Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5 1
Uploaded by
M0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageThe document outlines the growing imperialist sentiment in the United States in the late 19th century. It discusses the economic and military competition with European powers that convinced many Americans the US should become a world power. It also describes the desire for new overseas markets for raw materials and goods, as well as places to invest capital. The document then discusses the belief in Anglo-Saxon cultural superiority and the role of naval power in expanding American influence abroad through events like the opening of Japan by Commodore Perry in 1853. It concludes with the annexation of Hawaii and Samoa in the Pacific for naval bases and trade.
Original Description:
Original Title
5-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document outlines the growing imperialist sentiment in the United States in the late 19th century. It discusses the economic and military competition with European powers that convinced many Americans the US should become a world power. It also describes the desire for new overseas markets for raw materials and goods, as well as places to invest capital. The document then discusses the belief in Anglo-Saxon cultural superiority and the role of naval power in expanding American influence abroad through events like the opening of Japan by Commodore Perry in 1853. It concludes with the annexation of Hawaii and Samoa in the Pacific for naval bases and trade.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 page5 1
Uploaded by
MThe document outlines the growing imperialist sentiment in the United States in the late 19th century. It discusses the economic and military competition with European powers that convinced many Americans the US should become a world power. It also describes the desire for new overseas markets for raw materials and goods, as well as places to invest capital. The document then discusses the belief in Anglo-Saxon cultural superiority and the role of naval power in expanding American influence abroad through events like the opening of Japan by Commodore Perry in 1853. It concludes with the annexation of Hawaii and Samoa in the Pacific for naval bases and trade.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
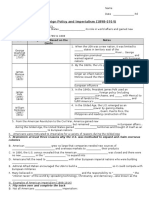
Lesson 5-1: The Imperialist Vision Name: ___________________
I. Building Support for Imperialism
a. In the 1880s, economic & military competition from ________ & a growing feeling of cultural ___________
convinced many Americans that the US should become a _______ power
II. A Desire for New Markets
a. Imperialism is the domination of a _______ nation over _________ ones. Reasons; 1) Needed to import raw
__________ for manufacturing, 2) Companies looked for new ___________ overseas; 3) Looking overseas
for places to ___________ their capital
b. made some into __________ and others into _________________ (protected against rebellions/invasions)
III. A feeling of Superiority
a. Fiske argued that _________-speaking nations had superior character, ideas, and systems of gov’t – many
linked his ideas, known as Anglo-Saxonism, with the idea of ___________ ____________
b. Strong linked Anglo-Saxonism to _____________ missionary ideas
IV. Building a Modern Navy
a. The US became more assertive in __________ affairs.
b. Captain Alfred T. _________ - “The Influence of Sea Power Upon ________”. Two powerful senators, Henry
Cabot _______ & Beveridge, used position to convince Congress to support a new ______.
V. American Expansion in the Pacific
a. From the earliest days of the Republic, Americans had expanded their nation by moving _____________
VI. Perry Opens Japan: In 1853, __________ under Perry’s command entered Edo Bay (Now Tokyo). Japans rulers
had _______ contact with West. In 1854, Japan signed the Treaty of Kanagawa, giving US __________ rights
VII. Annexing Samoa and Hawaii
a. As trade with Asia grew, the US needed ports for its ships to _______ and resupply as they crossed the
Pacific. An 1899 agreement divided _______ between Germany and the US
b. Hawaii: Americans found that ______________ grew well in Hawaii – in 1875, the US signed a treaty
exempting Hawaiian sugar from ________. When treaty was up for renewal, the US insisted Hawaii grant it
exclusive rights to a naval base at _______ __________
c. In 1887, wealthy sugar planters led by Sanford ______ forced the Hawaiian king to accept a new constitution
. The next year, Queen __________________ ascended the Hawaiian throne and tried to restore the
monarchy authority.
