Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chap 3 e Commerce
Uploaded by
Jannatul FardusOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chap 3 e Commerce
Uploaded by
Jannatul FardusCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 03
E-Business Applications, E-Procurement and E-Payment Systems
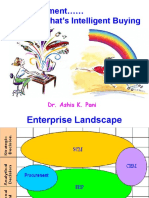
1. What is ERP?
• ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning.
• It's a software system that integrates various business processes within an
organization.
• The goal is to streamline operations and improve efficiency.
• ERP systems encompass functions like finance, HR, supply chain,
manufacturing, and CRM.
• Key features include integration, automation, centralized data, real-time
insights, and standardized processes.
• They provide a unified platform for data and communication across
departments.
• ERP systems offer reporting, analytics, and scalability.
• Well-known vendors include SAP, Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics, and Infor.
Examples of ERP systems Below are a few examples of ERP systems that can
be implemented in a business.
• Actian
• Acumatica ERP
• Brightpearl
• IQMS ERP
• Microsoft Dynamics
• Oracle Netsuite ERP
• Sage ERP
• SAP ERP
___________end_________
Difference between Supply chain and e-Supply Chain Management
Aspects
e-Supply Chain
Supply Chain Management Management
Manage goods, info, and Enhance using electronic
Definition finance flow tech
Focus Physical goods movement Digital coordination
Communication Phone, fax, in-person Email, EDI, online tools
Information Flow Manual data, paper docs Real-time digital sharing
Coordination Less efficient Seamless through digital
Inventory Automated, demand
Management Manual tracking forecasting
Automated, real-time
Order Processing Manual entry, delays tracking
Real-time chain
Visibility Limited insight monitoring
Agile, real-time
Flexibility Limited adaptation adjustments
Automated workflows,
Efficiency Constrained by manual analytics
Optimize processes, cost
Cost Reduction Possible, limited savings
Integration, security
Challenges Data issues, coordination concerns
_________________End_________________
Activities and Infrastructure of E-SCM
E-Supply Chain Management (e-SCM)
➢ E-Supply Chain Management (e-SCM) is the collaborative use of technology to
improve the operations of supply chain activities as well as the management of
supply chains.
➢ To enhance B2B processes and improve speed, agility, real time control, and
customer satisfaction.
➢ It involves the use of information technologies to improve the operations of
supply chain activities (e.g., e procurement), as well as the management of the
supply chain (e.g., planning, coordination, and control).
➢ The success of an e-supply chain depends on the following:
o The ability of all supply chain partners to view partner collaboration as a
strategic asset.
o A well-defined supply chain strategy.
o information visibility along the entire supply chain.
o speed, cost, quality and customer service.
o integrating the supply chain more tightly.
➢ Activities include the following:
I. Supply Chain Replenishment.
II. E-Procurement.
III. Supply Chain Monitoring and Control Using RFID.
IV. Inventory Management Using Wireless Devices.
V. Collaborative Planning.
VI. collaborative Design and Product Development.
VII. E-Logistics.
i.Supply Chain Replenishment
➢ Supply chain replenishment encompasses the integrated production and
distribution processes.
➢ Companies can use replenishment information,
o to reduce inventories,
o eliminate stocking points, and
o increase the velocity of replenishment by
o synchronizing supply and demand information across
o the extended enterprise.
ii. E-Procurement
➢ It is the use of web-based technology to support the key procurement
processes, including:
requisitioning,
o sourcing,
o contracting,
o ordering,
o and payment.
➢ Supports direct and indirect material purchasing.
➢ Employs online tools like catalogs, contracts, purchase orders, and shipping
notices.
iii.Supply Chain Monitoring and Control Using RFID
➢ This is one of the most promising applications of RFID (Radio-Frequency
Identification)
➢ Utilizes RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology for real-time
tracking and management of items throughout the supply chain.
➢ RFID involves tags and readers to transmit and receive data via radio
frequencies.
➢ Tags are attached to items; readers capture tag data wirelessly.
➢ Provides enhanced visibility and accuracy in tracking inventory,
shipments, and assets.
iv. Inventory Management Using Wireless Devices
➢ Many organizations are now achieving improvements in inventory
management by using combinations of bar coding technologies (or RFID)
and wireless devices.
