Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MCQ Q.B Answers
Uploaded by
mahmoud.elshahawy3330 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views13 pagesOriginal Title
MCQ_Q.B_Answers
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views13 pagesMCQ Q.B Answers
Uploaded by
mahmoud.elshahawy333Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
Choose the best answer(s) [10 Points]
1. What is the oldest and most common type of artificial lift?
a) Gas Lift
b) Rod pumping
c) Plunger Lift
d) Hydraulic Pumping
2. Which is NOT an advantage of using rod pumping?
a) Surface unit may be changed to other wells with minimum cost
b) Can pump a well down to very low pressure
c) Capable of pumping depths to 17,000 ft and deeper
d) Gas or electricity can be used as power source
3. A continuous gas lift operation is
a) a steady-state flow of the aerated fluid from the bottom of the well to
the surface.
b) an unsteady-state flow of the aerated fluid from the bottom of the
well to the surface.
c) a semi steady state flow of the aerated fluid from the bottom of the
well to the surface.
d) Used for high PI wells
4. In continuous gas lift operations, for constant gas injection rate, as the
injection depth increases,
a) the production rate increases
b) the production rate decreases
c) the GLR increases
d) the density increases
5. PCPs are ----------------
a) positive displacement pumps
b) centrifugal pumps
c) electric pumps
d) hydraulic pumps
6. In 2007, there are over one million producing oil well, more than 50 % of them
are artificially lifted by
a) Gas lift
b) ESP
c) Sucker rod
d) Jet pumps
7. Which of the following pump is not applied in offshore operations
a) ESP
b) Sucker rod
c) Jet pumps
d) Hydraulic piston pump
8. The Class-I lever system which has its speed (gear) reducer rear-mounted
with the fulcrum at mid beam, represented by
a) the conventional unit
| Dr. Adel Salem: Final Exam _ Fall 2016 Page 1 of 13
b) the air balanced unit
c) Lufkin Mark II units
d) All above
9. The Class-II lever system, a push-up geometry with its speed reducer
frontmounted, represented by
a) the conventional unit
b) the air balanced unit
c) Lufkin Mark II units
d) Item b and c
10. the Reverse Mark Units of sucker rod geometry can reduce -------------
requirements on many pumping applications
a) the torque
b) power
c) the torque and power
d) flow rate
11. A Complete pump attached to, and inserted into, well tubing with sucker rod
string is a
a) Rod Insert Pump
b) Tubing pump
c) Casing pump
d) All above
12. The pump barrel is an integral part of the tubing string, means
a) Rod Insert Pump
b) Tubing pump
c) Casing pump
d) All above
13. For the following API Sub Surface Pump Designation “25-175-RHAM-16-4-
3”, the pump bore is
a) 25”
b) 175”
c) 1.75”
d) 16 ¾”
14. For the following API Sub Surface Pump Designation “25-175-RHAM-16-43”,
the pump type is
a) Rod Insert Pump
b) Tubing pump
c) Casing pump
d) All above
15. For the API Surface Pump Designation, “C-456D-256-144” the surface unit is
a) Class I Lever system
b) Unconventional type
c) Air balanced unit
d) Lufkin Mark II units
16. For the API Surface Pump Designation, “C-456D-256-144” the maximum
available stroke length is
| Dr. Adel Salem: Final Exam _ Fall 2016 Page 2 of 13
a) 456 in
b) 256 in
c) 144 in
d) 256-144 = 112 in
17. For the API Surface Pump Designation, “C-456D-256-144” the peak torque of
gear box is
a) 456 00 in-lbs
b) 456 000 in-lbs
c) 256 000 in-lbs
d) 256 00 in-lbs
18. The utilization of fiberglass reinforced plastic materials in rod manufacture
----------- total rod string weight, improves corrosion resistance.
a) decreases
b) increases
c) rises
d) elongates
19. The typical length of the steel rod is
a) 25 or 30 ft
b) 30 or 40 ft
c) 20 or 30 ft
d) All above are available
20. Which of the following is not a sucker rod pump problem?
a) Fluid pound
b) TV leakage
c) Gas cooling
d) SV leakage
21. Rod elongation is -------- tubing elongation in sucker rod pumps
a) Greater than
b) Less than
c) Equal the
d) ten times the
22. the accelerated load of the fiberglass reinforced plastic sucker rod is ---------
--- the dead weight
a) Less than
b) Equal the
c) Greater than
d) ten times the
23. ------ can produce up to 100,000 bpd as along as the reservoir capable to
deliver.
