Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 23
Uploaded by
shiva23020 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesThe document discusses the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which measures inflation and the price level in an economy. It is calculated by tracking the prices of goods in a "basket" that represents typical household spending over time. The composition and weights assigned to items in the basket are adjusted periodically to reflect changing consumer behavior and spending patterns. The Producer Price Index (PPI) measures changes in prices at the wholesale level paid by manufacturers. It can help indicate future trends in consumer inflation measured by the CPI, though there may be a time lag between movements in the two indices.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which measures inflation and the price level in an economy. It is calculated by tracking the prices of goods in a "basket" that represents typical household spending over time. The composition and weights assigned to items in the basket are adjusted periodically to reflect changing consumer behavior and spending patterns. The Producer Price Index (PPI) measures changes in prices at the wholesale level paid by manufacturers. It can help indicate future trends in consumer inflation measured by the CPI, though there may be a time lag between movements in the two indices.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesChapter 23
Uploaded by
shiva2302The document discusses the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which measures inflation and the price level in an economy. It is calculated by tracking the prices of goods in a "basket" that represents typical household spending over time. The composition and weights assigned to items in the basket are adjusted periodically to reflect changing consumer behavior and spending patterns. The Producer Price Index (PPI) measures changes in prices at the wholesale level paid by manufacturers. It can help indicate future trends in consumer inflation measured by the CPI, though there may be a time lag between movements in the two indices.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
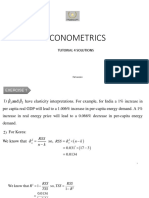
Consumer Price Index (CPI):
- Measures the price level and inflation in an economy.
- Allows for international comparisons as it adheres to international standards.
- Presented as an index, with a base year's index set at 100.
- Inflation rate is calculated by comparing the current year's index to the previous year's index.
Calculation of CPI:
1. Identify a "basket of goods" that represents what a typical household spends money on.
2. Collect data from a sample of households to determine their spending patterns.
3. For each item in the basket, surveyors record its price regularly (e.g., monthly) from various
sources and regions.
4. Calculate the percentage change in the price of each item over time.
5. Convert these price changes into index numbers.
6. Calculate the weighted average of the index numbers to determine the overall CPI.
Changes Over Time:
- The composition of the basket of goods changes over time to reflect evolving consumer
preferences and spending behavior.
- The weights assigned to each item in the basket are updated to account for changes in
spending patterns, income levels, and other factors.
- For example, new items like smartphones may be added to the basket, and items such as
leisure travel may receive greater weight as incomes rise.
Here are the key points regarding measuring unemployment and the Producer Price Index
(PPI):
Consumer Price Index (CPI):
- Measures inflation and the price level in an economy.
- Represents changes in the cost of living.
- Calculated by comparing the prices of a "basket of goods" over time.
- The basket reflects the spending patterns of a typical household.
- Adjustments are made to account for quality improvements in goods.
- May not include certain housing-related costs, such as mortgage interest payments.
Producer (Wholesale) Price Index (PPI):
- Measures changes in the prices of goods bought and sold by manufacturers.
- Includes input prices (materials and fuels purchased by manufacturers) and output prices
(factory gate prices).
- Input price indices reflect changes in materials and fuel prices.
- Output price indices measure changes in prices of goods sold by manufacturers.
- Used as an indicator of future trends in consumer inflation (CPI).
- A rise in PPI may lead to an increase in CPI, but the relationship is not perfect and may have a
time lag.
Measuring Unemployment (ILO Measure):
- An essential measure of economic performance.
- Standardized by the International Labour Organization (ILO) for international comparisons.
- Defines the population of working age as those within a specific age range (e.g., 16-65).
- Unemployed individuals, according to the ILO measure, are those without a job, actively
seeking work in the past four weeks, and available for work in the next two weeks.
- Includes individuals who have found a job and are awaiting its commencement in the next two
weeks.
