Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Courts (Criminal) Chart
Uploaded by
Jarrod Jong 楊智仁Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Courts (Criminal) Chart
Uploaded by
Jarrod Jong 楊智仁Copyright:
Available Formats
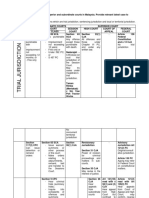
Courts Jurisdiction (Criminal)
Introduction
- Sec 6 CPC: The Courts which are involved in the administration of
criminal justice are:
Courts to be Open vs In Chambers
a) Federal Court - All inquiry and trial of offence shall be deemed an open court and public court
b) Court of Appeal to which the public generally may have access (Sec 101 SCA 1948) and in #Lee
Boon Tuan v PP[1960] there is nothing in the code which limits the right of the
c) High Court court to conduct any inquiry
d) Sessions Court - In Chambers usually only with the judge without the public
e) Magistrate Court
f) Court for Children
REDZA ZAKARIA LLM (UKM), LLB (HONS) LONDON, CLP 1
2nd class magistrate
-Trial jurisdiction: Section 88 SCA 1948: Can try offences:-
a) Max term of imprisonment does not exceed 12 mths; or
b) Punishable with a fine only (provided that if he opines punishment will be inadequate, he shall adjourn
the case for trial by 1st class Magistrate
- Sentencing jurisdiction: Section 89 SCA 1948: May pass any sentence allowed by law:-
a) Not exceeding 6 mths imprisonment;
b) Fine of not more than RM1k; or
c) Any combination above
- Other powers:
a) Section 83 SCA 1984: May issue summons, writ, warrant, may make orders on bail, remand,
adjournment, execution of judgment, and transfer of Session Court
b) Section 117 CPC May issue remand order
1st class magistrate
- Trial jurisdiction Section 85 SCA 1984, can try offences:-
a) The max imprisonment does not exceed 10 yrs; or
b) Punishable with fine only; or
c) Section 392 & 457 PC
- Sentencing jurisdiction: Section 87(1) SCA 1948:- may pass any sentence not exceeding:-
a) 5 yrs imprisonment;
b) Fine of RM10k;
c) Whipping up to 12 strokes; or
d) Any combination above
REDZA ZAKARIA LLM (UKM), LLB (HONS) LONDON, CLP 2
1st class magistrate
Exceptions:-
Other Powers:
- Proviso to Section 87(1) SCA 1948
- 3rd Schedule & Section 99A SCA 1948: Dismiss proceedings
- Section 41 DDA 1952: Can i) Try an offence except Section 39B; ii)Prison –
for res judicata and multiplicity of proceedings, lateral
not exceeding 5 yrs
transfer, punishment of corporation (#Dunlop Malaysian
- Section 118 Customs Act 1967: May order max fine of RM25k Industries Bhd v PP: Mg fined corp for pollution and 1 day
- Section 87(2) SCA 1948 imprisonment, later appealed was allowed Sentence of
imprisonment set aside)
#Tengku Hitam (Hashim J): Held Mg may invoke Section 87(2) if evidence
shows sentence is inadequate - Section 83 SCA 1948: May issue summons, writ, warrant;
may make orders on bail, remand, adjournment, execution
#Abdul Wahab (Sharma J): Section 87(2) only invoked if evidence of his of judgment, and transfer to Session Ct
previous convictions or antecedents is given after conviction but before
sentence -Section 9 CPC: Shall hear criminal trials; inquire into
complaints of offences and summon and examine
#Govindan: Mg passed 3 yrs imprisonment for theft even though A had 11 witnesses; issue search and arrest warrants; hold death
previous convictions. HC (Augustine Paul J) said that Section 87(2) should have inquiries; do as given in any written law
been invoked as A deserved heavier punishment
- Reference of constitutional question by subordinate court
to HC: Section 30(1) CJA 1964 (#Repco Holdings Bhd)
REDZA ZAKARIA LLM (UKM), LLB (HONS) LONDON, CLP 3
Sessions Court
Trial jurisdiction:
- Section 63 SCA 1948: May try all offences other than offences punishable with death
- #Nadarajah [2000]: A was tried in the Sess Ct for an offence under Section 506 PC. Defence objected
that it should be tried in MC Held: Section 85 does not exclude the trial jurisdiction of Ses Ct
(Article145(3) FC & Section 376 CPC, PP has power to institute proceedings in any court)
Sentencing jurisdiction:
- Section 64 SCA 1948: Ses Ct may pass any sentence allowed by law other than sentence of death
- Ses Ct may also pass sentence of whipping up to max 24 strokes: #Bachik b Abdul Rahman [2004]
- Reference of constitutional question by subordinate court: Section 30(1) CJA 1964: Ses Ct President
may stay proceedings and transmit record to HC (#Repco Holdings Bhd)
High Court
- Article 121(1) FC Est 2 HCs of co-ordinate jurisdiction: a) HC of Malaya; and b) HC of
Borneo
- Trial jurisdiction: Section 22(1) CJA 1964 Can try all offences under PC and written law
-Power to determine effect of constitutional provision referred by Sub Ct: Section 30 CJA - Sentencing jurisdiction: Section 22(2) CJA 1964 HC may pass any sentence allowed by
1964; #Repco Holdings Bhd law
- Appellate jurisdiction: HC shall hear appeal from subordinate courts
Inherent jurisdiction:- a) #Chew Wai Keong v PP: A’s application to acquit and discharge for
Revisionary powers: a) Section 31 CJA 1964: HC may exercise powers of revision; b)
kidnapping under the inherent powers of the court was dismissed. The inherent powers of HC Section 35 CJA 1964: HC hall have general supervisory and revisionary jurisdiction
is to prevent injustice/abuse of the process of the court. It cannot be used to override an
express provision of law/where there is alternative remedy.
