Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Revision Worksheet 2 - Ix
Uploaded by
tirzahann.ashley0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageOriginal Title
REVISION WORKSHEET 2- IX
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageRevision Worksheet 2 - Ix
Uploaded by
tirzahann.ashleyCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
SHERWOOD HIGH
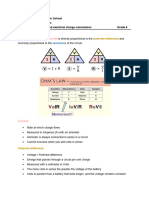
CHAPTER 9: CURRENT ELECTRICITY
WORKSHEET
1. What do you understand by electric circuit?
2. What do you understand by closed electric circuit?
3. What do you understand by open electric circuit?
4. What do you understand by the term electric resistance?
5. What do you understand by the term electric potential?
6. Define electric potential in terms of energy spent.
7. What do you mean by quantity of electric charge?
8. What do you understand by the term electric current?
9. Define the term potential difference.
10. What is an electric cell?
11. Define the two types of cells.
12. Define one ampere current.
13. What is a rheostat?
14. State ohm's law.
15. Define insulators and conductors.
16. Define 1 ohm.
17. Using a cell, key, rheostat, bulb, voltmeter and ammeter, draw an electric circuit to light a
bulb.
18. Draw the symbols of open key, closed key, open switch, closed switch, fixed resistor,
variable resistor,ammeter and voltmeter.
19. Write the SI units of current, potential difference, resistance and charge.
20. Name the instrument used to measure current and potential difference.
21. Distinguish between a closed circuit and an open circuit, with the use of suitable labelled
diagrams.
22. State two differences between a primary cell and a secondary cell.
NUMERICALS
1. A charge of 75 C is brought from infinity to a given point in an electric field, when
amount of work done is 3.75 J. Calculate the electric potential at that point.
2. A charge of 5000 C flows through an electric circuit in 2 hours and 30 minutes. Calculate
the magnitude of current in the circuit.
3. A charge of 8860 C flows through an electric circuit in 2 mins and 40 s. Calculate the
magnitude of current in the circuit
4. A battery can supply a charge of 25 × 104 C. If the current is drawn from the battery at the
rate of 2.5 A, calculate the time in which the battery will discharge completely.
5. Calculate the potential difference across the ends of a wire of resistance 2 Ω when a
current of 1.5 A passes through it.
6. Calculate the current flowing through a wire of resistance 7.5 Ω connected to a battery of
potential difference 1.5 V.
7. In transferring 1.5 C charge through a wire, 9 J of work is needed. Find the potential
difference across the wire.
1. A cell of potential difference 12 V is connected to a bulb. The resistance of filament of
bulb when it glows is 24 Ω. Find the current drawn from the cell.
2. A bulb draws current 1.5 V at 6.0 V. Find the resistance of filament of bulb while
glowing.
3. A current of 0.2 A flows in a wire of resistance 15 Ω. Find the potential difference across
the ends of the wire.
You might also like
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- ElectricityDocument78 pagesElectricityAryan Kaul CeNtErNo ratings yet
- Reduced Syllabus Questions (Physics)Document15 pagesReduced Syllabus Questions (Physics)Saher SaghirNo ratings yet
- Is Electric Current A Scalar or Vector QuantityDocument3 pagesIs Electric Current A Scalar or Vector QuantityAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Ans Electricity Additional Questions 1Document5 pagesAns Electricity Additional Questions 1Rohit JindalNo ratings yet
- 12thQuestionBank (KSU)Document9 pages12thQuestionBank (KSU)sohailmushtaq1001No ratings yet
- Is Electric Current A Scalar or Vector QuantityDocument3 pagesIs Electric Current A Scalar or Vector QuantityAshok Pradhan100% (1)
- CNS-EE 1: Electricity, Magnetism, Circuits & SemiconductorsDocument9 pagesCNS-EE 1: Electricity, Magnetism, Circuits & SemiconductorsLanbert FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Question Bank BeeDocument25 pagesQuestion Bank Beedhruv goraiNo ratings yet
- Sample Problem For Quiz 1Document3 pagesSample Problem For Quiz 1Christelle Cha LotaNo ratings yet
- II PUC PHYSICS Enrichment PackageDocument4 pagesII PUC PHYSICS Enrichment PackageSohum VenkatadriNo ratings yet