You might also like
- Automatic Gearbox 0B6 Four-Wheel DriveDocument185 pagesAutomatic Gearbox 0B6 Four-Wheel DriveergdegNo ratings yet
- Quiz # 4Document27 pagesQuiz # 4Kking ChungNo ratings yet
- 011 - Measuring The Cost of LivingDocument24 pages011 - Measuring The Cost of LivingRanjitNo ratings yet
- The Wholesale Price IndexDocument3 pagesThe Wholesale Price IndexKunal MahajanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Index NumberDocument7 pagesChapter 6 Index NumberOm JainNo ratings yet
- Measuring InflationDocument25 pagesMeasuring InflationAnonymous E9ESAecw8x0% (2)
- Market Basket Consumer Goods Services: Consumer Price Index (CPI)Document4 pagesMarket Basket Consumer Goods Services: Consumer Price Index (CPI)Maxme't X JamaNo ratings yet
- Measuring The Cost of LivingDocument27 pagesMeasuring The Cost of LivingAnikNo ratings yet
- Measuring Inflation and DeflationDocument24 pagesMeasuring Inflation and DeflationSara AbouhilalNo ratings yet
- Measuring The Cost of Living: Aman 22 February 2013Document37 pagesMeasuring The Cost of Living: Aman 22 February 2013safdar2020No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 (Data Makro Ekonomi)Document31 pagesChapter 11 (Data Makro Ekonomi)Kevin HutabaratNo ratings yet
- MACROECONOMICSDocument31 pagesMACROECONOMICSიზა ცაგარელიNo ratings yet
- And Compute The Index:: - The Inflation Rate Is Calculated As FollowsDocument4 pagesAnd Compute The Index:: - The Inflation Rate Is Calculated As FollowsAmna NawazNo ratings yet
- Measuring The Cost of LivingDocument4 pagesMeasuring The Cost of LivingAmna NawazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Measuring The Cost of LivingDocument4 pagesChapter 11 Measuring The Cost of LivingGiang LinhNo ratings yet
- Consumer Price IndexDocument10 pagesConsumer Price IndexAbdullah ShabbirNo ratings yet
- Consumer Price IndexDocument12 pagesConsumer Price IndexMumtaj MNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 - Measuring The Cost of LivingDocument35 pagesChapter 24 - Measuring The Cost of LivingFTU K59 Trần Yến LinhNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument8 pagesEconomicsJayashree ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics: Measuring The Cost of LivingDocument11 pagesMacroeconomics: Measuring The Cost of LivingMd Mehedi HasanNo ratings yet
- Consumer Price IndexDocument4 pagesConsumer Price Indexbt0826100% (2)
- Consumer Price IndexDocument5 pagesConsumer Price Indexdildar89No ratings yet
- ECON1102 Complete NotesDocument60 pagesECON1102 Complete NotesJustin100% (1)
- Total Value Final Goods Services Income Income Non-Residents Economic Condition Assumption Leads QualityDocument3 pagesTotal Value Final Goods Services Income Income Non-Residents Economic Condition Assumption Leads QualityNishant JayaleNo ratings yet
- Macro Revision NotesDocument1 pageMacro Revision NotesThaminah ThassimNo ratings yet
- Copilot: Powered by AIDocument1 pageCopilot: Powered by AI768balochNo ratings yet
- Consumer Price Index: Significance of CPIDocument10 pagesConsumer Price Index: Significance of CPInitish kumar twariNo ratings yet
- UniTutor - Note of Theory C24 To C26 and C28.docx 1Document10 pagesUniTutor - Note of Theory C24 To C26 and C28.docx 1Lan AnhNo ratings yet
- Consumer Price Index: Market Basket ServicesDocument11 pagesConsumer Price Index: Market Basket ServicesHiro Ryu King MakiseNo ratings yet
- MACROECONOMICSDocument14 pagesMACROECONOMICSShovee Kyle DelantesNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics For Managers: Measures of InflationDocument29 pagesMacroeconomics For Managers: Measures of InflationRomit BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Document 17 PDFDocument2 pagesDocument 17 PDFGweyneth DadorNo ratings yet
- Consumer Price IndexDocument20 pagesConsumer Price IndexBritt John Ballentes0% (1)
- Consumer Price IndexDocument11 pagesConsumer Price IndexNihal LamgeNo ratings yet
