Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes - Prof - Video - Revenue Cycle
Uploaded by
Jasmin Abigail MoradasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Notes - Prof - Video - Revenue Cycle
Uploaded by
Jasmin Abigail MoradasCopyright:
Available Formats
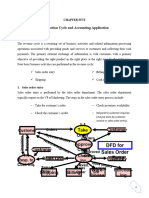
Revenue Cycle Overview
Prof – Video – Revenue Cycle
Revenue Cycle: Sales to Cash Collection
What is a Revenue Cycle?
- It is a recurring set of business activities and
related information processing operations.
- It is associated with providing goods or
services to a customer.
- It is a collection of cash in payment for the
sales.
- It is what it takes to provide a customer the
goods and services they want and collect
payments from those customers.
Primary Objective:
- It is to provide the right product in the right
place at the right time for the right price.
Four Basic Revenue Cycle Activities:
1. Sales Order Entry
2. Shipping
3. Billing
4. Cash Collection
*Sale a Ship with Billy Cash
Threats:
- Theft of Cash
- Cyber Attacks
- Inaccurate Journal Entries
- Running Out of Inventories
General Threats:
- Gather Inaccurate or Invalid Master Data
- Unauthorized Disclosure of Sensitive
Information
- Losing or Destroying Valuable Data
- Poor Performance Throughout the Entire
Cycle
Real-Life Threats:
- Ordering online without an address would
make it difficult to deliver the order.
- Using a third party to deliver the goods and
only half of the order makes it to the
destination (one to the order address and one
to the delivery guy’s house).
- The billing clerk forgets to send the bill to the
customer.
Sales Order Entry
Prof – Video – Revenue Cycle
Four Steps of Sales Order Entry:
1. Take Order
2. Approve Credit
3. Check Inventory Availability
4. Respond to the Customer
Threats of Sales Order Entry:
Threats Prevention
Customer could fill out Data Entry Controls
an incomplete or (only allow real items to be
inaccurate order. filled).
Invalid Order (Agent – Digital/Written
Commission – Signature
Cancellation).
Uncollectible Accounts Credit Limits (existing
(customers cannot pay the customers);
order that they made) New Customer
Approval (new
customers)
Stockouts or Excess Use BAR codes or
Inventory (not tracking RFID tags;
the inventory on hand) Periodically count
inventories;
Use Sales Forecast and
Activity Reports (to
project how much inventory
to make);
Loss of Customers: CRM System (to
improve customer
Poor Customer service and meet
Service: customer’s needs.
- Taking too
long to get
back to a
customer
- Not catering to
the customer’s
needs
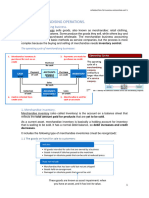
Shipping
Prof – Video – Revenue Cycle
Process of Shipping:
1. Pick and Packing the Orders
2. Shipping the Goods
Inputs and Outputs of Shipping Process:
When you make a sale, the
Sales Order Entry Process
produces a Sales Order and a
Picking Ticket.
Picking Ticket identifies
Sales Order Entry whic products, and quantity
of each product, to remove
from inventory and ship:
"what you need to pick from
the inventory"
Warehouse (Pick The Picking Ticket is sent to the
warehouse and the goods are
and Pack) picked and packed.
The Packed goods are sent to
shipping along with the Picking
Ticket and Sales Order.
These documents are reconciled
and the shipping departments
creates two copies of the Packing
Slip and Bill of Lading.
Shipping Packing Slip - a document that
itemises the contents of a package,
shows the delivery adress.
Bill of Lading - it is legal contract
that defines responsibility of the
goods in transit. Lading means the
action or process of Loading a
shipor other vessel with a cargo.
Carrier The goods are then given to the
Carrier along with the Packing
Slip and Bill of Lading.
Billing and The second copy of Packing
Slip and Bill of Lading are
Accounts then sent to the Billing and
Receivable Accounts Receivable.