a) Sucker rod pump
b) ESP pump
c) Jet pump
d) Piston pump
24. In the typical ESP pump installation,
a) The pump is located above the electric motor
| Dr. Adel Salem: Final Exam _ Fall 2016 Page 3 of 13
b) The electric motor is installed above the pump
c) The pump intake is below the electric motor
d) The gas separator is installed below the motor
25. In ESP pump, each stage consists of ----------------
a) A double impeller and two diffusers
b) a rotating impeller and a stationary diffuser
c) a stationary impeller and a rotating diffuser
d) a set of impeller and diffuser
26. Each stage of a submergible pump handles -------------------of fluid in the
absence of free gas and produces a certain amount of head.
a) the same volume
b) different volume
c) various volume
d) all above
27. the major causes of ESP motor problems
a) drilling pipe stuck
b) overloading
c) depth problem
d) fluid pound
28. The ------------is normally a bolt-on section between the protector and the
pump where it serves as the pump intake.
a) gas separator
b) pump intake
c) ESP motor
d) Electric cable
29. In ESP pump, Advance Gas Handler (AGH) used to
a) Homogenize the mixture
b) Reduce bubble size
c) Put gas back into solution
d) All above
30. The proper cable size is governed by the
a) amperage, voltage drop and space available between the tubing
collar and casing.
b) Tuning size
c) Casing size
d) All above
31. The best power cable type is selected based on
a) the bottomhole temperature and fluids encountered.
b) The bottomhole pressure and fluid types
c) Reservoir depth and lithology
d) All above
32. The power cable is constructed in either --------- configuration.
a) square or round
b) round or flat
c) flat or rectangle
| Dr. Adel Salem: Final Exam _ Fall 2016 Page 4 of 13
d) all above
33. the conductor types of ESP power cable may be ---------
a) solid
b) compacted
c) stranded
d) all above
34. -------- is an operating control and protective device consisting of a motor
starter, overload and under load protection, manual disconnected switch
time delay.
a) Junction box
b) Switchboard
c) Power supply and transformer
d) Amp chart
35. The junction box should be located at least 15 feet (minimum) from the
-------------- and is normally mounted 2 to 3 ft above ground.
a) Power supply
b) Transformer
c) Wellhead
d) Amp chart
36. ESP is shrouded when
a) It is located below the perforation
b) It is located above the perforation
c) We want to use it for injection
d) We want to use for production
37. ESP pumps can be installed in
a) Horizontal wells
b) Vertical well
c) Cooked well
d) All above
38. ESP Ammeter is used to record the ----------------- of the motor.
a) input amperage
b) output amperage
c) input voltage
d) output voltage
39. the ESP problem in the next figure is called:
a) overload
b) underload
c) gas lock
d) spikes
40. the ESP problem in the next figure is called:
a) overload
b) underload
c) gas lock
| Dr. Adel Salem: Final Exam _ Fall 2016 Page 5 of 13
d) gassy well
41. which artificially lifting pump is reverse flow retrievable
a) sucker rod pump
b) ESP pump
c) Jet pump
d) Gear pump
42. Progressing cavity pumps, are called
a) screw pumps or Moineau pumps.
b) screw pumps or centrifugal pumps
c) hydraulic pumps
d) electric pump
43. --------- can achieve low bottom hole flowing pressure (BHFP)
a) Gas lift
b) Sucker rod pump
c) ESP pump
d) PCP pump
44. In electrical submersible cable, the conductor elements used are
a) copper and aluminum
b) Iron and aluminum
c) Steal and copper
d) Nickel and copper
45. In electrical submersible cable, the stranded conductor types are
a) Greater damage resistance
b) More conductor than other types
c) less advantages than the other types
d) made from fiberglass
46. The produced liquid from gas lift is
a) Increased by increasing injection depth
b) Increased by decreasing injection depth
c) Decreased by decreasing injection depth
47. The produced liquid from gas lift is
a) Increased with increasing gas injection rate
b) decreased with increasing gas injection rate
c) Increased with increasing gas injection rate to certain extent
48. In gas lift operations, all valves are
a) Always opened entering the gas inside the tubing in continuous gas
lift
b) Opened entering the gas inside the tubing only at the beginning
c) Opening and closing alternatively,
49. A continuous gas lift operation is
a) a steady-state flow of the aerated fluid from the bottom (or near
bottom) of the well to the surface.
