Professional Documents
Culture Documents
11 UT1 Revision
Uploaded by
dhageaaryan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesThis document contains a revision on redox reactions with 10 multiple choice and short answer questions:
1. The questions cover topics like oxidation states, identifying oxidation and reduction in reactions, oxidizing and reducing agents, distinguishing between redox and non-redox reactions, writing balanced redox equations, and naming ionic compounds.
2. Sample questions include identifying the oxidation state of cobalt in hexacyanoferrate(III), determining if a reaction involving carbon and oxygen is oxidation or reduction, and writing the balanced equation for the reaction of ferrous sulfate with acidified potassium dichromate.
3. The final question asks why the reductant sodium thiosulfate reacts differently with iod
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains a revision on redox reactions with 10 multiple choice and short answer questions:
1. The questions cover topics like oxidation states, identifying oxidation and reduction in reactions, oxidizing and reducing agents, distinguishing between redox and non-redox reactions, writing balanced redox equations, and naming ionic compounds.
2. Sample questions include identifying the oxidation state of cobalt in hexacyanoferrate(III), determining if a reaction involving carbon and oxygen is oxidation or reduction, and writing the balanced equation for the reaction of ferrous sulfate with acidified potassium dichromate.
3. The final question asks why the reductant sodium thiosulfate reacts differently with iod
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pages11 UT1 Revision
Uploaded by
dhageaaryanThis document contains a revision on redox reactions with 10 multiple choice and short answer questions:
1. The questions cover topics like oxidation states, identifying oxidation and reduction in reactions, oxidizing and reducing agents, distinguishing between redox and non-redox reactions, writing balanced redox equations, and naming ionic compounds.
2. Sample questions include identifying the oxidation state of cobalt in hexacyanoferrate(III), determining if a reaction involving carbon and oxygen is oxidation or reduction, and writing the balanced equation for the reaction of ferrous sulfate with acidified potassium dichromate.
3. The final question asks why the reductant sodium thiosulfate reacts differently with iod
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Bal Bharati Public School, Navi Mumbai
Class 11, 2023-24
Revision-Redox Reactions
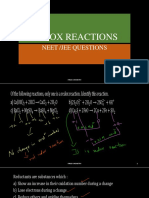
1. The oxidation state of Co in [Co(CN)6]3- is
(i) -6
(ii) -3
(iii) +6
(iv) +3
2. The conversion of C12H22O11 → CO2 is
(i) Oxidation of Carbon
(ii) Reduction of Carbon
(iii) Both Oxidation and Reduction of
(iv) Neither Oxidation nor reduction
3. In the reaction MnO4- + SO32- + H+ → Mn2+ + SO42- + H2O
(i) MnO4- and H+ both are reduced
(ii) MnO4- is reduced and H+ is oxidised
(iii) MnO4- is reduced and SO32- is oxidised
(iv) H+ and SO32- both are oxidised.
4. Which of the following can not be used as oxidising agent
(i) KMnO4
(ii) NH3
(iii) O3
(iv) HNO3
5. Which of the following is not a redox reaction
(i) Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
(ii) CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
(iii) 3Mg + N2 → Mg3N2
(iv) Al + Cl2 → AlCl3
6. Write the balanced redox equation when ferrous sulphate is treated with acidified
(H2SO4) Potassium dichromate.
7. Balance the following reaction in the basic medium by ion-electron method.
P4 → PH3 + H2PO2-
8. Justify that the following reactions are redox reactions:
(a) CuO(s) + H2(g) —–> Cu(s) + H20(g)
(b) Fe2O3(s) +3CO(g) —-> 2Fe(s) + 3CO2(g)
(c) 4BCl3(g) +3LiAlH4(s) ——> 2B2H6(g) + 3LiCl(s) + 3AlCl3(s)
(d) 2K(s) +F2(g)——> 2K+F–(s)
9. Write formulas for the following compounds:
(a) Mercury (II) chloride
(b) Nickel (II) sulphate
(c) Tin (IV) oxide
(d) Thallium (I) sulphate
(e) Iron (III) sulphate
(f) Chromium (III) oxide.
10. Consider the reactions:
Why does the same reductant, thiosulphate react differently with iodine and bromine?