Threats:
Threats Control
Picking the wrong item
or quantity.
- Misunderst > Reconcile the Picking
ood the Ticket to the Sales Order
ordered (to make sure the order is
correct)
item.
> Use of Bar Codes or
RFID tags (to track
- Mistook inventory)
the amount
of the item.
Theft of Inventory. > Restriction of physical
Shipping
Prof – Video – Revenue Cycle
- Stealing of access to the inventories
inventory. > Use of RFID tags or
Bar Codes (to track where
inventory moves through the
warehouse)
> Document inventory
transfers
> Periodically count the
inventory and reconcile
what’s in the system
Shipping Errors. > Compare the Shipping
- Failure to Documents to the Sales
ship Order, Packing Slip, and
- Sending Picking Ticket (to ensure
duplicate that the correct items are being
shipped)
orders
> Setup an RFID System
- Sending to (which will identify delays)
the wrong > Configure ERO System
address. (to prevent duplicate orders)
Billing and Cash Collection
Prof – Video – Revenue Cycle
Process: Threats of Billing:
Threats Controls
Receiving Counter Failure to bill > Separate billing and shipping
Receives the Sales Orderfrom the Sales Order Entry process along with (customers never get
the Packing Slip and Bill of Lading from the Shipping Department functions
their invoice) > Periodically reconcile
(compare) Sales Invoice to
Sales Order, Picking Ticket,
Invoicing and Shipping Documents
Those documents are then used to Which are then sent to the Billing Errors > Data Entry Controls
create invoices. customers.
(customers are billed > Automatically enter the
to the wrong amount Pricing Data (auto-increment the
based on the quantity
amount due based on the pricing data
ordered)
saved on the system)
Record of Sales
Then record it to the Sales Journal and update the Accounts Receivable Posting Errors in > Data Entry Controls
for the customer. Accounts > Sending Monthly Statement
Receivable (errors to the customer
are posted in the > Reconcile Batch Totals and
Accounts Receivable) Subsidiary Accounts (compare
Monthly Statement Accounts Receivable against Batch
At the end of the month, the Receicing Counter drafts a Monthly Totals and General Ledger)
Statement and that is also sent to the customer.
Inaccurate or > Segregation of Duties (separate
Invalid Credit Customer Account Maintenance,
Memos (wrong Credit Memo Authorization, and Sales
Order Entry)
amount of credit for
Cash Collections returned goods) > ERP Configuration (configure
The cash is then collected when the customer pays for the invoice. the system to block any credit memos
that don’t have the corresponding
documentation)
Threats of Cash Collections:
Remittance List Threats Controls
After the payment comes in, it is then recorded in the Remittance List. Theft of Cash > separate cash handling
(payments are functions from Accounts
pocketed by Receivable, Cash Handling,
employees)
and Authorization of Credit
Bank Memos
The payment is then deposited to the bank. > reconcile what’s in the bank
with what we have recorded
> Lockbox, Electronic Funds
Transfer, and Financial
Accounts Receivable Electronic Data Interchange
The Remittance List is then sent to the Accounts Receivable to update Cash Flow > Have 2 People open all mail
the Accounts Recevable of the customer.
Problems > Deposit Cash Daily
(payments are not
coming in for the
Remittance Slips File regular basis)
Then files away the Remittance List.
