Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Colorectal Cancer Genetic Syndromes
Uploaded by
Ryan Gosser0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageOriginal Title
COLORECTAL CANCER GENETIC SYNDROMES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageColorectal Cancer Genetic Syndromes
Uploaded by
Ryan GosserCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
COLORECTAL CANCER GENETIC SYNDROMES
Gene/Chr Signaling pathway Criteria Manifestations Surveillance
FAP APC/5q21 Adenoma-carcinoma >100 polyps at age 15 Duodenal adenomas – Colorectal cancer:
Autosomal sequence. Spiegelman criteria (number, size, - Annual flexi sig from age 10-12 until polyps detected then annual colonoscopies until
dominant APC = tumour suppressor Gardners syndrome = Colonic polyps, histology, dysplasia). Incr risk of colectomy.
gene for Wnt/b-catenin Desmoids, Osetomas of jaw, duodenal cancer. - AFAP/FAP – TC + IRA ~18 years – surveillance flexi sign annually.
pathway leading to sebaceous cysts Gastric fundic polyps - FAP - Completion proctocolectomy + IPAA after childbearing to preserve fertility and
excessive b-catenin Desmoids erectile function.
accumulation and Turcott’s = colonic polyps + childhood Papillary Thyroid cancer Duodenal adenomas:
oncogenesis. medulloblastoma. - Gastroscopies from age 25, frequency dependent on Spiegelman.
Loss of APC KRAS Thyroid cancer:
SMAD2/4 p53 AFAP = <100 polyps - Thyroid US from age 18 then 2-5 yearly.
HNPCC dMMR = dMMR of MLH1, MSH2, Modified Amsterdam II: CEO-GUO – CR, Endometrial, Colorectal cancer:
MLH1, MSH2, MSH6 and PMS2 DNA - 3 family members effected with Ovarian, Gastric, Urothelial, - Annual colonoscopies from age 25 or 5 years earlier than youngest affected relative.
MSH6, MPS2 mismatch and frameshift HRC, 1 of whom is a first degree Other (Breast and Pancreas) - Aspirin chemoprophylaxis 300mg daily to decrease hance of cancer, not polyps.
errors increased relative of the other two. cancers. - Segmental resection vs total colectomy + IRA and screening of rectal stump depends on
Autosomal microsatellites – - 2 successive generations compliance and other polyps.
dominant segments of repeated affected with HRC. Histology: LAMPS2 Endometrial cancer:
nucleotides (MSI) - 1 family member diagnosed age - Lymphoid aggregates - Recommend hysterectomy after childbearing complete or from age 40-50 years
Incr MSI = cancer <50 - Assoc. extra colonic cancers Ovarian cancer:
- FAP is excluded. - Mucinous cancers - Consider risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy at time of risk-reducing hysterectomy.
- Tumours should be verified by - Poorly Gastric cancer:
pathological examination differentiated/Proximal - Annual gastroscopy from age 25 or 5 years earlier than youngest affected relative.
HRC*= HNPCC related cancers. cancers
- Synchronous and signet cell
Muir Torre – skin tumours and breast cancer.
cancer.
MUTYH MUTYH gene Germline MUTYH Colonic adenomas and/or CR cancer <age 40 Colorectal cancer:
mutation predispose to serrated/hyperplastic polyp. Duodenal adenomas - Annual or 2-yearly colonoscopies from age 20
Autosomal developing APC ‘Lynch’ like – right sided, synchronous, Ovarian, Endometrial, Breast, - Consider prophylactic subtotal colectomy depending on polyp burden and/or dysplasia.
recessive mutations and the KRAS mucinous, high grade tumour with Bladder, Thyroid (PTC) Duodenal adenomas:
‘hotspot’ mutation. lymphoid aggregates. - Gastroscopy at age 35 then as per Spigelman.
Cowdens PTEN Germline mutation in Multiple hamartomatous syndrome. BETRC – Breast, Endometrial, Breast cancer:
(PTEN) PTEN, PIK3CA, AKT1. Thyroid, Renal, Colorectal - Annual MRI +/- US from age 30-50.