➢ Tracking and managing inventory levels, movement, and data.
➢ Utilizing wireless technologies like smartphones, tablets, RFID readers, and
sensors.
➢ Eliminating manual data entry, improving accuracy and efficiency.
➢ Enabling real-time updates and visibility into inventory status.
➢ Supporting inventory control throughout the supply chain.
v. Collaborative Planning
➢ A business practice merging expertise and forecasts from multiple supply
chain participants to enhance customer demand planning and fulfillment.
➢ Involves various stakeholders along the supply chain.
➢ Aims to optimize customer demand anticipation and satisfaction.
➢ Demands coordination between buyers and sellers.
➢ Joint development of demand forecasts and supply strategies.
➢ Improved accuracy in predicting customer demand.
➢ Enhanced synchronization of supply with actual requirements.
➢ Minimized inventory carrying costs and stockout.
Vi .Collaborative Design and Product Development
➢ Utilizes shared design and development practices among multiple firms to
enhance product launch effectiveness and speed to market.
➢ Improve product launch success and reduce time to market.
➢ Involves various companies collaborating on product design and
development.
➢ Focuses on sharing design drawings, engineering data, and technical
information.
➢ Accelerated time to market due to streamlined processes.
➢ Enhanced product quality through diverse expertise.
➢ Cost savings through shared resources and knowledge.
➢ Secure network facilitates sharing among involved parties.
➢ Collaboration spans from concept to manufacturing.
➢ Teams include contract firms, testing facilities, marketers, manufacturers,
and service providers.
vii.E-Logistics
➢ It is the use of web-based technologies to support the material acquisition,
warehousing, and transportation processes.
➢ E-logistics enables distribution to couple routing optimization with
inventory-tracking information.
➢ For example, Internet-based freight auctions enable spot buying of trucking
capacity.
➢ Utilizes technology-driven solutions to improve supply chain agility.
➢ Enhances data accuracy and real-time tracking of goods.
➢ Supports better decision-making through data analytics and insights.
➢ Promotes seamless collaboration among various supply chain partners.
➢ Contributes to overall supply chain optimization and competitive advantage.
________-end________--
Activities and Infrastructure of E-SCM
The following are the major infrastructure elements and tools of e-supply
chains:
I. electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
II. Extranets
III. Intranets
IV. Corporate Portals
V. Workflow systems and tools
VI. Groupware and other collaborative tools
VII. Identification and tracking tools
i.Electronic data interchange (EDI):
➢ It is the major tool used by large corporations to facilitate supply chain
relationships.
➢ Many companies are shifting from traditional EDI to Internet-based
EDI.
ii.Extranets:
• Secure networks that connect an organization with external parties.
• Facilitate controlled sharing of information, collaboration, and transactions.
• Extend certain intranet resources to partners, suppliers, or customers.
iii.Intranets:
• Internal networks accessible only within an organization.
• Share information, resources, and communication among employees.
• Enhance information dissemination, communication, and collaboration.
iv.Corporate Portals:
• Web-based gateways providing personalized access to information and
services.
• Aggregate data, applications, and communication tools in one interface.
• Tailored for employees, partners, or customers for efficient interaction.
v.Workflow Systems and Tools:
• Manage, automate, and optimize business processes.
• Streamline tasks, approvals, and information flow within an organization.
• Enhance efficiency, reduce errors, and ensure process compliance.
vi.Groupware and other collaborative tools:
o Many tools facilitate collaboration and communication between two parties and
among members of small as well as large groups.
o Various tools, some of which are collectively known as groupware, enable such
collaboration.
o Blogs and wikis are beginning to play an important role.
o A major purpose of these tools is to provide visibility to all, namely, let people
know where items are and when they arrive at certain locations.
vii. Identification and tracking tools:
These tools are designed to identify items and their location along the supply chain.
____end________-
Customer relationship management (CRM)
➢ Customer relationship management (CRM) is a customer service approach
that focuses on building long term and sustainable customer relationships
that adds value for both the customers and the merchants.
➢ When delivered online, it is referred to as e-CRM. A major area of e-CRM is
social CRM.
➢ Strategies, technologies, and practices for managing interactions with
customers.
➢ Focuses on building and maintaining strong customer relationships.