b) #Karpal Singh & Anor v PP: Supreme Ct held HC has inherent powers where there are
obvious abuses of its process and other forms of material defects. A’s application to strike out
the proceedings for oppression and prejudice under the inherent jurisdiction were rejected
1964
REDZA ZAKARIA LLM (UKM), LLB (HONS) LONDON, CLP 4
Court of Appeal
Appellate jurisdiction:
- Section 50(1) CJA 1964: CA shall have jurisdiction to hear and determine any appeal against any
decision made by HC: In exercise of its original jurisdiction; and in exercise of its appellate or
revisionary jurisdiction in respect of any criminal matter decided by the Ses Ct
- Criminal matter was originally decided by Mg Ct:
a) Section 50(2): If the accused appeals, leave of CA must be obtained, such appeal shall be
confined to only questions of law
b) Section 50(3): If the prosecution appeals, no leave of CA is required but notice of appeal must
be signed by PP, SG or any officer authorised by PP
- Criminal matter was originally decided by Ses Ct/HC: Section 50(4) No leave is required, appal
may lie on a question of fact/law or both
Other powers: CA may punish for any contempt of court Article 126 FC & Section 13 CJA 1964
Federal Court
Appellate jurisdiction:
- Articles 121(2)(a) & 128(3) FC, Sections 86 & 87 CJA 1964 Federal Ct shall have jurisdiction to determine appeals from
decisions of CA, HC or a judge
- Section 87(2) CJA 1964: Notice of any appeal by PP shall be given by PP, SG or any officer authorised by PP
- Determination of constitutional qn referred to it by HC: Section 84 CJA 1964
Inherent jurisdiction:-
- Rule 137 RFC 1995: FC has inherent powers to hear any application or to make any order to prevent injustice or abuse of the
process of the court
- #Tan Sri Eric Chia Eng Hock v PP [2007]: FC cannot use its appellate jurisdiction bcos HC used its revisionary jurisdiction under
Section 31 and 35 CJA 1964. However FC (Augustine Paul FCJ) may invoke its inherent power under r.137 to prevent injustice or
abuse of the process of the court where there is no other remedy
Other powers: FC may punish for any contempt of court Article 126 FC & Section 13 CJA 1964
REDZA ZAKARIA LLM (UKM), LLB (HONS) LONDON, CLP 5
Others
Local Jurisdiction
Irregularities Proceedings
GR:
- GR: Irregularities in criminal proceedings may be cured if there is no
failure of justice:- - Sec 121 CPC
a) Sec 419 CPC - Sec 2(1) CPC
b) Sec 420 CPC - Sec 3 CJA 1964: ‘Local jurisdiction’:- i) HC in Malaya all
territories; ii) HC in Sabah & Sarawak all territories
c) Sec 421 CPC
Exceptions to GR A may be tried where: Sec 122 CPC: Act is
d) Sec 422 CPC done or the consequence ensues: Illus (a)
- Sec 123: Act is an offence by reason of relation to other
offence:- Illus (a) Illus (b) Illus (c)
Extra Territorial Jurisdiction:- Sec 127A CPC: A may be tried for offences committed out of
M’sia such as those under; Chapter IV PC; Offences against the State; Chapter IVA PC - Sec 124
;Offences relating to terrorism; Any written laws specified in the Schedule to the Extra- - Sec 125
Territorial Offences Act 1976; or Any other written law certified by the AG to affect the - Sec 126
security of M’sia - Sec 127
#Rajappan [1986]: SC said that the extra-territorial offences include:- a Offences under Where offence runs from outside M’sia to within M’sia,
Chapter VI of the PC; b) Offences under OSA 1972; c) Offences under Sedition Act 1948; d)
offender will be tried within jurisdiction:-
Offences under the Prevention of Corruption Act 1961 a) #Yong Nam Seng