Two Ways Companies Can Build Customers:
Open Invoice Method Balance – Forward
Method
1 payment: 1 invoice 1 payment: Many
invoices (invoice and
monthly statement)
You might also like
- Revised Edition Entrepreneurship A Level Revision NotesDocument128 pagesRevised Edition Entrepreneurship A Level Revision NotesDuete Emma85% (48)
- SAP Intercompany Issues and ResolutionsDocument67 pagesSAP Intercompany Issues and ResolutionsNaveed Arshad80% (5)
- 1759 Syllabus Spring 2016 PDFDocument10 pages1759 Syllabus Spring 2016 PDFEricNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5: The Revenue Cycle: Sales To Cash CollectionsDocument12 pagesCHAPTER 5: The Revenue Cycle: Sales To Cash Collectionssamuel tekelehanaNo ratings yet
- AIS Chapter 5Document22 pagesAIS Chapter 5Getachew JoriyeNo ratings yet
- Expenditure CycleDocument3 pagesExpenditure CycleAnnaNo ratings yet
- Module 7: Introduction To Manufacturing Operations (New Account Titles The Financial Statements)Document3 pagesModule 7: Introduction To Manufacturing Operations (New Account Titles The Financial Statements)Ashitero YoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 The Revenue CycleDocument6 pagesChapter 4 The Revenue CycleRose Vera Mae EncinaNo ratings yet
- Accounting, Information Technology, and Business Solutions, 2nd EditionDocument37 pagesAccounting, Information Technology, and Business Solutions, 2nd EditionSabrina Nur HidayatNo ratings yet
- Lesson G - 1 Ch09 Rev. Cycle Act. Tech.Document79 pagesLesson G - 1 Ch09 Rev. Cycle Act. Tech.Blacky PinkyNo ratings yet
- AT 06-06 Transaction Cycles Part 1Document9 pagesAT 06-06 Transaction Cycles Part 1Eeuh100% (1)
- Summer Internship Project Report SreelakshmiDocument33 pagesSummer Internship Project Report SreelakshmiSreelakshmi P NairNo ratings yet
- AIS Reviewer AIS Reviewer: Accountancy (The National Teachers College) Accountancy (The National Teachers College)Document13 pagesAIS Reviewer AIS Reviewer: Accountancy (The National Teachers College) Accountancy (The National Teachers College)Aldwin CalambaNo ratings yet
- The Expenditure Cycle: Part I: Purchases and Cash Disbursements ProceduresDocument24 pagesThe Expenditure Cycle: Part I: Purchases and Cash Disbursements ProceduresNAVISTA DITA FAIRUZINo ratings yet
- Distribution Centers. Activities. KPI. p1Document23 pagesDistribution Centers. Activities. KPI. p1Sherzod AxmedovNo ratings yet
- Summary SIA Ch.13 - Expenditure CycleDocument3 pagesSummary SIA Ch.13 - Expenditure CycleAthiyya Nabila AyuNo ratings yet
- AIS Chapter 4 Revenue CycleDocument6 pagesAIS Chapter 4 Revenue CycleKate Alvarez100% (1)
- Week 10 The Expenditure CycleDocument8 pagesWeek 10 The Expenditure CycleAldwin CalambaNo ratings yet
- Discussion - InventoriesDocument3 pagesDiscussion - InventoriesVel JuneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document6 pagesChapter 4Christine Joy Original100% (1)
- Accounting - Lesson 5Document11 pagesAccounting - Lesson 5Richel ArmayanNo ratings yet
- Inventories 2024Document27 pagesInventories 2024Charish Ann SimbajonNo ratings yet
- Accounting For InventoryDocument26 pagesAccounting For InventoryOgahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document8 pagesChapter 4Christine Joy OriginalNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Corporations: ACT B861FDocument54 pagesAccounting For Corporations: ACT B861FCalvin MaNo ratings yet
- CH 4 - Inventories-1Document44 pagesCH 4 - Inventories-1Hammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Materials 2020 AugustDocument3 pagesMaterials 2020 AugustKingsley MweembaNo ratings yet