You might also like
- Worksheets RRDocument4 pagesWorksheets RRHrithik JerathNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 10 Redox Reactions: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument9 pagesUNIT - 10 Redox Reactions: Multiple Choice QuestionsYogy YNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry-Sheet: 2 (Balancing of Reactions) : Level - 1 1. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7Document2 pagesStoichiometry-Sheet: 2 (Balancing of Reactions) : Level - 1 1. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7Aarnav JainNo ratings yet
- Redox - C1 - Oxidation NumberDocument3 pagesRedox - C1 - Oxidation Numberpraggyapal2020No ratings yet
- Redox Reactions: Neet /jee QuestionsDocument27 pagesRedox Reactions: Neet /jee QuestionsAsher LaurierNo ratings yet
- Assignment ElectrochemistryDocument12 pagesAssignment ElectrochemistryAnas AhmadNo ratings yet
- Redox - C2 - Reaction BalanceDocument3 pagesRedox - C2 - Reaction Balancepraggyapal2020No ratings yet
- Practice Questions For Class 10 ChemistryDocument1 pagePractice Questions For Class 10 Chemistrychankya chankyaNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactionstest PDFDocument1 pageRedox Reactionstest PDFaleena'No ratings yet
- Exercise 1 - 2-1Document14 pagesExercise 1 - 2-1Rijul BiradarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Assignment 5 Class 11Document3 pagesChemistry Assignment 5 Class 11Nayan ShahNo ratings yet
- Q - Oxidation - ReductionDocument2 pagesQ - Oxidation - ReductionBisad Abu CuriNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Class10 Chem t1Document4 pagesChemical Reactions Class10 Chem t1amittheapex312No ratings yet
- Chemistry Test Class 10thDocument2 pagesChemistry Test Class 10thW.B. LeoNo ratings yet
- Transition Elements - Model Questions PDFDocument6 pagesTransition Elements - Model Questions PDFSubhasish Sau100% (1)
- Cma CHEMISTRY ASIGNMENT RedoxDocument4 pagesCma CHEMISTRY ASIGNMENT RedoxUdayNo ratings yet
- 1001B B.P.S. X S.A. I Science Chapterwise 5 Printable Worksheets With Solution 2014 15Document111 pages1001B B.P.S. X S.A. I Science Chapterwise 5 Printable Worksheets With Solution 2014 15RajeevLochanNo ratings yet
- Balancing Redox ReactionsDocument1 pageBalancing Redox Reactionsmanisha awasthiNo ratings yet
- Problems For Balancing of Redox ReactionsDocument1 pageProblems For Balancing of Redox ReactionsUtsavNo ratings yet
- Task #6 - Hermo, Kathleen Mae M.Document3 pagesTask #6 - Hermo, Kathleen Mae M.KATHLEEN MAE HERMONo ratings yet
- 40 Questions Inorganic JEE Mains 2022 10 JuneDocument57 pages40 Questions Inorganic JEE Mains 2022 10 JuneMadhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions and Volumetric Analysis - DPP 01 (Of Lec-02) - Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Legend)Document3 pagesRedox Reactions and Volumetric Analysis - DPP 01 (Of Lec-02) - Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Legend)robysingh2005No ratings yet
- Class X - Chem - CH 1Document3 pagesClass X - Chem - CH 1saiNo ratings yet
- Chem Equation WWW MCQDocument17 pagesChem Equation WWW MCQrp2683387No ratings yet
- A - Oxidation - ReductionDocument2 pagesA - Oxidation - ReductionAlyasin FrougaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet-1 (Chemical Reaction)Document6 pagesWorksheet-1 (Chemical Reaction)Sachin Garg100% (1)
- Topic 9 Redox Booklet C ANSWERS 2014 (Amended Sept 2015)Document39 pagesTopic 9 Redox Booklet C ANSWERS 2014 (Amended Sept 2015)mickey mouseNo ratings yet
- Ncert Exemplar (CN)Document13 pagesNcert Exemplar (CN)RetroNo ratings yet
- C11.04 - Mole Concept - 24-07-2019 - 1563955592165 - Z5y8T - 1564301569428 - 51jcj PDFDocument12 pagesC11.04 - Mole Concept - 24-07-2019 - 1563955592165 - Z5y8T - 1564301569428 - 51jcj PDFOviya V100% (1)
