Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Jamie Grace AbitOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Jamie Grace AbitCopyright:
Available Formats
Jamie Grace A.
Abit February 3, 2024
Lexus Dayne G. German
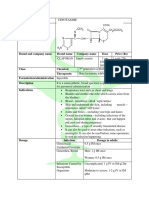
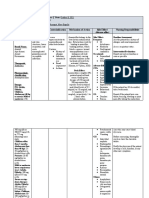
DRUG STUDY
DRUG NAME CLASSIFICATION MECHANISM OF ACTION INDICATIONS
Generic Name: Cephalosporin Interferes with bacterial ✓ Moderate to severe infections,
Cefuroxime Sodium Antibiotics cell-wall synthesis and including those of skin, bone,
division by binding to cell joints, urinary or respiratory tract,
Brand Name:
wall, causing cell to die. gynecologic infections
Eroxime
Active against gram- Adults and children ages 12 and older:
Actual dosage, Route, negative and gram-positive 750 mg to 1.5 g I.M. or I.V. q 8 hours for 5
Frequency: bacteria, with expanded to 10 days or 250 to 500 mg P.O. q 12
Adults and children activity against gram- hours
ages 12 and older: negative bacteria. Children ages 3 months to 12 years: 50
Up to 3 g I.V. or I.M. Exhibits minimal to 100 mg/kg/day I.V. or I.M. in divided
q 8 hours immunosuppressant activity. doses q 6 to 8 hours
Children ages 3 ✓ Gonorrhea
months to 12 years: Adults: 750 mg to 1.5 g I.M. or I.V. as a
200 to 240 mg/kg I.V. single dose, or 1.5 g I.M. (750 mg in two
daily in divided doses separate sites), given with 1 g probenecid
q 6 to 8 hours P.O.
✓ Bacterial meningitis
Adults and children ages 12 and older:
Up to 3 g I.V. or I.M. q 8 hours
Children ages 3 months to 12 years: 200
to 240 mg/kg I.V. daily in divided doses q
6 to 8 hours
✓ Otitis media
Children ages 3 months to 12 years: 15
mg/kg P.O. q 12 hours (oral suspension)
for 10 days, or 250 mg (tablets) P.O. q 12
hours for 10 days
✓ Pharyngitis; tonsillitis
Adults and children ages 13 and older:
250 mg P.O. b.i.d. for 10 days
Children ages 3 months to 12 years: 125
mg P.O. q 12 hours for 10 days, or 20
mg/kg/day P.O. in two divided doses for 10
days as oral suspension (maximum 500
mg/day)
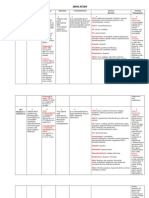
CONTRAINDICATIONS ADVERSE REACTIONS NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
• Hypersensitivity to CNS: headache, hyperactivity, Patient monitoring:
cephalosporins or hypertonia, seizures ✓ Monitor patient for life-
penicillins GI: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, threatening adverse effects,
• Carnitine deficiency abdominal pain, dyspepsia, including anaphylaxis, Stevens-
pseudomembranous colitis Johnson syndrome, and
GU: hematuria, vaginal candidiasis, renal pseudomembranous colitis.
dysfunction, acute renal failure ✓ Monitor neurologic status,
Hematologic: hemolytic anemia, aplastic particularly for signs of
anemia, hemorrhage impending seizures.
Hepatic: hepatic dysfunction ✓ Monitor kidney and liver function
Metabolic: hyperglycemia test results and intake and output.
Skin: toxic epidermal necrolysis, ✓ Monitor CBC with differential
erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson and prothrombin time; watch for
syndrome signs and symptoms of blood
Other: allergic reaction, drug fever, dyscrasias.
superinfection, anaphylaxis ✓ Monitor temperature; watch for
signs and symptoms of
superinfection.
Patient Teaching:
✓ Advise patient to immediately
report rash or bleeding tendency.
✓ Instruct patient to take drug with
food every 12 hours as prescribed.
✓ Teach patient how to recognize
signs and symptoms of
superinfection. Instruct him to
report these right away.
✓ Advise patient to report CNS
changes.
