Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MAJOR LANDFORMS - Terms and Definations - Self Study
Uploaded by
jophy roy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views8 pagesOriginal Title
c4f0126e-28be-42bf-b8f4-0849319b2546_MAJOR LANDFORMS_Terms and Definations_ Self Study
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views8 pagesMAJOR LANDFORMS - Terms and Definations - Self Study
Uploaded by
jophy royCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
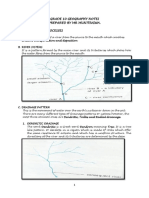
MAJOR LANDFORMS-SELF STUDY
TERMS AND DEFINITIONS
1. Landform A landform is a natural
feature of the Earth’s
surface.
2. Weathering Wearing away from a
surface through a number
of factors or agents such as
heat, cold, frost action,
plants, animals and
chemical reactions helps in
weathering.
3. Erosion A process by which the
broken rock materials are
removed and deposited
elsewhere is called
erosion.
4. Mouth The place where the river
joins another water body
is called the mouth.
5. River Basin The area drained by the
river and its tributaries is
called the river basin.
6. Source The place where the river
originates is called the
source
7. Waterfall The waterfall is vertical
stream of water that flows
down the river.
The best example of
waterfalls are: -
-Angel Fall in Venezuela in
South America,
-Niagara Falls in North
America and
-Jog Falls at Karnataka in
India.
8. Rapid The steep sloping segment
of the swift-flowing river is
called a rapid.
9. Meanders When the river enters the
plain, it loses its swiftness
and the valley widens due
to the continuous erosion
of the banks of the river.
The river makes several
bends along its flow and
these bends and loops are
termed as meanders
10. Ox-bow lakes As a result of a continuous
flow of the river, in the
long run, the bends and
loops come closer and with
time, the river cuts across
and the loops separate
them from the
mainstream. These circular
loops that get separated
from the mainstream are
termed as oxbow lakes.
11. Flood plains During floods, rivers bring
with them a huge amount
of silt and alluvium that
gets deposited along the
bank of rivers raising their
height and forming fertile
flood plains
12. Natural Long ridges with relatively
levees lesser height formed at the
bank of rivers are termed
as natural levees due to
the coarse material
deposited by the river.
13. Sand bars These are the landforms
formed inside the river at
the mouth by the
deposition of large volume
of sand, pebbles, alluvium
and water.
14. Distributaries Due to the excessive load
of water and silt at the
mouth of the river, the
mainstream gets divided
into several small channels
of water known as
distributaries.
15. Delta When soil gets deposited
between the distributaries
in a triangular form, it is
referred to as Delta
Sundarbans is the world's
largest delta, located in
West Bengal, India.
16. Sea caves Strong sea waves dash
against the coast and
dissolve or break down the
rocks into fragments. In
due course of time, these
cracks become wide and
form large cavities. With
continuous action of sea
waves, these cavities
develop into sea caves.
17. Sea arch When a headland
projecting into the sea is
attacked by sea waves
from both the sides, a
thorough passage is
created. This is called sea
arch.
18. Stacks When the roof of arch is
further eroded, it
collapses. The pillars of
rocks are left standing in
the open water. These are
called stacks
19. Sea cliff A steep vertical wall facing
the sea is called sea cliff.
20. Lagoon Sometimes the sea water
is enclosed between the
coast and the sand bar. It
then becomes a partially
enclosed lake, which is
called a lagoon.
-Blue Lagoon is the world's
most famous Lagoon in
Iceland.
-Chilika Lake in Odisha is
the largest lagoon in India.
21. Beaches Beaches are the deposition
of sand, gravel and
pebbles on the shore.
22. Snowline A line above which there is
permanent deposition of
snow.
23. Glacier The river of snow and ice,
which moves very slowly is
called a glacier.
24. U-shaped When the moving ice
valley moves down the
mountains with the rocks,
rubs against the sides and
the valley floor. This
creates U-shaped valley.
Yosemite Valley, a glacial U-
shaped valley is located
California
25. Cirque The glacier carves out deep
hollows along the slope of
the mountains. It develops
an armchair-like
depression, called a cirque.
26. Tarn When the glacial ice melts,
the depression is filled up
with water and forms a
lake. This is called tarn.
27. Glacial When the glacier starts
Moraine melting, its capacity to
carry load is reduced. Thus,
rock materials are
deposited on the sides and
floor of the valley.
