Professional Documents
Culture Documents
11th Chem Annual QP
11th Chem Annual QP
Uploaded by
tara.joji0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views6 pagesOriginal Title
11th chem annual qp
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views6 pages11th Chem Annual QP
11th Chem Annual QP
Uploaded by
tara.jojiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
THE SAMHITA ACADEMY
Date: 23-01-2023 Annual Examination-2022-23
11 Subject: Chemistry Marks: 70
General Instructions:
‘There are 35 questions in the question paper with internal choice. All questions are compulsory.
Section A : Question number 1 to 18 are objective type questions each carrying 1 mark.
Section B : Question number 19 to 25 are short answer type questions each carrying 2 marks.
Section C : Question number 26 to 30 are short answer type questions each carrying 3 marks.
Section D : Question number 31 and 32 are passage based questions each carrying 4 marks.
Section E : Question number 33 to 35 are long answer type questions each carrying 5 marks.
‘© Use of calculators and log tables are not permitted.
Section-A,
1. Density of 2.05 M solution of acetic acid in water is 1.02 g/mL. The molality of the solution is
a)1.14m b)3.28m ) 2.28m, 4)0.44m
2. The amount of CO? produced from combustion of one mole of CaHio on complete combustion
is
a) 176g b) 44g, ©) 88g d) 132g,
3. 12 LH reacts with 11.2 L of Clzare mixed and exploded, The composition of final mixture is
a) 24 Lof HCl b) 0.8 Lof Ch, 20.8 L of HCI
¢) 22.4 Lof HCI, 0.8 Lof He d) 22.4 Lof HCI
4.
What is the maximum number of orbitals that can be identified with the following quantum,
numbers? n= 3, != 1, m=O
a)i b)2 3 d)4
5. Which elements is expected to have lowest ionisation enthalpy?
a) Sr b) As xe ds
6. Which of the following does not have zero dipole moment?
a) CO, b)CS2 «S02 d) CC
7. The species which has bond angle 120°.
a) ClFs b) NC ©) BCs d) Pls
The bond order for Of, C; are
a)25,2 b)2,3 3,2 15,20
10.
1.
14
16.
£
‘The correct thermodynamic conditions for spontaneous reaction at all temperatures is
b) AH<0&45<0
a) OH0
©) OH<08AS=0 _ d)BH> 0&AS<0
1
«6,
For the reaction, CO + Chin = COChig, the eS equal to
a) VAT b)RT °: iz d)1.0
Which of the following can act as oxidising as well as reducing agent? 1
a) Hy dk ) 202 d) All of these
‘The element which does not undergo disproportionation 1
aa b) Br OF di
‘The order of priority functional groups in IUPAC ‘system 1
a) -CONHa, ~CHO, “SO3H, COOH b) -COOH, -sosH, ~CONH2, -CHO
©) -SOsH, ~COOH, ~CONH2, ~CHO. 4) -CHO, -cooH, ~SOsH, ~CONH2
srw ang ets ted wth ene wih Et (product and select the comet 1
‘answer using the codes given below the lists,
Uist ist
1 Hydrogen in presence of catalyst AT Benzene
uw Heat at 600°C B | Acetaldehyde
Ai Hydrogen in presence of Pd and CaCO, at a7aK TC Ethene |
IV | __Water in presence of H:S0« and HesOe [D| Ethane
2) 18, IC, IED, I-A b) LA, IED, TIC, 1V-B
) FA, 1-0, 1-8, 1v-c.
4) LD, ILA, ILC, 1V-B
‘The correct IUPAC name of the following compound is aN 1
b) S-ethyl-4-propyldecane
4) 4-(I-methylethy)-5-(1-methylpropyl}-decane
Solution containing a mixture of acetic acid and sodium acetate maintains 1
Eonstant value of Pon addition of small amounts of acid or alll
Reason: A solution containin,
1 a mixture of acetic acid and sodium acetate acts asa buffer
solution around P* = 4.75
a) Both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not a correct
b) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct e
¢) Assertion is false but Reason is true.