You might also like
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Gi Gu Pregnancy - BoardsDocument12 pagesGi Gu Pregnancy - BoardsSoojung NamNo ratings yet
- Drug STUDY CefotaximeDocument5 pagesDrug STUDY CefotaximeCrystal Jade100% (1)
- Drug Study: Pharmacologic AlDocument7 pagesDrug Study: Pharmacologic AlFrudz Orjaleza100% (1)
- Cii Seniorcareindustryreportindia2018 180524043125Document36 pagesCii Seniorcareindustryreportindia2018 180524043125N InbasagaranNo ratings yet
- Finding Dory Ed GuideDocument43 pagesFinding Dory Ed GuideMirelaCojocaruNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport WorksheetDocument2 pagesCell Transport WorksheetVictoria Niño D100% (1)
- Construction Techniques For Bored Piling in Sand Using Polymer FluidsDocument10 pagesConstruction Techniques For Bored Piling in Sand Using Polymer FluidsjohnNo ratings yet
- 2nd Drug StudyDocument39 pages2nd Drug StudyYanna Habib-Mangotara100% (3)
- Microsoft Office 365 Customer Decision FrameworkDocument14 pagesMicrosoft Office 365 Customer Decision FrameworkthinkofdevilNo ratings yet
- Types of Malware and Importance of Malware AnalysisDocument10 pagesTypes of Malware and Importance of Malware AnalysisshaletNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Drug Dosage - All in OneDocument15 pagesPediatric Drug Dosage - All in OneBJ Tiew100% (1)
- The Best of Bruce's Postgres Slides: Ruce OmjianDocument26 pagesThe Best of Bruce's Postgres Slides: Ruce OmjianPhotoHawkNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report On Reading InterventionDocument5 pagesNarrative Report On Reading InterventionDyelain 199x100% (1)
- Pediatric Drug Dosage - All in One PDFDocument15 pagesPediatric Drug Dosage - All in One PDFHuang Hasjim33% (9)
- Static Var CompensatorDocument29 pagesStatic Var CompensatorCarlos Fabian GallardoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudybaniniycsebNo ratings yet
- Autonomy of Art or Dignity of The Artwork? - Agnes HellerDocument20 pagesAutonomy of Art or Dignity of The Artwork? - Agnes HellerProfrFer100% (1)
- 8th Sem BE VTU Seminar FormatDocument6 pages8th Sem BE VTU Seminar FormatSourabhAdike80% (15)
- Ampicillin PDFDocument3 pagesAmpicillin PDFandriNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Machado Oct 172022Document2 pagesDrug Study Machado Oct 172022RenNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Tract Infections - Med DidacticsDocument59 pagesRespiratory Tract Infections - Med Didacticsapi-649060644No ratings yet
- Material, Vincent M. Drug Study - (Ceftriaxone and Salbutamol)Document6 pagesMaterial, Vincent M. Drug Study - (Ceftriaxone and Salbutamol)vincent materialNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument15 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionsAnonymous elSqPhzKNo ratings yet
- AmoxicillinDocument2 pagesAmoxicillinjedisay1No ratings yet
- YOUNG MIN LEE CASE STUDY Update 2Document7 pagesYOUNG MIN LEE CASE STUDY Update 2E.R.ONo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument12 pagesGeneric NameDeborah Mae MondoyNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Guidelines Nephrotic Syndrome 2018Document8 pagesPaediatric Guidelines Nephrotic Syndrome 2018lilydariniNo ratings yet
- 4th Bi Oral TopicsDocument18 pages4th Bi Oral TopicsPuguinGamingNo ratings yet
- Enteral InfectionsDocument6 pagesEnteral InfectionsAshley CheungNo ratings yet
- FlagylDocument2 pagesFlagylianecunarNo ratings yet
- CececeDocument57 pagesCececeBSRT1A BERBANO, IAN JEWEL M.No ratings yet
- CefotaximeDocument5 pagesCefotaximerimarahmadiptaNo ratings yet
- Vince Drug Study LaboratoryDocument6 pagesVince Drug Study LaboratoryUzziel Galinea TolosaNo ratings yet