b) unsteady state flow.
c) Laminar flow regime
50. Intermittent gas lift operation is
| Dr. Adel Salem: Final Exam _ Fall 2016 Page 6 of 13
a) characterized by a start-and-stop flow from the bottom (or near
bottom) of the well to the surface.
b) unsteady state flow.
c) Turbulent flow regime
51. Production Pressure Operated Valves (PPO) is suitable for:
a) Deeper injection points
b) Shallow injection points
c) Ultra-deep wells
52. Injection Pressure Operated Valves (IPO) is suitable for:
a) High rate applications
b) Low rate applications
c) Lifting a heavy crude oil
53. Gas lift valve spacing is
a) Decreasing with depth
b) Increasing with depth
c) Equal
54. kick-off pressure (Pko) is
a) equal to operating casing pressure (Pso)
b) greater than operating casing pressure (Pso)
c) less than operating casing pressure (Pso)
55. Upon entering the tubing, the compressed gas affects liquid flow in a way:
a) the energy of expansion propels (pushes) the oil to the surface.
b) the gas aerates the oil so that the effective density of the fluid is less.
c) The hydrostatic head will be greater than the reservoir pressure
56. One of the functions of the Junction box is to
a) Provide a vent to the atmosphere of any gas that may migrate up the
power cable from the well.
b) Cool the ESP motor
c) Protect the motor from the underload and overload
d) Change the primary incoming voltage
57. Which of the following pump is not applied in offshore operations
a) ESP
b) Sucker rod
c) Jet pumps
d) Hydraulic piston pump
58. The Class-I lever system which has its speed (gear) reducer rear-mounted
with the fulcrum at mid beam, represented by
a) the conventional unit
b) the air balanced unit
c) Lufkin Mark II units
d) All above
59. The Class-II lever system, a push-up geometry with its speed reducer
frontmounted, represented by
a) the conventional unit
b) the air balanced unit
| Dr. Adel Salem: Final Exam _ Fall 2016 Page 7 of 13
c) Lufkin Mark II units
d) Item b and c
60. The Reverse Mark Units of sucker rod geometry can reduce -------------
requirements on many pumping applications
a) the torque
b) power
c) the torque and power
d) flow rate
61. A Complete pump attached to, and inserted into, well tubing with sucker rod
string is a
a) Rod Insert Pump
b) Tubing pump
c) Casing pump
d) All above
62. The pump barrel is an integral part of the tubing string, means
a) Rod Insert Pump
b) Tubing pump
c) Casing pump
d) All above
63. For the following API Sub Surface Pump Designation “25-175-RHAM-16-43”,
the pump bore is
a) 25”
b) 175”
c) 1.75”
d) 16 ¾”
64. For the following API Sub Surface Pump Designation “25-175-RHAM-16-43”,
the pump type is
a) Rod Insert Pump
b) Tubing pump
c) Casing pump
d) All above
65. For the API Surface Pump Designation, “C-456D-256-144” the surface unit is
a) Class I Lever system
b) Unconventional type
c) Air balanced unit
d) Lufkin Mark II units
66. For the API Surface Pump Designation, “C-456D-256-144” the maximum
available stroke length is
a) 456 in
b) 256 in
c) 144 in
d) 256-144 = 112 in
67. For the API Surface Pump Designation, “C-456D-256-144” the peak torque of
gear box is
a) 456 00 in-lbs
| Dr. Adel Salem: Final Exam _ Fall 2016 Page 8 of 13
b) 456 000 in-lbs
c) 256 000 in-lbs
d) 256 00 in-lbs
68. The utilization of fiberglass reinforced plastic materials in rod manufacture
----------- total rod string weight, improves corrosion resistance.
a) decreases
b) increases
c) rises
d) elongates
69. The typical length of the steel rod is
a) 25 or 30 ft
b) 30 or 40 ft
c) 20 or 30 ft
d) All above are available
70. Which of the following is not a sucker rod pump problem?
a) Fluid pound
b) TV leakage
c) Gas cooling
d) SV leakage
71. Rod elongation is -------- tubing elongation in sucker rod pumps
a) Greater than
b) Less than
c) Equal the
d) ten times the
72. The accelerated load of the fiberglass reinforced plastic sucker rod is --------
---- the dead weight
a) Less than
b) Equal the
c) Greater than
d) ten times the
73. ------ can produce up to 100,000 bpd as along as the reservoir capable to
deliver.
