Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nouveau Document Texte
Uploaded by
zrhoudzakaria04Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nouveau Document Texte
Uploaded by
zrhoudzakaria04Copyright:
Available Formats
Morocco, officially known as the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country located in North
Africa. Its history is rich and diverse, spanning thousands of years and
encompassing various civilizations, conquests, and cultural influences. Here is a
brief overview of the history of Morocco:
Ancient History:
The region of present-day Morocco has been inhabited since prehistoric times, with
evidence of human presence dating back to the Paleolithic era. The area was
subsequently inhabited by various Berber tribes, who established several kingdoms
and city-states.
Phoenician and Carthaginian Influence:
Around the 12th century BCE, Phoenician traders established colonies along the
Moroccan coast, introducing elements of their culture and establishing commercial
links with the indigenous Berber populations. Later, Carthaginians, who were an
offshoot of the Phoenician civilization, also exerted their influence in the
region.
Roman Period:
In the 2nd century BCE, the Roman Empire expanded into North Africa, including
present-day Morocco. The region became part of the Roman province of Mauretania
Tingitana and experienced significant urbanization and Romanization. Some notable
Roman sites, such as Volubilis, bear witness to this period.
Islamic Conquest:
In the 7th century CE, Arab armies swept across North Africa, bringing Islam to the
region. Morocco was initially under the Umayyad Caliphate and later came under the
control of various Muslim dynasties, including the Almoravids, Almohads, and
Marinids. These dynasties played a crucial role in shaping Morocco's cultural and
architectural heritage.
European Influence:
During the 15th century, European powers, particularly Portugal and Spain, sought
to establish trade routes and colonies in Morocco. Portuguese traders and explorers
reached Moroccan shores, and Spain established enclaves in the northern part of the
country, including Melilla and Ceuta.
Saadian and Alaouite Dynasties:
The Saadian dynasty emerged in the 16th century and managed to unite much of
Morocco under their rule. They established Marrakesh as their capital and oversaw a
period of relative stability and prosperity. However, their rule eventually
declined, and in the 17th century, the Alaouite dynasty came to power. The
Alaouites continue to rule Morocco today, making it one of the world's oldest
surviving monarchies.
French and Spanish Protectorates:
In the late 19th century, Morocco became the subject of rivalry between European
powers. In 1912, France and Spain established protectorates over Morocco, dividing
the country into different zones of influence. The French protectorate was more
extensive and lasted until 1956 when Morocco regained its independence.
Independence and Modern Era:
Morocco gained independence from France in 1956 under the leadership of King
Mohammed V. His son, King Hassan II, succeeded him and ruled for several decades.
During his reign, Morocco faced political challenges, including territorial
disputes and social unrest. King Mohammed VI ascended to the throne in 1999 and
initiated a series of reforms aimed at modernization, political liberalization, and
economic development.
Today, Morocco is a constitutional monarchy with a diverse cultural heritage,
blending Arab, Berber, and European influences. It is known for its vibrant cities,
historic medinas, stunning landscapes, and rich traditions.
Please note that this is a brief summary of Morocco's history, and there are many
more details and events that have shaped the country over the centuries.
You might also like
- Library of Congress - Federal Research Division Country Profile: Morocco, May 2006Document20 pagesLibrary of Congress - Federal Research Division Country Profile: Morocco, May 2006IMAR100% (1)
- History PartDocument6 pagesHistory PartAmine BouattiouiNo ratings yet
- International Business PartDocument2 pagesInternational Business Partaiyenpiqa88No ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument1 pageExecutive SummarySteven ShearingNo ratings yet
- SurfaceDocument1 pageSurfaceBlender CreationNo ratings yet
- MoroccoDocument12 pagesMoroccoEssihi Dhj100% (1)
- "the French Colonization of Morocco/"Document8 pages"the French Colonization of Morocco/"Kelsey Rose Weber100% (3)
- Moroccan Foreign Policy in Sub Saharan ADocument24 pagesMoroccan Foreign Policy in Sub Saharan AAdie Nugraha NatanegaraNo ratings yet