- Moderate To Severe Infections: Nursing Related Learning Experience ManualDocument3 pagesModerate To Severe Infections: Nursing Related Learning Experience Manualclint xavier odangoNo ratings yet
- CPG On Acute Infectious Diarrhea 2021Document42 pagesCPG On Acute Infectious Diarrhea 2021babbettemdNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument4 pagesGeneric NamePharmacist Amy CharlieNo ratings yet
- Clinical Practice Guidelines ON Acute Gastro-Enteritis: Santissima Trinidad HospitalDocument3 pagesClinical Practice Guidelines ON Acute Gastro-Enteritis: Santissima Trinidad HospitalEspie FerrerNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin (Amoxycillin) : PresentationDocument4 pagesAmoxicillin (Amoxycillin) : PresentationRavikiran SuryanarayanamurthyNo ratings yet
- Penicillin: Libre, Princess Melanie SDocument19 pagesPenicillin: Libre, Princess Melanie SIrene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - IbuprofenDocument7 pagesDrug Study - IbuprofenajNo ratings yet
- Parasitic WormsDocument4 pagesParasitic WormsEricNo ratings yet
- Questions:: Clinical Case Analysis Name of Patient Age: 52 Gender: M Address Date Admitted: Diagnosis Nursing HistoryDocument12 pagesQuestions:: Clinical Case Analysis Name of Patient Age: 52 Gender: M Address Date Admitted: Diagnosis Nursing Historyaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Rle Neonate DrugsDocument13 pagesRle Neonate DrugsLhara Vhaneza CuetoNo ratings yet
- BaxetDocument1 pageBaxetjtehdz22No ratings yet
- Final Drug Study MeropenemalbendazoleDocument10 pagesFinal Drug Study MeropenemalbendazoleLuis WashingtonNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Chronic Diarrhea Mild Dehydration-Corrected: Was Diagnosed With PneumoniaDocument5 pagesPneumonia Chronic Diarrhea Mild Dehydration-Corrected: Was Diagnosed With PneumoniaLyan SamsonNo ratings yet
- INF (Isonicotinic Acid Hydrzide or Isoniazide) : Adult: Patient MonitoringDocument4 pagesINF (Isonicotinic Acid Hydrzide or Isoniazide) : Adult: Patient MonitoringEem Khaye YamsonNo ratings yet
- Kumpulan Daftar ObatDocument6 pagesKumpulan Daftar ObatZega AgustianNo ratings yet
- DrugDocument2 pagesDrugmitsuki_sylphNo ratings yet
- Giardiasis Causing Both Endemic and Epidemic Intestinal Disease and DiarrheaDocument7 pagesGiardiasis Causing Both Endemic and Epidemic Intestinal Disease and Diarrheanathan asfahaNo ratings yet
- Acyclovir (Systemic) - Pediatric Drug Information - UpToDate PDFDocument34 pagesAcyclovir (Systemic) - Pediatric Drug Information - UpToDate PDFAndreea LupuNo ratings yet
- Dumlao, Michelin H.Document20 pagesDumlao, Michelin H.Mich DumlaoNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: Mos.: 25-50 Mg/kg/day in 3 Divided Doses. Children 3 Mos and Younger: 30Document9 pagesAntibiotics: Mos.: 25-50 Mg/kg/day in 3 Divided Doses. Children 3 Mos and Younger: 30Kath TagamolilaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Policy - Final GovtMP - 211215 - 121049Document40 pagesAntibiotic Policy - Final GovtMP - 211215 - 121049Charchit MehtaNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Placenta Previa: Patient's Demographic DataDocument9 pagesCase Study of Placenta Previa: Patient's Demographic DataImee JenNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Amoxicillin - Abad & Bumagat - BSN 214Document4 pagesDrug Study - Amoxicillin - Abad & Bumagat - BSN 214Ysabel Francesca AbadNo ratings yet
- NAG Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument14 pagesNAG Urinary Tract InfectionsJun JimenezNo ratings yet