d. Backed by the American ambassador and US Marines, the planters forced ____________ to give up power
and asked ______ to serve as president of the new Hawaiian Republic. Dole requested the US annex Hawaii;
President __________, who opposed imperialism, tried instead to restore the _______ to power, but
Hawaii’s new leaders refused. Instead, they waited till a new president took office; in 1898, under President
___________, the US annexed Hawaii.
You might also like
- Lawyers, Particularly Members of The BAR Association, From Serving in Government!Document12 pagesLawyers, Particularly Members of The BAR Association, From Serving in Government!joy larsonNo ratings yet
- European Colonization in North America: Spanish, French, Dutch, & British ColoniesDocument3 pagesEuropean Colonization in North America: Spanish, French, Dutch, & British Coloniesapi-294843376No ratings yet
- Neogenesis - Reconstructing The SelfDocument6 pagesNeogenesis - Reconstructing The SelfSteven Ferrel100% (2)
- Copyof 3 Empiresguidednotes 2016Document9 pagesCopyof 3 Empiresguidednotes 2016api-335205448No ratings yet
- CIA History Staff: Eagle and Swastika: CIA and Nazi War Criminals and CollaboratorsDocument654 pagesCIA History Staff: Eagle and Swastika: CIA and Nazi War Criminals and CollaboratorsCantankerous Buddha100% (1)
- American Revolution 1Document3 pagesAmerican Revolution 1api-294843376No ratings yet
- Hawaii WorksheetDocument3 pagesHawaii WorksheetJeremyJWBNo ratings yet
- 1 U S Foreign Policy and ImperialismDocument3 pages1 U S Foreign Policy and Imperialismapi-301854263No ratings yet
- America The Story of Us Rebels Episode 1Document1 pageAmerica The Story of Us Rebels Episode 1beedefNo ratings yet
- 1 U.S. Foreign Policy and Imperialism PDFDocument2 pages1 U.S. Foreign Policy and Imperialism PDFsashaNo ratings yet
- U.S History SparkCharts 1492-1877Document14 pagesU.S History SparkCharts 1492-1877Nicole Key100% (4)
- Popular Culture and World Politics FedericaDocument188 pagesPopular Culture and World Politics FedericaFariz Abi KaramiNo ratings yet
- Gems and Jewelry Sector in IndiaDocument18 pagesGems and Jewelry Sector in IndiaMurali_Dhar_1824No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Pre Test and PracticeDocument23 pagesChapter 7 Pre Test and PracticeHarry NagraNo ratings yet
- 5 2Document2 pages5 2MNo ratings yet
- 23 1Document2 pages23 1MNo ratings yet
- 1 U.S. Foreign Policy and Imperialism PDFDocument2 pages1 U.S. Foreign Policy and Imperialism PDFsashaNo ratings yet
- 5 3Document2 pages5 3MNo ratings yet
- U.S. Foreign Policy and ImperialismDocument2 pagesU.S. Foreign Policy and Imperialismclautide winterNo ratings yet
- 8 Ah C456notesDocument9 pages8 Ah C456notesMNo ratings yet
- 6 6bDocument1 page6 6bMNo ratings yet
- 7 C7oultillllDocument5 pages7 C7oultillllMNo ratings yet
- Anticipatory Activity Instructions: Using The Provided KWL Chart Answer TheDocument5 pagesAnticipatory Activity Instructions: Using The Provided KWL Chart Answer TheDaniel PoncianoNo ratings yet
- 4 The U S Battlefront and Homefront in Wwi 1Document2 pages4 The U S Battlefront and Homefront in Wwi 1api-301854263No ratings yet