a) Sucker rod pump
b) ESP pump
c) Jet pump
d) Piston pump
74. In the typical ESP pump installation,
a) The pump is located above the electric motor
b) The electric motor is installed above the pump
c) The pump intake is below the electric motor
d) The gas separator is installed below the motor
75. In ESP pump, each stage consists of ----------------
a) A double impeller and two diffusers
b) a rotating impeller and a stationary diffuser
c) a stationary impeller and a rotating diffuser
| Dr. Adel Salem: Final Exam _ Fall 2016 Page 9 of 13
d) a set of impeller and diffuser
76. Each stage of a submergible pump handles -------------------of fluid in the
absence of free gas and produces a certain amount of head.
a) the same volume
b) different volume
c) various volume
d) all above
77. The major causes of ESP motor problems
a) drilling pipe stuck
b) overloading
c) depth problem
d) fluid pound
78. The ------------is normally a bolt-on section between the protector and the
pump where it serves as the pump intake.
a) gas separator
b) pump intake
c) ESP motor
d) Electric cable
79. In ESP pump, Advance Gas Handler (AGH) used to
a) Homogenize the mixture
b) Reduce bubble size
c) Put gas back into solution
d) All above
80. The proper cable size is governed by the
a) amperage, voltage drop and space available between the tubing
collar and casing.
b) Tuning size
c) Casing size
d) All above
81. The best power cable type is selected based on
a) the bottomhole temperature and fluids encountered.
b) The bottomhole pressure and fluid types
c) Reservoir depth and lithology
d) All above
82. The power cable is constructed in either --------- configuration.
a) square or round
b) round or flat
c) flat or rectangle
d) all above
83. the conductor types of ESP power cable may be ---------
a) solid
b) compacted
c) stranded
| Dr. Adel Salem: Final Exam _ Fall 2016 Page 10 of 13
d) all above
84. -------- is an operating control and protective device consisting of a motor
starter, overload and under load protection, manual disconnected switch
time delay.
a) Junction box
b) Switchboard
c) Power supply and transformer
d) Amp chart
85. The junction box should be located at least 15 feet (minimum) from the
-------------- and is normally mounted 2 to 3 ft above ground.
a) Power supply
b) Transformer
c) Wellhead
d) Amp chart
86. ESP is shrouded when
a) It is located below the perforation
b) It is located above the perforation
c) We want to use it for injection
d) We want to use for production
87. ESP pumps can be installed in
a) Horizontal wells
b) Vertical well
c) Cooked well
d) All above
88. ESP Ammeter is used to record the ----------------- of the motor.
a) input amperage
b) output amperage
c) input voltage
d) output voltage
89. The ESP problem in the next figure is called:
a) overload
b) underload
c) Pump Off with Gas Interference
d) Pump Off with False Restarts
90. This Amp Chart in the next figure shows high
current after startup which eventually drops down to
a "normal" value, this is due to
a) Unloading light fluid
b) Unloading heavy fluid
c) gas lock
d) gassy well
| Dr. Adel Salem: Final Exam _ Fall 2016 Page 11 of 13
91. Which artificially lifting pump is reverse flow retrievable
a) Sucker rod pump
b) ESP pump
c) Jet pump
d) PCP pump
92. Which of the following pumps does not have moving parts?
a) Sucker rod pump
b) ESP pump
c) Jet pump
d) PCP pump
93. --------- can achieve low bottom hole flowing pressure (BHFP)
a) Gas lift
b) Sucker rod pump
c) ESP pump
d) PCP pump
94. Cavitation is a common problem in this pump
a) Sucker rod pump
b) ESP pump
c) Jet pump
d) PCP pump
95. --------- is usually double-acting pump, that is, fluid is being displaced from
the pump on both the upstroke and the downstroke
a) Gas lift
b) Sucker rod pump
c) ESP pump
d) HPP pump
96.
