Professional Documents
Culture Documents
87 PDFsam Al Manu
Uploaded by
fordownload useOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
87 PDFsam Al Manu
Uploaded by
fordownload useCopyright:
Available Formats
.
.
.
.
equation: .
.
Allowable downward capacity (Q allow) can be calculated by the following
.
.Q Q
allow
ult
. F .S .
8.3.2 Capacity for Combined Loading
8.3.2.1 Vertical (Compression) Load (Q) Only
If there is only a vertical load, Q, without any lateral loading, i.e. shear loads
and bending moment, the Factor of Safety of the shallow foundation can be
calculated using the equation below:
Q ult
F .S .
Q.
Where, Qult = ultimate bearing capacity
Q = total vertical load
Users can also check the ratio between Q and the allowable bearing capacity,
Qallow, to see if the shallow foundation is considered stable. If Q > Qallow, the
foundation is insufficient.
8.3.2.2 Vertical Load With Moment (Q + M)
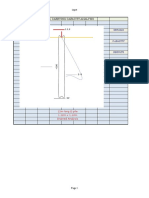
Typical lateral loads on the foundation include bending moment (M) and
shear load (P) as illustrated in the next diagram. In this section, we will study
the procedures used to determine footing capacity against the combination of
vertical load and bending moment (Q+M).
Eccentricity (e) will be generated by the moment and vertical load (see Figure
8-12):
M
e
Q
a.) If e D/6, the pressure on the foundation can be determined by:
Q 6M
q max 2
DB D B
Q 6M
q min 2
DB D B
86
You might also like
- QT1-PVE-00HTK-M-M5A-0004 Bucket Elevator CalculationDocument8 pagesQT1-PVE-00HTK-M-M5A-0004 Bucket Elevator Calculationjack-bc67% (3)
- PILE CAPACITY CALCULATION METHODSDocument11 pagesPILE CAPACITY CALCULATION METHODSparvejNo ratings yet
- Some Application: Recent Research and DesignDocument17 pagesSome Application: Recent Research and Designsabareesan09No ratings yet
- DESIGN OF A CONTINUOUS BEAMDocument30 pagesDESIGN OF A CONTINUOUS BEAMAnthony KoNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Design of Driven Piles Under Axial Loads: 10.1 Comment On The Nature of The ProblemDocument53 pagesGeotechnical Design of Driven Piles Under Axial Loads: 10.1 Comment On The Nature of The ProblemAndré OliveiraNo ratings yet
- E3sconf Gceece2021 02041Document5 pagesE3sconf Gceece2021 02041dejfioefNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundation Design and Load TestingDocument4 pagesPile Foundation Design and Load TestingNaveed AliNo ratings yet
- Design of Reinforced Concrete FoundationsDocument16 pagesDesign of Reinforced Concrete Foundationsanirbanpwd76No ratings yet
- Solid Meachanics MaterialsDocument4 pagesSolid Meachanics MaterialsShivendra SinghNo ratings yet
- CE325 - 12 Terzaghis BC EquationsDocument17 pagesCE325 - 12 Terzaghis BC EquationsRobert PrinceNo ratings yet
- 93_PDFsam_al_manuDocument1 page93_PDFsam_al_manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 86 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page86 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- Lecture 17 - Calculation of Shear Force and Bending Moment For Big Aspect Ratio WingDocument9 pagesLecture 17 - Calculation of Shear Force and Bending Moment For Big Aspect Ratio WingAnonymous kUC6DyhlLNo ratings yet
- PILE CAPACITY CALCULATION METHODSDocument12 pagesPILE CAPACITY CALCULATION METHODScelalunal58No ratings yet
- Bucket Elevator Calculation for Quang Trach 1 Thermal Power PlantDocument8 pagesBucket Elevator Calculation for Quang Trach 1 Thermal Power PlanthbookNo ratings yet
- Structural Design Calculation of CabanaDocument36 pagesStructural Design Calculation of CabanasaravqwertyNo ratings yet
- KosoDocument4 pagesKosoamar100% (1)
- SEC. 9:2 STABILITY-BEARING CAPACITYDocument8 pagesSEC. 9:2 STABILITY-BEARING CAPACITYjihadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationsDocument64 pagesLecture 2 - Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationsanilNo ratings yet
- Theory PresentationDocument28 pagesTheory PresentationIcaNo ratings yet
- Bearing CapacityDocument6 pagesBearing CapacityYarid Poma CastellanosNo ratings yet
- Example 18: Pile and Hammer Gravity Changes: GRLWEAP Standard ExamplesDocument3 pagesExample 18: Pile and Hammer Gravity Changes: GRLWEAP Standard ExamplesbozarromegustaNo ratings yet
- Slab On Grade Excel Sheet PDF FreeDocument10 pagesSlab On Grade Excel Sheet PDF FreeImaduddin KhajaNo ratings yet
- 79 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page79 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- Cam Clay and Modified Cam Clay Material Models ExplainedDocument11 pagesCam Clay and Modified Cam Clay Material Models ExplainedJonathan TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Midterm exam questions CE 117 Summer 2020Document4 pagesMidterm exam questions CE 117 Summer 2020Mohammad JavedNo ratings yet
- Vdocuments - MX - Sea Fastening Desig MannualDocument36 pagesVdocuments - MX - Sea Fastening Desig MannualRiyan EsapermanaNo ratings yet
- Pile Capacity EN 1997 PDFDocument11 pagesPile Capacity EN 1997 PDFErick IgogoNo ratings yet
- Determination of Excess Pore Pressure in Earth Dam after EarthquakeDocument11 pagesDetermination of Excess Pore Pressure in Earth Dam after EarthquakeCepiNo ratings yet
- Ta3 Is456 enDocument11 pagesTa3 Is456 enkyle IRSYADNo ratings yet
- Base Plate LSD SubramanianDocument20 pagesBase Plate LSD SubramanianShakil AkhterNo ratings yet
- F Q V W F: 100 P. ZającDocument3 pagesF Q V W F: 100 P. ZającPbNo ratings yet
- Bucket Elevator Calculation Rev 1Document8 pagesBucket Elevator Calculation Rev 1Irfan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Wrana 2015 4 PDFDocument11 pagesWrana 2015 4 PDFarslanpasaNo ratings yet
- RC Assignment 1 - 9septDocument6 pagesRC Assignment 1 - 9septBa Thanh Dinh100% (1)
- Lecture 25 - Frames and Ribs Strength AnalysisDocument7 pagesLecture 25 - Frames and Ribs Strength AnalysisJony Oliver Lazo RamosNo ratings yet
