0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views5 pagesWeek 2 Ha Rle Post Test Answer Key
The document contains a health assessment test with multiple choice questions. It tests knowledge of key concepts in health assessments including:
1) The health history format is used to organize patient information for other providers.
2) Nurses can detect areas needing health adjustments, continuous care, hospital care or specialist referral through assessments.
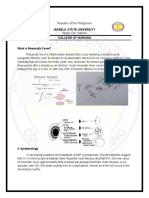
3) "Health" is defined by the WHO as complete physical, mental and social well-being, not just absence of disease.
Uploaded by
Danelyn PerezCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views5 pagesWeek 2 Ha Rle Post Test Answer Key
The document contains a health assessment test with multiple choice questions. It tests knowledge of key concepts in health assessments including:
1) The health history format is used to organize patient information for other providers.
2) Nurses can detect areas needing health adjustments, continuous care, hospital care or specialist referral through assessments.
3) "Health" is defined by the WHO as complete physical, mental and social well-being, not just absence of disease.
Uploaded by
Danelyn PerezCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
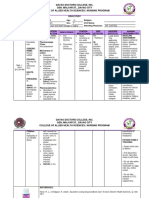
- Health Assessment Overview
- Health Situations and Needs
- Patient Interaction and Data Gathering
- Psychosocial Assessments
- Family History and Genetic Considerations
- Skills and Developmental Milestones