0% found this document useful (0 votes)
89 views2 pagesARP
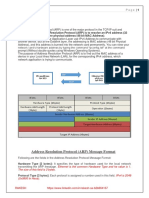
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) maps IP addresses to MAC addresses to allow communication between devices on the same local network. When a device needs to communicate, it checks its ARP cache for the MAC address corresponding to the destination IP. If not found, it broadcasts an ARP request and the device with the matching IP responds with its MAC address. ARP caches are dynamic to reflect network changes and avoid conflicts by ensuring unique mappings between IP and MAC addresses. Understanding ARP is essential for network administrators to enable communication and maintain network integrity.
Uploaded by
Kamran ShahidCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
89 views2 pagesARP
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) maps IP addresses to MAC addresses to allow communication between devices on the same local network. When a device needs to communicate, it checks its ARP cache for the MAC address corresponding to the destination IP. If not found, it broadcasts an ARP request and the device with the matching IP responds with its MAC address. ARP caches are dynamic to reflect network changes and avoid conflicts by ensuring unique mappings between IP and MAC addresses. Understanding ARP is essential for network administrators to enable communication and maintain network integrity.
Uploaded by
Kamran ShahidCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd