Professional Documents
Culture Documents
84 PDFsam Al Manu
Uploaded by
fordownload useOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
84 PDFsam Al Manu
Uploaded by
fordownload useCopyright:
Available Formats
.
.
.
.
.
.
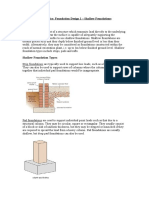
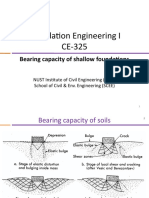
8.3 SHALLOW FOOTING ANALYSES
. Shallow foundations are designed to transfer
. vertical load to soils at relatively shallow depths.
. Typical shallow foundations include spread
footings, strip footings, and mats. The bearing
capacity of shallow foundations is influenced by
a number of factors, which will be covered in the
next section. Shallow foundations are often
subject to lateral loading or eccentricity. The
stability of shallow foundations against
eccentricity is controlled primarily by the ability
to withstand overturning. AllPile uses procedures
and recommendations given in Principles of
Foundation Engineering, Brooks/Cole
Engineering Division, Braja M. Das., 1984, as the
primary references for shallow foundation
analyses.
Figure 8-13. Shallow Footing
8.3.1 Vertical Analysis
8.3.1.1 Vertical (Compression) Load Capacity Calculation
Ultimate downward capacity (qult) can be determined by the following
equation:
qult = c N c s c d c i c g c + q N q sq d q i q g q + 0.5 D N s d i g
Where c = cohesion
q = effective stress of soil at foundation base
= unit weight of soil
D = width or diameter of foundation
N = bearing capacity factors
s = shape factors
d = depth factors
i = load inclination factors
g = ground inclination factors
a.) Bearing Capacity Factors (N):
N c N q 1cot
N q tan 2 45 e tan
2
83
You might also like
- 2 - Bearing Capacity LectureDocument10 pages2 - Bearing Capacity LectureRedik .D ShanksNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity - Shallow FoundationsDocument47 pagesBearing Capacity - Shallow FoundationsVuyo SigaukeNo ratings yet
- Shallow FoundationsDocument44 pagesShallow FoundationsIqi Iqah100% (2)
- ECG553 - CHAP 3A - BC of Shallow FoundationDocument39 pagesECG553 - CHAP 3A - BC of Shallow FoundationAinur NasuhaNo ratings yet
- Vesic 1975 Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationsDocument27 pagesVesic 1975 Bearing Capacity of Shallow Foundationst.w.c.100% (2)
- CE-403 Bearing Capacity Handout#2 Deep FoundationDocument12 pagesCE-403 Bearing Capacity Handout#2 Deep FoundationYeyo NainuNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity 2019Document32 pagesBearing Capacity 2019Ahmed SaberNo ratings yet
- Vesic (1989) Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationsDocument27 pagesVesic (1989) Bearing Capacity of Shallow Foundationsjuancmontoya98No ratings yet
- UNIT 3 Bearing Capacity of FodnDocument15 pagesUNIT 3 Bearing Capacity of FodnBhagyashri RodeNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Intro Design and Analysis of Shallow FoundationDocument33 pagesWeek 5 - Intro Design and Analysis of Shallow FoundationMUSLIHAH AQILAH MUSAFFENDY100% (1)
- 3.2-Bearing Capacity of SoilsDocument23 pages3.2-Bearing Capacity of SoilsSamson Yonas100% (1)
- Fe Week 10&11 Reviewer For FinalDocument4 pagesFe Week 10&11 Reviewer For Finalbsce.delossantos.rizza.mNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity of SoilsDocument44 pagesBearing Capacity of SoilsEba GetachewNo ratings yet
- 8 Behaviour of Piled Raft FoundationsDocument5 pages8 Behaviour of Piled Raft FoundationshatlanNo ratings yet
- (E) Chapter 1 - Shallow FoundationDocument27 pages(E) Chapter 1 - Shallow FoundationMoses HonNo ratings yet
- CH-3 Pile FoundationsDocument85 pagesCH-3 Pile FoundationsDejene Ambese100% (1)
- SpsiDocument33 pagesSpsiAnup ShirhattiNo ratings yet
- The Bearing Capacity of Soils: DR Omar Al HattamlehDocument64 pagesThe Bearing Capacity of Soils: DR Omar Al HattamlehHusam Adnan HamoutaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: Bearing Capacity of Soils (Shallow Foundations)Document15 pagesChapter Three: Bearing Capacity of Soils (Shallow Foundations)Wubetie MengistNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Exc and Layered Soil BC 2019Document53 pagesChapter 5 Exc and Layered Soil BC 2019Kaiser CarloNo ratings yet