- A Beautiful White Cat Walks with Me: A NovelFrom EverandA Beautiful White Cat Walks with Me: A NovelRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- The Renaissance: A Captivating Guide to a Remarkable Period in European History, Including Stories of People Such as Galileo Galilei, Michelangelo, Copernicus, Shakespeare, and Leonardo da VinciFrom EverandThe Renaissance: A Captivating Guide to a Remarkable Period in European History, Including Stories of People Such as Galileo Galilei, Michelangelo, Copernicus, Shakespeare, and Leonardo da VinciNo ratings yet
- Colonization of MoroccoDocument18 pagesColonization of MoroccoGaren50% (2)
- History of MauritaniaDocument7 pagesHistory of MauritaniaafifatoniNo ratings yet
- The British Empire and The Muslim WorldDocument32 pagesThe British Empire and The Muslim WorldRajendraNo ratings yet
- Eudo C O: Itizenship BservatoryDocument27 pagesEudo C O: Itizenship BservatoryismailrachidiNo ratings yet
- Input 1 Historical Situationer On Mindanao 2016Document7 pagesInput 1 Historical Situationer On Mindanao 2016wilson siyNo ratings yet
- SL00 - History of MoroccoDocument20 pagesSL00 - History of MoroccoKarim CK100% (1)
- The History of Romania Is Rich and Spans Thousands of YearsDocument2 pagesThe History of Romania Is Rich and Spans Thousands of YearsLAM ENG HO G11L-14No ratings yet
- Western Sahara - HistoryDocument3 pagesWestern Sahara - HistoryRodrick JohnsonNo ratings yet
- R 4Document2 pagesR 4AlexandruNo ratings yet
- MANSA MUSA: Emperor of The Wealthy Mali EmpireFrom EverandMANSA MUSA: Emperor of The Wealthy Mali EmpireRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- History of SpainDocument2 pagesHistory of SpainAymanHQNo ratings yet
- Subject Section Task Title WordingDocument8 pagesSubject Section Task Title WordingAmanda GyarmatiNo ratings yet
- The History of Northern AfricaDocument196 pagesThe History of Northern AfricaCosmin_Isv75% (4)
- Historical Globalization Imperialism ProjectDocument4 pagesHistorical Globalization Imperialism ProjectnardeenftslmNo ratings yet
- Moustala7at Jihawi 2018Document3 pagesMoustala7at Jihawi 2018Chadidi33No ratings yet
- Spain HistoryDocument2 pagesSpain Historyqaiserfiaz11No ratings yet
- Capital and Largest City (2011 Est.)Document2 pagesCapital and Largest City (2011 Est.)Jahzeel Y. NolascoNo ratings yet
- Portugal HistoryDocument1 pagePortugal Historymobimirxa2No ratings yet
- Spain HistoryDocument1 pageSpain Historymobimirxa2No ratings yet
- Spanish EmpireDocument4 pagesSpanish EmpireRobin TimkangNo ratings yet
- The French Revolution: A Captivating Guide to the Ten-Year Revolution in France and the Impact Made by Napoleon BonaparteFrom EverandThe French Revolution: A Captivating Guide to the Ten-Year Revolution in France and the Impact Made by Napoleon BonaparteNo ratings yet
- HistoryDocument8 pagesHistoryAna LuNo ratings yet
- SpeakingDocument1 pageSpeakingasiergallego2008No ratings yet
- Summary Of "1945-1995 The Decolonization Of The World" By García De Cortázar & Lorenzo Espinosa: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESFrom EverandSummary Of "1945-1995 The Decolonization Of The World" By García De Cortázar & Lorenzo Espinosa: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- Living Tangier: Migration, Race, and Illegality in a Moroccan CityFrom EverandLiving Tangier: Migration, Race, and Illegality in a Moroccan CityNo ratings yet
- HISTORY 8 - Changes in Africa and Asia, The Building of The Western Global Colonial Empire in The Late 19th CenturyDocument26 pagesHISTORY 8 - Changes in Africa and Asia, The Building of The Western Global Colonial Empire in The Late 19th Centuryrajeev_khanna_15No ratings yet
- Culture Briefing: Morocco- Your Guide to Moroccan Culture and CustomsFrom EverandCulture Briefing: Morocco- Your Guide to Moroccan Culture and CustomsNo ratings yet
- Simion Claudia - English ProjectDocument15 pagesSimion Claudia - English ProjectMiscoci ClaudiaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide to The Prince and Other Works by Niccolò MachiavelliFrom EverandStudy Guide to The Prince and Other Works by Niccolò MachiavelliNo ratings yet
- The Modern Middle East by James L GalvinDocument10 pagesThe Modern Middle East by James L GalvinLea CelinNo ratings yet
- History of MauritaniaDocument2 pagesHistory of MauritaniaAbass Med FadelNo ratings yet
- MYP3 GH U1 NotesDocument7 pagesMYP3 GH U1 NotestufygiuohiNo ratings yet
- Mali Ka Fasojamana, Renndaandi MaaliDocument4 pagesMali Ka Fasojamana, Renndaandi MaaliOana CrețuNo ratings yet
