Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adobe Scan 05 Feb 2024
Adobe Scan 05 Feb 2024
Uploaded by
krishrajput88888888Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adobe Scan 05 Feb 2024
Adobe Scan 05 Feb 2024
Uploaded by
krishrajput88888888Copyright:
Available Formats
294
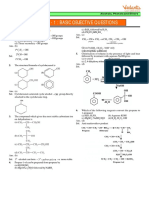
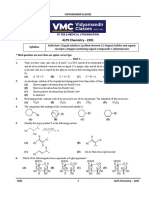
wtG Objectiye NCERT
Thus. strongelectron
R
group and resonance
base are responsible for wistatthebh1ldriaswatiinogn etfecthe
of
oi
0:
R
atoms of carbonylcompoundsacidity of
Aldehydes and ketones
cconatgbn o
() () (1) atom undergo reactioncontaining atleast
a in
Resonancestabilisation of carboxvlate anion is more alkali as catalyst to he
(aldol) or ß-hydroxy ketoncs. presence ofonmedirHhte
forrm
than that ot undissociated carboxyic acid. Therefore.
greater stability of carboxylate ion is responsible tor
the acidic character of carboxylic acids.
5 Binthe f-hydroxy
following sequence is aldehvder
1. The strongest acid among the following is dil \aOtt,AZnHg
(a) salicylic acid HC>B
(b) m-hydroxvbenzoic acid (a)
(c) p-hydroxybenzoic acid (b)
(d) benzoic acid. OH OH
2. Arrange the following carboxylic acids in their
decreasing acidity : (c) (d)
(1) ÇOOH Oxalicacid
OH
COOH
OH
(2) HOOC-CH,-COOH Malonic acid 6. How many aldols are formed
when
(3) CH,-COoH Succinic acid
and
(a) 2
propanaldehyde undergo aldol
(b) 4 (c) 3 acetaldehvde cond(d)ensa8tion?
CH,-COOH 7. Astrong base can abstract
an
(a) 3> 2>1
(c) 2> 3>1
(b) 1> 2 >3
(d) 2>1>3
(a) ketone (b) a-hydrogen(d) tromamin.
alkane (c) alkene
8. A compound
3 In the anion HCOO, the two carbon-oxygen bonds possessing a-hydrogen atom, in the
presence of dilute
are found to be of equal length. What is the reason alkali
This product on heatingforms B-hydroxy aldehvàe
for it? with dilute acid forms an
(a) Electronic orbitals of carbon atom are unsaturated crotonaldehyde.
The compound is
(a) CH,CHO (b) CH,CH,CHO
hybridised. (c) CH, CH- CHO (d)
(b) The C-0 bond is weaker than the C-Cbond.
(c) The anion HCO0 has two resonating structures. 3. HCEC-CHO
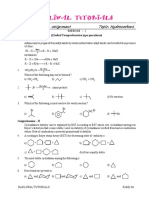
Aldehydes differ from ketones in their oxidation
(d) The anion is obtained by removal of a proton reactions. Aldehydes are easily oxidised to
from the acid molecule. carboxylic acids containing the same number of
carbon atoms because aldehydes contain H-atom
4 Which of the following has the maximum acidic attached tocarbonyl group, which can be converted
strength? into -OH group without involving the cleavage of
(a) o-nitrobenzoic acid (b) m-nitrobenzoic acid
(c) any other bond. Thus, they are oxidised not only
p-nitrobenzoic acid (d) p-nitrophenol by strong oxidising agents like HNO, KMn0, and
The carbon atom next to carbonyl group is called K,Cr,0, but also by weak oxidising agents lie
0-carbon atom and hydrogens attached to -carbon Tollens' reagent, Fehling's solution and Benedits
atom are
-hydrogens. Due to strong electron reagent.
withdrawing effect of carbonyl group, the c-carbon R-CHO + [0] R-COOH
atom becomes electron deficient which in turn, Aldehyde Carboxylic acid
withdraws electrons from C-H bond. As a result, Unlikealdehydes, ketones do not contain H-alon
the electron density in Co-H bond decreases and cannot
hence, a-H atom becomes weakly held which can attached to C=0 group and hence, thhevTheseare
agents.
be oxidised by weak oxidising
be easily abstracted by strong bases agentslke
ion which is stabilised by resonance forming enolate
as given below: generally oxidised by strong oxidising
IK,CrO-athigh
HNO, acidified KMnO., , acidified
Ö: temperature. seleniumdioxide
9 Oxidation of acetaldehvde with
produces (b) oxalicacid
H :B (a) glyoxal (d) methanoicacid.
