Professional Documents
Culture Documents
S1 - Earth Our Home 1 Chapter-9
S1 - Earth Our Home 1 Chapter-9
Uploaded by
KHAING LYNN0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views10 pagesOriginal Title
S1 -Earth Our Home 1 Chapter-9
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views10 pagesS1 - Earth Our Home 1 Chapter-9
S1 - Earth Our Home 1 Chapter-9
Uploaded by
KHAING LYNNCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
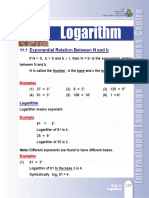
Chapter 9
Rocky Matter
Before advanced technology was
available, people in the past made use of
‘materials in theit surroundings, such as
rocks, to make useful tools. This Hoko
knife (a modern model of the original
knife) consists of a very small, sharp stone
tied to a wooden handle with a spruce
root, The otiginal knife was found near
the Hoko River in western Washington,
Archaeologists (people who study objects
used by people of the past) think that it
‘was used by people who were living there
about 2 700 years ago for cutting fish.
102 Chaptera
Rocks
You yj] LEARN
* about the origins and
characteristics of the
main rock types
© todescribe the
distribution of the main
k types in Singapore
using a map
Fig 1 Rocks are classified itn thee
main ypes — igneous, sedimentary and
mmetamophic rocks. Can you describe hoe
tho rocks wathin each ype ae similar to
‘one another?
of the Earth
What Are Rocks?
Landforms, such as mountains and volcanoes, are made up entirely of
rocks. Without rocks, there would be no landforms on Earth, Let us now.
earn about rocks, what they are made of and how they are formed.
Roeks are solid materials of the Earth’s crust. They are made up of
substances known as minerals, such as quartz and sand. Rocks are
formed in various ways, such as when lava cools and hardens on the
Earth's surface. Geologists (people who study rocks) have classified
rocks into three main types, according to how they are formed. The
three types are igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks.
eon
© Basait
Uses: oor ties, basalt os
and textiles
© Grenite
Uses: Buildings, monuments
Sedimentary rocks
© Limestone
Uses: Camont, blackboard chalk
© Stale
Uses: aw material for making
potter and tiles
© Sandstone
Uses: Canstuctio, raw
‘material fo making pottery
Rocks of the Earth 103
Igneous rocks
The word ‘igneous’ comes from the Latin word ignis, which
‘fire’. Does this give you a clue as to where igneous rocks come from?
Remember that magma, a very hot molten material, makes up the Earth’s
interior. Geologists describe igneous rocks as magma that has cooled
and hardened, either beneath or above the Earth’s surface.
neans,
Fig92 Whenta
cool and hare i)
peau racks
it forms extus
a How are igneous
rocks formed? fine-grained igneous rocks are
ferred when lava cools and
Corso grand ignous rocks a tee
‘a formed when magma cools pe eatin
‘and hardans nso the Earth
lve
Fig93. Igneous works ao formed
when magma cols and hardens inthe
arth or when ava cols and hardens
nthe Earth’ surface
Coarse-grained igneous rocks
‘The appearance of igneous rocks is affected by how fast magma
cools. When magma cools and hardens slowly in the Barth's interior,
coarse-grained igneous rocks are formed. This means that we can see
individual grains on the rocks with the naked eye. An example of a
coarse-grained igneous rock is granite. Granite can be used to make
many things, such as pavements and stone walls,
Fig94 Thegairs
afigneos orks that
foe in ho Earth are
vate Fine-grained igneous rocks
When lava cools and hardens quickly on the Earth's surface, fine-
grained igneous rocks are formed. The individual grains are very
small and a microscope is needed to see them in detail. An example
of a fine-grained igneous rock is basalt. Basalt is very hard and
for floor tiles
Fig95 Tho grains és
af gnanus rocks that resistant to weathering, It can be used as a materi
form onthe Earths
surface ae ne. and basalt fibres. Basalt fibres are used in the construction industry
to make concrete stronger.
104 Chopior9
Sedimentary rocks
Weathering and erosion cause rocks to break
down into smaller pieces. Tiny pieces of
broken rocks, together with grains of sand,
clay and silt, are known as sediments. Being
small and light, sediments are easily carried
away by wind and water, Eventually, some
of the sediments are deposited into rivers
and oceans.
As the sediments pile up in layers, the weight of the layers on top
presses down on the layers below. Eventually, the sediments cement
together and harden, These solid, hardened layers of sediments are
Layers of souiments
Fig 96 As the layers of sediments pile
called sedimentary rocks. upon tho sea bed, the sediments coment
‘gether and hardon,
‘The appearance of sedimentary rocks depends on the type and size of the
sediments. When the sediments are very small, fine-grained sedimentary
rocks are formed. An example of a fine-grained sedimentary rock is
shale, which is often used to make bricks.
With larger sand-sized particles, coarse-grained sedimentary rocks are
formed. An example of a coarse-grained sedimentary rock is sandstone.
Another example is conglomerate, which is a mixture of pebbles and
sand grains cemented together. Fig 97 Conglomerate isa
sedimentary rock tats made up
1 patos an ahr sina
Not all sedimentary rocks, however, are formed from sediments. Some cemented together
are formed from the hardened remains of animals and plants. An example
of such a sedimentary rock is limestone. Some types of limestone are.
made up of the remains of coral, shell and even bone.
mesione may IAG
also contain fossils, which are the preserved parts of marine animals How are sedimentary
rocks formed?
and plants that lived long ago.
Fig 98 We can cast recognise
laniformsthat are made of sedimentary
‘orks bacause of her distinctive layers.
How do we differentiate sedimentary rocks from other types of rocks?
‘Well, the main characteristic of sedimentary rocks is that they form in
layers which vary in thickness and appearance. ‘The bottom layer is,
usually the oldest and the top layer, the newest.
Rocks sometimes give a place its
identity. Jaipur, the capital of the i,
‘state of Rajasthan in North India, Metamorphic vocks ‘
is ropalariy ricum(asthe Pink hy Sedimentary and igneous rocks sometimes become completely
because many houses there are transformed or changed under intense heat and pressure. This could
made of pink sandstones! Read, ‘occur due to crustal movements or when the rock comes into contact with
view and play games about rocks molten magma. When that happens, metamorphic rocks are formed.
a itary ane ayes gos ‘The word meramorphosis is the Greek word for ‘transformation’. For
last accessed on 1 June 2008).
: d example, when an igneous rock like granite is subjected to extreme high
temperatures and intense pressure, it transforms into a metamorphic rock
called gneiss. Under similar conditions, sedimentary rocks like shale
changes into slate, whereas limestone changes into marble.
a How are metamorphic
rocks formed?
Intense pressure causes Intense haat causes
sedimentary rocks to change igneous rocks to cheme
into metamorphic rok. into metemerphic ros.
Sedimantay rocks
Fg 39 When tno
Plats clide, one pate
sinks beneath anotho,
This causes rocks tobe
sabjectd to inense heat
and pressure, and change
into metamaxpte os
Heat and pressure sometimes cause metamorphic rocks to have a foliated
appearance, that is, to have bands. Slate is an example of a metamorphic
rock with a foliated texture. This means that the different minerals are
aligned in parallel layers. It is formed from shale, a sedimentary rock,
Metamorphic rocks can be used as materials for buildings and
decorations. For example, marble is commonly used as a building
material in homes, and as a sculpting material by artists. Slate is often
used as a construction material for fireplaces and flooring,
Fig 9.10_Slato isa fre rained,
foliated motamorphic rock Em,
106 Chapter 9
The Rock Cycle
‘The three main types of rocks are interrelated in the ways they are
formed. Over time, one type of rock can change into another.
Rocks of any type that are broken into pieces may form sedimentary
rocks. Igneous and sedimentary rocks may change into metamorphic
rocks, Metamorphic rocks sometimes get buried deep in the Earth where
there is intense heat and pressure. They melt and become magma, which
then cools and hardens to form igneous rocks. Hence, rocks constantly
undergo a cycle of change. This continual process of change in rocks
is known as the rock eyele.
41. Igneous rocks are formed
from magma,
oT
3. Metamorphic rocks
that are buried deep
in the Earth melt in
the mantl,
4. Under intense heat and
pressure, sodimentary
and igneous rocks change
into metamorphic rocks.
ete
@ What isthe rock
cycle?
Figg11
The rockoyie
2. Weathering and erosion of rocks
resuitin sediments
3. Large and small
sediments pile up in
layers, and are cemented
‘and hardened to form
sedimentary rocks
Rocks of the Earth 107
Main Rock Types in Singapore
We have learnt that rocks are classified into igneous, sedimentary and
metamorphic. All the three types of rocks are present in Singapore.
Igneous rocks make up the central part of Singapore, while sedimentary
rocks occupy the eastern and westem parts of the island. A small area
of metamorphic rocks is located in Pulau Tekong,
Fg9.12 A geological map
showing te distribution of
he three main rok typos in
Singapore
LEGEND
neous eos
Sedimentary ooks
Metamorphic ook
Igneous rocks in Singapore
‘The type of rock most commonly seen in Singapore is granite. It is
located largely in the central part of Singapore, in the area known as the
Bukit Timah Granite Formation, This large area of granite measures
some 8 kilometres from north to south and 7 kilometres from east
fo west.
