Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cfas (Chap 1) P1 Notes
Cfas (Chap 1) P1 Notes
Uploaded by
fernandezmaekyla1330Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cfas (Chap 1) P1 Notes
Cfas (Chap 1) P1 Notes
Uploaded by
fernandezmaekyla1330Copyright:
Available Formats
OVERVIEW OF ACCOUNTING
Definition of Accounting
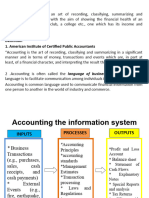
Accounting is the process of identifying, measuring, and communicating economic information to permit informed
judgements and decisions by the user of information.
I. IDENTIFYING – the process of analyzing events and transactions to determine whether or not they will be
recognized.
Recognition refers to the process of including the effect of an accountable event in the statement of financial
position or the income statement through a journal entry.
Only accountable events are recognized. Accountable events are the ones that affect the asset, liability, equity,
income or expense of an entity. This is also known as economic activity.
Non-accountable events are not recognized but disclosed only in the notes, if they have accounting relevance. A
non-accountable event that has accounting relevance may be recorded through a memorandum entry.
TYPES OF EVENTS OR TRANSACTIONS
a. External events- events that involve an entity and another external party.
Types of External Events
Exchange (reciprocal transfer)- an event wherein there is a reciprocal giving and receiving of economic resources
or discharging of economic obligations between an entity and external party. Examples: sale, purchase, payment
of liabilities, receipt of notes receivable, etc.
Non-reciprocal transfer- a “one way” transaction in which the party giving something does not receive anything
in return, the party receiving does not give anything in exchange. Examples: donations, gifts or charitable
contributions, payment of taxes, imposition of fines, etc.
External events other than transfer- an event that involves changes in economic resources or obligations of an
entity caused by an external party or source but does not involve transfers of resources or obligations. Examples:
changes in fair values and price levels, obsolescence, technological changes, vandalism, etc.
b. Internal events- events that do not involve an external party. These events happen inside the company.
Types of Internal Events
Production- resources are transformed into finished goods. Examples: production of farm products, conversion
of raw materials into finished products
Casualty- unanticipated loss from disasters or other similar events. Examples: loss from fire, flood, and other
catastrophe
II. MEASURING-
You might also like
- Definition of AccountingDocument3 pagesDefinition of AccountingalexanndrabernalNo ratings yet
- Con FrasDocument3 pagesCon FrasYsa belNo ratings yet
- Overview of Accounting DHESSYDocument3 pagesOverview of Accounting DHESSYDhessy FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Overview of AccountingDocument5 pagesOverview of Accountingcamilleorpilla xNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument13 pagesPDF DocumentMaureen MahusayNo ratings yet
- Cfas NotesDocument654 pagesCfas NotesOjv FgjNo ratings yet
- Acctg Book SummaryDocument3 pagesAcctg Book SummaryMaimona SemaNo ratings yet
- Cfass NotesDocument3 pagesCfass Notes22-59012No ratings yet
- I Am Sharing 'UPDATED' With YouDocument258 pagesI Am Sharing 'UPDATED' With Youjessamae gundanNo ratings yet
- CfasDocument42 pagesCfasCleofe Mae Piñero AseñasNo ratings yet
- Midterms - CFAS ReviewerDocument3 pagesMidterms - CFAS Reviewershyn llnsNo ratings yet
- Accounting: Wilma G. OstanDocument11 pagesAccounting: Wilma G. OstanHelpo BadoyNo ratings yet
- Overview of AccountingDocument12 pagesOverview of AccountingKristine Joy ArceNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 CFASDocument14 pagesLesson 1 CFASkenneth coronelNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework and Accounting Standards: Marian G. Magcalas, CPA, MBADocument120 pagesConceptual Framework and Accounting Standards: Marian G. Magcalas, CPA, MBAMicaela Encinas100% (1)