- The Revenue CycleDocument10 pagesThe Revenue CycleMarjorie IsonNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 1 Accounting For InventoryDocument9 pagesTOPIC 1 Accounting For Inventorykirah raraNo ratings yet
- CH 4 - InventoriesDocument38 pagesCH 4 - InventoriesShehzad QureshiNo ratings yet
- Wuolah Free Apuntes Unit 5 Gulag FreeDocument12 pagesWuolah Free Apuntes Unit 5 Gulag FreeNOA PEREZ FERRERNo ratings yet
- Auditing The Production CycleDocument5 pagesAuditing The Production CycleTiana Ling Jiunn LiNo ratings yet
- ACCTSYS Unit 4Document13 pagesACCTSYS Unit 4Finneth AchasNo ratings yet
- Qa Inventories Substantive TestingDocument6 pagesQa Inventories Substantive TestingAsniah M. RatabanNo ratings yet
- Revenue Cycle (Part I)Document34 pagesRevenue Cycle (Part I)Rosario TaguinotNo ratings yet
- Customer Order ManagemetDocument21 pagesCustomer Order ManagemetRujumba DukeNo ratings yet
- Sales Order ProceduresDocument12 pagesSales Order ProceduresHerman BlomNo ratings yet
- 4Document16 pages4Asal IslamNo ratings yet
- Unit 5-6 - Checking and Recieving MerchandiseDocument28 pagesUnit 5-6 - Checking and Recieving MerchandiseJabari BrowneNo ratings yet
- A.1. General Objective: Input OutputDocument11 pagesA.1. General Objective: Input OutputLia SyNo ratings yet
- AIS ReportDocument9 pagesAIS ReportJessie CanoNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Bell StudioDocument19 pagesCase Study - Bell StudiosheetalsharmaNo ratings yet
- Ss Chain & Is in RetailDocument21 pagesSs Chain & Is in Retailsatyam bhardwajNo ratings yet
- Ijoart: Managed Inventory With Special Reference of Cost StructureDocument5 pagesIjoart: Managed Inventory With Special Reference of Cost StructureAngelica PostreNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information System Chapter 4 6 CompressDocument14 pagesAccounting Information System Chapter 4 6 CompressSharmaine LiasosNo ratings yet
- Logistics ManagementDocument64 pagesLogistics ManagementDibyesh Das100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Accounting IiDocument14 pagesFundamentals of Accounting IiNo MoreNo ratings yet
- Chap. 9 Cis Auditing The Revenue CycleDocument68 pagesChap. 9 Cis Auditing The Revenue CycleSergio, JesharelleNo ratings yet
- Module 7 13 No 11Document6 pagesModule 7 13 No 11LEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 AIS PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 5 AIS PDFAnne Rose EncinaNo ratings yet
- Practical QuestionsDocument9 pagesPractical QuestionsTrisha Lorraine RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: The Revenue CycleDocument4 pagesChapter 4: The Revenue CycleKrissha100% (1)
- EconomicsDocument2 pagesEconomicsdmiahalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Purchasing - 2022Document46 pagesChapter 2 - Purchasing - 2022Ten LeeNo ratings yet
- Abdulrehman 3175 18221 6 Revenue CycleDocument26 pagesAbdulrehman 3175 18221 6 Revenue CyclesanayaNo ratings yet
- Ch-1-Merchandising InventoriesDocument15 pagesCh-1-Merchandising Inventorieskenenisagetachew856No ratings yet
- Unit 4 The Expenditure CycleDocument35 pagesUnit 4 The Expenditure CycleBulelwa HarrisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument5 pagesChapter 4 PDFNur-aima MortabaNo ratings yet
- Chap 4Document7 pagesChap 4Christine Joy OriginalNo ratings yet