Autosomal cancers. - 1-2 yearly MMG + US from age 50 onwards.
dominant Skin – Trichollemas, - Consider bilateral risk-reducing mastectomy age <40.
mucocutaneous papillomas, acral Endometrial cancer:
keratosis. - Recommend hysterectomy after childbearing complete or from age 40-50 years
Head - Macocephaly Thyroid cancer:
- Annual clinical examination from age 5
Colorectal cancer:
- Colonoscopy from age 35 then as per polyp burden.
Peutz STK11 LKB1 protein is a tumour Multiple GI hamartomatous polyps GI cancers (CRC > Gastric > Gastrointestinal cancers:
Jeghers suppressor. and mucocutaneous pigmentation. Pancreatic) - Gastroscopy and Colonoscopy at age 8
Autosomal Breast cancer - If no polyps – recommence G+C scopes at age 18 then as per polyp burden.
dominant Gynecological cancers Breast cancer:
Testicular cancers - Annual MRI +/- US from age 30
- Tamoxifen from age 30
- Consider bilateral risk-reducing mastectomy
You might also like
- Breast Disease: Diagnosis and Pathology, Volume 1From EverandBreast Disease: Diagnosis and Pathology, Volume 1Adnan AydinerNo ratings yet
- Atypical Breast Proliferative Lesions and Benign Breast DiseaseFrom EverandAtypical Breast Proliferative Lesions and Benign Breast DiseaseFarin AmersiNo ratings yet
- COLORECTAL CANCER FINAL PPT To Be PresentedDocument53 pagesCOLORECTAL CANCER FINAL PPT To Be Presentedamanuel100% (1)
- 4-Ovarian Cancer PPDocument28 pages4-Ovarian Cancer PPtaha obaidNo ratings yet
- Endometrial Cancer: DR P Mukonoweshuro Consultant Pathologist RUH BathDocument59 pagesEndometrial Cancer: DR P Mukonoweshuro Consultant Pathologist RUH BathmesNo ratings yet
- Colorectal FAPDocument10 pagesColorectal FAPaizatamlikhaNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Risk and GeneticsDocument4 pagesBreast Cancer Risk and GeneticsRyan GosserNo ratings yet
- Singapore SalivaryDocument149 pagesSingapore Salivaryna huNo ratings yet
- CLINICAL CHEMISTRY 2 Tumor MarkersDocument3 pagesCLINICAL CHEMISTRY 2 Tumor MarkersSuzzaine EniazzusNo ratings yet
- Germ Cell TumoursDocument32 pagesGerm Cell Tumoursapi-3705046No ratings yet
- GYNCANCERDocument60 pagesGYNCANCERkieke123456No ratings yet
- Hereditary Cancer SyndromesDocument129 pagesHereditary Cancer SyndromesPooja BappannaNo ratings yet
- K8.Tumor Marker'sDocument47 pagesK8.Tumor Marker'sDwi Meutia IndriatiNo ratings yet
- Colorectal CaDocument55 pagesColorectal CasuperjaxxxonNo ratings yet
- CEA Levels Monitor Colon Cancer TreatmentDocument3 pagesCEA Levels Monitor Colon Cancer TreatmentTanveerNo ratings yet
- Benign and Malignant Lesion of Lower GIDocument45 pagesBenign and Malignant Lesion of Lower GIAhmad Alzu3beNo ratings yet
- Colorectal CancerDocument77 pagesColorectal CancerYazeed AsrawiNo ratings yet
- What Do You Need To Know About Breast Cancer: DR / Mokhtar Gusmallah Clinical OncologistDocument26 pagesWhat Do You Need To Know About Breast Cancer: DR / Mokhtar Gusmallah Clinical OncologistjehemirNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer - PPTX 2013Document49 pagesBreast Cancer - PPTX 2013heba1997bshNo ratings yet
- Afp - Colorectal Cancer Screening and Surveillance in Individuals at Increased RiskDocument6 pagesAfp - Colorectal Cancer Screening and Surveillance in Individuals at Increased RiskekoNo ratings yet
- ProtoDocument5 pagesProtoraNo ratings yet
- Neoplasms of Testis NishDocument54 pagesNeoplasms of Testis NishRamesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Tumor MarkersDocument23 pagesTumor MarkersThe Egy NerdNo ratings yet
