Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic IP Servies - Assignment
Uploaded by
Yuvaraj V, Assistant Professor, BCAOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic IP Servies - Assignment
Uploaded by
Yuvaraj V, Assistant Professor, BCACopyright:
Available Formats
RATHNAVEL SUBRAMANIAM COLLEGE OF ARTS AND SCIENCE
(AUTONOUMUS), SULUR.
SCHOOL OF COMPUTER STUDIES (UG)
B.Sc., INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
ASSIGNMENT
S.No Class Batch Semester Subject
1 II – B.Sc., IT 2016-2019 IV MAJOR THEORY- Basic IP Services
UNIT-I
1. A DHCP server is used to assign IP addresses dynamically to the hosts on a network. The
address pool is configured with 192.168.10.0/24. There are 3 printers on this network that
need to use reserved static IP addresses from the pool. How many IP addresses in the pool are
left to be assigned to other hosts?
SOLUTION:
If the block of addresses allocated to the pool is 192.168.10.0/24, there are 254 IP addresses
to be assigned to hosts on the network. As there are 3 printers which need to have their
addresses assigned statically, then there are 251 IP addresses left for assignment.
2. If a network device has a mask of /28, how many IP addresses are available for hosts on
this network? Explain.
SOLUTION:
A /28 mask is the same as 255.255.255.240. This leaves 4 host bits. With 4 host bits, 16 IP
addresses are possible, but one address represents the subnet number and one address
represents the broadcast address. 14 addresses can then be used to assign to network devices.
3. A network administrator wants to have the same network mask for all networks at a
particular small site. The site has the following networks and number of devices:
IP phones – 22 addresses
PCs – 20 addresses needed
Printers – 2 addresses needed
Scanners – 2 addresses needed
School of Computer Studies (UG) Page 1
The network administrator has deemed that 192.168.10.0/24 is to be the network used at this
site. Which single subnet mask would make the most efficient use of the available addresses
to use for the four sub networks?
SOLUTION:
If the same mask is to be used, then the network with the most hosts must be examined for
the number of hosts, which in this case is 22 hosts. Thus, 5 host bits are needed. The /27 or
255.255.255.224 subnet mask would be appropriate to use for these networks.
4. You have a network with 50 workstations. You want to automatically configure
workstations with the IP address, subnet mask and default gateway values. Which device
should you use? Explain.
SOLUTION:
DHCP Sever
5. Explain the steps involved in configuring a DHCP server through Cisco Packet Tracer for
the following Topology.
SOLUTION:
Step 1: Open packettracer.
Step 2: Choose the end devices and select one server paste.
Step 3: And choose switch and paste.
Step 4: And collect N number of client pc and paste finally.
School of Computer Studies (UG) Page 2
Step 5: All the devices connected to the cable copper straight through.
Step 6: By clicking server choose services go to DHCP option-->click service on-->type pool
name-->type start IP address finally select add.
Step7: Select any client and go for desktop-->click option DHCP automaticlly the IP address
allocated by DHCP server.
6. How to reduce the troubleshooting configuration problems with IPConfig facts explain in
detail.
ipconfig /all to troubleshoot IP configuration problems. The following table describes how
the output for this command changes, based on how IP settings are configured and for
specific problem situations:
Condition ipconfig /all Output
If the workstation is configured with static IP information, the
following conditions will exist:
Static IP
Configuration The DHCP Enabled line will show No.
The DHCP Server line will not be shown.
If the workstation has received configuration information from
a DHCP server, the following conditions will exist:
DHCP
The DHCP Enabled line will show Yes.
Configuration
The DHCP Server line will show the IP address of the
DHCP server that sent the configuration information.
A rogue DHCP server is an unauthorized DHCP server on the
network. Symptoms of a rogue DHCP server include:
Conflicting IP addresses on the network
Rogue DHCP
Server Incorrect IP configuration information on some hosts
To identify a rogue DHCP server using ipconfig, verify the
DHCP server address. If this address is not the address of your
DHCP server, you have a rogue DHCP server.
School of Computer Studies (UG) Page 3
When you have a rogue DHCP server on the network, some
hosts will likely receive configuration information from the
correct DHCP server and others from the rogue DHCP server.
Your DHCP server can send out various IP configuration
values, like the IP address and mask. If network hosts are
Incorrectly configured with incorrect IP values (such as incorrect default
Configured gateway or DNS server addresses), first verify that the
DHCP Server workstations are contacting the correct DHCP server. If the
correct server is being used, go to the DHCP server to verify
that it is sending out correct configuration information.