- 1 Jefferson Madison Monroe NotesDocument3 pages1 Jefferson Madison Monroe Notesapi-294843376No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Study Guide (The U.S. Becomes A World Power)Document9 pagesUnit 4 Study Guide (The U.S. Becomes A World Power)Morgan MunozNo ratings yet
- 7 WH C6outlineDocument5 pages7 WH C6outlineMNo ratings yet
- 2 SouthernnemiddlecoloniesDocument8 pages2 Southernnemiddlecoloniesapi-294843376No ratings yet
- 4 Sectionalism From 1820-1860 1Document4 pages4 Sectionalism From 1820-1860 1api-294843376No ratings yet
- Netw Rks Guided Reading Activity: Lesson 3 Ratifying The ConstitutionDocument1 pageNetw Rks Guided Reading Activity: Lesson 3 Ratifying The ConstitutionJoshua WhiteNo ratings yet
- 6 4Document2 pages6 4MNo ratings yet
- Name: - Study Guide Topic 7Document3 pagesName: - Study Guide Topic 7Anonymous cOVjD9dNo ratings yet
- Report - Philippines - History WorksheetDocument5 pagesReport - Philippines - History Worksheetrizielpingcas82No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument1 pageAssignmentJoshua WhiteNo ratings yet
- 18 3 WorksheetDocument2 pages18 3 WorksheetJeffrey S. Hyer100% (1)
- Story ElementsDocument3 pagesStory ElementsEliana CrespoNo ratings yet
- 8 - 4 1 Pre-Constitutional Convention CN Fill-InDocument1 page8 - 4 1 Pre-Constitutional Convention CN Fill-Inapi-242867432No ratings yet
- Key Terms and Places: The United States Lesson 2Document4 pagesKey Terms and Places: The United States Lesson 2Pamela Celada LinaresNo ratings yet
- Eoc Review ImperialismDocument7 pagesEoc Review Imperialismapi-252514619No ratings yet
- Ushistoryreview 2Document5 pagesUshistoryreview 2M MNo ratings yet
- Crash Course Us History 32 - The Roaring Twenties PDFDocument3 pagesCrash Course Us History 32 - The Roaring Twenties PDFJodie GreenNo ratings yet
- Fall 2019 Social Studies Benchmark Review Fill in The Blank ActivityDocument2 pagesFall 2019 Social Studies Benchmark Review Fill in The Blank ActivityjeffNo ratings yet
- Founding DocumentsDocument6 pagesFounding Documentsapi-262327064No ratings yet
- The Presidency of George Washington Slotted Notes Editable 1Document3 pagesThe Presidency of George Washington Slotted Notes Editable 1Zainab LawalNo ratings yet
- SSWH16 Study Guide: VocabularyDocument3 pagesSSWH16 Study Guide: VocabularyMuffierzNo ratings yet
- rkV8P2Cn71sM0SDjyELZNZN7NzrJvv4059n6gaptWfls2iBkiovj0Yoe65VJl4Dck0 - rtUMb8C3cvKEb9VsfdhafEJWL Q - 7sG tVNq0cDocument7 pagesrkV8P2Cn71sM0SDjyELZNZN7NzrJvv4059n6gaptWfls2iBkiovj0Yoe65VJl4Dck0 - rtUMb8C3cvKEb9VsfdhafEJWL Q - 7sG tVNq0cangkiongbohNo ratings yet
- 6 6cDocument1 page6 6cMNo ratings yet
- 08.10 Canal Americas Reading Questions WorksheetDocument2 pages08.10 Canal Americas Reading Questions WorksheetMNo ratings yet
- 2 SouthernnemiddlecoloniesDocument8 pages2 Southernnemiddlecoloniesapi-294843376No ratings yet
- Slavery and Secession 2Document2 pagesSlavery and Secession 2api-256560022No ratings yet
- 2 Progressive Era - Political ReformsDocument3 pages2 Progressive Era - Political Reformsapi-301854263No ratings yet
- 1 Progressive Era - Urban Social ReformsDocument12 pages1 Progressive Era - Urban Social Reformsapi-301854263No ratings yet
- Colonial Life Cornell NotesDocument2 pagesColonial Life Cornell NotesDerrick BurksNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Packet AnswersDocument3 pagesChapter 5 Packet Answersapi-270974388No ratings yet
- 3lifeinthebritishcolonies 2Document3 pages3lifeinthebritishcolonies 2api-294843376No ratings yet
- ImperialismDocument15 pagesImperialismIsabella LoretoNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Antebellum America HandoutDocument7 pagesUnit 4 Antebellum America HandoutJason SmithNo ratings yet
- 07.06 End of Reconstruction Reading Questions WorksheetDocument2 pages07.06 End of Reconstruction Reading Questions WorksheetA'Him Kridsada ThirasophonNo ratings yet
- Revolutionary War Vocabulary QuizDocument2 pagesRevolutionary War Vocabulary Quizapi-247477753100% (1)
- 15 1Document1 page15 1MNo ratings yet
- Apush Chapter 20 OutlineDocument3 pagesApush Chapter 20 OutlinebarglesnargleNo ratings yet
- Ap U.S. History: The New Nation (The Critical Period - 1781-1789)Document9 pagesAp U.S. History: The New Nation (The Critical Period - 1781-1789)zzoo4No ratings yet
- Hawaii: 1. What Do You Think of When You Think of Hawaii? 1Document4 pagesHawaii: 1. What Do You Think of When You Think of Hawaii? 1JeremyJWBNo ratings yet
- Us History Eoc Review Guide (Goes With Comprehensive Guide)Document21 pagesUs History Eoc Review Guide (Goes With Comprehensive Guide)api-2795578930% (1)
- Imperialism Worksheet-1Document11 pagesImperialism Worksheet-1api-280706116No ratings yet
- Spanish American War of 1898 - History for Kids - Causes, Surrender & Treaties | Timelines of History for Kids | 6th Grade Social StudiesFrom EverandSpanish American War of 1898 - History for Kids - Causes, Surrender & Treaties | Timelines of History for Kids | 6th Grade Social StudiesNo ratings yet
- c13 Christian c14 IslamDocument8 pagesc13 Christian c14 IslamMNo ratings yet
- GunpowderstuffDocument1 pageGunpowderstuffMNo ratings yet
- 8 Ah c10 QuizDocument2 pages8 Ah c10 QuizMNo ratings yet
- 8 Indians Webquest OptionalDocument1 page8 Indians Webquest OptionalMNo ratings yet
- 2 2Document1 page2 2MNo ratings yet
- 6 3Document3 pages6 3MNo ratings yet
- 6 6aDocument1 page6 6aMNo ratings yet
- 8 WashadamsmatchDocument1 page8 WashadamsmatchMNo ratings yet
- 6 3cDocument1 page6 3cMNo ratings yet
- 8 Ah c10 QuizpracticeDocument1 page8 Ah c10 QuizpracticeMNo ratings yet
- 6 6bDocument1 page6 6bMNo ratings yet
- 6 3ccDocument1 page6 3ccMNo ratings yet
- 6 4Document2 pages6 4MNo ratings yet
- 6 1Document1 page6 1MNo ratings yet
- 6 6cDocument1 page6 6cMNo ratings yet
- 8 Ah 13coloniesDocument1 page8 Ah 13coloniesMNo ratings yet
- 706 Unit2weeklyDocument1 page706 Unit2weeklyMNo ratings yet
- 8 c4 ReviewDocument2 pages8 c4 ReviewMNo ratings yet
- 6 2Document1 page6 2MNo ratings yet
- 7 WH C8outlineDocument5 pages7 WH C8outlineMNo ratings yet
- 7 Unit1scoreDocument1 page7 Unit1scoreMNo ratings yet
- 7 WH C7quizprepDocument1 page7 WH C7quizprepMNo ratings yet
- 7 C7oultillllDocument5 pages7 C7oultillllMNo ratings yet
- 7 WH HistorymovieDocument1 page7 WH HistorymovieMNo ratings yet
- 7 RomeclozeDocument1 page7 RomeclozeMNo ratings yet
- 7 RomemapDocument1 page7 RomemapMNo ratings yet
- 7 C11studysheetDocument1 page7 C11studysheetMNo ratings yet
- 7 Egypt ChallengesDocument3 pages7 Egypt ChallengesMNo ratings yet
- 8 c10 MiniquizDocument1 page8 c10 MiniquizMNo ratings yet