4) Assertion is true but Reason is false,
explanation of Assertion.
-xplanation of Assertion,
a7.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24,
25.
Assertion: Oxidation number of Cin HCHO is zero. 1
Reason: Formaldehyde is covalent compound.
2) Both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not a correct explanation of Assertion.
'b) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
€) Assertion is false but Reason is true.
4d) Assertion is true but Reason is false.
Assertion: Nitration of benzene with nitric acid req
acid.
Reason: The mixture of concentrated sulphui
electrophile (NOt).
Wires the use of concentrated sulphuric a
acid and concentrated Nitric acid produces the
a) Both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is hot a correct explanation of Assertion,
') Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reasons the correct explaniation of Assertion,
c) Assertion is false but Reason is true.
d) Assertion is true but Reason is false.
SECTION -~B
{()) Define mole fraction of solute (i) Define limiting reagent. 2
oR
Calculate the % of copper in a sample of CuCl (Atomic weights of Cu = 63.5 u, CI= 35.5 u)
Calculate wave number of the line having frequency 5 x 10% Hz, 2
oR
An element of atomic weight Z consists of two isotopes of mass number 2-1 and Z+2.
Calculate the % of the higher isotope.
(i) Why is dipole moment of BFs is zero? a
(li) Write the resonance structures of CO3-.
Explain the shape of the following based on VSEPR theory (a) ClFa (b) XeFs 2
(i) What is meant by electrochemical series? 2
ti
Give condensed and bond line structural formula of the following; 2
(a) Cycloocta-1,3,5,7-tetraene (b) 2-(4-isobutylphenyllpropancic acid,
What happens when F2 reacts with 420?
Write the structure and name of the products obtained by ozonolysis of pent-2-ene. 2
oR
How will you convert benzene to acetophenone?
3
oO
oy at At
Ps
»
‘
t
See oe EEE
26.
27.
29.
30.
31.
SECTION -C
A compound on analysis found to contain following percentage composition Na= 43.4%,
C=11.4% and 0=45,3%, Determine the empirical and molecular formulae. Given Molar mass of
the compound is 106 g mot.
OR
Hydrogen reacts with nitrogen to produce ammonia according to the equation:
3H2q) + Naj—>2NHsig. Determine how much ammonia would be produced if 100 g of Nz
reacts?
{i) Define uncertainty principle.
(ii) Calculate the uncertainty in the position of an electron (mass = 9.1 x 10°
kg) moving with
velocity of 300 ms”, accurate up to 0.001% (h = 6.626 x 10 Js),
oR
An ion with mass number 37 possesses one unit of negative charge. If the ion contains 11.1%
‘more neutrons than electrons, find the symbol of the ion.
()An element has atomic number 35. To which group and period does it belong?
(ii) Lanthanoids and actinoids belong to which block of the periodic table?
(ii) How does ionisation enthalpy vary across the period and down the group?
Write molecular orbital electronic configuration of the Nz molecule and comment on its bond
‘order and magnetic behaviour.
OR
(i) What is the state of hybridisation of nitrogen in NHf ion?
(ii) Draw the shape of PHs and SFe according to VSEPR theory.
(iii) What is the hybridisation of carbon atoms in CHs~CHO
a) Write the structural formulae for compounds name as
(i) 1-bromoheptane (ii) S-bromoheptanoic acid
b) What are electrophiles? Give one example of electrophilic substitution reaction.
SECTION-D
Thermodynamics involve energy changes and chemical reactions and other process. Internal
energy is the total energy stored in a substance. We can specify absolute value of volume but
not absolute value of internal energy. We can measure only change in internal energy (AU).
‘Work done on the system is taken as positive and work done by the system is taken as
negative. Q absorbed by the system is positive and heat given output system is narrative.