True or False
1. ESP pumps offer the advantage of having no moving parts, so dirty or
gassy fluids can be produced without the wear.
a. True
b. False
2. Water in a lift gas system may lead to problems with corrosion, liquid
slugging and hydrates.
a. True
b. False
3. In a continuous gas lift operation, the test rack pressure has to equal the
flowing bottom hole pressure
a. True
b. False
| Dr. Adel Salem: Final Exam _ Fall 2016 Page 12 of 13
4. Jet pump cannot be maintained by wireline operations
a. True
b. False
5. Gas lift can be maintained by wireline operations
a. True
b. False
6. In gas lift operations, the dome pressure must equal the maximum injection
pressure
a. True
b. False
7. Sucker rod pumps cannot be used for offshore operations
a. True
b. False
8. ESP pumps cannot be used for offshore operations
a. True
b. False
9. It is preferable to deepen the sucker rod pump to maximize the production
rate
a. True
b. False
10. Gas lift system can handle sand production relative to ESP pump
a. True
b. False
11. Plunger lift systems are expensive installations (false)
12. Water in a lift gas system may lead to problems with corrosion, liquid
slugging and hydrates (true)
13. In a continuous gas lift operation, the test rack pressure has to equal the
flowing bottom hole pressure (false)
14. Progressive cavity pumping systems can be used for lifting heavy oils at a
variable flow rate (true)
15. Gas lift can be maintained by wireline operations (true)
16. In gas lift operations, the dome pressure must equal the maximum injection
pressure (false)
17. Sucker rod pumps are preferable in deviated wells (false)
18. The liquid production rate is proportional to the power fluid injection rate in
Hydraulic Piston Pump (true)
19. Plunger Lift System operation consists of shut-in and flow periods (true)
20. The PCESP share the same electric motor, seal, cable and control
technology as the conventional ESP (true)
| Dr. Adel Salem: Final Exam _ Fall 2016 Page 13 of 13
You might also like
- Electricity Distribution Losses Reduced by Raising VoltageDocument164 pagesElectricity Distribution Losses Reduced by Raising Voltagearvidkumar87060100% (1)
- Draft Question Bank Module-3Document164 pagesDraft Question Bank Module-3pallavishraddhaNo ratings yet
- QUIZ_ECM_3ME41Document2 pagesQUIZ_ECM_3ME41MikNo ratings yet
- Set 15Document13 pagesSet 15rashmiameNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For Job Linked Test: Discipline: ElectricalDocument13 pagesQuestion Bank For Job Linked Test: Discipline: Electricalsiddudotcom@rediffmail.com100% (1)
- 100 New Questions General September 2014 Kolkata 1Document10 pages100 New Questions General September 2014 Kolkata 1Sahil MishraNo ratings yet
- Executive - Boiler MTCDocument4 pagesExecutive - Boiler MTCrameshNo ratings yet
- 2 National Certification Examination 2005 FOR: Energy Managers and Energy Auditors Model Test Series - ADocument8 pages2 National Certification Examination 2005 FOR: Energy Managers and Energy Auditors Model Test Series - Azoom2No ratings yet
- ES-EE401 - Questions With Answers PDFDocument11 pagesES-EE401 - Questions With Answers PDFSanjoy PathakNo ratings yet
- October Session 2005Document8 pagesOctober Session 2005Pritamjit RoutNo ratings yet
- October Session 2005Document8 pagesOctober Session 2005Pritamjit RoutNo ratings yet
- Jet Engine DGCA QuestionsDocument6 pagesJet Engine DGCA QuestionspankajmankotiaNo ratings yet
- Jet Engine Question Bank For DGCADocument101 pagesJet Engine Question Bank For DGCAGaurav Sharma0% (1)
- MCQ Question Bank - PE-ME 801B - Part IDocument8 pagesMCQ Question Bank - PE-ME 801B - Part IBibekNo ratings yet
- General September 2014 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument10 pagesGeneral September 2014 Multiple Choice QuestionsStabin Mathew100% (1)
- Jap-Motor General v1Document52 pagesJap-Motor General v1Pankaj Poonia100% (1)
- Jet EngineDocument83 pagesJet Enginedrsuyogm100% (1)
- Quizz 1Document8 pagesQuizz 1ali HatemNo ratings yet
- Cessna 172Document13 pagesCessna 172Daksh SinghNo ratings yet