If the workstation used APIPA to set configuration information,
the following conditions will exist:
The DHCP Enabled line will show Yes.
The DHCP Server line will not be shown.
The IP address will be in the range of 169.254.0.1 to
169.254.255.254, with a mask of 255.255.0.0.
The Default Gateway line will be blank.
The DNS Servers line will not include any IPv4
addresses.
APIPA
When APIPA is used, the workstation sets its own IP address
Configuration
and mask. It does not automatically configure default gateway
or DNS server values. When APIPA is being used:
Communication is restricted to hosts within the same
subnet (there is no default gateway set).
Hosts can communicate with other hosts that have used
APIPA. If some hosts are still using an address assigned
by the DHCP server (even if the DHCP server is down),
those hosts will not be able to communicate with the
APIPA hosts.
Name resolution will not be performed (there are no
DNS server addresses configured).
School of Computer Studies (UG) Page 4
If the workstation has been configured using an alternate
configuration, the following conditions will exist:
The DHCP Enabled line will show Yes.
Alternate The DHCP Server line will not be shown.
Configuration
The IP address and subnet mask will be values other
than the APIPA values.
Default gateway and DNS server addresses will be
configured using the alternate configuration values.
If the workstation has received configuration information from the wrong DHCP server or
has configured itself using APIPA, you may need to contact the DHCP server again once the
DHCP problems have been resolved. Use the following commands:
ipconfig /release to stop using the current dynamic IP configuration parameters.
ipconfig /renew to retry the DHCP server request process to obtain IP configuration
parameters.
UNIT-II
1. Find out the following cable types to make the initial connection to the switch or router for
device management in detail.
SOLUTION:
Pin-
Cable Type Use
outs
School of Computer Studies (UG) Page 5
Use a rollover Ethernet cable to
connect the device's console port
1'8 to the serial port on a PC.
2'7 Connect the RJ45 end to the
3'6 console port and connect the
4'5 serial end to the PC. A rollover
5'4 cable is also called a console
6'3 cable.
Rollover Ethernet Cable 7'2 Many newer Cisco devices use a
8'1 USB for the console connector
and can be accessed with any
standard USB cable.
Use a straight-through Ethernet
cable to connect an Ethernet port
on a router to an Ethernet port on
a hub or switch. The router can
1'1 then be accessed from another
2'2 PC connected to the same
3'3 network, using a VTY
6'6 connection.
Straight-through Ethernet Cable If the router has an AUI port,
connect one end to an AUI
transceiver before connecting to
the router.
Use a crossover Ethernet cable
to connect an Ethernet port on a
router directly to the NIC in a
1'3 PC. Establish a VTY session
2'6 from the PC to connect to the
3'1 device.
6'2 If the router has an AUI port,
connect one end to an AUI
Crossover Ethernet Cable
transceiver before connecting to
the router.
School of Computer Studies (UG) Page 6
2. 17. Refer and Exhibit the following image illustrates some of the configuration modes
available on a Cisco switch. Explain.
SOLUTION:
Mode Details CLI Mode Prompt
The switch has multiple interface
modes, depending on the physical
(or logical) interface type. For this
course, you should be familiar with
the following switch interface
modes:
Interface Ethernet (10 Mbps
Ethernet) Switch(config-if)#
Configuration
FastEthernet (100 Mbps
Ethernet)
GigabitEthernet (1 GB
Ethernet)
VLAN
School of Computer Studies (UG) Page 7
The VLAN interface configuration
mode is used to configure the
switch IP address, and for other
management functions. It is a
logical management interface
configuration mode, rather than the
physical interface configuration
modes used for the FastEthernet
and GigabitEthernet ports.
Details of the config-vlan mode
include the following:
It can be used to perform
all VLAN configuration
tasks.
Config-vlan Switch(config-vlan)#
Changes take place
immediately.
Do not confuse the config-vlan
mode with the VLAN interface
configuration mode.
Details of the VLAN configuration
mode include the following:
It allows you to configure a
subset of VLAN features.
Changes do not take effect
until you save them, either
VLAN before or while exiting the
configuration mode. Switch(vlan)#
Configuration
Changes are not stored in
the regular switch
configuration file.
For most modern Cisco switches, it
is recommended that you configure
VLAN parameters from config-
vlan mode, as VLAN configuration
School of Computer Studies (UG) Page 8
mode is being deprecated (phased
out).
Use this mode to configure
Line parameters for the terminal line,
Switch(config-line)#
Configuration such as the console, Telnet, and
SSH lines.