➢ Utilizes data analysis to understand and cater to customer needs.
➢ Enhances customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention.
➢ Centralizes customer information for personalized communication.
➢ Aids in sales, marketing, and customer service optimization.
➢ Includes tools for tracking interactions, sales leads, and support requests.
➢ Facilitates targeted marketing campaigns and customer segmentation.
➢ Supports businesses in understanding and forecasting customer behavior.
➢ Aims to foster long-term customer engagement and value.
➢ SCRM is based on social media, in support of companies’ stated goals and
objectives of optimizing the customer’s experience, and building trust and
loyalty.
➢ Success requires considering people, business processes, and technology
associated with the interactions between customers and enterprises.
➢ Like CRM, a major goal of SCRM is building trust and brand loyalty (Huba,
2013 ).
➢ The elements of social CRM
The Benefits of Social CRM
➢ Social CRM offers the following potential benefits to customers (“c”) and
enterprise (“e”)
➢ The benefits to iRobot (iRobot ( irobot.com ), which was founded in 1990 by
three roboticists at MIT with the vision of making practical robots a reality,
designs and builds some of the world’s most important robots) are marked
with an [I]. Drives quick resolution of customers’ problems (c)
➢ Provides for effective and efficient business-customer collaboration (c), (e)
➢ Improves the reputation of companies (e), (I)
➢ Provides a better understanding of customer needs and wants (e)
➢ Provides focused, intuitive, and easy-to-use CRM applications (e)
➢ Provides better marketing, better targeting, and improved products/services
due differ to customers’ creation of content, and WOM (e).
➢ Provides customer input for market research at a quicker rate and at a low
cost for improving products and customer service (e)
➢ Provides customers with more information about products/services quickly
(c), (I)
➢ Increases trust and loyalty (e)
➢ Provides a more complete view of the customer than what traditional CRM
can provide (e)
➢ Decreases overall customer care costs (e.g., through self-helping
communities) (e)
➢ Enables salespeople to find sales leads quickly and easily (e)
➢ Develops new revenue opportunities and turns new customers into repeat
customers (c)
➢ Increases CRM staff productivity by teaching them to use analytics and
collaboration 2.0 techniques (e)
➢ Improves employee performance by benefiting from knowledge sharing
gained in social networks (e)
➢ Improves customer satisfaction by providing them with opportunities for
engagement using social media platforms (c), (I)
➢ Converts leads to opportunities with more effective campaigns (e).
______End______-
E-Procurement Concepts
➢ E-procurement (electronic procurement) is the online purchase of supplies,
materials, energy, work, and services.
➢ It can be done via the Internet or via a private network such as electronic data
exchange (EDI).
➢ Includes requisitioning, ordering, vendor selection, and payment.
➢ Streamlined procurement cycle, reduced manual tasks.
➢ Increased transparency, real-time tracking, and audit trails.
➢ Cost savings through efficient supplier management.
➢ Enhanced accuracy in order processing and reduced errors.
The Goals and Process of E Procurement:
➢ As stated earlier, e-procurement frequently automates activities in the
purchasing process from multiple suppliers via the Web for better execution
and control.
➢ Improvements to procurement have been attempted for decades, usually by
using information technologies.
➢ Using e-procurement results in a major improvement.
➢ Essentially, e-procurement automates the process of auctions, contract
management, vendor selection, and management, etc.
Four major methods of e-procurement are available:
1. Buy at own website,
2. Buy at sellers’ store,
3. Buy at exchanges, and
4. Buy at others’ e-market sites.
1. Buy at Own Website:
• Organizations have their own e-commerce platforms.
• Buyers purchase directly from the organization's website.
• Offers a controlled buying environment with tailored options.
• Ensures brand consistency and direct customer interaction.
• Requires investment in website development and maintenance.
2. Buy at Sellers' Store:
• Buyers access suppliers' e-commerce platforms.
• Similar to online retail shopping but for business needs.
• Wide range of suppliers and products to choose from.
• Offers convenience and comparison shopping.
• Requires trust in supplier's reliability and quality.
3. Buy at Exchanges:
• Online marketplaces bringing multiple buyers and sellers together.
• Focus on specific industries or categories (e.g., B2B marketplaces).