- Well Iadc 27Document4 pagesWell Iadc 27cyrel carl moloNo ratings yet
- Jet - Engine DGCA QuestionsDocument6 pagesJet - Engine DGCA Questionsstuartb4uNo ratings yet
- EAs 3 BDocument12 pagesEAs 3 BNeeraj Singh GautamNo ratings yet
- M11 XLDocument50 pagesM11 XLTharrmaselan manimaranNo ratings yet
- Examen Final ACBS CGA Sys AlumnoDocument15 pagesExamen Final ACBS CGA Sys AlumnoDanny_P123No ratings yet
- Energy Adulator Exam PaperDocument17 pagesEnergy Adulator Exam PaperravandkumarNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument12 pagesQuestionskushal thapaNo ratings yet
- Sem II 2016 Plumber TheoryDocument5 pagesSem II 2016 Plumber TheoryVijay100% (1)
- Atg PPL Revision CatDocument8 pagesAtg PPL Revision Catstan_gatei100% (1)
- EAs 3 ADocument13 pagesEAs 3 ANeeraj Singh GautamNo ratings yet
- 2015 Gas Turbines Final QuestionsDocument14 pages2015 Gas Turbines Final QuestionsEnaj Olea Buenviber100% (1)
- 10 - NG L Zce22Document43 pages10 - NG L Zce22canberkNo ratings yet
- Jet Engine 2 of 2020 With RefDocument22 pagesJet Engine 2 of 2020 With RefPartha Sarathi DattaNo ratings yet
- Utilities Sample QuestionDocument26 pagesUtilities Sample QuestionNel Colene Borja CaminianNo ratings yet
- EA3ADocument7 pagesEA3AMayukh DebdasNo ratings yet
- Technical General Question Bank For Dgca Prep PPL CPLDocument39 pagesTechnical General Question Bank For Dgca Prep PPL CPLprachat100% (1)
- Aircraft Paper Exam QuestionsDocument11 pagesAircraft Paper Exam QuestionsGanesh SivasankaranNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Hydraulic Machines MCQDocument10 pagesMechanical Engineering Hydraulic Machines MCQJunaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficiency Solutions for Electrical UtilitiesDocument8 pagesEnergy Efficiency Solutions for Electrical UtilitiesBrahmananda TaraiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Utilities Energy EfficiencyDocument18 pagesElectrical Utilities Energy EfficiencycynaiduNo ratings yet
- One Mark Paper 3Document32 pagesOne Mark Paper 3YogaAnandNo ratings yet
- Ame Ha Exam Dgca Part 1Document15 pagesAme Ha Exam Dgca Part 1prsnjt11No ratings yet
- Improve Electrical Utility Efficiency Exam SolutionsDocument23 pagesImprove Electrical Utility Efficiency Exam SolutionsnipunawijesekaraNo ratings yet
- National Certification Exam 2007 Paper 3 SolutionDocument16 pagesNational Certification Exam 2007 Paper 3 SolutioncynaiduNo ratings yet
- SUP3SetA PDFDocument16 pagesSUP3SetA PDFcynaiduNo ratings yet
- 735'lik PDF Testi Benim ÇalışmammmDocument250 pages735'lik PDF Testi Benim ÇalışmammmBurak GökbudakNo ratings yet
- Deaerator Post MCQ'sDocument50 pagesDeaerator Post MCQ'sEhtisham ul haqNo ratings yet
- DGCA AME Paper 2 June 2013Document10 pagesDGCA AME Paper 2 June 2013Melwin Saji0% (1)
- Turbomachinery Exit Exam TutorialsDocument22 pagesTurbomachinery Exit Exam TutorialsteddiyfentawNo ratings yet
- National Certification Examination 2005 FOR Energy Managers & Energy AuditorsDocument17 pagesNational Certification Examination 2005 FOR Energy Managers & Energy AuditorsErin WardNo ratings yet
- Question Bank On PPF ModuleDocument7 pagesQuestion Bank On PPF ModuleMY NAME IS NEERAJ..:):)No ratings yet
- Radharaman Institute of Technology & Science (RITS) Gate-2018Document18 pagesRadharaman Institute of Technology & Science (RITS) Gate-2018paragmishra1986No ratings yet
- WAPDADocument8 pagesWAPDASibghatullah SiyalNo ratings yet
- Khaire Sir Classes: All Imp Question of Unit 2 Sub: EtmDocument6 pagesKhaire Sir Classes: All Imp Question of Unit 2 Sub: EtmAkshay KhangreNo ratings yet
- PPL Exam Secrets Guide: Aircraft General & Principles of FlightFrom EverandPPL Exam Secrets Guide: Aircraft General & Principles of FlightRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsFrom EverandPipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Survey&mwd& LWD-2Document75 pagesSurvey&mwd& LWD-2mahmoud.elshahawy333No ratings yet
- Exploration and Production DepartmentDocument26 pagesExploration and Production Departmentmahmoud.elshahawy333No ratings yet