3. Illustrate the Trunking facts when you configure VLANs that span multiple switches as
shown in the following diagram.
SOLUTION:
In this example, each switch has two VLANs configured, with one port on each VLAN.
Workstations in VLAN 1 can only communicate with other workstations in VLAN 1. This
means that workstations connected to the same switch in this example cannot communicate
directly with each other. Communications between workstations within each VLAN must
pass through the trunk link to the other switch.
Additional facts regarding trunking and VLANs are as follows:
Access ports are connected to endpoint devices (such as workstations), while trunk
ports are connected to other switches.
An access port can be a member of only a single VLAN.
Trunk ports are members of all VLANs on the switch by default.
School of Computer Studies (UG) Page 9
Any port on a switch can be configured as a trunk port.
By default, trunk ports carry traffic for all VLANs between switches. However, you
can reconfigure a trunk port so that it carries only specific VLANs on the trunk link.
When trunking is used, frames that are sent over a trunk port are tagged with the VLAN ID
number so the receiving switch knows which VLAN the frame belongs to. In VLAN tagging:
Tags are appended by the first switch in the path and removed by the last.
Only VLAN-capable devices understand the frame tag.
Tags must be removed before a frame is forwarded to a non-VLAN capable device.
A trunking protocol defines the process that switches use to tag frames with a VLAN ID. One
widely implemented trunking protocol is the IEEE 802.1Q standard, which supports a wide
range of switches from many device manufacturers. 802.1Q supports VLAN numbers 1
through 4094.
With 802.1Q trunking, frames from the default VLAN are not tagged, but frames from all
other VLANs are tagged. For example, suppose VLAN 1 is the default VLAN on a switch
(the default setting on most Cisco switches). In this configuration, any frame on VLAN 1 that
is placed on a trunk link will not be assigned a VLAN tag. If a switch receives a frame on a
trunk port that doesn't have a VLAN tag, the frame is automatically put onto VLAN 1
4. Computers A and B are on the same VLAN and are separated by two switches, as shown
below. Computer A sends a frame to Computer B. Find that the composition of the frame as
it travels from A to B?
SOLUTION:
Computer A sends a normal frame. The first switch appends a VLAN ID to the frame. The
second switch removes the VLAN ID before forwarding it to Computer B.
School of Computer Studies (UG) Page 10
5.Assume that you have just connected four switches as shown below. Find the default switch
configuration and which switch will become the root bridge?
SOLUTION:
UNIT-III
1. You manage a server that runs your company website. The web server has reached its
capacity and the number of client requests is greater than the server can handle. Find the
solution so that static web content can be offloaded to a different server, while the web server
continues to process dynamic content?
SOLUTION:
2. Based on the following diagram find the type of the proxy server is handling the client’s
request?
School of Computer Studies (UG) Page 11
SOLUTION:
3. Which solution should you use when you have been given a laptop to use for work. You
connect the laptop to your company network, use it from home, and use it while traveling
and also you want to protect the laptop from Internet-based attacks?
SOLUTION:
Host-based firewall
4. Explain in detail about Network Ports that correspond to common Internet services.
SOLUTION:
Well known ports range from 0 to 1023 and are assigned to common protocols and
services.
Registered ports range from 1024 to 49151 and are assigned by ICANN to a specific
service.
Dynamic (also called private or high) ports range from 49152 to 65535 and can be
used by any service on an ad hoc basis. Ports are assigned when a session is
established, and ports are released when the session ends.
The following table lists the well-known ports that correspond to common Internet services:
Port(s) Service
School of Computer Studies (UG) Page 12
20 TCP and UDP
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
21 TCP and UDP
22 TCP and UDP Secure Shell (SSH)
23 TCP Telnet
25 TCP and UDP Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
53 TCP and UDP Domain Name Server (DNS)
67 TCP and UDP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
68 TCP and UDP
69 TCP and UDP Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP)
80 TCP and UDP Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
110 TCP Post Office Protocol (POP3)
119 TCP Network News Transport Protocol (NNTP)
123 TCP and UDP Network Time Protocol (NTP)
137 TCP and UDP NetBIOS Name Service
138 TCP and UDP NetBIOS Datagram Service
139 TCP and UDP NetBIOS Session Service
143 TCP Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP4)
161 UDP
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
162 TCP and UDP
School of Computer Studies (UG) Page 13
389 TCP and UDP Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
443 TCP and UDP HTTP over Secure Sockets Layer (HTTPS)
445 TCP Microsoft Server Message Block (SMB) File Sharing
1720 TCP H.323 Call Signaling
2427 UDP Cisco Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP)
3389 TCP and UDP Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)
5004 TCP and UDP Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) Data
5005 TCP and UDP Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) Control
5060 TCP and UDP Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
5061 TCP Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) over TLS
To protect a server, ensure that only the necessary ports are open. For example, if the server
is being used only for email, then shut down ports that correspond to FTP, DNS, HTTP, etc.