- Week 1 - Lesson 1 Overview of AccountingDocument10 pagesWeek 1 - Lesson 1 Overview of AccountingRose RaboNo ratings yet
- 2nd Term - CFASDocument6 pages2nd Term - CFASPam LlanetaNo ratings yet
- Ptma Module FinalDocument12 pagesPtma Module FinalLodie OloteoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Conceptual Framework and Accounting Standard (Draft)Document2 pagesReviewer in Conceptual Framework and Accounting Standard (Draft)Marian grace DivinoNo ratings yet
- Far 1abDocument242 pagesFar 1abPanda CocoNo ratings yet
- Theory of Accounts by MillanDocument241 pagesTheory of Accounts by MillanRheu Reyes94% (53)
- Xi AccDocument4 pagesXi AccLaghari ShafquatNo ratings yet
- Test Bank: Theory of AccountsDocument241 pagesTest Bank: Theory of Accountsdeeznuts100% (1)
- Test Bank: Theory of AccountsDocument241 pagesTest Bank: Theory of AccountsMa Yra YmataNo ratings yet
- Elements of Financial Statements: Lesson 4Document30 pagesElements of Financial Statements: Lesson 4Aices Jasmin Melgar BongaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Overview of AccountingDocument9 pagesChapter 1. Overview of AccountingFMNo ratings yet
- CFAS Chapter 1 SummaryDocument5 pagesCFAS Chapter 1 SummaryCINDY BALANONNo ratings yet
- Intoduction To Accounting PART 1-LLB 1Document34 pagesIntoduction To Accounting PART 1-LLB 1brandywilliam203No ratings yet
- Far Theory Test Bank NaDocument242 pagesFar Theory Test Bank NaFRANCINE THEA LANTAYANo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework and Accounting Standards 1 1 1 2Document182 pagesConceptual Framework and Accounting Standards 1 1 1 2akosiisaakNo ratings yet
- Theory of Accounts by MillanDocument266 pagesTheory of Accounts by MillanBrian Torres100% (2)
- Basic Financial Accounting and Reporting (Bfar) : Philippine Based (Summary and Class Notes)Document22 pagesBasic Financial Accounting and Reporting (Bfar) : Philippine Based (Summary and Class Notes)LiaNo ratings yet
- Overview MillanDocument27 pagesOverview MillanPinero JatheuzelNo ratings yet
- CFAS ReviewerDocument15 pagesCFAS ReviewerEvangeline Shane ManaloNo ratings yet
- Overview of AccountingDocument76 pagesOverview of AccountingCARLINE KATE ALMINANANo ratings yet
- OVERVIEW (Part 1)Document7 pagesOVERVIEW (Part 1)Jen BadanaNo ratings yet
- 1st YearDocument59 pages1st YearswahadashNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AccountingDocument4 pagesIntroduction To AccountingaminNo ratings yet
- Analyzing and Recording Financial TransactionsDocument2 pagesAnalyzing and Recording Financial TransactionsFranze Beatriz FLORESNo ratings yet
- CBSC Class XI - Accounting For BusinessDocument228 pagesCBSC Class XI - Accounting For BusinessSachin KheveriaNo ratings yet
- Introduction With SyllabusDocument16 pagesIntroduction With SyllabusAbhishek BaliarsinghNo ratings yet
- Faa IDocument18 pagesFaa Iabhiseknanda82495No ratings yet
- Test Bank Theory of Accounts PreviewDocument15 pagesTest Bank Theory of Accounts PreviewMarjorie PalmaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Accounting-Introduction To AccountingDocument14 pagesCBSE Class 11 Accounting-Introduction To AccountingRudraksh PareyNo ratings yet
- 2021 Cfas Mte Wreviewer QuizletDocument144 pages2021 Cfas Mte Wreviewer QuizletCleofe Mae Piñero AseñasNo ratings yet
- The Accounting Profession Definition of Accounting: Important PointsDocument9 pagesThe Accounting Profession Definition of Accounting: Important PointsShoyo HinataNo ratings yet
- Actg1 - Chapter 3Document37 pagesActg1 - Chapter 3Reynaleen Agta100% (1)
- PDF Document 3Document37 pagesPDF Document 3Micaella JanNo ratings yet
- ACCOUNTING1Document12 pagesACCOUNTING1Trixie GabatinoNo ratings yet
- Prelims Reviewer - Financial Accounting and ReportingDocument10 pagesPrelims Reviewer - Financial Accounting and ReportingKristine SantosNo ratings yet
- BASIC FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING and REPORTINGDocument18 pagesBASIC FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING and REPORTINGEian chin mana-ayNo ratings yet