- Exploration and Production DepartmentDocument26 pagesExploration and Production Departmentmahmoud.elshahawy333No ratings yet
- Exploration and Production DepartmentDocument26 pagesExploration and Production Departmentmahmoud.elshahawy333No ratings yet
- The Standard ModelDocument15 pagesThe Standard ModelAditya GuptaNo ratings yet
- NanoCeram Presentation ArgonideDocument34 pagesNanoCeram Presentation ArgonideEnzo PracucciNo ratings yet
- 3 Cleaning Wet EtchDocument34 pages3 Cleaning Wet EtchPieter RobaeysNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and of The Company/UndertakingDocument3 pagesSafety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and of The Company/UndertakinghelveciotfNo ratings yet
- Determining Relative Spectral Correction Factors For Emission Signal of Fluorescence SpectrometersDocument5 pagesDetermining Relative Spectral Correction Factors For Emission Signal of Fluorescence Spectrometersmohammed karasnehNo ratings yet
- Darcy-Weisbach Equation PDFDocument5 pagesDarcy-Weisbach Equation PDFMihir Soni80% (10)
- SusicDocument19 pagesSusicALVARO DIEGO MACHACA CONDORINo ratings yet
- Pollution: Causes, Effects and SolutionsDocument16 pagesPollution: Causes, Effects and SolutionsVibNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Waste Water 1Document10 pagesLab Report Waste Water 1eidalinNo ratings yet
- Colville 1970Document5 pagesColville 1970Jorge Álef Estevam Lau BomfimNo ratings yet
- GEA Spray Drying: Small-Scale Solutions For R&D and ProductionDocument20 pagesGEA Spray Drying: Small-Scale Solutions For R&D and ProductionPatricio ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Iec41 PDFDocument211 pagesIec41 PDFSwatiSawalkar100% (1)
- LX-111 Color Mark SensorDocument2 pagesLX-111 Color Mark SensorGopinath KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project 1Document13 pagesChemistry Project 1novemberNo ratings yet
- Statistical Physics PDFDocument36 pagesStatistical Physics PDFdayannaNo ratings yet
- Physics 12 Formula SheetDocument3 pagesPhysics 12 Formula SheetJacob TamashiroNo ratings yet
- First Exam - Physics 101Document2 pagesFirst Exam - Physics 101ahmadNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Polymers ATR FTIR AN PDFDocument3 pagesAnalysis of Polymers ATR FTIR AN PDFHasan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Exhaust Gas Silencer Data SheetDocument4 pagesExhaust Gas Silencer Data Sheetabuya3kubmNo ratings yet
- Zanuri 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 414 012032Document6 pagesZanuri 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 414 012032Amir HafiyNo ratings yet
- Stability - Sample of ParacetamolDocument10 pagesStability - Sample of ParacetamolLibyan Uprising WarNo ratings yet
- Oseointegracion 2019Document4 pagesOseointegracion 2019Javier Figueroa FuentesNo ratings yet
- J Fail. Anal. and Preven. research oxide layer growth T92 steel superheaterDocument7 pagesJ Fail. Anal. and Preven. research oxide layer growth T92 steel superheaterYogesh DewangNo ratings yet
- Procedures and Observations For Chemical and Physical Changes LabDocument6 pagesProcedures and Observations For Chemical and Physical Changes LabkmwawersNo ratings yet
- Rate Expression and Activation Energy: 1a. (1 Mark)Document7 pagesRate Expression and Activation Energy: 1a. (1 Mark)senna0% (1)
- Drainage Basin Morphometric Parameters of River Lamurde - Implication For Hydrologic and Geomorphic ProcessesDocument11 pagesDrainage Basin Morphometric Parameters of River Lamurde - Implication For Hydrologic and Geomorphic ProcessesPatrick Joseph RoblesNo ratings yet
- H2 Dai RifiutiDocument258 pagesH2 Dai RifiutiMariaIlariaNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature Dinesh QuestionsDocument3 pagesDual Nature Dinesh QuestionsPankaj MishraNo ratings yet
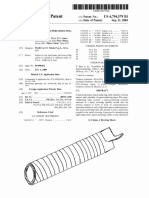
- High Temperature Superconducting Cable US6794579Document10 pagesHigh Temperature Superconducting Cable US6794579Leon MutambalaNo ratings yet
- Media OptimisationDocument90 pagesMedia OptimisationMohanan C VarshaNo ratings yet