• Enables competitive bidding and efficient supplier discovery.
• Offers potential cost savings and expanded supplier options.
• Requires adherence to marketplace rules and terms.
4. Buy at Others' E-Market Sites:
• Purchasing from third-party e-commerce platforms.
• These platforms host products from various sellers.
• Provides access to diverse product offerings in one place.
• Offers convenience and variety for buyers.
• Requires trust in both the e-market platform and individual sellers.
You might also like
- The Digital LawyerDocument14 pagesThe Digital LawyerJem MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Sharepoint Knowledge BaseDocument716 pagesSharepoint Knowledge BaseCG HedmannNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain TechnologyDocument26 pagesSupply Chain TechnologyjosetaqueoNo ratings yet
- IT in Supply Chain ManagementDocument62 pagesIT in Supply Chain Managementrohitsingh17No ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence in Supply ChainDocument19 pagesArtificial Intelligence in Supply ChainKiran MittalNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Information TechnologyDocument11 pagesSupply Chain Information TechnologyKishore JohnNo ratings yet
- Introduction To E-Business SystemsDocument19 pagesIntroduction To E-Business SystemsArtur97% (79)
- JNU ITpolicyDocument46 pagesJNU ITpolicyHari Hara SudhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 03 (E-Business Infrastructure)Document37 pagesChapter # 03 (E-Business Infrastructure)Fatima Khan100% (2)
- The Role in Technology in Supply Chain ManagementDocument6 pagesThe Role in Technology in Supply Chain ManagementAnonymous MZRzaxFgVLNo ratings yet
- SCM Technologies and Their Applicability in The SC Operations AisDocument11 pagesSCM Technologies and Their Applicability in The SC Operations AisaiswaryaNo ratings yet
- IT in SCM - FinalDocument21 pagesIT in SCM - Finalrjrahulsrk100% (1)
- Supply Chain Management ProjectDocument23 pagesSupply Chain Management ProjectUtkarsh VermaNo ratings yet
- E Supply Chain ManagementDocument52 pagesE Supply Chain ManagementSubrata Halder100% (2)
- Chapter 6 - Supply Chain Technology, Managing Information FlowsDocument26 pagesChapter 6 - Supply Chain Technology, Managing Information FlowsArman100% (1)
- Role of Information Technology in Supply Chain ManagementDocument4 pagesRole of Information Technology in Supply Chain ManagementKanika ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 08 Apr 2023Document15 pagesAdobe Scan 08 Apr 2023passports654No ratings yet
- IT & Retail ReplenishmentDocument17 pagesIT & Retail ReplenishmentKristian TarucNo ratings yet
- Financial Issues in Supply Chain Management: Unit-VDocument6 pagesFinancial Issues in Supply Chain Management: Unit-VA M MAHABOOB BASHANo ratings yet
- Logistics & ITDocument19 pagesLogistics & ITTufail MallickNo ratings yet
- Role of E-Commerce in Supply Chain Management: Group No. - 7Document24 pagesRole of E-Commerce in Supply Chain Management: Group No. - 7azharscribdNo ratings yet
- Information System For Supply Chain ManagementDocument18 pagesInformation System For Supply Chain ManagementashishlordNo ratings yet
- St. Gonsalo Garcia College: Logistics ManagementDocument22 pagesSt. Gonsalo Garcia College: Logistics Managementk_suryaNo ratings yet
- Management Information System Chapter 10 NotesDocument5 pagesManagement Information System Chapter 10 Notesgut78No ratings yet
- Retail Management Unit 5Document31 pagesRetail Management Unit 5VidhwanNo ratings yet
- O Human Resource Management o Firm Infrastructure o Procurement o Marketing Sales and Service o Technology DevelopmentDocument4 pagesO Human Resource Management o Firm Infrastructure o Procurement o Marketing Sales and Service o Technology Developmentakhil pillaiNo ratings yet