b) #Loh Ah Hoo
Offence of bigamy – Previously in #Nai Prasit & #Rajappan: HELD that the Court had no
c) NB: #Lee Szu Yin
jurisdiction to try the offence of bigamy committed outside of Msia; Presently, Sec 494 PC
& Law Reform (Marriage & Divorce) Act 1976
REDZA ZAKARIA LLM (UKM), LLB (HONS) LONDON, CLP 6
You might also like
- A Guide to Recent Criminal Legislation: Pergamon Modern Legal OutlinesFrom EverandA Guide to Recent Criminal Legislation: Pergamon Modern Legal OutlinesNo ratings yet
- Trial JurisdictionDocument4 pagesTrial JurisdictionBobo KhoNo ratings yet
- Criminal CourtsDocument9 pagesCriminal CourtsKelvine DemetriusNo ratings yet
- Jurisdiction of CourtsDocument15 pagesJurisdiction of CourtsLorie Jean UdarbeNo ratings yet
- JurisdictionDocument23 pagesJurisdictionEarleen Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- 4PENALTIES2Document7 pages4PENALTIES2Pablo EschovalNo ratings yet
- Jurisdiction of Courts - Prepared by Research CorpsDocument17 pagesJurisdiction of Courts - Prepared by Research CorpsJOHN FLORENTINO MARIANONo ratings yet
- Tan - Special Civil ActionsDocument52 pagesTan - Special Civil ActionsDennis VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Act 92 - Subordinate Courts Act 1948Document53 pagesAct 92 - Subordinate Courts Act 1948Syafiq SapriNo ratings yet
- 47 Miguel v. Director of The Bureau of Prisons, UDK-15368, 15 September 2021Document8 pages47 Miguel v. Director of The Bureau of Prisons, UDK-15368, 15 September 2021Irone VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court: Sec 5. Par 1. Art VIII. 1987 ConstitutionDocument4 pagesSupreme Court: Sec 5. Par 1. Art VIII. 1987 ConstitutionduanepoNo ratings yet
- 1 LW The Code of Civil Procedure All Que BankDocument25 pages1 LW The Code of Civil Procedure All Que BankGirish WaruNo ratings yet
- CPC Express NotesDocument56 pagesCPC Express NotesAnilah SubraNo ratings yet
- Indeterminate Sentence LawDocument4 pagesIndeterminate Sentence LawAbel Francis88% (8)
- CLP Criminal Procedure - CourtDocument15 pagesCLP Criminal Procedure - CourtVanila PeishanNo ratings yet
- Jurisdictioncivilcases PDFDocument13 pagesJurisdictioncivilcases PDFAriel Joseph NicolasNo ratings yet
- Notes On Jurisdiction of CourtsDocument7 pagesNotes On Jurisdiction of CourtsJacinto Jr Jamero100% (1)
- Bidangkuasa Mahkamah JenayahDocument5 pagesBidangkuasa Mahkamah JenayahLina KhalidaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Civil Procedure December 12, 2020Document3 pagesNotes On Civil Procedure December 12, 2020DUN SAMMUEL LAURENTENo ratings yet
- (Ed2) Jurisdiction of Civil CourtsDocument17 pages(Ed2) Jurisdiction of Civil CourtsAaliya DayanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Ii SCDocument41 pagesChapter Ii SCTinnyNo ratings yet
- RA No 4103Document2 pagesRA No 4103Kristina Dacayo-GarciaNo ratings yet
- MLS (Subordinate Courts)Document46 pagesMLS (Subordinate Courts)Mia GeorgeNo ratings yet
- The Revised Rules of Criminal Procedure Dismissal: A R R A I G N M E N T A N D P L E ADocument4 pagesThe Revised Rules of Criminal Procedure Dismissal: A R R A I G N M E N T A N D P L E APRINCESS APRIL JOY PACILANNo ratings yet
- XII: Appeal (Rules 122, 124, 125) 1. Effect of An AppealDocument6 pagesXII: Appeal (Rules 122, 124, 125) 1. Effect of An AppealJlo HeheNo ratings yet
- Bar Questions and Answers Remedial Law 1997 2006-33-38Document6 pagesBar Questions and Answers Remedial Law 1997 2006-33-38John VillaverNo ratings yet
