Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AMINES Xii
Uploaded by
ZONE OF CUBE0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views17 pagesAmines
Original Title
AMINES-xii (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAmines
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views17 pagesAMINES Xii
Uploaded by
ZONE OF CUBEAmines
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
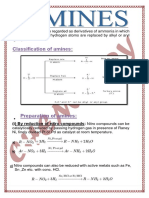
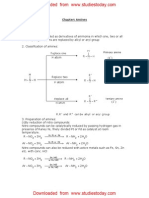
Ammonolysis has the disadvantage of
yielding a mixture of primary, secondary and
tertiary amines and also a quaternary
ammonium salt.
However, primary amine is obtained as a
major product by taking large excess of NH3.
Order of reactivity of halides ‘with amines is
RI > RBr > RCI.
Aromatic amines could not be prepared since
aryl halides are much less reactive towards
nucleophilic substitution reactions.
It only produces 1 0 amines. This method is not suitable for
1° arylamine because aryl halide does not give
nucleophilic substitution reaction.
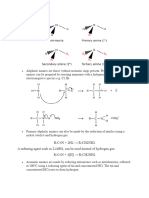
All the three types of amines react with alkyl
halides to form quaternary ammonium salt as the
final product provided alkyl halide is present in
excess.
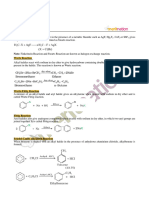
[Hinsberg reagent] The reaction of
benzenesulphonyl chloride with primary amine
yield N-ethyl benzenesulphonyl amide.
Schiff base is obtained.
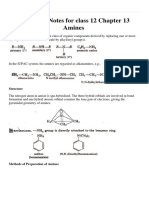
Aniline is ortho and para directing towards
electrophilic substitution reaction due to
high electron density at ortho and para-
positions.
Direct nitration of aniline is not possible as it
is susceptible to oxidation, thus amino
group is first protected by acetylation.
In strongly acidic medium, aniline is protonated as
anilinium ion which is meta directing so it gives
meta product also.
Aniline does not undergo Friedel-Crafts
reaction due to salt formation with aluminium
chloride, the Lewis acid, which is used as a
catalyst. Due to this, nitrogen of aniline
acquires positive charge and hence. behave
like a strong deactivating group for further
chemical reaction
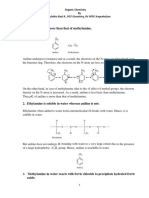
(C6H5N2+;Cl–)
Preparation (Diazotisation reaction)
It is relatively more stable than the alkyldiazonium
salt. The arenediazonium ion is resonance
stabilised as is indicated by the following
resonating structures:
You might also like
- Amines, Amide and Derivatives: Edit and Compiled By: Hafiz Abdul Rafay Latif KayaniDocument26 pagesAmines, Amide and Derivatives: Edit and Compiled By: Hafiz Abdul Rafay Latif KayaniPalwasha KardarNo ratings yet
- 13 AminesDocument8 pages13 AminesShesha krishnaNo ratings yet
- Anubhav Chemistry ProjectDocument15 pagesAnubhav Chemistry ProjectManojNo ratings yet
- AMINEDocument38 pagesAMINErabindeka887No ratings yet
- Notes For Chemistry Class 12 Chapter 13 AminesDocument22 pagesNotes For Chemistry Class 12 Chapter 13 AminesVanshika JainNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes For Class 12 CBSE Chemistry, Amines - TopperlearningDocument11 pagesRevision Notes For Class 12 CBSE Chemistry, Amines - TopperlearningRishabh BhandariNo ratings yet
- Note For EJU 29Document3 pagesNote For EJU 29mr.draungnaingwinNo ratings yet
- Amines NCERTDocument10 pagesAmines NCERTvishwak.boddukuriNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Notes ch13 AminesDocument11 pages12 Chemistry Notes ch13 AminesAkNo ratings yet
- AMINESDocument4 pagesAMINESMudit SharmaNo ratings yet
- AMINESDocument4 pagesAMINESmuhammadNo ratings yet
- STD XII Class Note Chapter 12 13 2021 22Document16 pagesSTD XII Class Note Chapter 12 13 2021 22Saurabh ShekharNo ratings yet
- Amines: Structure of Amines-Nitrogen Orbitals in Amines Are, SP Hybridised With One Lone PairDocument20 pagesAmines: Structure of Amines-Nitrogen Orbitals in Amines Are, SP Hybridised With One Lone PairVicky VigneshNo ratings yet
- PK of Aniline Is More Than That of Methylamine.: Organic Chemistry by Sulekha Rani.R, PGT Chemistry, KV NTPC KayamkulamDocument6 pagesPK of Aniline Is More Than That of Methylamine.: Organic Chemistry by Sulekha Rani.R, PGT Chemistry, KV NTPC KayamkulamAneesh PBNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument3 pagesDocumentShreeNo ratings yet
- AMINESDocument59 pagesAMINESJanna May Acierto100% (1)
- 12 Notes Ammines and AcidsDocument11 pages12 Notes Ammines and AcidsXyzdevuNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature: Chapter 19: AminesDocument5 pagesNomenclature: Chapter 19: AminesRobert GardnerNo ratings yet