- Measuring The Cost of LivingDocument34 pagesMeasuring The Cost of LivingSarfaraj OviNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Index Numbers: According To The SpiegelDocument7 pagesUnit Iii Index Numbers: According To The SpiegelDr Swati RajNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4. Macro 1Document41 pagesLecture 4. Macro 1ShaneNo ratings yet
- Session 3 - C23 To C26 and C28 To C30Document15 pagesSession 3 - C23 To C26 and C28 To C30Nguyệt LêNo ratings yet
- 19th International Input-Output ConferenceDocument20 pages19th International Input-Output ConferenceMaydita Ayu NursaskiawatiNo ratings yet
- GDP Deflator Vs CpiDocument6 pagesGDP Deflator Vs CpiAli HasanNo ratings yet
- How Is Inflation Measured?: Measure of Inflation: Consumer Price Index (CPI) OR Retail Price Index (RPI)Document5 pagesHow Is Inflation Measured?: Measure of Inflation: Consumer Price Index (CPI) OR Retail Price Index (RPI)17xoNo ratings yet
- Understanding CPI 2016Document16 pagesUnderstanding CPI 2016Anonymous UpWci5No ratings yet
- Ap Exam Supplement: Specifically Developed For This Year's AP ExamDocument13 pagesAp Exam Supplement: Specifically Developed For This Year's AP ExamGan PentonNo ratings yet
- Econ1102 Macroecnomics 1 Mid-Semester Exam 2013 S2 Question Bank Solutions by Zhi Ying FengDocument17 pagesEcon1102 Macroecnomics 1 Mid-Semester Exam 2013 S2 Question Bank Solutions by Zhi Ying FengJakeRohaldNo ratings yet
- Competitive Exams: Index Numbers: ExamraceDocument3 pagesCompetitive Exams: Index Numbers: ExamraceRAHUL RANJANNo ratings yet
- Price Index: Example: Price Indices Generally Select A Base Year and MakeDocument5 pagesPrice Index: Example: Price Indices Generally Select A Base Year and MakeEducationNo ratings yet
- 3 & 4 - National Income AccountingDocument27 pages3 & 4 - National Income AccountingAshish SinghNo ratings yet
- Add Maths ProjectDocument4 pagesAdd Maths ProjectSiti AmirahNo ratings yet
- Topic3 - StudentsDocument14 pagesTopic3 - StudentsTy VoNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Data (CH 20) PDFDocument11 pagesMacroeconomic Data (CH 20) PDFAlicia CataláNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Chapter IntroductionDocument16 pages1.0 Chapter IntroductionnoorsidiNo ratings yet
- Measuring The Cost of Living (Ch:11 P.O.M.E) : ECO 104 Faculty: Asif ChowdhuryDocument12 pagesMeasuring The Cost of Living (Ch:11 P.O.M.E) : ECO 104 Faculty: Asif ChowdhuryKaziRafiNo ratings yet
- Macro Session 15 - 16 InflationDocument37 pagesMacro Session 15 - 16 InflationSHRESTI ANDENo ratings yet
- Measuring The Cost of Living: Author: Prof. Sharif MemonDocument21 pagesMeasuring The Cost of Living: Author: Prof. Sharif MemonHardip MaradiaNo ratings yet
- Week 7 - Chapter 14 Index Numbers (COQTA1-B33)Document42 pagesWeek 7 - Chapter 14 Index Numbers (COQTA1-B33)KAT? LWANA?No ratings yet
- Macro NotesDocument9 pagesMacro NotesVarshini NagarajuNo ratings yet
- Canadian Securities: Overview of EconomicsDocument81 pagesCanadian Securities: Overview of EconomicsNikku SinghNo ratings yet
- Index Number and Time Series AnalysisDocument20 pagesIndex Number and Time Series AnalysisDraganMilenkovićNo ratings yet
- Methodology of Price Collection and Computing Price IndicesDocument11 pagesMethodology of Price Collection and Computing Price Indicessafdar2020No ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document3 pagesLesson 3Maurice AgbayaniNo ratings yet
- Shwe Htun AssignmentDocument8 pagesShwe Htun AssignmentDrEi Shwesin HtunNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Business Economics Study Resource: CIMA Study ResourcesFrom EverandFundamentals of Business Economics Study Resource: CIMA Study ResourcesNo ratings yet
- Quarter I Review QuestionsDocument8 pagesQuarter I Review Questionsshiva2302No ratings yet