- I Chapter Two Bearing Capacity of Soil: Foundation Engineering CourseDocument39 pagesI Chapter Two Bearing Capacity of Soil: Foundation Engineering Coursearno assassinNo ratings yet
- 3esicno'rceciame:er: OorecDocument8 pages3esicno'rceciame:er: OorecSaiful Azhar Ahmad TajudinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Rock PDFDocument74 pagesIntroduction To Rock PDFrabindrachyNo ratings yet
- Shallow Foundations For Seismic Loads Design ConsiderationsDocument17 pagesShallow Foundations For Seismic Loads Design ConsiderationsLuis MendietaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 (B) Bearing Capacity Theorems: Dr. Taeseo KuDocument16 pagesLecture 2 (B) Bearing Capacity Theorems: Dr. Taeseo KuwinminthetgeoNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity PDFDocument3 pagesBearing Capacity PDFWilliam LoveNo ratings yet
- 99 - Structural Design For Eccentric Loading of Footing PDFDocument5 pages99 - Structural Design For Eccentric Loading of Footing PDFsanthosh kpNo ratings yet
- Notes 2 - Bearing CapacityDocument51 pagesNotes 2 - Bearing Capacitytimothy_wong_47No ratings yet
- Chap1 Shallow Foundations Bearing Capacity StdsDocument31 pagesChap1 Shallow Foundations Bearing Capacity Stdsfyqah100% (2)
- Deep FoundationsDocument34 pagesDeep FoundationsJake BloggerNo ratings yet
- Hapter Hree Bearing Capacity of Soils: Soil and TheDocument16 pagesHapter Hree Bearing Capacity of Soils: Soil and TheNegesaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationsDocument64 pagesLecture 2 - Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationsanilNo ratings yet
- Understanding Eccentricity of Loading On Verticall Loaded Masonry WallsDocument34 pagesUnderstanding Eccentricity of Loading On Verticall Loaded Masonry Wallsmarc_youngNo ratings yet
- Shallow FoundationDocument56 pagesShallow FoundationAastha Soni50% (2)
- Geotechnical and Foundation Engineering CE-3333: Bearing Pressure & Bearing Capacity of SoilsDocument89 pagesGeotechnical and Foundation Engineering CE-3333: Bearing Pressure & Bearing Capacity of SoilsTalha.jNo ratings yet
- ch3 Bearing Capacity of Shallow Foundations PDFDocument53 pagesch3 Bearing Capacity of Shallow Foundations PDFRafi Mahmoud SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Em - 1110 1 1905Document196 pagesEm - 1110 1 1905julesjusayanNo ratings yet
- Laterally Loaded PilesDocument21 pagesLaterally Loaded PilesKunwarKhaliqeAhmadNo ratings yet
- 333-010 Part1 PDFDocument1 page333-010 Part1 PDFpmali2No ratings yet
- International Society For Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical EngineeringDocument9 pagesInternational Society For Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical EngineeringAlex Sandro Borges PereiraNo ratings yet
- Raftfoundations 160423143909Document26 pagesRaftfoundations 160423143909VIGNESH ANo ratings yet
- Chapter8 ShallowfoundationDocument69 pagesChapter8 ShallowfoundationAfiq FawwazNo ratings yet
- Soil Structure InteractionDocument1,602 pagesSoil Structure InteractionStructural SpreadsheetsNo ratings yet
- 9 Bearingc2Document30 pages9 Bearingc2Azman ScxNo ratings yet
- Foundation DesignDocument7 pagesFoundation DesignJayan JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Foundation DesignDocument7 pagesFoundation DesignJayan JoshuaNo ratings yet
- F17 CVL600 4 ShallowFDocument20 pagesF17 CVL600 4 ShallowFAudi DzhamolovichNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity Shallow FoundationsDocument73 pagesBearing Capacity Shallow FoundationsRakesh Reddy100% (1)
- PPTDocument21 pagesPPTKunwarKhaliqeAhmadNo ratings yet
- Foundation Analysis: Ultimate Bearing Capacity: Shallow FoundationDocument21 pagesFoundation Analysis: Ultimate Bearing Capacity: Shallow FoundationShiela Marie Cruz100% (1)