Resonance stabilised enolate anion
(c) ethanoicacid
You might also like
- General Chemistry - Darrell D. EbbingDocument724 pagesGeneral Chemistry - Darrell D. Ebbingnglok100% (9)
- General Chemistry Notes For SHS PDFDocument20 pagesGeneral Chemistry Notes For SHS PDFAlwyn Dave Ambatali100% (5)
- F AlkanesAlkenesStereochemTutorial 3Document4 pagesF AlkanesAlkenesStereochemTutorial 3Leong Yue YanNo ratings yet
- Molecular PolarityDocument4 pagesMolecular PolarityTea RadicNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science TermsDocument40 pagesEnvironmental Science TermsNasraRealinoNo ratings yet
- (Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology) Robert A. Meyers (Editor) - Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology - Polymers-Academic Press (2001)Document339 pages(Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology) Robert A. Meyers (Editor) - Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology - Polymers-Academic Press (2001)_Titchão_No ratings yet
- 2nd Periodical Examination in Sci g9Document4 pages2nd Periodical Examination in Sci g9george barnachea100% (6)
- Alkane: Preparation of Alkanes (6-Methods)Document20 pagesAlkane: Preparation of Alkanes (6-Methods)siddanshNo ratings yet
- Second Periodical Test in Science 9Document2 pagesSecond Periodical Test in Science 9tolisNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Carboxylic Acids and Its DerivativesDocument40 pagesReactions of Carboxylic Acids and Its DerivativesRoger ReyesNo ratings yet
- 02 - Carboxylic Acid (Theory) Module-5Document12 pages02 - Carboxylic Acid (Theory) Module-5Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons EX 1 - Tatva ModuleDocument19 pagesHydrocarbons EX 1 - Tatva ModuleS. S. Naren Karthik ShunmugamNo ratings yet
- 509Document19 pages509محمد رزاق مزهر جبرNo ratings yet
- Organic Synthesis Via Enolates BSC III CH IVDocument10 pagesOrganic Synthesis Via Enolates BSC III CH IVSanjay ShirodkarNo ratings yet
- 10.0 Carboxylic Acid 2022 (Lecturer)Document15 pages10.0 Carboxylic Acid 2022 (Lecturer)naderaqistina23No ratings yet
- Pre-Prelims Revision PaperDocument6 pagesPre-Prelims Revision PaperaaaaNo ratings yet
- Alkene and Alkyne - by Resonance PDFDocument45 pagesAlkene and Alkyne - by Resonance PDFPrasad Yarra100% (1)
- Organic CH Emistry Ii CHM301: Carboxylic AcidsDocument53 pagesOrganic CH Emistry Ii CHM301: Carboxylic AcidsWAN NUR AISYAH WAN AZIZANNo ratings yet
- CarbonylsDocument7 pagesCarbonylsThanadet PhongchompornNo ratings yet
- Ak Carboxylic AcidDocument2 pagesAk Carboxylic AcidsuryaisonemailNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid & Derivatives-01 - TheoryDocument21 pagesCarboxylic Acid & Derivatives-01 - TheoryRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Bottom of Pyramid - Test # 15 - Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsDocument7 pagesBottom of Pyramid - Test # 15 - Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsJay PatelNo ratings yet
- AlkynesDocument10 pagesAlkynesnafaamezzoudjNo ratings yet
- Pioneer Junior College Higher 2 Chemistry (9647) Carboxylic Acids and DerivativesDocument18 pagesPioneer Junior College Higher 2 Chemistry (9647) Carboxylic Acids and DerivativesTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- 07 IntegralsDocument27 pages07 IntegralsSubhangi MohantyNo ratings yet
- Alchol, Ethor Phenol Ex-1Document12 pagesAlchol, Ethor Phenol Ex-1Subhangi MohantyNo ratings yet
- 10 Acyl Chlorides and Acids NotesDocument18 pages10 Acyl Chlorides and Acids Noteswith love, alisha.No ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidDocument28 pagesCarboxylic AcidManthan HaritashNo ratings yet
- MCQ Chemistry Practice Qwestions Class 12thDocument8 pagesMCQ Chemistry Practice Qwestions Class 12thMithun ChakladarNo ratings yet
- Race-5 - Chem - Carbon & Its CompoundsDocument2 pagesRace-5 - Chem - Carbon & Its CompoundsShivang sharmaNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Their DerivativesDocument22 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Their DerivativesEugene OkpanteyNo ratings yet