- Douglas Lachance v. Janet Reno, in Her Capacity As Attorney General of The United States, and The United States Parole Commission, 13 F.3d 586, 2d Cir. (1994)Document6 pagesDouglas Lachance v. Janet Reno, in Her Capacity As Attorney General of The United States, and The United States Parole Commission, 13 F.3d 586, 2d Cir. (1994)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- LW - 501 - 9001 The Code of Civil Procedure, 1908 and The Limitation Act. 1963Document2 pagesLW - 501 - 9001 The Code of Civil Procedure, 1908 and The Limitation Act. 1963Red TigerNo ratings yet
- Summary Procedure Vs Small ClaimsDocument3 pagesSummary Procedure Vs Small ClaimsLorelie SantosNo ratings yet
- Dlsu-Lcbo LMT Cremedial LawDocument44 pagesDlsu-Lcbo LMT Cremedial LawmyownperfectbubbleNo ratings yet
- Court The JurisdictionDocument13 pagesCourt The JurisdictionTaroy CeeNo ratings yet
- GR No. 159418-19Document2 pagesGR No. 159418-19Roselyn PascobelloNo ratings yet
- Jurisdiction of SC CA RTC FC and Sharia MTCDocument54 pagesJurisdiction of SC CA RTC FC and Sharia MTCMBDJrNo ratings yet
- CRIMPRO - EnumerationsDocument13 pagesCRIMPRO - EnumerationsMarianne AgunoyNo ratings yet
- Ahul's: Answers With The ExplanationsDocument17 pagesAhul's: Answers With The ExplanationsNoor OberoiNo ratings yet
- Jurisdiction On Provisional Remedies - REVIEWERDocument3 pagesJurisdiction On Provisional Remedies - REVIEWERjuna luz latigayNo ratings yet
- People Vs GacottDocument2 pagesPeople Vs Gacottralph_atmosferaNo ratings yet
- Jurisdiction of CourtsDocument22 pagesJurisdiction of CourtsLaurene Ashley Sore-YokeNo ratings yet
- Contempt - Low Hop BingDocument54 pagesContempt - Low Hop BingRajesh NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Code of Criminal Procedure by Muhammad Kamran Bhatti AdvDocument7 pagesCode of Criminal Procedure by Muhammad Kamran Bhatti AdvMuhammad KamranNo ratings yet
- Jurisdiction of CourtsDocument7 pagesJurisdiction of CourtsCzarina BantayNo ratings yet
- June 11, 2020 - Civil Procedure - Post-Judgement Remedies: Rules 41, 42, 43, 44, 45Document3 pagesJune 11, 2020 - Civil Procedure - Post-Judgement Remedies: Rules 41, 42, 43, 44, 45Jul A.No ratings yet
- Jurisdiction of CourtsDocument6 pagesJurisdiction of CourtsElaine FallarcunaNo ratings yet
- Civpro Page 108-400 PDFDocument121 pagesCivpro Page 108-400 PDFA Z L YNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Task 1Document4 pagesAsynchronous Task 1Ambra Kaye AriolaNo ratings yet
- BP 129 As AmendedDocument8 pagesBP 129 As AmendedNica DecenaNo ratings yet
- Criminal Procedure ReviewerDocument7 pagesCriminal Procedure ReviewerDelos Santos, Raniel M.No ratings yet
- Court Hierarchy in The PhilippinesDocument1 pageCourt Hierarchy in The PhilippinespyaplauaanNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answer:: Former Rule 39 Sec, 47 (B) of New Rule 39)Document9 pagesSuggested Answer:: Former Rule 39 Sec, 47 (B) of New Rule 39)Your Public ProfileNo ratings yet
- Chapter Iii CaDocument45 pagesChapter Iii CaTinnyNo ratings yet
- Ias IiiDocument11 pagesIas IiiAdeesha thodthillayaNo ratings yet
- 02 Jurisdiction of The SCDocument13 pages02 Jurisdiction of The SCfiNixzzNo ratings yet
- Week 13 - Court Pillar Part 1Document2 pagesWeek 13 - Court Pillar Part 1Jaenard GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Questions 1Document10 pagesQuestions 1saditha manjulahariNo ratings yet
- Adr NotesDocument31 pagesAdr NotesMadelene Grace CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Death: Penalty Accessory Duration When Not Executed: PAD & CI IndivisibleDocument4 pagesDeath: Penalty Accessory Duration When Not Executed: PAD & CI IndivisibleAnonymous ZXUO1k3sNo ratings yet