- Dreamorbit Softech Private LimitedDocument54 pagesDreamorbit Softech Private LimitedjayeshNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Big Data Analytics PDFDocument18 pagesModule 6 Big Data Analytics PDFNaveenNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: Online Exchange of ValueDocument7 pagesChapter-1: Online Exchange of ValueShohagNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Technology II: BLCP 201Document33 pagesSupply Chain Technology II: BLCP 201Khai Wen OnexoxNo ratings yet
- Ome752 - SCM Unit VDocument11 pagesOme752 - SCM Unit VlingeshNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management Online Module 46 52Document7 pagesSupply Chain Management Online Module 46 52Vincent Glen QuintoNo ratings yet
- Role of Information Systems in Strategic Business Development in RMG IndustryDocument13 pagesRole of Information Systems in Strategic Business Development in RMG IndustrySangya SinghNo ratings yet
- SCM Technologies, and Their Applicability in The SC Operations - AnandDocument12 pagesSCM Technologies, and Their Applicability in The SC Operations - AnandAnand VenugopalNo ratings yet
- E-Supply Chain Management: Presented byDocument56 pagesE-Supply Chain Management: Presented byMohamed ElhariryNo ratings yet
- A Study On Role of E-Commerce in Supply Chain 2015Document5 pagesA Study On Role of E-Commerce in Supply Chain 2015babu chyNo ratings yet
- BL PDFDocument4 pagesBL PDFsunny saroarNo ratings yet
- SCM AssignmentDocument2 pagesSCM AssignmentKING ME Gaming channelNo ratings yet
- E CommerceprojectDocument5 pagesE Commerceprojectsisayderiba936No ratings yet
- Intra-Organizational Electronic CommerceDocument16 pagesIntra-Organizational Electronic CommercePadma Reddy ChNo ratings yet
- Atal Bihari Vajpayee Indian Institute of Information Technology & Management, GwaliorDocument18 pagesAtal Bihari Vajpayee Indian Institute of Information Technology & Management, GwaliorAayush SinghNo ratings yet
- Supply ChainDocument3 pagesSupply ChainNaveen SanampudiNo ratings yet
- PPT W6Document53 pagesPPT W6Hilda mayang sariNo ratings yet
- Internet Marketing Ch.2Document15 pagesInternet Marketing Ch.2Hafiz RashidNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Consumer ApplicationsDocument15 pagesE-Commerce Consumer ApplicationsRam KumarNo ratings yet
- Final ProjectDocument50 pagesFinal Projectshiv infotechNo ratings yet
- Ecommerce 2Document6 pagesEcommerce 2Vishesh NagdevNo ratings yet
- Ebm Model KeyDocument23 pagesEbm Model KeyVasugi KumarNo ratings yet
- SCM Alisha Assignment1Document8 pagesSCM Alisha Assignment1alishaNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Managemet:: SCM On ItDocument3 pagesSupply Chain Managemet:: SCM On ItbadushamsmNo ratings yet
- Digital Supply Chain ManagementDocument3 pagesDigital Supply Chain ManagementTowsif SalauddinNo ratings yet
- 21st-Century Supply ChainsDocument46 pages21st-Century Supply ChainsnurmukhammadkhudayberdievNo ratings yet
- Priya Anand PG20101207 E-SCMDocument38 pagesPriya Anand PG20101207 E-SCMPriya AnandNo ratings yet
- newtrendsinitanditsimpactscm-ppt-HPC 3 Final TopicDocument18 pagesnewtrendsinitanditsimpactscm-ppt-HPC 3 Final TopicDanica Patricia SeguerraNo ratings yet
- Infomation Flow IntegrationDocument26 pagesInfomation Flow IntegrationRaajKumarNo ratings yet
- Information Technology in Supply Chain ManagementDocument27 pagesInformation Technology in Supply Chain ManagementSatya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To E-Business: Course OutlineDocument32 pagesIntroduction To E-Business: Course OutlineRuchi ShahNo ratings yet
- Tata Steel-MDP SessionDocument69 pagesTata Steel-MDP Sessionsasharma82No ratings yet
- "Unlocking Potential: Digital Transformation at Wesgroup Equipment LTD." "Revolutionizing Operations, Elevating Customer ExperienceDocument22 pages"Unlocking Potential: Digital Transformation at Wesgroup Equipment LTD." "Revolutionizing Operations, Elevating Customer ExperiencerickykheraNo ratings yet