Fi
213. TheLitle Guilin at Bukit Batok
Nature Pak s made up of igneous
The ladon is ramad alter Gulin
caus it oc ke te hil there
‘There are several abandoned quarries in the central part of Singapore,
where people once extracted granite for the construction of roads and.
buildings, Some of the quarties have been changed into parks. An hed
example is the Little Guilin at Bukit Batok Nature Park, Other than
the main island, granite quarries are also found in Pulau Ubin. ale
‘more about the geology of
Singapore: htphomepage.
mac.comioyagerINoPlace!
tect htm (last accassed on
4-1 June 2008),
Fig 9.14. Quaryng was a major activity
‘which proved es fr the people on
Pulau Ubin The last granite quary was
‘lose in 1999
Sedimentary rocks in Singapore
‘We can find different types of sedimentary rocks in the southern,
eastern and western parts of Singapore, Rocks in these parts are layered,
consisting of mainly sandstone and conglomerate
Metamorphic rocks in Singapore
‘We can find a small area of metamorphic rocks called the Sajahat
Formation on Pulau Tekong. The rocks here are formed under intense
heat and pressure, and are very hard,
CENA BE na sonnonope
: 2 of rock found in Singapore?
Rocks in Our Environment Whece can we find it?
environment, Besides
\dforms like mountains and voleanoes,
Rocks are present everywhere in our physi
being the building blocks of I
rocks are used by people to build structures like buildings and roads.
Rocks of the Earth 109
Skills
For each of the following rocks, identify its main rock type and the name
based on the given information.
lam the most
‘common type of rock
found in Singapore!
‘May individual grains
are very small and you
cannot see them with
‘your naked eye. | am
very hard and resistant
10 weathering.
‘lam coarse-grained
vith pebbles and sand
{grains cemented on
mel
Hi everyone, | used
‘tobe a limestone,
Now that I have been
transformed, [am
‘much tougher!
110 Chapter
at It
leans.
‘An igneous rock is a rock formed from magma that has cooled and hardened
beneath or above the Earth’s surface.
‘A metamorphic rock is a rock that is completely transformed or changed,
from an igneous or sedimentary rock under intense heat and pressure.
‘A rock is a solid material of the Earth's crust, and is made up of substances
known as minerals,
‘The rock cycle is the continual process by which rocks change from one
type to another.
‘A sedimentary rock is @ rock formed by the cementing and hardening of
layers of sediments under pressure from the overlying layers.
Silt.
This diagram illustrates the processes that result in the formation
of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks.
‘Weathering and erosion break down rocks to produce sedi
+ Layers of sediments are pressed and cemented together,
and hardened to form sedimentary
Lava coos and hardens
‘quickly on the Earths
surface to form fine-
grained igneous rocks.
Magma coo's and hardens
slowly inside the Earth to
form coarse-grained
igneous rocks.
‘© Intense heat and pressure cause igneous and
sedimentary rocks to change into metamorphic rocks.
Rocks of the Earth 411
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5811)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Unit-4 Targeting Comprehension ExercisesDocument20 pagesUnit-4 Targeting Comprehension ExercisesKHAING LYNNNo ratings yet
- Sec 1 History Course Book Semester TwoDocument38 pagesSec 1 History Course Book Semester TwoKHAING LYNNNo ratings yet
- Sec 1 Classical Period (Wk3&4)Document20 pagesSec 1 Classical Period (Wk3&4)KHAING LYNNNo ratings yet
- P6 Maths CB Unit 11Document4 pagesP6 Maths CB Unit 11KHAING LYNNNo ratings yet
- Owl ArticleDocument1 pageOwl ArticleKHAING LYNNNo ratings yet
- Arduino ProjectDocument1 pageArduino ProjectKHAING LYNNNo ratings yet
- P6 Project 5 SB (Unit 6)Document20 pagesP6 Project 5 SB (Unit 6)KHAING LYNNNo ratings yet
- First AidDocument31 pagesFirst AidKHAING LYNNNo ratings yet
- Thomas Alva EdisonDocument9 pagesThomas Alva EdisonKHAING LYNNNo ratings yet
- Edison, Thomas AlvaDocument4 pagesEdison, Thomas AlvaKHAING LYNNNo ratings yet
- T T 14318 Thomas Edison Powerpoint Presentation Ver 5Document13 pagesT T 14318 Thomas Edison Powerpoint Presentation Ver 5KHAING LYNNNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument1 pageElectricityKHAING LYNNNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument6 pagesElectricityKHAING LYNNNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Mixing and SeparatingDocument8 pages3.2 Mixing and SeparatingKHAING LYNNNo ratings yet
- Primary - 6 Geography Chapter - 6Document14 pagesPrimary - 6 Geography Chapter - 6KHAING LYNNNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Soluble and Insoluble SolidsDocument2 pages3.3 Soluble and Insoluble SolidsKHAING LYNNNo ratings yet
- Is It Cyberbullying - Sondra's Story Student HandoutDocument2 pagesIs It Cyberbullying - Sondra's Story Student HandoutKHAING LYNNNo ratings yet
- Differences and Similarities Between 2D & 3DDocument2 pagesDifferences and Similarities Between 2D & 3DKHAING LYNNNo ratings yet
- Primary - 6 Geography Chapter - 5Document8 pagesPrimary - 6 Geography Chapter - 5KHAING LYNNNo ratings yet