- Bridge Course Financial and Management AccountingDocument35 pagesBridge Course Financial and Management AccountingsrinivasanscribdNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 1: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideFrom EverandIntermediate Accounting 1: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- CPA Financial Accounting and Reporting: Second EditionFrom EverandCPA Financial Accounting and Reporting: Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Koyas PerfumeryDocument2 pagesKoyas PerfumeryTANUJ CHAKRABORTYNo ratings yet
- Module 4-Operating, Financial, and Total LeverageDocument45 pagesModule 4-Operating, Financial, and Total LeverageAna ValenovaNo ratings yet
- Systematic Risk of Select Banking Scripts Traded in NSE MBA ProjectDocument83 pagesSystematic Risk of Select Banking Scripts Traded in NSE MBA ProjectSuresh Raghav100% (2)
- Vodafone Total RewardsDocument10 pagesVodafone Total RewardspsmysticNo ratings yet
- Massachusetts: Uquu JuncprnxrDocument17 pagesMassachusetts: Uquu JuncprnxrMarco RomeoNo ratings yet
- Bank Fraud and Its SolutionsDocument19 pagesBank Fraud and Its SolutionsRituparn UniyalNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Financial StatementsDocument11 pagesPresentation of Financial StatementsHasnain MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Project Management For Construction and Civil Engg.Document487 pagesProject Management For Construction and Civil Engg.TauseefNo ratings yet
- Big Short Presentation - Tulane TemplateDocument25 pagesBig Short Presentation - Tulane TemplateDave SislenNo ratings yet
- PWC Global Annual Review 2021Document97 pagesPWC Global Annual Review 2021Sarah AndoNo ratings yet
- PDF OnlineDocument9 pagesPDF OnlinePratik SinghNo ratings yet
- Capstone Corporate Training Report - Q2 2016Document11 pagesCapstone Corporate Training Report - Q2 2016srinath12No ratings yet
- Pureplay Skin Sciences - Annual Report - FY21Document45 pagesPureplay Skin Sciences - Annual Report - FY21Sagar SangoiNo ratings yet
- Investment AccountDocument2 pagesInvestment AccountQuestionscastle Friend67% (3)
- Constitution of Boards of Public Sector Banks in IndiaDocument6 pagesConstitution of Boards of Public Sector Banks in IndiaGyan RanjanNo ratings yet
- Ue - Notes On Gen. Prin & VatDocument21 pagesUe - Notes On Gen. Prin & VatpatrixiaNo ratings yet
- Components of Balance of PaymentsDocument8 pagesComponents of Balance of PaymentsAnonymous dZpgL93UNo ratings yet
- Corporate FinanceDocument142 pagesCorporate FinancetagashiiNo ratings yet
- Marketing-of-Financial-Services SAKSHIDocument9 pagesMarketing-of-Financial-Services SAKSHINageshwar SinghNo ratings yet
- Teledyne 001 41000006Document2 pagesTeledyne 001 41000006DavidNo ratings yet
- CPF Retirement Booklet PDFDocument24 pagesCPF Retirement Booklet PDFHadi Rosli100% (1)
- Annual Report 2011Document203 pagesAnnual Report 2011SachithHiroshanaWijethungaNo ratings yet
- ABM ComputationsDocument4 pagesABM ComputationsGerard Dean EmbogNo ratings yet
- Advantage of Taking An Abm StrandDocument11 pagesAdvantage of Taking An Abm StrandMione GrangerNo ratings yet
- Long-Term Debt-Paying AbilityDocument23 pagesLong-Term Debt-Paying AbilitymohamedNo ratings yet
- Challenges To Retail Banking in IndiaDocument2 pagesChallenges To Retail Banking in IndiapadmajammulaNo ratings yet
- Vedanta Consulting Private Limited - Business ProfileDocument15 pagesVedanta Consulting Private Limited - Business Profileceo_vedantaNo ratings yet
- No Accounting Document Generated: No Accounting Document Generated: Based On The Purchase Order and The Quantity Actually ReceivedDocument5 pagesNo Accounting Document Generated: No Accounting Document Generated: Based On The Purchase Order and The Quantity Actually ReceivedAmanNo ratings yet
- Paul Tudor JonesDocument3 pagesPaul Tudor Jonesyong829100% (3)
- Examiners Mind BiologyDocument12 pagesExaminers Mind BiologymbalaziveraNo ratings yet