28. Mushroom Rocks with narrow base &
rocks a broad top.
29. Loess The dust and the silt blown
by the wind, blanket the
land and these fine dust
particles deposited
extensively are known as
loess.
China is known for
extensive loess deposits.
30. Sand dunes Winds carry sand over the
desert and the coarse
particles are deposited in
the form of hillocks known
as sand dunes.
You might also like
- Desert LandformsDocument8 pagesDesert Landformsamanah islamicNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 GeologyDocument5 pagesQuiz 2 Geologyhaha xdNo ratings yet
- Water On Land Paper 1 Physical RiversDocument14 pagesWater On Land Paper 1 Physical RiversTrevor Chad100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Our Changing EarthDocument5 pagesChapter 3 Our Changing EarthPrameela PrameelaNo ratings yet
- CH-3 Our Changing EarthDocument7 pagesCH-3 Our Changing EarthSUHANEERIYANo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - GlaciersDocument6 pagesChapter 7 - GlaciersJulius BorrisNo ratings yet
- BembaDocument35 pagesBembaThe wooNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledBB KivinesNo ratings yet
- Weathering Erosion StemscopediaDocument6 pagesWeathering Erosion Stemscopediaapi-506851645No ratings yet
- Upper Course of A River (Processes and Land Forms)Document12 pagesUpper Course of A River (Processes and Land Forms)cgmalia100% (2)
- LandformsDocument7 pagesLandformsAtulJhaKumarNo ratings yet
- Hydrology: Hydrological Cycle River Formation Underground WaterDocument16 pagesHydrology: Hydrological Cycle River Formation Underground WaterSN2-0620 Theeban Rau A/L ChanthiranNo ratings yet
- CH 3 - Our Changing Earth Class 7 - 2021Document45 pagesCH 3 - Our Changing Earth Class 7 - 2021OJAS TOMAR100% (1)
- Basic Geography: SUMMER - A.Y. 2019-2020Document122 pagesBasic Geography: SUMMER - A.Y. 2019-2020Freshie PascoNo ratings yet
- Landforms and Their EvolutionDocument22 pagesLandforms and Their EvolutionTsudrawsNo ratings yet
- Agents of Landform Change Chapter 2 Converted 1Document3 pagesAgents of Landform Change Chapter 2 Converted 1Rabab KashifNo ratings yet
- Deposition and Depositional LandformsDocument2 pagesDeposition and Depositional LandformsJann Vic SalesNo ratings yet
- 11 Geography Notes 07 Landforms and Their EvolutionDocument12 pages11 Geography Notes 07 Landforms and Their EvolutionPrateek Sharma50% (2)
- 6 - Deposition On LandDocument24 pages6 - Deposition On Landperazajimena77No ratings yet
- Landforms of The EarthDocument8 pagesLandforms of The EarthAdyasha MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Unit - 5 GMDocument22 pagesUnit - 5 GMa80143200No ratings yet
- Notes - Our Changing EarthDocument2 pagesNotes - Our Changing EarthjpadmmiNo ratings yet
- River Processes - Erosion, Transport, DepositionDocument8 pagesRiver Processes - Erosion, Transport, DepositionF A L L E NNo ratings yet
- 1.1 River Processes and Landforms (Foundation) : Source: Where A Watershed: TheDocument34 pages1.1 River Processes and Landforms (Foundation) : Source: Where A Watershed: TheFifie OjifinniNo ratings yet
- Geography 2 - Coastal and Marine Geography ReportDocument60 pagesGeography 2 - Coastal and Marine Geography ReportRuby BelecinaNo ratings yet
- Aquatic EnvironmentDocument32 pagesAquatic EnvironmentChhavi ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Processes and Landforms Along Plate BoundariesDocument47 pagesProcesses and Landforms Along Plate BoundariesMille GrayNo ratings yet
- Landforms Part-II: What Is The Landform Made by Wind?Document11 pagesLandforms Part-II: What Is The Landform Made by Wind?Adyasha MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Karst Geomorpholog Y: Work of Underground WaterDocument49 pagesKarst Geomorpholog Y: Work of Underground Waterabila asokNo ratings yet
- Erosion and Deposition Action of Running Water and GroundwaterDocument12 pagesErosion and Deposition Action of Running Water and GroundwaterDevraj H SNo ratings yet