- Making Morocco: Colonial Intervention and the Politics of IdentityFrom EverandMaking Morocco: Colonial Intervention and the Politics of IdentityNo ratings yet
- France. FinalDocument112 pagesFrance. FinalgelNo ratings yet
- The Great African KingdomsDocument4 pagesThe Great African KingdomsMuhammad Bilal AfzalNo ratings yet
- Mozambican War of IndependenceDocument18 pagesMozambican War of IndependenceXINKIANGNo ratings yet
- Resilience of A City at War: Territoriality, Civil Order and Economic Exchange in MogadishuDocument2 pagesResilience of A City at War: Territoriality, Civil Order and Economic Exchange in Mogadishumohamedr55104No ratings yet
- The Modern EraDocument2 pagesThe Modern EramarialopezcabreraNo ratings yet
- History of SpainDocument9 pagesHistory of SpainAlain DaccacheNo ratings yet
- History of SpainDocument1 pageHistory of Spainurban egoNo ratings yet
- Duas For WishesDocument5 pagesDuas For Wishes12MOHAMMED92% (49)
- The Awaited Imam MahdiDocument334 pagesThe Awaited Imam MahdiSyed Abidi0% (1)
- Chapter 8 OutlineDocument3 pagesChapter 8 OutlineFerrari82% (11)
- Absen Awal Sharing MotivationDocument33 pagesAbsen Awal Sharing Motivationedwina retha maharaniNo ratings yet
- Muslim Conquests of The Indian SubcontinentDocument21 pagesMuslim Conquests of The Indian Subcontinentsingh1910511753100% (1)
- Jadwal Pengurusan SKCK Bagi Calon PPPK Guru Formasi Tahun 2022 Di Polres JemberDocument31 pagesJadwal Pengurusan SKCK Bagi Calon PPPK Guru Formasi Tahun 2022 Di Polres JemberVahmiNo ratings yet
- SURAT ALfilDocument13 pagesSURAT ALfillpk BNHNo ratings yet
- Texto Sobre A Fala Inspirada de Um Sheikh NaqshbandiDocument2 pagesTexto Sobre A Fala Inspirada de Um Sheikh NaqshbandiRodrigo BittencourtNo ratings yet
- (TG3) (Responses)Document17 pages(TG3) (Responses)asimNo ratings yet
- Template Nilai Harian-XII - AGAMA.I-Bahasa IndonesiaDocument90 pagesTemplate Nilai Harian-XII - AGAMA.I-Bahasa IndonesiaAnang Danik AlsyahNo ratings yet
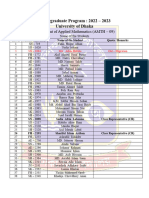
- All Students Name With Roll and Merit Position (AMTH-09, Dhaka University)Document2 pagesAll Students Name With Roll and Merit Position (AMTH-09, Dhaka University)Eagle SubbirNo ratings yet
- Unit 4. Islam and Al-AndalusDocument13 pagesUnit 4. Islam and Al-AndalusmariacaballerocobosNo ratings yet
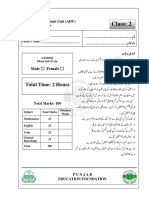
- Class: 2: Total Time: 2 HoursDocument12 pagesClass: 2: Total Time: 2 HoursZuniButtNo ratings yet
- Jadwal PasDocument2 pagesJadwal PasMoh Safii hidayatNo ratings yet
- Rekap SF Periode 1 S/D 22 Juni 2020 Update Jam: 10.00: NO SF SSL NO SFDocument1,044 pagesRekap SF Periode 1 S/D 22 Juni 2020 Update Jam: 10.00: NO SF SSL NO SFaudy alfathan nisaNo ratings yet
- Arihant Pathfinder Nda Na WWW - Examsakha.in A883b5ec 1081 1084Document4 pagesArihant Pathfinder Nda Na WWW - Examsakha.in A883b5ec 1081 1084yashgalgat319No ratings yet
- Nilai Pai & B.arabDocument10 pagesNilai Pai & B.arabtutyeNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Divine Love According ToDocument6 pagesThe Concept of Divine Love According ToAbdur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Compiled Participants List of ToTDocument7 pagesCompiled Participants List of ToTAsiful HasanNo ratings yet
- Sunnat-ul-Qawliyyah: This Sunnah Is The Sayings of The Holy: SignificanceDocument8 pagesSunnat-ul-Qawliyyah: This Sunnah Is The Sayings of The Holy: SignificancealiaNo ratings yet
- How To Send Salawat On Prophet - When To Send Sal PDFDocument6 pagesHow To Send Salawat On Prophet - When To Send Sal PDFImanhanna Goling100% (1)
- Bimbingan PA Genap 2022-2023Document7 pagesBimbingan PA Genap 2022-2023Fachry maulanaNo ratings yet
- Doa Habis SolatDocument2 pagesDoa Habis SolatSusi LestariNo ratings yet
- The Rulings of Menstruation and Postpartum Bleeding 1Document100 pagesThe Rulings of Menstruation and Postpartum Bleeding 1toothfairynansNo ratings yet
- Jadwal Salat Nov 23Document6 pagesJadwal Salat Nov 23beebbob30No ratings yet
- U21 To L21 Tracker Final Account Till 17 JunDocument71 pagesU21 To L21 Tracker Final Account Till 17 JunRatul MollickNo ratings yet
- Abs Dates TestDocument88 pagesAbs Dates TestKhuram IqbalNo ratings yet
- Pernikahan Di Bawah Umur Perspektif Maqashid Al-QuDocument34 pagesPernikahan Di Bawah Umur Perspektif Maqashid Al-QuSuci HelibNo ratings yet
- Protecting and Cleaning The House From Magic and JinnDocument5 pagesProtecting and Cleaning The House From Magic and JinnMohammed Ghouse0% (1)
- 4 EEE 17203021 Shah Md. Abdullahil KabirDocument4 pages4 EEE 17203021 Shah Md. Abdullahil Kabirআমানুর আকাশNo ratings yet