UNIT-IV
1. Draw a neat sketch of WAN structure and explain about the WAN technologies.
SOLUTION:
School of Computer Studies (UG) Page 14
Technologies:
1. T-carrier systems
2. E-carrier systems
3. Optical carrier levels
4. Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM)
5. Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM)
2. Assume that you are travel away from the office. While traveling, you would like to use a
modem on your laptop computer to connect directly to a server in your office and access files
on that server that you need and also you want the connection to be as secure as possible Which
type of connection will you need? Explain.
SOLUTION:
3. Illustrate the Facts of Firewall ACLs in detail.
SOLUTION:
Firewalls use access control lists (ACLs) to manage incoming or outgoing traffic. You should
be familiar with the following characteristics of an ACL:
ACLs describe the traffic type that will be controlled.
ACL entries:
o Describe traffic characteristics.
o Identify permitted and denied traffic.
o Can describe a specific traffic type, or allow or restrict all traffic.
When created, an ACL usually contains an implicit deny any entry at the end of the
list.
Each ACL applies only to a specific protocol.
Each router interface can have up to two ACLs for each protocol: one for incoming
traffic and one for outgoing traffic.
School of Computer Studies (UG) Page 15
When an ACL is applied to an interface, it identifies whether the list restricts incoming
or outgoing traffic.
Each ACL can be applied to more than one interface. However, each interface can have
only one incoming and one outgoing list.
ACLs can be used to log traffic that matches the list statements.
Many hardware routers, such as those from Cisco, also provide a packet filtering firewall.
These devices are frequently used to fill both network roles (router and firewall) at the same
time.
When you create an ACL on a Cisco device, a deny any statement is automatically added at
the end of the list (this statement does not appear in the list itself). For a list to allow any traffic,
it must have at least one permit statement that either permits a specific traffic type or permits
all traffic not specifically restricted.
There are two general types of access lists used on Cisco devices:
Access List Type Characteristics
Standard ACLs:
Can filter only on source hostname or host IP address.
Should be placed as close to the destination as possible.
Standard ACL
Use the following number ranges:
o 1–99
o 1300–1999
Extended ACLs:
Can filter by:
o Source IP protocol (IP, TCP, UDP, etc.)
Extended ACL o Source hostname or host IP address
o Source or destination socket number
o Destination hostname or host IP address
o Precedence or TOS values
School of Computer Studies (UG) Page 16
Should be placed as close to the source as possible.
Use the following number ranges:
o 100–199
o 2000–2699
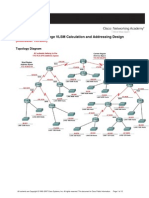
4. Consider the network shown in the exhibit.
SOLUTION:
School of Computer Studies (UG) Page 17
UNIT-V
1. Which tool should you use when you have a WAN link that connects two sites? The WAN
link is supposed to provide 1.5 Mbps of bandwidth. You want to perform a test to see the actual
bandwidth of the link.
SOLUTION:
2. Assume that Cisco devices send all log messages for all severity levels to the console. If a
network contains a limited number of devices, this default configuration is usually acceptable.
However, on a large network, it is impractical to visit each device to view log messages.
Instead, you can configure your Cisco devices to redirect logging to a syslog server somewhere
in the network. Write down the commands to implement log redirection.
SOLUTION:
Use the following commands to implement log redirection:
Command Action
(config)#logging on Enables the message logging process.
(config)#logging
host [address] Specifies the host IP address or hostname of the
(config)#logging syslog server that will receive the messages.
host [hostname]
(config)#logging buffered Specifies that the messages are to be buffered.
School of Computer Studies (UG) Page 18
Specifies which messages will be redirected to the
syslog server based on severity. Messages at or
numerically lower than the specified level are
logged. System logging message severity levels
include the following:
{Emergencies | 0} - System unusable
{Alerts | 1} - Immediate action needed
{Critical | 2} - Critical conditions
{Errors | 3} - Error conditions
(config)#logging
trap [severity-level] {Warnings | 4} - Warning conditions
(config)#logging trap [0-7]
{Notifications | 5} - Normal but significant
conditions
{Informational | 6} - Informational
messages only
{Debugging | 7} - Debugging messages
By default, the logging trap command will send
level 0 to level 6 system messages to the syslog
server. On some servers and IOS versions, the
device also buffers the messages.