- Remedial Law 1 Notes Atty. Jesus ObraDocument2 pagesRemedial Law 1 Notes Atty. Jesus ObraSam VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Let's Try This: Incident: Thoughts: Feelings: Behavior: Incident: Thoughts: Feelings: BehaviorDocument2 pagesLet's Try This: Incident: Thoughts: Feelings: Behavior: Incident: Thoughts: Feelings: BehaviorJannet Viacruses LarcenaNo ratings yet
- Reflection (The We Entrepreneur)Document2 pagesReflection (The We Entrepreneur)Marklein DumangengNo ratings yet
- SKZ TrackDocument6 pagesSKZ TrackOliviaNo ratings yet
- A Review of Cassiterite Beneficiation PraticesDocument23 pagesA Review of Cassiterite Beneficiation PraticesLevent ErgunNo ratings yet
- 9 - Digest - Mari Vs BonillaDocument2 pages9 - Digest - Mari Vs BonillaMarivic Escueta100% (1)
- GK-604D Digital Inclinometer System PDFDocument111 pagesGK-604D Digital Inclinometer System PDFKael CabezasNo ratings yet
- Doloran Auxilliary PrayersDocument4 pagesDoloran Auxilliary PrayersJosh A.No ratings yet
- EmanDocument3 pagesEmanCh NawazNo ratings yet
- Pplied Hysics-Ii: Vayu Education of IndiaDocument16 pagesPplied Hysics-Ii: Vayu Education of Indiagharib mahmoudNo ratings yet
- FBFBFDocument13 pagesFBFBFBianne Teresa BautistaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 & CH 3 John R. Schermerhorn - Management-Wiley (2020)Document9 pagesCH 2 & CH 3 John R. Schermerhorn - Management-Wiley (2020)Muhammad Fariz IbrahimNo ratings yet
- MMW CH4 L2Document20 pagesMMW CH4 L2Charles Patrick GarciaNo ratings yet
- Sections 3 7Document20 pagesSections 3 7ninalgamaryroseNo ratings yet
- RARC Letter To Tan Seri Razali Ismail July 26-2013Document4 pagesRARC Letter To Tan Seri Razali Ismail July 26-2013Rohingya VisionNo ratings yet
- Academic Calendar 2014 15Document6 pagesAcademic Calendar 2014 15D Geetha DuraiNo ratings yet
- scn615 Classroomgroupactionplan SarahltDocument3 pagesscn615 Classroomgroupactionplan Sarahltapi-644817377No ratings yet
- Contents:: Project ProgressDocument22 pagesContents:: Project ProgressJosé VicenteNo ratings yet
- English Preparation Guide DAF 202306Document12 pagesEnglish Preparation Guide DAF 202306TIexamesNo ratings yet
- Potato Lab ReportDocument10 pagesPotato Lab ReportsimplylailaNo ratings yet
- Unilateral Lower Limb SwellingDocument1 pageUnilateral Lower Limb SwellingLilius TangNo ratings yet
- Examination of Conscience Ten Commandments PDFDocument2 pagesExamination of Conscience Ten Commandments PDFAntonioNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Foundations of NursingDocument22 pagesTheoretical Foundations of Nursingattilaabiidn100% (3)
- ECON2100 CO Abdool W21Document5 pagesECON2100 CO Abdool W21Imran AbdoolNo ratings yet
- Chapter (1) The Accounting EquationDocument46 pagesChapter (1) The Accounting Equationtunlinoo.067433100% (3)
- Linear Arrangement 3rdDocument30 pagesLinear Arrangement 3rdSonu BishtNo ratings yet
- Armor MagazineDocument56 pagesArmor Magazine"Rufus"100% (2)
- Timing Light Schematic or DiagramDocument2 pagesTiming Light Schematic or Diagramprihharmanto antokNo ratings yet
- Nurse Implemented Goal Directed Strategy To.97972Document7 pagesNurse Implemented Goal Directed Strategy To.97972haslinaNo ratings yet
- Dribssa Beyene Security Sector Reform Paradox Somalia PublishedDocument29 pagesDribssa Beyene Security Sector Reform Paradox Somalia PublishedNanny KebedeNo ratings yet