- Chapelle - The Encyclopedia of Applied LinguisticsDocument7 pagesChapelle - The Encyclopedia of Applied LinguisticscarolinherediaNo ratings yet
- Colleges and Universities Offering Early ActionDocument13 pagesColleges and Universities Offering Early ActionpalanitNo ratings yet
- De-Trumping U.S. Foreign Policy Can Biden Bring America Back (Stanley R. Sloan)Document108 pagesDe-Trumping U.S. Foreign Policy Can Biden Bring America Back (Stanley R. Sloan)Pablo Fernando Suárez RubioNo ratings yet
- Wisconsin Firearms Freedom ActDocument5 pagesWisconsin Firearms Freedom ActTenth Amendment CenterNo ratings yet
- You're Attempt To Prioritize Extinction Over Structural Criticisms Reifies Antiblackness by Using Military Terror To Destroy Meaningful ResistanceDocument3 pagesYou're Attempt To Prioritize Extinction Over Structural Criticisms Reifies Antiblackness by Using Military Terror To Destroy Meaningful ResistanceNelson OkunlolaNo ratings yet
- Facing The Colonels-British and American Diplomacy Towards The Colonels Junta in Greece 1967-1970 PDFDocument321 pagesFacing The Colonels-British and American Diplomacy Towards The Colonels Junta in Greece 1967-1970 PDFCHRISTOSOFATHENS100% (1)
- What Are Entity Health Checks and Why Are They ImportantDocument3 pagesWhat Are Entity Health Checks and Why Are They ImportantrdiazeplaNo ratings yet
- The Geopolitics of Mexico - A Mountain Fortress Besieged - StratforDocument13 pagesThe Geopolitics of Mexico - A Mountain Fortress Besieged - StratforAbe Schreier100% (1)
- Hephzibah ElementaryDocument4 pagesHephzibah ElementaryJeremy TurnageNo ratings yet
- WikiLeaks - Sensitive Cables, GY Tag (Single Document)Document445 pagesWikiLeaks - Sensitive Cables, GY Tag (Single Document)Brigadier David GrangerNo ratings yet
- Super PacsDocument3 pagesSuper Pacsapi-98469116No ratings yet
- Henry FordDocument5 pagesHenry FordSherren Marie NalaNo ratings yet
- Good Hopes For Global OutsourcingDocument3 pagesGood Hopes For Global OutsourcingRaktim MajumderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Agabin Legal System of The PhilippinesDocument49 pagesChapter 7 Agabin Legal System of The PhilippinesBetel AntaNo ratings yet
- Placement BrochureDocument44 pagesPlacement BrochureJaya GummalaNo ratings yet
- Sustentable Medio AmbienteDocument425 pagesSustentable Medio AmbienteCatalina NaimaNo ratings yet
- Annotated BibliographyDocument4 pagesAnnotated BibliographyDoris LinNo ratings yet
- Gabriel ProsserDocument4 pagesGabriel ProsserHidden Truth100% (1)
- Enslavedcommunity ReportDocument36 pagesEnslavedcommunity Reportapi-254433141No ratings yet
- All Combined Economics Paper 4Document142 pagesAll Combined Economics Paper 4DhruvaAgrwalNo ratings yet
- Cases For 1st YearDocument1,394 pagesCases For 1st YearPwede Akon KalaNo ratings yet
- Map of Montana - Federal Lands and Indian ReservationsDocument1 pageMap of Montana - Federal Lands and Indian ReservationsHistoricalMapsNo ratings yet
- Sociology of DevelopmentDocument17 pagesSociology of DevelopmentSahil VermaNo ratings yet
- Pepsi-Cola Bottling Company of The Phlippines, Inc., vs. Municipality of Tanauan, Leyte, The Municipal Mayor, Et AlDocument2 pagesPepsi-Cola Bottling Company of The Phlippines, Inc., vs. Municipality of Tanauan, Leyte, The Municipal Mayor, Et AlHenri VasquezNo ratings yet