- Si Ak Chapter 15 - Kelompok 9Document8 pagesSi Ak Chapter 15 - Kelompok 9Eko Wahyudi AK 2021No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 The Revenue Cycle SummaryDocument5 pagesChapter 4 The Revenue Cycle SummaryAngela Erish CastroNo ratings yet
- Purchasing, Inventory, and Cash Disbursements: Common Frauds and Internal ControlsFrom EverandPurchasing, Inventory, and Cash Disbursements: Common Frauds and Internal ControlsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Fls Scheme LetterDocument2 pagesFls Scheme Letterrahuldbajaj2011No ratings yet
- Annexure A-18 Declaration of Repatriation of Proceeds From Sale of Assets OR Maturity Proceeds Withdrawal of My InvestmentsDocument1 pageAnnexure A-18 Declaration of Repatriation of Proceeds From Sale of Assets OR Maturity Proceeds Withdrawal of My InvestmentstooheyshroffNo ratings yet
- Origin, History and Types of Banking SystemDocument44 pagesOrigin, History and Types of Banking Systemriajul islam jamiNo ratings yet
- Securitiization & Asset ReconstructionDocument6 pagesSecuritiization & Asset ReconstructionGunjeetNo ratings yet
- Final Black Book CONSUMER FINANCE FOR MOINDocument78 pagesFinal Black Book CONSUMER FINANCE FOR MOINirfan khanNo ratings yet
- B - B - A - (Banking) 122 13 Banking Theory Juhb PDFDocument254 pagesB - B - A - (Banking) 122 13 Banking Theory Juhb PDFGargi MehrotraNo ratings yet
- Review of LiteratureDocument4 pagesReview of Literaturemaha lakshmiNo ratings yet
- The Bankers' Book Evidence Act, 1891Document4 pagesThe Bankers' Book Evidence Act, 1891nurul000No ratings yet
- Latest Resume of Gina Mad A Rang 052019Document3 pagesLatest Resume of Gina Mad A Rang 052019Na GiNo ratings yet
- RBI ECB GuidelinesDocument19 pagesRBI ECB GuidelinesnareshkapoorsNo ratings yet
- Public DebtDocument16 pagesPublic Debtimran2233888No ratings yet
- Corporate Governance BankDocument84 pagesCorporate Governance BankfkkfoxNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument32 pagesUntitledAswinNo ratings yet
- Kalinga Institute of Industrial Technology, Deemed To Be University, BhubaneswarDocument10 pagesKalinga Institute of Industrial Technology, Deemed To Be University, BhubaneswarVikas RanjanNo ratings yet
- Q. Is There A Relationship Between Financial Institutions and Financial Markets?Document3 pagesQ. Is There A Relationship Between Financial Institutions and Financial Markets?Zabir Tahzin HassanNo ratings yet
- The Rajasthan State Cooperative BankDocument11 pagesThe Rajasthan State Cooperative BankHimanshi SinghNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument14 pagesPDFfkamaliyahNo ratings yet
- JANKIDocument47 pagesJANKIJankiNo ratings yet
- Monetary PolicyDocument34 pagesMonetary PolicyYogesh Kende89% (9)
- Digested CasesDocument47 pagesDigested CasesIvy Paz100% (3)
- Group 6 Jawaban Bahasa Inggris IPA UN 2000Document7 pagesGroup 6 Jawaban Bahasa Inggris IPA UN 2000sauma agnitaNo ratings yet
- 08 - Chapter 2 MudraDocument27 pages08 - Chapter 2 Mudrayogesh sharmaNo ratings yet
- Jan 2021 To March 2021Document8 pagesJan 2021 To March 2021AKSHAY GHADGENo ratings yet
- Recent Income Tax Case LawsDocument65 pagesRecent Income Tax Case LawsMADHAVNo ratings yet
- BRAC BankDocument64 pagesBRAC BankHumaira HossainNo ratings yet
- Intacc 1 Notes Part 1Document13 pagesIntacc 1 Notes Part 1Crizelda BauyonNo ratings yet
- Pacioles v. Pacioles G.R. No. 214415, October 15, 2018Document15 pagesPacioles v. Pacioles G.R. No. 214415, October 15, 2018Yuri NishimiyaNo ratings yet
- Business Finance Q3 Module 2Document21 pagesBusiness Finance Q3 Module 2Jomar Benedico0% (1)