- G8 Q1 Module No.6 Week No.5-To-7Document22 pagesG8 Q1 Module No.6 Week No.5-To-7Nickary RaineNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit ConceptsDocument22 pagesElectric Circuit ConceptsNickary RaineNo ratings yet
- Electricity Assignment HHWDocument5 pagesElectricity Assignment HHWAditya GoelNo ratings yet
- 1st Module of PhysicsDocument16 pages1st Module of Physicsଚିତ୍ତରଞ୍ଜନ ପାଣିNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 S4Document17 pagesUnit 5 S4sekanyanaalbert471No ratings yet
- Electricity WorksheetDocument11 pagesElectricity Worksheetsrijankanduri14No ratings yet
- Electric Circuits - Ohms LawDocument11 pagesElectric Circuits - Ohms LawCarmenNo ratings yet
- Suggestion PhysicsDocument4 pagesSuggestion PhysicsAltaf AliNo ratings yet
- Printer Plugin Job #1703819677323Document3 pagesPrinter Plugin Job #1703819677323jeevadharshiniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Basic Atomic Theory: Key PointsDocument4 pagesChapter 1: Basic Atomic Theory: Key PointsDaahirshiiq MadoobeNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument490 pagesPhysicsrevamanianNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law: Understand Circuit Elements and Power DissipationDocument19 pagesOhm's Law: Understand Circuit Elements and Power Dissipationrazel besagasNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For Volume 1Document3 pagesQuestion Bank For Volume 1yaro oruvanNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet Class: X Chapter: ElectricityDocument2 pagesPhysics Worksheet Class: X Chapter: ElectricityMohit GargNo ratings yet
- XLL - Physics Question BankDocument11 pagesXLL - Physics Question BankKanagaraj RNo ratings yet
- Electricity worksheet solvedDocument2 pagesElectricity worksheet solvedMohit GargNo ratings yet
- Tutorial QuestionsDocument20 pagesTutorial Questionsharshiika kathiravanNo ratings yet
- Qdoc - Tips Current Electricity Question BankDocument6 pagesQdoc - Tips Current Electricity Question BanknunjapiznesNo ratings yet
- Sample QuestionsDocument8 pagesSample QuestionsSong BrokerNo ratings yet
- SH 1Document9 pagesSH 1moh99eidNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Internal Resistance em 1587263355Document12 pagesFactors Affecting Internal Resistance em 1587263355SHIBU PRASAD SAHOO100% (1)
- DC Current Physics Project GuideDocument34 pagesDC Current Physics Project GuideAmrita SinghNo ratings yet
- Super Elex 4Document10 pagesSuper Elex 4Charles Adrian CNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - 14ELE15Document6 pagesQuestion Bank - 14ELE15Rakesh ThapliyalNo ratings yet
- MODULE 5 TABAOelectricity and CircuitsDocument13 pagesMODULE 5 TABAOelectricity and Circuitsannetabao01No ratings yet
- Class 12-Phy-Em - Class - 12 - Three Mark Questions and AnswerDocument22 pagesClass 12-Phy-Em - Class - 12 - Three Mark Questions and AnswerMohammed SulaimonNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICITYDocument3 pagesELECTRICITYMohan SuyalNo ratings yet
- Question - 2022 01 24Document1 pageQuestion - 2022 01 24John HayesNo ratings yet
- Sr. PhysicsDocument6 pagesSr. PhysicsMavuluri UmamaheshNo ratings yet
- Electricity - Assignment - 1: PhysicsDocument5 pagesElectricity - Assignment - 1: PhysicsCRUEL HUNTERNo ratings yet
- Electricity - Revision WorksheetDocument7 pagesElectricity - Revision Worksheetmk.afeefuddinNo ratings yet
- Ac311 MDocument6 pagesAc311 MjerkNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic and Magnetism ModuleDocument42 pagesElectrostatic and Magnetism ModuleANGELO NINO ALVARADONo ratings yet
- Physics 12 Imp Questions by Fortune AcademyDocument4 pagesPhysics 12 Imp Questions by Fortune AcademyKamran KhanNo ratings yet
- Physics ADS Past PaperDocument6 pagesPhysics ADS Past Paperkhanrameen747No ratings yet
- Cicuits REVISIONDocument3 pagesCicuits REVISIONSally SargentNo ratings yet
- Electricity Workshop 2020Document8 pagesElectricity Workshop 2020zaxNo ratings yet
- Second Year Physics QuestionsDocument6 pagesSecond Year Physics QuestionsRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics Shorthand Guide by Ri DaDocument5 pagesPhysics Shorthand Guide by Ri DaGAME DEVNo ratings yet
- EE1100 Spring 2020 Tutorial 1Document2 pagesEE1100 Spring 2020 Tutorial 1Ram Lakhan MeenaNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 1Document5 pagesPhysics 1 109 Ethan Ho Zehn Hee 何政希No ratings yet
- Ts SR Physics Imp Questions 2023-24Document5 pagesTs SR Physics Imp Questions 2023-24s.pranay11.reddy100% (1)