(config)#logging source- Specifies the source IP address of system logging
interface [type] [number] packets.
Displays logging settings on the device, as well as
#show logging
the number of messages logged.
In the following example, the router is configured to redirect log messages with a severity
level of 4 and lower to a syslog server with an IP address of 17.17.8.200:
Router(config)#logging on
Router(config)#logging host 172.17.8.200
Router(config)#logging trap 4
School of Computer Studies (UG) Page 19
3. Consider the following log message, generated on a router:
*Aug 8 11:18:12.081: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface
FastEthernet0/0, changed state to state down
What facility generated this message?
SOLUTION:
%LINEPROTO
4. What must be done to ensure that you are protected against data loss even if you perform
regular backups?
SOLUTION:
Regularly test restoration procedures.
School of Computer Studies (UG) Page 20
You might also like
- APIPA (Automatic Private IP Addressing)Document5 pagesAPIPA (Automatic Private IP Addressing)Giri RajNo ratings yet
- DCCN DHCPDocument19 pagesDCCN DHCPYehualashet BelaynehNo ratings yet
- DHCPDocument2 pagesDHCPደስታ ጌታውNo ratings yet
- CCNA 2 Ch10 ExamDocument10 pagesCCNA 2 Ch10 ExamBryant Villarin BaldivicioNo ratings yet
- CCNA 2 Chapter 10 PDFDocument8 pagesCCNA 2 Chapter 10 PDFMarc Jason YuNo ratings yet
- Practice Skills Assessment Part IIDocument6 pagesPractice Skills Assessment Part IImalickNo ratings yet
- Explain Apipa Ip Address and Subnet Mask PDFDocument2 pagesExplain Apipa Ip Address and Subnet Mask PDFLuisNo ratings yet
- CSS - Info Sheet 3.2-5 - Respond To Unplanned Events or Conditions - DHCPDocument6 pagesCSS - Info Sheet 3.2-5 - Respond To Unplanned Events or Conditions - DHCPomarNo ratings yet
- DHCP Protocol: Purpose, Types, Configuration and TroubleshootingDocument15 pagesDHCP Protocol: Purpose, Types, Configuration and TroubleshootingLeslav MazeikoNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking IP Address: Client-ServerDocument3 pagesComputer Networking IP Address: Client-ServerMuhammad Usman Ashraf KhanNo ratings yet
- CCNA 2 Chapter 10 v5.0 Exam QuestionsDocument8 pagesCCNA 2 Chapter 10 v5.0 Exam QuestionsmacebferNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 v7 de 7 9Document19 pagesCCNA 1 v7 de 7 9Riadh SalhiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Work No. 5: Connectivity To The NetworkDocument10 pagesLaboratory Work No. 5: Connectivity To The NetworkAlex NbNo ratings yet
- BÀI TẬP 07 - CÁC GIAO THỨC ĐỊNH TUYẾNDocument4 pagesBÀI TẬP 07 - CÁC GIAO THỨC ĐỊNH TUYẾNHoàng AnhNo ratings yet
- DHCP Protokolas: Paskirtis Ir KonfigūravimasDocument13 pagesDHCP Protokolas: Paskirtis Ir KonfigūravimasLeslav MazeikoNo ratings yet
- Capitulo2 PDFDocument18 pagesCapitulo2 PDFAngel MartinolisNo ratings yet
- DHCP QuestionDocument9 pagesDHCP QuestionLalit KaushikNo ratings yet
- (DHCP) : Dynamic Host Configuration ProtocolDocument5 pages(DHCP) : Dynamic Host Configuration ProtocoltirupathiNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 - Creating DHCP InfrastructureDocument27 pagesChapter4 - Creating DHCP InfrastructureJh0n Fredy H100% (1)
- DHCP Server ConfigurationDocument9 pagesDHCP Server ConfigurationTan TaroNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 CCNDocument7 pagesLab 4 CCNAreeba NoorNo ratings yet
- DHCPDocument17 pagesDHCPPong DaroNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Work No. 5: Connectivity To The NetworkDocument10 pagesLaboratory Work No. 5: Connectivity To The NetworkJayson C. LagareNo ratings yet
- DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration ProtocolDocument12 pagesDHCP Dynamic Host Configuration ProtocolRough MetalNo ratings yet