- Bearing CapacityDocument70 pagesBearing CapacityhanaalnaasNo ratings yet
- Bearing CapacityDocument28 pagesBearing CapacityjoshjethNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Bearing Capacity: StructureDocument25 pagesUnit 2 Bearing Capacity: StructureNISAR SHAIKHNo ratings yet
- Bearing CapacityDocument59 pagesBearing CapacityAlaaGaballaNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity of SoilsDocument5 pagesBearing Capacity of SoilsSamuel GalatNo ratings yet
- CE325 - 12 Terzaghis BC EquationsDocument17 pagesCE325 - 12 Terzaghis BC EquationsRobert PrinceNo ratings yet
- Bearing CapacityDocument77 pagesBearing CapacitySheikh Muneeb100% (1)
- Uplift Capacity of Plate Anchors: Application To Transmission PolesDocument12 pagesUplift Capacity of Plate Anchors: Application To Transmission PolesNoura SobhyNo ratings yet
- Basic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandBasic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- 87 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page87 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 64 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page64 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 36 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page36 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 45 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page45 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 40 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page40 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 81 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page81 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- Convert UnitDocument1 pageConvert UnitOssa SetiawanNo ratings yet
- 83 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page83 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 22 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page22 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 21 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page21 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 23 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page23 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 17 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page17 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 20 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page20 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 18 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page18 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 19 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page19 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 16 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page16 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 12 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page12 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 9 - PDFsam - Manual Pengguna EDPLAS Online - PerundingDocument1 page9 - PDFsam - Manual Pengguna EDPLAS Online - Perundingfordownload useNo ratings yet
- 9 PDFsam MeyerWhatisliteratureDocument1 page9 PDFsam MeyerWhatisliteraturefordownload useNo ratings yet
- 13 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page13 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 15 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page15 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 14 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page14 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 8 PDFsam MeyerWhatisliterature PDFDocument1 page8 PDFsam MeyerWhatisliterature PDFfordownload useNo ratings yet
- Mona Lisa: Weak Implicatures and OpennessDocument1 pageMona Lisa: Weak Implicatures and Opennessfordownload useNo ratings yet
- 6 PDFsam MeyerWhatisliteratureDocument1 page6 PDFsam MeyerWhatisliteraturefordownload useNo ratings yet