- Balancing Redox Reactions by Ion-Electron MethodDocument2 pagesBalancing Redox Reactions by Ion-Electron Methodpeter_br3adNo ratings yet
- Reoxreaction Quick Revision - 2022Document9 pagesReoxreaction Quick Revision - 2022Hamad FarooqueNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science (CHEMISTRY) MCQs Chapter 1,2,3 QuestionsDocument53 pagesClass 10 Science (CHEMISTRY) MCQs Chapter 1,2,3 QuestionsKSA TEXTILENo ratings yet
- Kiangsu-Chekiang College (Shatin) Form 4 Chemistry TOPIC: Redox Reactions ExerciseDocument3 pagesKiangsu-Chekiang College (Shatin) Form 4 Chemistry TOPIC: Redox Reactions Exercise4D (05) Chan Wing Sum - 陳穎心No ratings yet
- XI Chemistry Open Book Test (Chap # 12 Electrochemistry)Document2 pagesXI Chemistry Open Book Test (Chap # 12 Electrochemistry)Newton's InnNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Worksheet - Redox ReactionsDocument2 pagesChemistry Worksheet - Redox Reactionsaryaaayush2006No ratings yet
- Equation AnswersDocument12 pagesEquation AnswersMark CalawayNo ratings yet
- Chem Class 10 Term 1 MCQ S & ARDocument78 pagesChem Class 10 Term 1 MCQ S & ARINDHRA VARMANo ratings yet
- Raffles Junior College JC2 H2 Chemistry 2007/8 Suggested Answers To Nov 2007 Chemistry 9746 Paper 1Document16 pagesRaffles Junior College JC2 H2 Chemistry 2007/8 Suggested Answers To Nov 2007 Chemistry 9746 Paper 1Ah XiuNo ratings yet
- 1chemical Reactions & Equations Top 25 Questions Prashant KiradDocument12 pages1chemical Reactions & Equations Top 25 Questions Prashant KiradKshitiz sharma100% (1)
- 9.coordination CompoundsDocument13 pages9.coordination CompoundsStatusNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Worksheet - Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 10 Chemistry Worksheet - Chemical Reactions and EquationsJai Prakash JingarNo ratings yet
- Üsküdar American Academy Grade 10 Chemistry Worksheet # 2 Subject: Chemical ReactionsDocument2 pagesÜsküdar American Academy Grade 10 Chemistry Worksheet # 2 Subject: Chemical ReactionsMustafa Ayhan DuduNo ratings yet
- P Block 1Document19 pagesP Block 1Sambhav Singhal100% (1)
- P BlockDocument3 pagesP BlockSambhav SinghalNo ratings yet
- 11th Worksheet 2022-23 Unit 7,8,12,13Document8 pages11th Worksheet 2022-23 Unit 7,8,12,13ADITYA SONINo ratings yet
- 17 - All Reaction Types Worksheet AnswersDocument8 pages17 - All Reaction Types Worksheet AnswersCubicatNo ratings yet
- All Batch Test Paper 18-09-2022Document9 pagesAll Batch Test Paper 18-09-2022Satish RajNo ratings yet
- Test - 3 Single Choice QuestionsDocument10 pagesTest - 3 Single Choice QuestionsGod is every whereNo ratings yet
- Taler Chemical Reactios. General Chemistry Teacher: William Alejandro Andrade BarreiroDocument8 pagesTaler Chemical Reactios. General Chemistry Teacher: William Alejandro Andrade BarreiroENITH HERRERA MONTALVONo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2 - 2003Document4 pagesChemistry 2 - 2003Emanuel John BangoNo ratings yet
- Tranisition Elements-03 - Assignments (New)Document13 pagesTranisition Elements-03 - Assignments (New)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Answers To ExercisesDocument5 pagesTopic 6 Answers To ExercisesKizzy-Anne BoatswainNo ratings yet
- Keep508 PDFDocument9 pagesKeep508 PDFshubhammukriNo ratings yet
- Unit3 Stoichiometry QnsDocument14 pagesUnit3 Stoichiometry QnsLokesh Kumar100% (1)
- Tutorial 8 - CHM420 - Sept 2020Document2 pagesTutorial 8 - CHM420 - Sept 2020Hai AwakNo ratings yet
- Chem Academy: Exercise - IDocument14 pagesChem Academy: Exercise - IHamit RanaNo ratings yet
- Probleme IiDocument16 pagesProbleme IisorinikloveNo ratings yet
- IOC - IRP - Home Test-2 (Without Answer) - SendDocument11 pagesIOC - IRP - Home Test-2 (Without Answer) - SendNicholas BourbakiNo ratings yet
- Redox and Equivalent ConceptDocument6 pagesRedox and Equivalent ConceptajaxNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)