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) : Tcp/IpDocument11 pagesDHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) : Tcp/Ipfalcon_oneNo ratings yet
- Lab 2: Introduction To Networking Command IpconfigDocument11 pagesLab 2: Introduction To Networking Command IpconfignoumanNo ratings yet
- Rpi Raspbianwheezy DHCP ServerDocument2 pagesRpi Raspbianwheezy DHCP ServerIqbal PerxNo ratings yet
- Ipv4 Reserved Addresses PDFDocument2 pagesIpv4 Reserved Addresses PDFRifat IqbalNo ratings yet
- CCNA 2 Chapter 10 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 100Document9 pagesCCNA 2 Chapter 10 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 100ovidiu0702No ratings yet
- Mugiraneza: Window Server AdministratorDocument8 pagesMugiraneza: Window Server AdministratorMugïrañeza JøšhűåNo ratings yet
- CCN - 10Document7 pagesCCN - 10Naveed LatifNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol DHCP (Part1)Document51 pagesLesson 6: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol DHCP (Part1)Mahmmoud MahdiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-NMADocument66 pagesUnit 2-NMANisarg ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Work No. 4: Connectivity To The NetworkDocument10 pagesLaboratory Work No. 4: Connectivity To The Networkuser_iuliNo ratings yet
- Dhcpdiscover: Router (Config) # Interface g0/1 Router (Config-If) # Ip Address DHCPDocument26 pagesDhcpdiscover: Router (Config) # Interface g0/1 Router (Config-If) # Ip Address DHCPadelalezzawiNo ratings yet
- Safe and Reliable Configuration. DHCP Minimizes Configuration Errors Caused by Manual IPDocument3 pagesSafe and Reliable Configuration. DHCP Minimizes Configuration Errors Caused by Manual IPtitassarkerNo ratings yet
- Setting Up A DHCP Server in Windows 2003Document7 pagesSetting Up A DHCP Server in Windows 2003Jalel Bejo GudinaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Host Configuration ProtocolDocument5 pagesDynamic Host Configuration Protocolartsan3No ratings yet
- Configuring A Lan With DHCP and Vlans: "Switch Port Configurations" Section On Page 5-7Document10 pagesConfiguring A Lan With DHCP and Vlans: "Switch Port Configurations" Section On Page 5-7Leandro Rodriguez AlvearNo ratings yet
- MikroTik Basic Training Class PDFDocument69 pagesMikroTik Basic Training Class PDFGodyNo ratings yet
- Ccna 2 v7 Srwe v7 79Document51 pagesCcna 2 v7 Srwe v7 79Riadh SalhiNo ratings yet
- How To Configure DHCP in Cisco Packet TracerDocument12 pagesHow To Configure DHCP in Cisco Packet TracerLuis FfNo ratings yet
- Setting Up A DHCP Server in Cisco Packet TracerDocument5 pagesSetting Up A DHCP Server in Cisco Packet TracerGodsendNo ratings yet
- W12 Presentation Chapter 10 DHCPDocument15 pagesW12 Presentation Chapter 10 DHCPWendellNo ratings yet
- Learn DHCP in 5 MinutesDocument3 pagesLearn DHCP in 5 MinutesCCNAResourcesNo ratings yet
- Configuring DHCP ServerDocument4 pagesConfiguring DHCP Serverlalit kumarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet: 3.2 Student Name: Uid: Branch: CSE Section/Group: Semester:4 Semester Date of Performance: Subject Name:Computer NetworsDocument5 pagesWorksheet: 3.2 Student Name: Uid: Branch: CSE Section/Group: Semester:4 Semester Date of Performance: Subject Name:Computer NetworsPratham ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Q&A NetworkingDocument15 pagesQ&A NetworkingChetan GoudarNo ratings yet
- What Is DHCP - Relay Agent - DORA Process - A Complete GuideDocument19 pagesWhat Is DHCP - Relay Agent - DORA Process - A Complete GuideCaremen BuzatuNo ratings yet
- Tle-12 q1 Las Css Wk7day3Document2 pagesTle-12 q1 Las Css Wk7day3marivic itongNo ratings yet
- 8.1.2.4 Lab - Configuring Basic DHCPv4 On A Router PDFDocument6 pages8.1.2.4 Lab - Configuring Basic DHCPv4 On A Router PDFJed Efraim Espanillo50% (2)