- Bakliwal Tutorials: Organic Chemistry Assignment Topic: HydrocarbonsDocument17 pagesBakliwal Tutorials: Organic Chemistry Assignment Topic: HydrocarbonsJonathan ParkerNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Ch-8.Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument53 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Ch-8.Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acidskingoo0f1No ratings yet
- Kj/mol Kj/mol, Respectively. The Standard Enthalpy of Combustion Per Gram of GlucoseDocument8 pagesKj/mol Kj/mol, Respectively. The Standard Enthalpy of Combustion Per Gram of GlucosekolodoloNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactn McqsDocument12 pagesRedox Reactn McqsIlma GaurNo ratings yet
- Alk Enes Al Kynes ExercisesDocument1 pageAlk Enes Al Kynes ExercisesAR LazagaNo ratings yet
- CH 18Document32 pagesCH 18Dimas MitraNo ratings yet
- 29 Carboxylic Acids Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument9 pages29 Carboxylic Acids Formula Sheets Quizrrpowerranger34873No ratings yet
- 2021 2022 Organic Chemistry I Elimination ReactionsDocument28 pages2021 2022 Organic Chemistry I Elimination ReactionsAhmed ZakyNo ratings yet
- Basara Saraswathi CampusDocument5 pagesBasara Saraswathi CampusKalyan ReddtNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21-25 PDFDocument134 pagesChapter 21-25 PDFHimanshu RanjanNo ratings yet
- Unit-8 Ionic Equilibrium Mini 2023Document4 pagesUnit-8 Ionic Equilibrium Mini 2023jagannathanNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids, Anhydrides, Esters, and AmidesDocument35 pagesCarboxylic Acids, Anhydrides, Esters, and AmidesHarshwardhan PhatakNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids: Chapter 10 Lecture Notes: Carboxylic Acids, Amines, and AmidesDocument20 pagesCarboxylic Acids: Chapter 10 Lecture Notes: Carboxylic Acids, Amines, and AmidesABHISHEK MISHRANo ratings yet
- Chapter 20: Introduction To Carbonyl Chemistry Organometallic Reagents Oxidation and ReductionDocument41 pagesChapter 20: Introduction To Carbonyl Chemistry Organometallic Reagents Oxidation and ReductionRavi JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Feb 27, 2023Document2 pagesAdobe Scan Feb 27, 2023yimisa2927No ratings yet
- 01 Carboxylic Acids & Their Derivatives Theory Final EDocument29 pages01 Carboxylic Acids & Their Derivatives Theory Final EChandrapal RathoreNo ratings yet
- Chem Wa2Document2 pagesChem Wa2Balarama RajuNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument1 pageProblem SetIrish Blanza PonceNo ratings yet
- Advanced Organic Test Questionnaire Practice KeyDocument8 pagesAdvanced Organic Test Questionnaire Practice KeyJuitchiboy Nunez DumaoNo ratings yet
- Copper (I) Acetylacetonate: Catalysis of Michael AdditionsDocument2 pagesCopper (I) Acetylacetonate: Catalysis of Michael AdditionsHoratiu MoldovanNo ratings yet
- 29 Carboxylic Acids Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument8 pages29 Carboxylic Acids Formula Sheets QuizrrArjunNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-1) - PaperDocument15 pagesChemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-1) - PaperAnanmay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Himilo University Course Name: Organic ChemistryDocument37 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Himilo University Course Name: Organic ChemistryAbdulkarim FagaaseNo ratings yet
- Marvel MHT-CET Chemistry Paper 2021-September 22Document5 pagesMarvel MHT-CET Chemistry Paper 2021-September 22albertfredo777No ratings yet
- Aldehyde Ketone and Carboxylic AcidDocument3 pagesAldehyde Ketone and Carboxylic Acidsonidhruv2206No ratings yet
- Chapter 9. Aldehydes and Ketones: RC O R RC O Ar Ar C O Ar CODocument8 pagesChapter 9. Aldehydes and Ketones: RC O R RC O Ar Ar C O Ar COhanna liuNo ratings yet
- Consider The Following Anion CH CH CHCHDocument13 pagesConsider The Following Anion CH CH CHCHbobNo ratings yet
- Liquid Solutions, Surface Chemistry, Solid State RevisionDocument3 pagesLiquid Solutions, Surface Chemistry, Solid State RevisionAnonymous AshwinBalajiNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenol, & Ether - DPP 01 - Lakshya JEE 2.0 2024Document3 pagesAlcohol, Phenol, & Ether - DPP 01 - Lakshya JEE 2.0 2024chitranshpriyanshu80No ratings yet