- Valgancyclovir MOA: Uses Pharmacokinetics Dosage Side Effects ContraindicationsDocument2 pagesValgancyclovir MOA: Uses Pharmacokinetics Dosage Side Effects ContraindicationsiSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- Cep Halo Sporin SDocument9 pagesCep Halo Sporin SJasper VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Cephalexin Drug Study RNpedia ComDocument2 pagesCephalexin Drug Study RNpedia ComTaraKyleUyNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime AxetilDocument4 pagesCefuroxime AxetilSebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- No Nama Indikasi Sediaan Kelas 1 Amoxicillin Tablet: 500mg PenicillinDocument3 pagesNo Nama Indikasi Sediaan Kelas 1 Amoxicillin Tablet: 500mg PenicillinwandawinkyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyJuliana LegarteNo ratings yet
- أروى حكميDocument16 pagesأروى حكميArwa HakamiNo ratings yet
- DrugmedsDocument52 pagesDrugmedsshirleyNo ratings yet
- Food Poisoning DefinitionDocument10 pagesFood Poisoning DefinitionMaria Pina Barbado PonceNo ratings yet
- AciclovirDocument8 pagesAciclovirEphrem LemmaNo ratings yet
- Ampicillin DRUG STUDYDocument2 pagesAmpicillin DRUG STUDYJuliana CarpinteroNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea: Bloody 1-2daysDocument3 pagesDiarrhea: Bloody 1-2daysKassem HijazyNo ratings yet
- Nutrition ToolsDocument6 pagesNutrition ToolsJamie Grace AbitNo ratings yet
- MINERALSDocument19 pagesMINERALSJamie Grace AbitNo ratings yet
- Mt. MicronutrientsDocument10 pagesMt. MicronutrientsJamie Grace AbitNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Excel WorksheetDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Excel WorksheetJamie Grace AbitNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Lab-Practicals-No3 StainingDocument2 pagesMicrobiology Lab-Practicals-No3 StainingJamie Grace AbitNo ratings yet
- Smart School EseiDocument15 pagesSmart School Eseiz89100% (1)
- Seward Stomacher 400Document2 pagesSeward Stomacher 400ugomiesterNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet According To EEC-Regulation 91/155/EECDocument6 pagesSafety Data Sheet According To EEC-Regulation 91/155/EECANIBALLOPEZVEGANo ratings yet
- Project Charter.: Project Title:-A Google GlassesDocument3 pagesProject Charter.: Project Title:-A Google GlassesAliceNo ratings yet
- Singtel Annual Report 2023 Higher ResDocument275 pagesSingtel Annual Report 2023 Higher ResJL ChuaNo ratings yet
- OCI Introduction: Presented By: Rahul MiglaniDocument21 pagesOCI Introduction: Presented By: Rahul Miglanisss pppNo ratings yet
- Hazyl Delerosario@ctu Edu PHDocument4 pagesHazyl Delerosario@ctu Edu PHDulce Amor del RosarioNo ratings yet
- What's in Your BackpackDocument31 pagesWhat's in Your Backpackjohn ezekiel de asisNo ratings yet
- Image Harmonization With Diffusion ModelDocument8 pagesImage Harmonization With Diffusion Modelzhangzhengyi443No ratings yet
- Tele BRANCHES 01.06.2021Document23 pagesTele BRANCHES 01.06.2021Abhishek BarwalNo ratings yet
- Constructing The Spatial Weights Matrix Using A Local StatisticDocument15 pagesConstructing The Spatial Weights Matrix Using A Local StatisticbwcastilloNo ratings yet
- Top Tips For Marriage Habits For A Happy Marriage 2019Document2 pagesTop Tips For Marriage Habits For A Happy Marriage 2019Marcel Henri Pascal Patrice Moudiki KingueNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Mount EverestDocument4 pagesAn Introduction To Mount EverestJihad HasanNo ratings yet
- Methods of Teaching 1 and 6Document68 pagesMethods of Teaching 1 and 6BUEN, RENZZELLE JOY B.No ratings yet
- Vitamins and Minerals Lecture NotesDocument9 pagesVitamins and Minerals Lecture NotesJoymae Olivares Tamayo100% (1)
- Gregg Djs Dict OcrDocument424 pagesGregg Djs Dict OcrscribdNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Pressure Distribution in FluidDocument22 pagesLecture 3 - Pressure Distribution in FluidChristophe EmerichNo ratings yet
- Master Thesis In-Depth InterviewsDocument5 pagesMaster Thesis In-Depth Interviewsrqopqlvcf100% (1)
- GRP 1Document2 pagesGRP 1Yuva RaniNo ratings yet