- Thing To Remember For Amines - MainDocument3 pagesThing To Remember For Amines - MainaayushhariharanNo ratings yet
- Chap 13 Nitrogen CompoundsDocument43 pagesChap 13 Nitrogen Compoundssukaina fatimaNo ratings yet
- Anims and UreaDocument25 pagesAnims and UreaShivam GuptaNo ratings yet
- AminesDocument10 pagesAminesDUHA GORASHINo ratings yet
- Hsslive XII Chemistry Amines NoteDocument4 pagesHsslive XII Chemistry Amines Notetrendzz youtuberNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry - Amines Chapter NotesDocument12 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry - Amines Chapter NotesGayathiriNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From SUPERCOPDocument11 pagesMaterial Downloaded From SUPERCOPSidNo ratings yet
- Amine IIDocument12 pagesAmine IIjohnsmithprayNo ratings yet
- 21st July 2020Document5 pages21st July 2020Aneesh MathewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22Document21 pagesChapter 22AbdulhafizNo ratings yet
- Topic:-Nomenclature: 1. Give IUPAC Name ofDocument16 pagesTopic:-Nomenclature: 1. Give IUPAC Name ofkannan2030No ratings yet
- Group 1-AMINES PART 1Document82 pagesGroup 1-AMINES PART 1Jana PaduaNo ratings yet
- Amines and Their Derivatives:Functional Groups Containing NitrogenDocument46 pagesAmines and Their Derivatives:Functional Groups Containing NitrogenKunjalNo ratings yet
- Amine: The General Structure of An AmineDocument16 pagesAmine: The General Structure of An AmineCarla WashingtonNo ratings yet
- ch20 Amines Part2Document7 pagesch20 Amines Part2kumber_singh5069No ratings yet
- Important Chemical Reactions For Class 12 Chemistry With MechanismDocument9 pagesImportant Chemical Reactions For Class 12 Chemistry With MechanismSoma SahaNo ratings yet
- AminesDocument12 pagesAminesEmelda BanumathyNo ratings yet
- AMINES Anil HssliveDocument9 pagesAMINES Anil HssliveRanit MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Naming Reactions Organic ChemistryDocument8 pagesNaming Reactions Organic Chemistrysaapldesign1 1No ratings yet
- CH 13Document12 pagesCH 13Tr Mazhar PunjabiNo ratings yet
- AminesDocument2 pagesAminesatharvdubey29No ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-02 Class - Xii Chemistry (Amines) (Answers) Topic:-Reasoning QuestionsDocument2 pagesCbse Test Paper-02 Class - Xii Chemistry (Amines) (Answers) Topic:-Reasoning QuestionsShreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry All Important ReactionsDocument14 pagesChemistry All Important Reactionsaayushnair2506100% (1)
- Important Chemical Reactions For Class 12 ChemistryDocument10 pagesImportant Chemical Reactions For Class 12 ChemistryRitishNo ratings yet
- AminesDocument62 pagesAminesmitul muhammedNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xii CH 9 Amines AnilDocument8 pagesHsslive Xii CH 9 Amines AnilFathima NithinshaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Revision Notes AminesDocument26 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Revision Notes AminesABHISEKNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Important Reagents-EditDocument19 pagesOrganic Chemistry Important Reagents-Edit10C 27 SAI VISHWA JETHNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Name ReactionDocument13 pagesOrganic Chemistry Name ReactionDeep GuptaNo ratings yet
- AMINESDocument58 pagesAMINESHarsh Shah100% (1)
- Amines WS 1 TheoryDocument3 pagesAmines WS 1 TheorytotallynotparthdubeyNo ratings yet
- Organic Named Reactions PDFDocument8 pagesOrganic Named Reactions PDFAshis BisoyiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry-Named ReactionsDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry-Named Reactionsatharvbaghel4444No ratings yet
- Ist Assignment On Amine 1.12.22Document7 pagesIst Assignment On Amine 1.12.22Sprabhu ParamNo ratings yet
- Iumportant ReactionsDocument9 pagesIumportant ReactionsAakash ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Named Reaction InDetail by MeritnationDocument9 pagesOrganic Chemistry Named Reaction InDetail by MeritnationAtif AteeqNo ratings yet
- 2 Name ReactionsDocument10 pages2 Name ReactionsArvindKumar100% (1)
- Silicon in Organic Synthesis: Butterworths Monographs in Chemistry and Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandSilicon in Organic Synthesis: Butterworths Monographs in Chemistry and Chemical EngineeringNo ratings yet