- Senior Physics Ipe Imp Question Bank 2019-20Document10 pagesSenior Physics Ipe Imp Question Bank 2019-20Soumendu KonaeNo ratings yet
- Bee MidtermsDocument103 pagesBee MidtermsROSABELLE CABADINNo ratings yet
- Charles Darwin discusses circuit analysis conceptsDocument7 pagesCharles Darwin discusses circuit analysis conceptsChristian Mayol SalvañaNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument9 pagesPhysics ProjectSYED ADNANNo ratings yet
- Mysuru Royal Institute of Technology, Mandya.: Question Bank-IDocument2 pagesMysuru Royal Institute of Technology, Mandya.: Question Bank-IJyothi M PNo ratings yet
- JRC127220 01Document74 pagesJRC127220 01GMNo ratings yet
- Notes CH 6Document10 pagesNotes CH 6Charlie RNo ratings yet
- Division Quarterly Unified Test English 6Document21 pagesDivision Quarterly Unified Test English 6rogielynNo ratings yet
- Grow Your Mindset CHDocument4 pagesGrow Your Mindset CHapi-468161460No ratings yet
- Fy2023 CBLD-9 RevisedDocument11 pagesFy2023 CBLD-9 Revisedbengalyadama15No ratings yet
- Din 2215 2Document7 pagesDin 2215 2Dule JovanovicNo ratings yet
- School of Mathematics and Statistics Spring Semester 2013-2014 Mathematical Methods For Statistics 2 HoursDocument2 pagesSchool of Mathematics and Statistics Spring Semester 2013-2014 Mathematical Methods For Statistics 2 HoursNico NicoNo ratings yet
- Cot Lesson Plan in Math 5 Q1Document11 pagesCot Lesson Plan in Math 5 Q1Gina VilloriaNo ratings yet
- ComparativeDocument5 pagesComparativeROUZBEH BANIHASHEMINo ratings yet
- Density and Unit Weight of Soil in Place by The Rubber Balloon MethodDocument6 pagesDensity and Unit Weight of Soil in Place by The Rubber Balloon MethodMarcos Verissimo Juca de PaulaNo ratings yet
- Add Math Form 4Document4 pagesAdd Math Form 4Nor Hanina88% (25)
- Read ChromaticDocument20 pagesRead ChromaticGURNOORNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Unit h156 02 Depth in Physics JuneDocument15 pagesMark Scheme Unit h156 02 Depth in Physics JunewillowchenchenNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 - MELC 11: Mathematics Activity SheetDocument9 pagesQuarter 4 - MELC 11: Mathematics Activity SheetSHAIREL GESIMNo ratings yet
- (Reuters Institute For The Study of Journalism) James Painter - Climate Change in The Media - Reporting Risk and Uncertainty-I. B. Tauris (2013)Document192 pages(Reuters Institute For The Study of Journalism) James Painter - Climate Change in The Media - Reporting Risk and Uncertainty-I. B. Tauris (2013)Thomas Ravelly Batista dos SantosNo ratings yet
- Avio Et Al., 2016Document10 pagesAvio Et Al., 2016Aditya RahmanNo ratings yet
- Mid Test. GrammarDocument3 pagesMid Test. GrammarAris Nack TavNo ratings yet
- Revised Both Curri 2021-V3Document105 pagesRevised Both Curri 2021-V3mezigebu100% (1)
- Lesson 10 Graphic OrganizersDocument22 pagesLesson 10 Graphic Organizersisabelcadagtan10No ratings yet
- Bms PCC and RCC PDFDocument27 pagesBms PCC and RCC PDFKeshav SethiNo ratings yet
- Listado 13Document436 pagesListado 13Abel Hernandez SoteloNo ratings yet
- Ilham Shalabi, Imam Muhammad Bin Saud Islamic UniversityDocument20 pagesIlham Shalabi, Imam Muhammad Bin Saud Islamic Universityaron victoryNo ratings yet
- PRINCIPLES OF DETERMINING WATER'S FORMULADocument1 pagePRINCIPLES OF DETERMINING WATER'S FORMULAMominul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Why Does Music Move UsDocument4 pagesWhy Does Music Move UskhanhngocnguyennnNo ratings yet
- Nichiyu Forklift 1 99gb PDF FBFBRHTPLDRBRFTSBW Spare Part Catalogue Service ManualDocument23 pagesNichiyu Forklift 1 99gb PDF FBFBRHTPLDRBRFTSBW Spare Part Catalogue Service Manualpaulfrazier090185apo100% (122)
- Avrami 1939 Kinetics of Phase Change. I General TheoryDocument11 pagesAvrami 1939 Kinetics of Phase Change. I General TheoryrobertNo ratings yet
- Trauma Stewardship: An Everyday Guide To Caring For Self While Caring For Others - Laura Van Dernoot LipskyDocument5 pagesTrauma Stewardship: An Everyday Guide To Caring For Self While Caring For Others - Laura Van Dernoot Lipskyhyficypo0% (3)
- TOPNOTCH DIGITAL HANDOUT - BIOCHEMISTRY Juan Dela CruzDocument2 pagesTOPNOTCH DIGITAL HANDOUT - BIOCHEMISTRY Juan Dela CruzJoy Fucanan100% (1)
- Isherwood A Single ManDocument66 pagesIsherwood A Single ManS A100% (3)
- UROP Proceedings 2015-16Document95 pagesUROP Proceedings 2015-16alex61937No ratings yet