- LandformsDocument24 pagesLandformsHana LimNo ratings yet
- Exogenic and Endogenic ProcessesDocument9 pagesExogenic and Endogenic ProcessesAndrea Trish NicolasNo ratings yet
- The Story of A RiverDocument4 pagesThe Story of A Riveramarpal07No ratings yet
- Y7 HT2 RiversDocument35 pagesY7 HT2 RiversMartina Di MauroNo ratings yet
- Assessment On Landform Processes: 1. Fluvial LandformsDocument14 pagesAssessment On Landform Processes: 1. Fluvial LandformsGayan Indunil JayasundaraNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 Landforms and Their Evolution 13Document16 pagesChap 5 Landforms and Their Evolution 13abhaykumarkans054No ratings yet
- Beach A River of Sand Docx - EditedDocument4 pagesBeach A River of Sand Docx - EditedPaul WahomeNo ratings yet
- Geomorphology of River (Group-D)Document32 pagesGeomorphology of River (Group-D)Rajesh ranaNo ratings yet
- River Basin ProcessesDocument16 pagesRiver Basin Processes3alliumcourtNo ratings yet
- ErosionDocument51 pagesErosionapi-21815836733% (3)
- IB River LandformsDocument4 pagesIB River LandformsAnonymous EmjOwX100% (1)
- Gess 205Document9 pagesGess 205balajiNo ratings yet
- Physiography of Lakes and Reservoirs: Formation: Geological ProcessesDocument11 pagesPhysiography of Lakes and Reservoirs: Formation: Geological ProcessesHasaan WaheedNo ratings yet
- Basic Petroleum Geology - DepositionDocument5 pagesBasic Petroleum Geology - DepositionAhmed FoudaNo ratings yet
- Active Recall Answers For Final ExamsDocument5 pagesActive Recall Answers For Final ExamsDcsantosNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Notes HydrologyDocument5 pagesWeek 10 Notes HydrologyGil GameshNo ratings yet
- FAJANILAN JEROME C.activityno.2 Depositional Sedimentary Environment and StructuresDocument11 pagesFAJANILAN JEROME C.activityno.2 Depositional Sedimentary Environment and StructuresJerome FajanilanNo ratings yet
- Earth Science: WeatheringDocument85 pagesEarth Science: WeatheringElijah Raphael YasaNo ratings yet
- Rivers 1652535475Document20 pagesRivers 1652535475paqurette3No ratings yet
- Rivers - Earth Processes - OneGeology Kids - EXtra - OneGeologyDocument4 pagesRivers - Earth Processes - OneGeology Kids - EXtra - OneGeologySubbareddyNo ratings yet
- The Condition or Process of Degrading or Being Degraded. The Deposition of Material by A River, Stream, or CurrentDocument30 pagesThe Condition or Process of Degrading or Being Degraded. The Deposition of Material by A River, Stream, or CurrentJann Vic SalesNo ratings yet
- Geology 107L - Lecture 4: Glacial Deposits and Landforms of Eastern North DakotaDocument36 pagesGeology 107L - Lecture 4: Glacial Deposits and Landforms of Eastern North DakotaDeron ZiererNo ratings yet
- Our Changing EarthDocument4 pagesOur Changing EarthNIdhi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Erosion and Deposition: by Moira Whitehouse PHDDocument33 pagesErosion and Deposition: by Moira Whitehouse PHDIlham El-sirazhyNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE Geography AnswersDocument34 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Geography Answerszohra hussainNo ratings yet
- Depositional EnvironmentDocument16 pagesDepositional EnvironmentIbrar UllahNo ratings yet
- Erosion and Deposition Action of Wind and WavesDocument6 pagesErosion and Deposition Action of Wind and WavesELEVATED KnowledgeNo ratings yet
- Agents of GradationDocument4 pagesAgents of Gradationsarayoo50% (2)
- Activityno.2 TableDocument16 pagesActivityno.2 Table22-08420No ratings yet
- Visualizing Geology 4th Edition Murck Test BankDocument29 pagesVisualizing Geology 4th Edition Murck Test Bankazuragwencr8ud100% (24)
- CE161P Homework 02Document5 pagesCE161P Homework 02Myca QuizaNo ratings yet
- Unesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Sedimentary Geology and PaleontologyDocument7 pagesUnesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: Sedimentary Geology and PaleontologySupriyanto DrsNo ratings yet
- Submarine Fans Characteristics, Models, Classification, and Reservoir PotentialDocument46 pagesSubmarine Fans Characteristics, Models, Classification, and Reservoir PotentialteguhwpNo ratings yet
- High Resolution Sequence Stratigraphic Analysis of The Late Miocene Abu Madi Formation, Northern Nile Delta BasinDocument9 pagesHigh Resolution Sequence Stratigraphic Analysis of The Late Miocene Abu Madi Formation, Northern Nile Delta BasinMohammed Atef ElsherbiniNo ratings yet
- Review MODULE - GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING (Soil Properties)Document1 pageReview MODULE - GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING (Soil Properties)I'm an EngineerNo ratings yet
- Lower Benue TroughDocument20 pagesLower Benue TroughIgbereyivwe TejiriNo ratings yet
- Constructive and Destructive Forces Power Point (Liz) New PDFDocument24 pagesConstructive and Destructive Forces Power Point (Liz) New PDFDecereen Pineda RodriguezaNo ratings yet
- Farm Field, Southern England Reservoir Architecture of The Upper Sherwood Sandstone, WytchDocument9 pagesFarm Field, Southern England Reservoir Architecture of The Upper Sherwood Sandstone, WytchASKY PNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0169555X23002842 MainDocument65 pages1 s2.0 S0169555X23002842 MainCarlos Saez MartinezNo ratings yet
- Importance of Soil TextureDocument3 pagesImportance of Soil TextureindriyaniNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Singapore Marine Clay at ChangiDocument11 pagesCharacteristics of Singapore Marine Clay at ChangichemodanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - River ErosionDocument6 pagesWorksheet - River Erosionjaisalshah20decNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Properties of Nearshore Sediments of Canso Strait, Nova ScotiaDocument14 pagesGeotechnical Properties of Nearshore Sediments of Canso Strait, Nova ScotiaFelipe PereiraNo ratings yet
- 07.glaciers Deserts and WindDocument33 pages07.glaciers Deserts and WindChristine ValerioNo ratings yet
- Soil & Rock Correlations-2Document25 pagesSoil & Rock Correlations-2Faris QoceyNo ratings yet
- GeologyDocument79 pagesGeologybinod2500No ratings yet
- Delta and Estuaries PDFDocument8 pagesDelta and Estuaries PDFIwan PrabowoNo ratings yet
- 1 Executive Summary PT. BJE - PT. MJENDocument37 pages1 Executive Summary PT. BJE - PT. MJENSinatra LimNo ratings yet
- Global Map of SoilsDocument2 pagesGlobal Map of SoilsMassimoNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 YU JAYBEN MARKs Quiz History - Quiz 1 Module 3.1 and 3.2Document7 pagesQuiz 1 YU JAYBEN MARKs Quiz History - Quiz 1 Module 3.1 and 3.2Dopias FakeNo ratings yet
- Erosion and Deposition 2015-2016 v3Document58 pagesErosion and Deposition 2015-2016 v3api-263382165No ratings yet
- Badlands: 2 FormationDocument4 pagesBadlands: 2 FormationNupur PalNo ratings yet
- Dolomitizatio, Qamch, 2010, GeoArabiaDocument28 pagesDolomitizatio, Qamch, 2010, GeoArabiaericespirituNo ratings yet
- Historical Geology BookDocument224 pagesHistorical Geology BookhoogggleeeNo ratings yet
- Facies Analysis of Volcano-Sedimentary Successions Hosting Massive Sulfide Deposits in The Iberian Pyrite Belt, SpainDocument16 pagesFacies Analysis of Volcano-Sedimentary Successions Hosting Massive Sulfide Deposits in The Iberian Pyrite Belt, Spainleon canavarroNo ratings yet
- Fiegel Kutter Idriss PDFDocument1 pageFiegel Kutter Idriss PDFAvaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - RocksDocument14 pagesModule 5 - Rocksadyaksa pradibtaNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics PDFDocument394 pagesSoil Mechanics PDFDevis Gimo100% (1)
- 131276-Article Text-354363-1-10-20160301Document16 pages131276-Article Text-354363-1-10-20160301Osaruchi MICHAEL100% (1)