- Newton's Laws Review CH 4 Force and motionAPDocument41 pagesNewton's Laws Review CH 4 Force and motionAPshiva2302No ratings yet
- Acing The GED ExamsDocument17 pagesAcing The GED Examsshiva2302No ratings yet
- Indian Timeline DetailsDocument5 pagesIndian Timeline Detailsshiva2302No ratings yet
- Performance Report: Cat 6050 FS and 6060 FS at La Herradura Gold Mine (Sonora, Mexico)Document24 pagesPerformance Report: Cat 6050 FS and 6060 FS at La Herradura Gold Mine (Sonora, Mexico)EVCY100% (1)
- Answerssa CtiDocument16 pagesAnswerssa CtiAerol MagpileNo ratings yet
- Intoduction of Tanning 5augDocument4 pagesIntoduction of Tanning 5augPriyankaNo ratings yet
- Harmonic Pattern Trading StrategiesDocument9 pagesHarmonic Pattern Trading StrategiesTim KanikaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Macro-Higher Education Institution: Statistik Pendidikan Tinggi 2018: Kementerian Pendidikan MalaysiaDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Macro-Higher Education Institution: Statistik Pendidikan Tinggi 2018: Kementerian Pendidikan MalaysiaStanley WongNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 SolutionsDocument24 pagesTutorial 4 Solutionseya KhamassiNo ratings yet
- More Than 60 Million People Are Employed in Globally in Aviation Industry .Discuss Direct and Indirect Revenue Contribution Towards Global GDPDocument4 pagesMore Than 60 Million People Are Employed in Globally in Aviation Industry .Discuss Direct and Indirect Revenue Contribution Towards Global GDPdawood xNo ratings yet
- Minutes For 51st NR LTA - Connectivity MeetingDocument20 pagesMinutes For 51st NR LTA - Connectivity MeetingjsvikasNo ratings yet
- Places To Stay Camino InglesDocument7 pagesPlaces To Stay Camino InglesAnitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 For StudentsDocument4 pagesChapter 3 For Studentsdesada testNo ratings yet
- Hotels in Laoag City Ilocos Norte With RoomratesDocument7 pagesHotels in Laoag City Ilocos Norte With RoomratesKHEVIN NACINONo ratings yet
- FARR CeramicsDocument17 pagesFARR CeramicsKawsurNo ratings yet
- NEFTE Compass November 25, 2009 IssueDocument12 pagesNEFTE Compass November 25, 2009 IssueCommittee for Russian Economic FreedomNo ratings yet
- APPLIED ECONOMICS-definition and Terms (Autosaved)Document31 pagesAPPLIED ECONOMICS-definition and Terms (Autosaved)Rhuzz Villanueva ZgirNo ratings yet
- Subject Expert Qa - 1 - (2015-16) Module - 2Document7 pagesSubject Expert Qa - 1 - (2015-16) Module - 2Keyur PopatNo ratings yet
- Micro Economics - PGDMDocument3 pagesMicro Economics - PGDMSAI CHARAN REDDY GALVANo ratings yet
- Classroom 1 BR Vs Other Europeans in IndiaDocument5 pagesClassroom 1 BR Vs Other Europeans in Indiasudip dasNo ratings yet
- For PSA - Export and Import - Revised - 052522Document4 pagesFor PSA - Export and Import - Revised - 052522Jacket TralalaNo ratings yet
- SalariesDocument8 pagesSalariespau mejaresNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Opman TQM: Chapter 1 - Operations and ProductivityDocument4 pagesModule 1 - Opman TQM: Chapter 1 - Operations and ProductivityApril GumiranNo ratings yet
- Prepaid Cards (VCC) @cashout - KingdomDocument3 pagesPrepaid Cards (VCC) @cashout - Kingdomradohi6352100% (1)
- Ge - CH 1Document25 pagesGe - CH 1Nur SyafawaniNo ratings yet
- DEED OF DONATION Brgy. San Juan BautistaDocument4 pagesDEED OF DONATION Brgy. San Juan BautistaAedrian MacawiliNo ratings yet
- Account Statement - 2022 10 01 - 2022 10 31 - en GB - Da9a44Document1 pageAccount Statement - 2022 10 01 - 2022 10 31 - en GB - Da9a44Alexandra ElenaNo ratings yet
- World Manufacturing Production 2021 Q2Document17 pagesWorld Manufacturing Production 2021 Q2Júlia BurnierNo ratings yet
- 02 - A Portfolio Restructuring DilemmaDocument10 pages02 - A Portfolio Restructuring DilemmaM45TANVI RANENo ratings yet
- Clay County Impact Fee Workshop - 11-28-22Document32 pagesClay County Impact Fee Workshop - 11-28-22JJNo ratings yet