- Hornick Carcinoma of Unknown Primary 8 June 1400Document87 pagesHornick Carcinoma of Unknown Primary 8 June 1400Olteanu Dragos-NicolaeNo ratings yet
- Ajdabya University Medical College - Colorectal Cancer Signs, Risks and ManagementDocument81 pagesAjdabya University Medical College - Colorectal Cancer Signs, Risks and Managementckyew64No ratings yet
- Endometrial Cancer An OverviewDocument47 pagesEndometrial Cancer An Overviewachala sahaiNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument4 pagesBreast CancerMaikka IlaganNo ratings yet
- Ajg 2017 212Document17 pagesAjg 2017 212afg_19No ratings yet
- Lynch SyndDocument4 pagesLynch SyndRamez AntakiaNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer: UnknownDocument3 pagesBreast Cancer: UnknownIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- Testicular Tumours 2020Document55 pagesTesticular Tumours 2020Ramesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Git 7 PDFDocument29 pagesGit 7 PDFafaq alismailiNo ratings yet
- Breast and Ovarian Cancer - PresentationDocument26 pagesBreast and Ovarian Cancer - PresentationRawa MuhsinNo ratings yet
- Thyroid CancersDocument10 pagesThyroid CancersskNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Tumours: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Classification, and ManagementDocument49 pagesOvarian Tumours: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Classification, and ManagementChoden JamyangNo ratings yet
- Triple Synchronous Malignancy CaseDocument21 pagesTriple Synchronous Malignancy CaseAshish SatyalNo ratings yet
- Dr. P. Karpagam Kiruba Rajeswari discusses risk factors and pathogenesis of breast carcinomaDocument59 pagesDr. P. Karpagam Kiruba Rajeswari discusses risk factors and pathogenesis of breast carcinomaIntan Eklesiana Napitupulu100% (1)
- CANCER GRADING VS STAGINGDocument40 pagesCANCER GRADING VS STAGINGKaren Joyce Costales MagtanongNo ratings yet
- Marnie and GidgetDocument33 pagesMarnie and GidgetMarnie ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cáncer Precoz, MastologíaDocument31 pagesCáncer Precoz, MastologíaDr. Pablo Maria Peralta LorcaNo ratings yet
- Management Gastric CancerDocument76 pagesManagement Gastric Cancerwawan siswokoNo ratings yet
- ReviewSheetExam2 (Pelvic)Document9 pagesReviewSheetExam2 (Pelvic)Solomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Carcinoma of UnknownDocument31 pagesCarcinoma of Unknownsamer falconNo ratings yet
- Unknown Primary - Diagnostic Approach Using IHC Hornick 7 Jan 2023Document70 pagesUnknown Primary - Diagnostic Approach Using IHC Hornick 7 Jan 2023na huNo ratings yet
- COLORECTAL CANCER: RISK FACTORS, ANATOMY, AND TREATMENT OPTIONSDocument80 pagesCOLORECTAL CANCER: RISK FACTORS, ANATOMY, AND TREATMENT OPTIONSElena CaterevNo ratings yet
- ManagementofColorectal CancerDocument13 pagesManagementofColorectal CancerAmbaNo ratings yet
- Tumor marker classification and applicationsDocument30 pagesTumor marker classification and applicationsnouval_iqbal100% (1)
- Lung CancerDocument22 pagesLung CancermandrakesMD100% (1)
- Malignant Diseases of The OvaryDocument64 pagesMalignant Diseases of The OvaryGÖKSU SAYGILINo ratings yet
- #Surgery - DR - Mohamed - Breast Tumors - 2Document53 pages#Surgery - DR - Mohamed - Breast Tumors - 2mariamNo ratings yet
- FM CasesDocument16 pagesFM CasesJameson87No ratings yet
- Colorectal CancerDocument6 pagesColorectal CancerAshiniNo ratings yet
- Dr. Pankaj Tejasvi: Dept. of Surgery MGMMC & MYH IndoreDocument76 pagesDr. Pankaj Tejasvi: Dept. of Surgery MGMMC & MYH IndoreDang HungNo ratings yet