- PILES CARRYING CAPACITY ANALYSIS SoftwareDocument7 pagesPILES CARRYING CAPACITY ANALYSIS SoftwareJhon Anaya VerdeNo ratings yet
- Pilescarrying Capacity AnalysisDocument7 pagesPilescarrying Capacity AnalysismathuNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity - Shallow FoundationsDocument47 pagesBearing Capacity - Shallow FoundationsVuyo SigaukeNo ratings yet
- Pile Capacity - Calculation MethodsDocument11 pagesPile Capacity - Calculation Methodsblithevincent100% (1)
- ch7 Deep Foundation Piles PDFDocument24 pagesch7 Deep Foundation Piles PDFJonathan SantosNo ratings yet
- Clarke and Park Transformation: Chapter at A GlanceDocument9 pagesClarke and Park Transformation: Chapter at A GlanceYudhis YudhistiraNo ratings yet
- Clark and Park TransformationDocument9 pagesClark and Park Transformationjm.mankavil6230100% (1)
- Chapter 8 - Combined LoadingDocument51 pagesChapter 8 - Combined Loadingfaiz fadhilahNo ratings yet
- 파일수평지지력 (Broms)Document8 pages파일수평지지력 (Broms)murthyspandan89No ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity PDFDocument13 pagesBearing Capacity PDFChoun OleNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Intro Design and Analysis of Shallow FoundationDocument33 pagesWeek 5 - Intro Design and Analysis of Shallow FoundationMUSLIHAH AQILAH MUSAFFENDY100% (1)
- FOUNDATION RCD of Footings 1 Square FTGDocument5 pagesFOUNDATION RCD of Footings 1 Square FTGChris Michelle JapinNo ratings yet
- Bearing CapacityDocument13 pagesBearing CapacityankitraginiNo ratings yet
- Zhong-Yuan KANG Ge-Ning XU, Heng YANG, Xin Wang, Jing LIDocument9 pagesZhong-Yuan KANG Ge-Ning XU, Heng YANG, Xin Wang, Jing LICamilo GuzmanNo ratings yet
- PILE LOAD CAPACITY CALCULATIONDocument10 pagesPILE LOAD CAPACITY CALCULATIONcelalunal58No ratings yet
- Electrostatics Test 1Document2 pagesElectrostatics Test 1Manash SinghaNo ratings yet
- 2395 AppaDocument8 pages2395 AppaDiego RamírezNo ratings yet
- Slenderness FormulasDocument2 pagesSlenderness FormulasSolaiman ShahriarNo ratings yet
- Calculate Foundation Bearing Capacity Using Theory and Empirical MethodsDocument14 pagesCalculate Foundation Bearing Capacity Using Theory and Empirical MethodsKathlene ZapantaNo ratings yet
- Column 3Document21 pagesColumn 3Ahmed EwisNo ratings yet
- 81 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page81 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 64 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page64 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 36 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page36 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 45 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page45 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 40 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page40 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 84 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page84 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- Convert UnitDocument1 pageConvert UnitOssa SetiawanNo ratings yet
- 83 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page83 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 22 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page22 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 21 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page21 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 23 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page23 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 17 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page17 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 20 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page20 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- Pile Properties Page Allows Choosing Pile Section PropertiesDocument1 pagePile Properties Page Allows Choosing Pile Section Propertiesfordownload useNo ratings yet
- 19 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page19 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 16 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page16 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 12 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page12 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 9 - PDFsam - Manual Pengguna EDPLAS Online - PerundingDocument1 page9 - PDFsam - Manual Pengguna EDPLAS Online - Perundingfordownload useNo ratings yet
- 9 PDFsam MeyerWhatisliteratureDocument1 page9 PDFsam MeyerWhatisliteraturefordownload useNo ratings yet
- 13 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page13 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 15 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page15 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 14 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page14 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 8 PDFsam MeyerWhatisliterature PDFDocument1 page8 PDFsam MeyerWhatisliterature PDFfordownload useNo ratings yet
- Mona Lisa: Weak Implicatures and OpennessDocument1 pageMona Lisa: Weak Implicatures and Opennessfordownload useNo ratings yet
- What is Literature? A Definition Based on PrototypesDocument1 pageWhat is Literature? A Definition Based on Prototypesfordownload useNo ratings yet
- References for Jim MeyerDocument1 pageReferences for Jim Meyerfordownload useNo ratings yet
- What is Literature? A Definition Based on PrototypesDocument1 pageWhat is Literature? A Definition Based on Prototypesfordownload useNo ratings yet
- References for Jim MeyerDocument1 pageReferences for Jim Meyerfordownload useNo ratings yet
- What is Literature? A Definition Based on PrototypesDocument1 pageWhat is Literature? A Definition Based on Prototypesfordownload useNo ratings yet