Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial Week 4 For Students
Tutorial Week 4 For Students
Uploaded by
Th3warrior5 is bAcKOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial Week 4 For Students
Tutorial Week 4 For Students
Uploaded by
Th3warrior5 is bAcKCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial Week 4: MS2220 – Introduction to Fluid Mechanics
Collaborative Learning
Date: 8 February 2023, 17:00-19:00
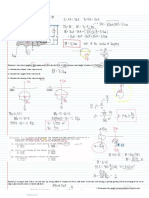
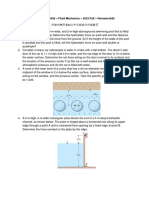
No.1:
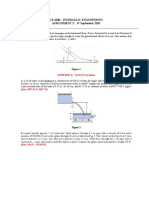
A gravity dam is shown in the figure. Calculate the magnitude and the location of the hydrostatic forces
acting on the headwater vertical wall of the dam and on the tailwater inclined wall of the dam. The slope
given is the ratio of the run to the rise. Consider a unit length of the dam ( b = 1 ft).
No2:
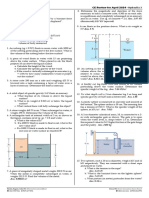
Assume a submarine can be modelled as a cylinder with length of 290 ft and diameter of 50 ft, with a
tower on top of it as shown in the figure. The submarine can dive a distance of 50 ft from the floating
position in about 30 s., by taking water into the ballast tank so the submarine will sink. When the
submarine reaches the desired depth, some of the water in the ballast tank is discharged leaving the
submarine in neutral bouyancy (it will not rise nor sink).
For the two conditions in the figure (partially submerged and totally submerged conditions), find:
a. The weight of the submarine, and
b. The volume of the water that must be in the ballast tank when the submarine is in neutral
bouyancy. Assume for the seawater, S.G. = 1.05. For pure water, 𝛾=62.4 lb/ft3.
You might also like
- Selected Problems in Physics with AnswersFrom EverandSelected Problems in Physics with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Seismic Response of Concrete Gravity DamDocument13 pagesSeismic Response of Concrete Gravity Damevan rulianNo ratings yet
- 206 Spring 2013 PDFDocument37 pages206 Spring 2013 PDFcombatps133% (3)
- Lecture HydraulicsDocument27 pagesLecture HydraulicsHarvey Pagaran0% (2)
- Fluid Mechanics 2Document10 pagesFluid Mechanics 2Jeffward Jaguio100% (1)
- Gravity Dam ForcesDocument15 pagesGravity Dam Forcesfaazizi100% (3)
- Hyd 3Document1 pageHyd 3Jocelyn CabarlesNo ratings yet
- Gravity DamDocument89 pagesGravity DamartiNo ratings yet
- The Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisFrom EverandThe Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisNo ratings yet
- Design of Concrete Gravity Dam SectionsDocument23 pagesDesign of Concrete Gravity Dam SectionsManan ParikhNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics 2Document12 pagesFluid Mechanics 2Acads by NagiNo ratings yet
- Compilation of Solved ProblemsDocument7 pagesCompilation of Solved ProblemsyslovillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Task 1Document2 pagesModule 2 Task 1Light HouseNo ratings yet
- SW - Buoyancy and Stability of Floating BodiesDocument4 pagesSW - Buoyancy and Stability of Floating Bodiesplm.riveralarissaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - CE2040Document4 pagesAssignment 2 - CE2040Ash0% (1)
- Dam AnalysisssDocument12 pagesDam AnalysisssCHOEYING DEMANo ratings yet
- The Effect of High Mercu On Water Jump On Type Vlughter (Laboratory Test)Document7 pagesThe Effect of High Mercu On Water Jump On Type Vlughter (Laboratory Test)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Lab 16 - Hydrostatic Forces and WorkDocument9 pagesLab 16 - Hydrostatic Forces and WorkMike JawNo ratings yet
- Booklet (Printable) PDFDocument8 pagesBooklet (Printable) PDFMarben Leynes-Cereno Agustin-ViernesNo ratings yet
- (01-25) Hydraulics 3Document2 pages(01-25) Hydraulics 3Ram CaniculaNo ratings yet
- Activity ManometerDocument7 pagesActivity ManometerSyamim HamizanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 3Document3 pagesProblem Set 3sweet mondayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Dams Part2 ModifiedDocument34 pagesChapter 4 Dams Part2 ModifiedAlkheder AlyazeediNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Force On A Plane Surface (Also See Lab Problems 2.122, 2.123, 2.124, and 2.125.)Document5 pagesHydrostatic Force On A Plane Surface (Also See Lab Problems 2.122, 2.123, 2.124, and 2.125.)JeanNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Chapter TwoDocument4 pagesAssignment On Chapter Twoalia balqisNo ratings yet