- 03 - Acid Derivatives (Level) Module-5Document14 pages03 - Acid Derivatives (Level) Module-5Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Group Two AssignmentDocument7 pagesGroup Two Assignmentmaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- Nyb U4 Acids Bases Part 2Document81 pagesNyb U4 Acids Bases Part 2Aindrila KaziNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid & Derivatives-02 - Solved ProblemsDocument15 pagesCarboxylic Acid & Derivatives-02 - Solved ProblemsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsFrom EverandCritical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 05 Feb 2024Document1 pageAdobe Scan 05 Feb 2024krishrajput88888888No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 05 Feb 2024Document1 pageAdobe Scan 05 Feb 2024krishrajput88888888No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 05 Feb 2024Document1 pageAdobe Scan 05 Feb 2024krishrajput88888888No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 05 Feb 2024Document1 pageAdobe Scan 05 Feb 2024krishrajput88888888No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 05 Feb 2024Document1 pageAdobe Scan 05 Feb 2024krishrajput88888888No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 05 Feb 2024Document1 pageAdobe Scan 05 Feb 2024krishrajput88888888No ratings yet
- 3QPHYSICALSCIENCEDocument6 pages3QPHYSICALSCIENCELANIFER SongahidNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Periodicity (STUDENT) Edited 20apr2017 PDFDocument116 pages3.2 Periodicity (STUDENT) Edited 20apr2017 PDFAliffuddin MohamadNo ratings yet
- AnswersDocument34 pagesAnswers신재호No ratings yet
- Level-V: Single Answer QuestionsDocument20 pagesLevel-V: Single Answer QuestionsSurya teja cvNo ratings yet
- CPP 20220411175640609369Document92 pagesCPP 20220411175640609369Ronit NigamNo ratings yet
- Coordination Chemistry Module 1Document35 pagesCoordination Chemistry Module 1Praveen PradeepNo ratings yet
- Siop Lesson Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesSiop Lesson Chemical Bondingapi-423859884No ratings yet
- Physical Sciences GR 11 Exam Guidelines 2024 EngDocument28 pagesPhysical Sciences GR 11 Exam Guidelines 2024 EngFavour EmeruhNo ratings yet
- Mesl ElementsDocument110 pagesMesl ElementsJay Mark CayonteNo ratings yet
- IMF Answer Keys Revised 2014Document6 pagesIMF Answer Keys Revised 2014Monia AliNo ratings yet
- Topic 3,4,5&6 CH 4 Class 11thDocument3 pagesTopic 3,4,5&6 CH 4 Class 11thLakshaya SainiNo ratings yet
- 4.2.8 Polar Bears and Penguins WSDocument2 pages4.2.8 Polar Bears and Penguins WSLuna SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Course 201N 1 Semester 2006-2007 Inorganic Chemistry Instructor: Jitendra K. BeraDocument11 pagesCourse 201N 1 Semester 2006-2007 Inorganic Chemistry Instructor: Jitendra K. BeraanoopNo ratings yet
- Metal and Alloy Bonding: An Experimental AnalysisDocument168 pagesMetal and Alloy Bonding: An Experimental AnalysisSumit MaityNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Optical PropertiesDocument26 pagesElectrical and Optical PropertiesReinhard Dapot ManurungNo ratings yet
- Syllabus in Chemistry 1 (Nursing)Document4 pagesSyllabus in Chemistry 1 (Nursing)Rodel Matulin Catajay100% (1)
- 8 - AP Chemistry Unit 2 Worksheet Practice ProblemsDocument6 pages8 - AP Chemistry Unit 2 Worksheet Practice ProblemsNesrine LaradjiNo ratings yet
- Chem ProblemsDocument82 pagesChem ProblemsBeverly RamosNo ratings yet
- Covalent BondingDocument20 pagesCovalent BondingNadji Gadji-BaxisNo ratings yet
- Rocks Minerals Notes Kean UniversityDocument38 pagesRocks Minerals Notes Kean Universityapi-323312952No ratings yet
- The Properties of ProteinDocument41 pagesThe Properties of ProteinekaipNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Glasser ReactionDocument7 pagesMechanism of Glasser ReactionNabila Nur FadhilahNo ratings yet
- 14th Ntrca Teacher Registration Exam Syllabus 2017 College LevelDocument40 pages14th Ntrca Teacher Registration Exam Syllabus 2017 College LevelSamiul SamimNo ratings yet