- Cancer Screening and Genetics Risk Assessment for Hereditary CancersDocument42 pagesCancer Screening and Genetics Risk Assessment for Hereditary CancersrafatrujNo ratings yet
- 2 GYN ONC REVIEW Ovarian Cancer Genetics and ChemoDocument119 pages2 GYN ONC REVIEW Ovarian Cancer Genetics and ChemoHernan ParraNo ratings yet
- Breast PathologDocument51 pagesBreast Pathologjusttin779No ratings yet
- Pathology Week 6 p18-35Document18 pagesPathology Week 6 p18-35zeroun24No ratings yet
- Biomarkers (Tumor Markers, Cardiac Markers) : Clinical Chemistry IiDocument38 pagesBiomarkers (Tumor Markers, Cardiac Markers) : Clinical Chemistry IiJannica Dominique ClarosNo ratings yet
- Carcinoma RectumDocument28 pagesCarcinoma RectumParul VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Blastic Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Neoplasm: Shedding light on a rare diseaseFrom EverandFast Facts: Blastic Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Neoplasm: Shedding light on a rare diseaseNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous System OverviewDocument4 pagesPeripheral Nervous System OverviewNavid GhahremaniNo ratings yet
- Hormones & Chemical MessengersDocument9 pagesHormones & Chemical MessengersRyan GosserNo ratings yet
- Renal PhsyiologyDocument9 pagesRenal PhsyiologyRyan GosserNo ratings yet
- Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid Base PhysiologyDocument7 pagesFluid, Electrolyte and Acid Base PhysiologyVanathy KarunamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Membrane Transport LectureDocument8 pagesMembrane Transport LectureRyan GosserNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Regions Q's AnsDocument1 pageMandibular Regions Q's AnsRyan GosserNo ratings yet
- Emergency Hartmann's Procedure and Its Reversal - A Totally Laparoscopic 2-Step Surgery For The Treatment of Hinchey III and IV Diverticulitis PDFDocument9 pagesEmergency Hartmann's Procedure and Its Reversal - A Totally Laparoscopic 2-Step Surgery For The Treatment of Hinchey III and IV Diverticulitis PDFRyan GosserNo ratings yet
- CdromanceDocument1 pageCdromanceRyan GosserNo ratings yet
- MOD 2016-11-07 General Surgery Curriculum - CombinedDocument103 pagesMOD 2016-11-07 General Surgery Curriculum - CombinedRyan GosserNo ratings yet
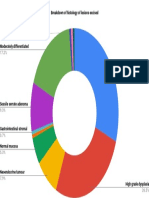
- Breakdown of Histology of Lesions ExcisedDocument1 pageBreakdown of Histology of Lesions ExcisedRyan GosserNo ratings yet
- MCQs in BasicDocument87 pagesMCQs in Basictausif0675% (4)
- Structure of Peritoneum: Where Does It Come From?Document40 pagesStructure of Peritoneum: Where Does It Come From?Ryan GosserNo ratings yet
- Head ExercisesDocument20 pagesHead ExercisesRyan GosserNo ratings yet
- Emergency Hartmann's Procedure and Its Reversal - A Totally Laparoscopic 2-Step Surgery For The Treatment of Hinchey III and IV Diverticulitis PDFDocument9 pagesEmergency Hartmann's Procedure and Its Reversal - A Totally Laparoscopic 2-Step Surgery For The Treatment of Hinchey III and IV Diverticulitis PDFRyan GosserNo ratings yet
- Back ExercisesDocument8 pagesBack ExercisesRyan GosserNo ratings yet
- Good and Cheap CookbookDocument67 pagesGood and Cheap CookbookSouthern California Public Radio100% (7)
- Icu GuidebookDocument43 pagesIcu Guidebookdrimran570100% (5)
- Spinach & Artichoke WonderpotDocument1 pageSpinach & Artichoke WonderpotRyan GosserNo ratings yet
- PGY3 and PGY3+ AH 2017Document4 pagesPGY3 and PGY3+ AH 2017Ryan GosserNo ratings yet
