0% found this document useful (0 votes)
429 views2 pagesTrig-PreCalculus Summer Review Worksheet - Answer Key
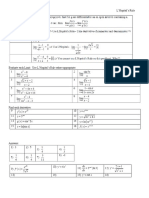
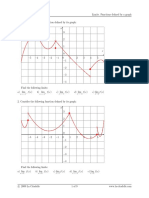
This document contains the answer key to a math test covering functions, equations, quadratic functions, simplifying fractions, exponents, radicals, trigonometry, and the unit circle. It provides the answers to multiple choice and free response questions testing concepts like domain and range of functions, solving equations, graphing quadratics, properties of exponents, trigonometric functions, and values on the unit circle.
Uploaded by
franklinmanlapaoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
429 views2 pagesTrig-PreCalculus Summer Review Worksheet - Answer Key
This document contains the answer key to a math test covering functions, equations, quadratic functions, simplifying fractions, exponents, radicals, trigonometry, and the unit circle. It provides the answers to multiple choice and free response questions testing concepts like domain and range of functions, solving equations, graphing quadratics, properties of exponents, trigonometric functions, and values on the unit circle.
Uploaded by
franklinmanlapaoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Quadratic Functions
- Functions
- Solving Equations
- Graphs
- Properties of Exponents and Radicals
- Trigonometry and the Unit Circle
- Simplifying Compound Fractions