- Configuring A Lan With DHCP and Vlans: Figure 5-1Document8 pagesConfiguring A Lan With DHCP and Vlans: Figure 5-1Neba Neba NebaNo ratings yet
- What Is DHCP?Document63 pagesWhat Is DHCP?Senthil Murugan PackiamNo ratings yet
- What Is DHCP?Document63 pagesWhat Is DHCP?Senthil Murugan PackiamNo ratings yet
- What Is DHCP?Document63 pagesWhat Is DHCP?Senthil Murugan PackiamNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 (DHCP)Document2 pagesLesson 7 (DHCP)Jeff LacasandileNo ratings yet
- What Is DHCPDocument7 pagesWhat Is DHCPTeenuJosephNo ratings yet
- 18mit13c U2Document13 pages18mit13c U2Yuvaraj V, Assistant Professor, BCANo ratings yet
- BGPDocument66 pagesBGPsimranjyotsuri7646No ratings yet
- IPV-4 ROUTING-Assignment Questions With SolutionsDocument15 pagesIPV-4 ROUTING-Assignment Questions With SolutionsYuvaraj V, Assistant Professor, BCANo ratings yet
- 7.6.3 Exploring IPv6 Addressing On RoutersDocument3 pages7.6.3 Exploring IPv6 Addressing On RoutersYuvaraj V, Assistant Professor, BCANo ratings yet
- PPP by Vanlalmawia 13.05.2016Document51 pagesPPP by Vanlalmawia 13.05.2016Pulokesh GhoshNo ratings yet
- Elective-I-Fundamental of Networks-AssignmentDocument42 pagesElective-I-Fundamental of Networks-AssignmentYuvaraj V, Assistant Professor, BCANo ratings yet
- B.SC - IT-UG-CBCS-2019-STRUCTURE & SCHEME-19.3.21 (WITHOUT COP) - MergedDocument17 pagesB.SC - IT-UG-CBCS-2019-STRUCTURE & SCHEME-19.3.21 (WITHOUT COP) - MergedYuvaraj V, Assistant Professor, BCANo ratings yet
- Software Reliability: Dr. R. MallDocument69 pagesSoftware Reliability: Dr. R. Mallgitu583No ratings yet
- Rajib Mall Lecture NotesDocument87 pagesRajib Mall Lecture NotesAnuj NagpalNo ratings yet
- Function-Oriented Software Design: Dr. R. MallDocument81 pagesFunction-Oriented Software Design: Dr. R. Mallgitu583No ratings yet
- Lecture 17Document136 pagesLecture 17Yuvaraj V, Assistant Professor, BCANo ratings yet
- Rajib Mall Lecture NotesDocument56 pagesRajib Mall Lecture NotesAnuj Nagpal100% (1)
- Rajib Mall Lecture NotesDocument73 pagesRajib Mall Lecture NotesAnuj NagpalNo ratings yet
- Formal Specification of Systems:: Lecture 3ADocument131 pagesFormal Specification of Systems:: Lecture 3Agitu583No ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document83 pagesLecture 3Tarachan RanaNo ratings yet
- C - Unit-IiiDocument25 pagesC - Unit-IiiYuvaraj V, Assistant Professor, BCANo ratings yet
- LECT3Document87 pagesLECT3Yuvaraj V, Assistant Professor, BCANo ratings yet
- Cyber Security-Unit-IIDocument29 pagesCyber Security-Unit-IIYuvaraj V, Assistant Professor, BCANo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document79 pagesLecture 5Devmani ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Rajib Mall Lecture NotesDocument63 pagesRajib Mall Lecture NotesAnuj NagpalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Software Engineering: Prof. R. MallDocument97 pagesIntroduction To Software Engineering: Prof. R. MallvenkatasureshNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security-Unit-IDocument64 pagesCyber Security-Unit-IYuvaraj V, Assistant Professor, BCANo ratings yet
- Unit III SEDocument99 pagesUnit III SEYuvaraj V, Assistant Professor, BCANo ratings yet
- PPT 05Document30 pagesPPT 05kh maNo ratings yet
- Os Unit IiDocument69 pagesOs Unit IiYuvaraj V, Assistant Professor, BCANo ratings yet
- Os Unit IvDocument62 pagesOs Unit IvYuvaraj V, Assistant Professor, BCANo ratings yet
- I-Mha - Unit-VDocument6 pagesI-Mha - Unit-VYuvaraj V, Assistant Professor, BCANo ratings yet
- I-Mha - Unit-IiiDocument23 pagesI-Mha - Unit-IiiYuvaraj V, Assistant Professor, BCANo ratings yet
- Package ProgramDocument1 pagePackage ProgramYuvaraj V, Assistant Professor, BCANo ratings yet
