersEryl Franz HerreraNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Tests: What Is The Thyroid?Document8 pagesThyroid Tests: What Is The Thyroid?JyotiNo ratings yet
- Thyroxine and OxytocinDocument53 pagesThyroxine and OxytocinUshna SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of The Endocrine System PDFDocument74 pagesPharmacology of The Endocrine System PDFGlenn Perez71% (7)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyDavid RefuncionNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Thyroid Gland. Endocrine Pancreatic DysfunctionsDocument12 pagesPathophysiology of Thyroid Gland. Endocrine Pancreatic Dysfunctionskate_borovicNo ratings yet
- Overview of Endocrine System BYDocument79 pagesOverview of Endocrine System BYAkwu AkwuNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of The Endocrine SystemDocument74 pagesPharmacology of The Endocrine SystemarpanabiswassshetyeNo ratings yet
- Hormones SubtopicsDocument77 pagesHormones SubtopicsSulaiman UmraniNo ratings yet
- Thyroid GlandDocument19 pagesThyroid GlandTanya SinghNo ratings yet
- 5 Thyroid Hormones محدث لبلاك بوردDocument27 pages5 Thyroid Hormones محدث لبلاك بوردRana Abdullah100% (1)
- Science Endocrine System NotesDocument6 pagesScience Endocrine System Notesstephanie adorioNo ratings yet
- BB Module IV Thyroid and Anti-Thyroid Drugs 26.08.2021Document17 pagesBB Module IV Thyroid and Anti-Thyroid Drugs 26.08.2021Gunjan KalyaniNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Group (5) Work 2Document8 pagesAnatomy Group (5) Work 2nanakwame5769No ratings yet
- Physiology of The Thyroid GlandDocument28 pagesPhysiology of The Thyroid GlandSecret AgentNo ratings yet
- HBB 2102 Endocrine System Student NotesDocument8 pagesHBB 2102 Endocrine System Student Notesjordanmusyoki19No ratings yet
- Thyroid Function Tests: What Is The Thyroid Gland?Document2 pagesThyroid Function Tests: What Is The Thyroid Gland?rastamaneazy269No ratings yet
- ENDOCRINE Systems Ad Its DisordersDocument21 pagesENDOCRINE Systems Ad Its DisordersAmir PermitivoNo ratings yet
- All About The ThyroidDocument6 pagesAll About The ThyroidΚυριακη ΖαρβαληNo ratings yet
- The Thyroid Gland and Disorders 02032021.1Document12 pagesThe Thyroid Gland and Disorders 02032021.1Leslie PaguioNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System IntroductionDocument5 pagesEndocrine System IntroductionAnnapurna DangetiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System LessonDocument47 pagesEndocrine System LessonMA. FRITZIE DE ASISNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of Endocrine SystemDocument34 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Endocrine SystemUzma Khan100% (1)
- AP-2 Lab Report - Lab 01 The Endrocine SystemDocument15 pagesAP-2 Lab Report - Lab 01 The Endrocine Systemrcdunfee86% (7)
- Thyroid and Thyroid DiseasesDocument22 pagesThyroid and Thyroid DiseasesAnushka Sharma82% (17)
- Corticotropins and GonadotropinsDocument39 pagesCorticotropins and GonadotropinsSudhakar LakavathNo ratings yet
- Session-9 Thyroid-2024Document29 pagesSession-9 Thyroid-2024LT DRAGONXNo ratings yet
- HyperthyroidismDocument24 pagesHyperthyroidismelaine grace arataNo ratings yet
- Thyroid DiseasesDocument47 pagesThyroid Diseasesbiniam MesfinNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland: Ruswana Anwar, Tono DjuwantonoDocument49 pagesThyroid Gland: Ruswana Anwar, Tono Djuwantonoyuyu tuptupNo ratings yet
- Thyroid & Parathyroid HormonesDocument53 pagesThyroid & Parathyroid Hormonesrehmanmughal87654No ratings yet
- V 1)Document3 pagesV 1)Ameyrh SHehabNo ratings yet
- Some Important MeaningsDocument1 pageSome Important MeaningsAmeyrh SHehabNo ratings yet
- Sleep and CreativityDocument2 pagesSleep and CreativityAmeyrh SHehabNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Week 3 1stDocument1 pageVocabulary Week 3 1stAmeyrh SHehabNo ratings yet
- Primary SchoolDocument2 pagesPrimary SchoolAmeyrh SHehabNo ratings yet
- OptionDocument9 pagesOptionAmeyrh SHehabNo ratings yet
- OptionDocument9 pagesOptionAmeyrh SHehabNo ratings yet
- NoorDocument1 pageNoorAmeyrh SHehabNo ratings yet
- March 2020: Ali Saad AlwanDocument13 pagesMarch 2020: Ali Saad Alwankameranduhoki1122No ratings yet
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Meltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalFrom EverandMeltdown: Nuclear disaster and the human cost of going criticalRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableFrom EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsFrom EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (146)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilFrom EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsFrom EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNo ratings yet
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeFrom EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookFrom EverandBioplastics: A Home Inventors HandbookRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Phase Equilibria in Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandPhase Equilibria in Chemical EngineeringRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeFrom EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireFrom EverandA Perfect Red: Empire, Espionage, and the Quest for the Color of DesireRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (129)
- Transformer: The Deep Chemistry of Life and DeathFrom EverandTransformer: The Deep Chemistry of Life and DeathRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)