- Final Report (Hydrolic Structure 2)Document30 pagesFinal Report (Hydrolic Structure 2)Ahmed AmediNo ratings yet
- Vertical forces-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesVertical forces-WPS OfficeJesusa EstradaNo ratings yet
- 3 Tutorial Force Sept19Document6 pages3 Tutorial Force Sept19hairinnisaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 NewDocument4 pagesAssignment 4 NewDeepika DeepuNo ratings yet
- S1 Hyd Thrust T+answersDocument22 pagesS1 Hyd Thrust T+answersprabathiyaNo ratings yet
- 04 Buoyancy and StabilityDocument5 pages04 Buoyancy and StabilityFalconer AldNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Gravity DamsDocument10 pagesAnalysis of Gravity DamskerbyreyesmanaloNo ratings yet
- Ahmed Moayad Jameel, (Hydrolic Structure 1)Document18 pagesAhmed Moayad Jameel, (Hydrolic Structure 1)Ahmed AmediNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Forces On A Submerged Curved PlaneDocument10 pagesHydrostatic Forces On A Submerged Curved PlaneBlack SkyNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment IDocument5 pagesGroup Assignment Ilelisagetachew90No ratings yet
- ECW 231 Tutorial and Answers Buoyancy Sept19Document5 pagesECW 231 Tutorial and Answers Buoyancy Sept19hairinnisaNo ratings yet
- 2022MAY HPGE UnlockedDocument2 pages2022MAY HPGE UnlockedKristelle V. TorrealbaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics 2Document6 pagesHydraulics 2Raqz TVNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Analyze and Answer Each of The Following Problems. Show Your Complete Solutions WithDocument8 pagesInstructions: Analyze and Answer Each of The Following Problems. Show Your Complete Solutions WithMarben Leynes-Cereno Agustin-ViernesNo ratings yet
- Gravity DamsDocument17 pagesGravity DamsParikshith PrasadNo ratings yet
- Gravity Dam Forces SummaryDocument11 pagesGravity Dam Forces SummaryMohamoud AbdulahiNo ratings yet
- Open Channel Hydraulics 2nd Edition Sturm Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesOpen Channel Hydraulics 2nd Edition Sturm Solutions ManualWilliamDanielsezgj98% (47)
- Ece 2203 Assign Ii-2011Document2 pagesEce 2203 Assign Ii-2011Benson Mwathi MungaiNo ratings yet
- H&i NotesDocument17 pagesH&i Notesdr hs govardhana swamyNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document3 pagesHomework 2Kyle LuNo ratings yet
- Open Channel LabDocument27 pagesOpen Channel Labஅருண்ராஜ் கிருஷ்ணன்சாமிNo ratings yet
- Quiz No 1 Dams, Gates, and Outlet Works (Hydraulics)Document3 pagesQuiz No 1 Dams, Gates, and Outlet Works (Hydraulics)Erwin Jed RachoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics - Unit 2 Part 3Document27 pagesHydraulics - Unit 2 Part 3akhjazrNo ratings yet
- FLMC - 323 Tut 2Document2 pagesFLMC - 323 Tut 2christella machumiNo ratings yet
- 4 Module Hydraulics Gravity Dam1Document27 pages4 Module Hydraulics Gravity Dam1Eleazar Tami-ingNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document6 pagesTutorial 2nurulzamrinaNo ratings yet
- Ch13 SSMDocument18 pagesCh13 SSMJuanca AbadNo ratings yet
- 8b-Fluids FR Practice ProblemsDocument11 pages8b-Fluids FR Practice ProblemsdilsharakaviNo ratings yet
- Set ADocument2 pagesSet Aᜎᜒᜌᜓᜈᜒᜎ᜔ ᜄ᜔ᜏᜇᜒᜈ᜔100% (1)
- 2 2-AnalysisofgravitydamDocument12 pages2 2-AnalysisofgravitydammorganNo ratings yet
- H&i NotesDocument41 pagesH&i Notesdr hs govardhana swamyNo ratings yet
- Module 3 SW5Document13 pagesModule 3 SW5hgfhfghfghgNo ratings yet
- Submerged BreakwaterDocument19 pagesSubmerged Breakwaterananda dwi setiawan kresfiapriliantoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Sorsogon State University Engineering-Architecture Department Sorsogon City CampusDocument2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Sorsogon State University Engineering-Architecture Department Sorsogon City CampusArianne Mae De Vera GallonNo ratings yet
- Pressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910From EverandPressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910No ratings yet