- Additional Provider NumberDocument3 pagesAdditional Provider NumberRyan GosserNo ratings yet
- hw062 1503enDocument7 pageshw062 1503enRyan GosserNo ratings yet
- hw062 1503enDocument7 pageshw062 1503enRyan GosserNo ratings yet
- Sealed with a Kiss Hit Song from 1962Document1 pageSealed with a Kiss Hit Song from 1962mrmarcoguimaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Flexible Learning EnvironmentDocument2 pagesModule 4 Flexible Learning EnvironmentRyan Contratista GimarinoNo ratings yet
- Ky203817 PSRPT 2022-05-17 14.39.33Document8 pagesKy203817 PSRPT 2022-05-17 14.39.33Thuy AnhNo ratings yet
- Smith Bell v. Sotello MattiDocument3 pagesSmith Bell v. Sotello MattijrvyeeNo ratings yet
- School RulesDocument2 pagesSchool RulesAI HUEYNo ratings yet
- Diagrama RSAG7.820.7977Document14 pagesDiagrama RSAG7.820.7977Manuel Medina100% (4)
- Tax 1Document351 pagesTax 1AbbyNo ratings yet
- A Powerful Graphic Liquid Crystal Display: Column #47, March 1999 by Lon GlaznerDocument16 pagesA Powerful Graphic Liquid Crystal Display: Column #47, March 1999 by Lon GlaznerVijay P PulavarthiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 of LPL Textbook PDFDocument26 pagesChapter 3 of LPL Textbook PDFandreaNo ratings yet
- Window On The Wetlands BrochureDocument2 pagesWindow On The Wetlands BrochureliquidityNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - LISDocument24 pagesUnit 2 - LISThục Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 6 - 2010 Chapter 5 - Contrasting Cultural ValuesDocument39 pages6 - 2010 Chapter 5 - Contrasting Cultural ValuesHari KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engines 16V 4000 M23/M33: 50 HZ 60 HZDocument2 pagesDiesel Engines 16V 4000 M23/M33: 50 HZ 60 HZAlberto100% (1)
- On Healing Powers: Asclepius, Caduceus and AntibodiesDocument4 pagesOn Healing Powers: Asclepius, Caduceus and AntibodiesasclepiuspdfsNo ratings yet
- Teaching As Noble ProfessionDocument1 pageTeaching As Noble ProfessionJeric AcostaNo ratings yet
- CLASS 7B Result Software 2023-24Document266 pagesCLASS 7B Result Software 2023-24JNVG XIB BOYSNo ratings yet
- Guide To Kulchur 1938Document374 pagesGuide To Kulchur 1938Jonathan CarsonNo ratings yet
- OOD ch11Document31 pagesOOD ch11Pumapana GamingNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 4 - Group 6Document15 pagesLab Report 4 - Group 6ClarisshaNo ratings yet
- Ume Mri GuideDocument1 pageUme Mri GuideHiba AhmedNo ratings yet
- IFCRecruitment Manual 2009Document52 pagesIFCRecruitment Manual 2009Oklahoma100% (3)
- UTH homework template for English exercisesDocument8 pagesUTH homework template for English exercisesCinthya Peña de MezaNo ratings yet
- EASE Module 1 Geometric RelationsDocument26 pagesEASE Module 1 Geometric RelationsMarlon MiclatNo ratings yet
- TNPSC Vas: NEW SyllabusDocument12 pagesTNPSC Vas: NEW Syllabuskarthivisu2009No ratings yet
- Quality Management in Apparel Industry PDFDocument9 pagesQuality Management in Apparel Industry PDFJyoti Rawal0% (1)
- Engineers Guide To Microchip 2018Document36 pagesEngineers Guide To Microchip 2018mulleraf100% (1)
- Wiring Diagram Obp 1 v2Document5 pagesWiring Diagram Obp 1 v2Jorge Luis Vera AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion: Problem SetDocument9 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion: Problem SetRoda Gayle RañadaNo ratings yet
- Our Lady of Consolation Orchestra InstrumentsDocument2 pagesOur Lady of Consolation Orchestra InstrumentsCelestian Valensario PaderangaNo ratings yet
- Bruce MoenDocument4 pagesBruce MoenGeorge Stefanakos100% (5)