- DhanusenkDocument19 pagesDhanusenkranjeetkadam2003No ratings yet
- PrintDocument10 pagesPrintDella CharistaNo ratings yet
- Week3 - SCM and CRM - May2019Document46 pagesWeek3 - SCM and CRM - May2019Li ZHANGNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce and Industry 4.0Document9 pagesE-Commerce and Industry 4.0Bhushan BhoirNo ratings yet
- Logistics and Supply Chain Information SystemsDocument22 pagesLogistics and Supply Chain Information SystemsNani SatyaNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 Note Roy SirDocument70 pagesChap 5 Note Roy SirJannatul FardusNo ratings yet
- 4 - Managing LiabilitiesDocument7 pages4 - Managing LiabilitiesJannatul FardusNo ratings yet
- Econometrics Chap 3Document19 pagesEconometrics Chap 3Jannatul FardusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 (Strategic Management)Document27 pagesChapter 8 (Strategic Management)Jannatul FardusNo ratings yet
- Standard+SANS10111 1Document95 pagesStandard+SANS10111 1preneshthulsiNo ratings yet
- Ch03-Network Computing Discovery, Communication, and CollaborationDocument31 pagesCh03-Network Computing Discovery, Communication, and CollaborationMegha MattaNo ratings yet
- Q2-423-01Control of DocumentsDocument5 pagesQ2-423-01Control of DocumentsBrazilemio RoswithaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The E-Commerce Business ModelsDocument88 pagesChapter 2 - The E-Commerce Business ModelsAnnaNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Network: Introduction To NetworksDocument64 pagesExploring The Network: Introduction To NetworksDuy TanNo ratings yet
- Business Communication - Case - Josh Miller Is A Finance Student - 2Document4 pagesBusiness Communication - Case - Josh Miller Is A Finance Student - 2Sailpoint CourseNo ratings yet
- Using Information Technology 10Th Edition Williams Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesUsing Information Technology 10Th Edition Williams Test Bank Full Chapter PDFxaviahienfbm9100% (8)
- RHD Management Manual Vol-1Document93 pagesRHD Management Manual Vol-1Sadia Hossain DristiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ACCA F1Document4 pagesChapter 2 ACCA F1sikshaNo ratings yet
- PH.D Course Work Syllabus 2022 2023Document3 pagesPH.D Course Work Syllabus 2022 2023neha jainNo ratings yet
- IND3 BMS For Project Team MembersDocument48 pagesIND3 BMS For Project Team Membersawwal.salisuNo ratings yet
- Technology On HRDocument14 pagesTechnology On HRHassan Jamel MiaseNo ratings yet
- (James A. O'Brien) 10th Ed, Management Information System (048-053) PDFDocument6 pages(James A. O'Brien) 10th Ed, Management Information System (048-053) PDFKen Caesar Balawan TunggadewaNo ratings yet
- M 4 - Introduction of Server FarmsDocument32 pagesM 4 - Introduction of Server Farmsalan sibyNo ratings yet
- BSCMCAJDocument25 pagesBSCMCAJSayan Sarkar100% (1)
- E-Business in Organization: Term ProjectDocument34 pagesE-Business in Organization: Term ProjectZidan Zaif100% (1)
- Week 4 TutorialDocument15 pagesWeek 4 TutorialRabindra PoudelNo ratings yet
- ICTICT618Document43 pagesICTICT618Ajay YadavNo ratings yet
- Acolad Case Study Ethias Valo IntranetDocument4 pagesAcolad Case Study Ethias Valo IntranetDuy AnhNo ratings yet
- BSBDIV601 Assignment 2Document14 pagesBSBDIV601 Assignment 2Burichiku69100% (4)
- Service Case 12Document3 pagesService Case 12Г. СаруулNo ratings yet
- MIS - Chapter 1Document12 pagesMIS - Chapter 1tesfayeNo ratings yet
- AS&AL Information Technology SoW v1Document62 pagesAS&AL Information Technology SoW v1Ahmed ZiadNo ratings yet
- Key To The University of Iceland: Handbook For New EmployeesDocument24 pagesKey To The University of Iceland: Handbook For New EmployeesBenjamin LassauzetNo ratings yet
- Software Requirements Specification: Version 1.0 ApprovedDocument14 pagesSoftware Requirements Specification: Version 1.0 ApprovednurtureNo ratings yet