- Cisco 2 Activity 6.4.2 Challenge VLSM Calculation and Addressing Design ANSWERSDocument12 pagesCisco 2 Activity 6.4.2 Challenge VLSM Calculation and Addressing Design ANSWERSjohndoe6745100% (2)
- Modicon M340 For EthernetDocument398 pagesModicon M340 For EthernetPaul BunyanNo ratings yet
- The AD-OD Sandbox: A Quickstart Guide For Setting Up Active Directory and Open Directory in Your Test EnvironmentDocument33 pagesThe AD-OD Sandbox: A Quickstart Guide For Setting Up Active Directory and Open Directory in Your Test EnvironmentChris MayNo ratings yet
- SMS Playstation 2 Simple Media System Manual PDFDocument76 pagesSMS Playstation 2 Simple Media System Manual PDFRenéEmilioPariAlaveNo ratings yet
- T1h-Ebc (100) User ManualDocument75 pagesT1h-Ebc (100) User ManualclaudiocbmNo ratings yet
- 02 575 722 075 DNA A211 I - UserManualDocument103 pages02 575 722 075 DNA A211 I - UserManualAditya Guru0% (1)
- Quick Start: Espace Iad104HDocument49 pagesQuick Start: Espace Iad104Hcadillac24No ratings yet
- Teles Voipbox Pri 17.1 ReferencemanualDocument214 pagesTeles Voipbox Pri 17.1 ReferencemanualvadlapatisNo ratings yet
- Configuration Guide For MOXA Nport With SMS PASSCODEDocument17 pagesConfiguration Guide For MOXA Nport With SMS PASSCODERinto HarahapNo ratings yet
- Websense GuideDocument25 pagesWebsense GuideGirikikkeriNo ratings yet
- Cisco SD-WAN SegmentationDocument15 pagesCisco SD-WAN SegmentationalexNo ratings yet
- DS-3WF0AC-2NT User ManualDocument37 pagesDS-3WF0AC-2NT User ManualPedro MacielNo ratings yet
- Tutorial CX ProgrammerDocument193 pagesTutorial CX ProgrammerDejan MihailovicNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Lesson 4 - Understanding Internet ProtocolDocument6 pagesTest Bank Lesson 4 - Understanding Internet ProtocolmeixfuuNo ratings yet
- Data Comm Part 2.ppt NewDocument48 pagesData Comm Part 2.ppt Newmuhabamohamed21No ratings yet
- PGDCHN SDocument14 pagesPGDCHN SSelvakumar RNo ratings yet
- IPICO User ManualDocument39 pagesIPICO User ManualChube TuxNo ratings yet
- Different Networking Systems Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument71 pagesDifferent Networking Systems Advantages and Disadvantagesshabir AhmadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer SystemsDocument293 pagesIntroduction To Computer SystemsAchieng Okoth Joseph67% (3)
- Share Cable IPTV & Internet RB951G - CRS125 - MikroTikDocument16 pagesShare Cable IPTV & Internet RB951G - CRS125 - MikroTikLeri FirdianNo ratings yet
- 2.3.2.5 Packet Tracer - Implementing Basic ConnectivityDocument4 pages2.3.2.5 Packet Tracer - Implementing Basic ConnectivityMpaphi Map'z DambeNo ratings yet
- How To Configure Nokia Mobile VPN For Cisco ASA Gateway CertificatesDocument26 pagesHow To Configure Nokia Mobile VPN For Cisco ASA Gateway CertificatesMario RocaNo ratings yet
- IN03、IN04 User Manual V1.0Document82 pagesIN03、IN04 User Manual V1.0Edd PONo ratings yet
- CCNA 2 v7 Modules 7 - 9 - Available and Reliable Networks Exam AnswersDocument7 pagesCCNA 2 v7 Modules 7 - 9 - Available and Reliable Networks Exam AnswersSuperheavy Rockshow Go'tNo ratings yet
- Lab 8.3.4 Planning, Configuring and Verifying Extended AclsDocument5 pagesLab 8.3.4 Planning, Configuring and Verifying Extended AclsFery ArdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Communication Guide, Tricon v9.6 PDFDocument248 pagesCommunication Guide, Tricon v9.6 PDFMohamed AmineNo ratings yet
- Agilent Testing GPRS SignallingDocument24 pagesAgilent Testing GPRS SignallingPrasant KumarNo ratings yet
- Darktrace Network Deployment GuideDocument16 pagesDarktrace Network Deployment GuideIvan Popov50% (4)
- 7TS7TCPDocument11 pages7TS7TCPwiryana_mdNo ratings yet
- NAT Integration With MPLS VPNsDocument26 pagesNAT Integration With MPLS VPNsRichard VillanuevaNo ratings yet