- References: View Publication Stats View Publication StatsDocument1 pageReferences: View Publication Stats View Publication Statsfordownload useNo ratings yet
- 10 PDFsam MeyerWhatisliterature PDFDocument1 page10 PDFsam MeyerWhatisliterature PDFfordownload useNo ratings yet
- References: View Publication Stats View Publication StatsDocument1 pageReferences: View Publication Stats View Publication Statsfordownload useNo ratings yet
- 10 PDFsam MeyerWhatisliterature PDFDocument1 page10 PDFsam MeyerWhatisliterature PDFfordownload useNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Quantum Metrology by Waldemar Nawrocki (2015)Document287 pagesIntroduction To Quantum Metrology by Waldemar Nawrocki (2015)Vallik TadNo ratings yet
- Oslo 1Document69 pagesOslo 1Roberto Carlos Barragán CamposNo ratings yet
- DIN 18134 2012-04 Eng.Document25 pagesDIN 18134 2012-04 Eng.rolando rettigNo ratings yet
- Base Module For Experiments in Fluid MechanicsDocument5 pagesBase Module For Experiments in Fluid MechanicsMichael VillameNo ratings yet
- Landau RSTDocument11 pagesLandau RSTpbaculimaNo ratings yet
- Hegarty Revision List - FOUNDATIONDocument2 pagesHegarty Revision List - FOUNDATIONMihaela GrosuNo ratings yet
- Mod 2 - History of NumbersDocument1 pageMod 2 - History of Numbersapi-550214604No ratings yet
- Ee001a HW 2 - SolutionsDocument7 pagesEe001a HW 2 - SolutionsAllen NguyenNo ratings yet
- BU FCAI BS111 P&S Lec08Document66 pagesBU FCAI BS111 P&S Lec08صلاح متوليNo ratings yet
- Dpp-05 Quantum Chemistry: XL P PDocument3 pagesDpp-05 Quantum Chemistry: XL P Panurag pandeyNo ratings yet
- Calculation SheetDocument14 pagesCalculation SheetmohitNo ratings yet
- S ParametersDocument29 pagesS ParameterseloiseNo ratings yet
- Random Variables and Stochastic Processes - April-2016Document4 pagesRandom Variables and Stochastic Processes - April-2016rajeshkumar_niceNo ratings yet
- BRAUN A5S0-Manual ENDocument20 pagesBRAUN A5S0-Manual ENSureshNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 11Document10 pagesProblem Set 11mmccomas08No ratings yet
- Thermal Radiation30Document1 pageThermal Radiation30Nirmal SubudhiNo ratings yet
- ABPR OperatorManual PDFDocument36 pagesABPR OperatorManual PDFLola Karvajal100% (2)
- Criminal Law and Jurisprudence, Law Enforcement Administration, CriminalisticDocument211 pagesCriminal Law and Jurisprudence, Law Enforcement Administration, Criminalisticsacli.valentin mjNo ratings yet
- CE211F-18 FW#2 Angular Measurement by Tape - 2CE-3Document8 pagesCE211F-18 FW#2 Angular Measurement by Tape - 2CE-3Bea BachillerNo ratings yet
- Design of Waste Paper Baler Machine: AuthorsDocument50 pagesDesign of Waste Paper Baler Machine: AuthorsCherinet MathewosNo ratings yet
- Kalkulasi Steam Trap MFO Rev 00Document20 pagesKalkulasi Steam Trap MFO Rev 00Rifka AisyahNo ratings yet
- X-Ray: Prepared byDocument21 pagesX-Ray: Prepared bylaith adnanNo ratings yet
- 101.1 AlumAssoc EPD ColdRolled 20141016 0Document14 pages101.1 AlumAssoc EPD ColdRolled 20141016 0esivaks2000No ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document2 pagesExperiment 7Zariq NazaruddinNo ratings yet
- 2004 An Insight Into The New Austrian TunnellDocument14 pages2004 An Insight Into The New Austrian TunnellafuhcivNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic EngineDocument2 pagesElectromagnetic EngineGiri Wip NxNo ratings yet
- How Does Oxygen Get Into The BloodDocument14 pagesHow Does Oxygen Get Into The Bloodapi-247243068No ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Design Indian Code Is 456Document136 pagesReinforced Concrete Design Indian Code Is 456onyejekwe100% (1)
- Structural Silicone Sealants: Standard Specification ForDocument4 pagesStructural Silicone Sealants: Standard Specification ForZiyad KubbaNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of Three Phase Induction MotorDocument48 pagesSpeed Control of Three Phase Induction MotorChancy Dash100% (3)