‘AU=q+w according to first law of thermodynamics. AH(enthalpy change) is measured at
constant pressure, AU is measured at constant volume. OH, OS(entropy change), MG(Free
energy change) and temperature help to decide spontaneity of the process.
3
3
4
32.
i. Which of the following is true for adiabatic process?
(a) a= (b) BU=Wraabave (c) both (a) and (b) (d) None of these
fi. 1f 701.4 of heat is absorbed by the system and 394 J of work is done by the system. The
value of AU is equal to
(a) 3073 (by3945 (700 aq
UW. 2 litres of an ideal gas at a pressure of 10 atmosphere expands isothermally into vacuum
until its total volume is 10 litres. Which of the following is true?
(a) q=0 (b) W=
(c) au=0 (4) all of these
\v. For an equilibrium H20y) = H204p, which of the following is/are correct?
(a)aG=0 — (b) AH>0 ()as>0 (4) all of these
OR
V. For N20s = 2NOnig, AH-AU is equal to
(a) RT (b)-RT ()42RT (d)-2RT
Equilibrium can be established for both physical and chemical processes at equilibrium rate of
forward and reverse processes or equal. Equilibrium constant Kc is expressed as concentration
of products divided by reactants each raise to the power stoichiometric coefficients, Ke has
fixed value of constant temperature at this stage concentration, pressure..ete become
Constant. Ke is equilibrium constant in terms of partial pressure of gases or vapours. The
direction of reaction can be hey predicted by the reaction quotient Qc and Qp. Qc is equal to Ke
at equilibrium. Le-chatelier's principle states equilibrium will shift in direction to counter
balance the effect of change in temperature pressure and concentration film between ions
and unionized molecules in weak electrolyte is called ionic equilibria.
2NOnig;= N2O«, + 60.0 kd, the increase in temperature
(2) Favour the formation of N20,
(6) Does not affect the eq
(b) Favours the decomposition of NOs
ibrium, (d) stops the process
For the reaction, COig) + Clajg) COCK, the Ko/Ke is equal to
(a) VRT (b) RT Oz (d)1.0
{In which condition, the reaction proceeds in the forward direction?
(2) Qc=Ke — (b) Qe> Ke (6) Qe< ke (4) Qe # Ke
{In the equilibrium, AB = A+ 8, ifthe e
equilibrium concentration of 8 will be
quilibrium concentration of A is double, then
(a) half (b) twice (pth (deh
oR
¥. Of the following which change will shift the reaction towards the product at
equilibrium?
(2) increase in total pressure
(b) increase in temperature
(c) Decrease in concentration of lz
(4) increase in concentration of |
SECTION-€
33, Answer the following:
(a)n + /value for the 14" electron in an atom.
(b) increasing order of filing electron in 4f, Sp and 6d subshells.
(€) mand / value for last electron of Mg{12] atom.
(4) subshell in which last electron in Ga[33).
(e) sum of spin of all electrons in element having atomic number 14.
OR
(a) In.a hydrogen atom, an electron jumps from the 5! orbit to the 2"4 orbit. Calculate the
wavelength and frequency of the radiation emitted.
(b) Calculate the energy of one mole photons from a radiation of frequency 5.8 x 10™ Hz.
34, (a) Give three points of differences between inductive effect and resonance effect.
(b) Which of the following compounds will not exist as a resonance hybrid. Give reason for
your answer (i) CH30H (ii) R-CONH2 (iii) CHsCH=CHCH2NH2
‘OR
(a) Give condensed and bond line structural formulas and identify the functional group(s)
present, if any, for:
(i)2,2,4-trimethylpentane (ii) 2-Hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylic acid
(b) Explain functional isomerism with a suitable example.
i) Hexanedial
35. (a) Explain the mechanism for nitration of benzene.
(b) Explain Wurtz reaction for the preparation of butane.
oR
(a) Give the mechanism for chlorination of methane.
(b) Classify the following compounds as oO O
0 o
”
aromatic/non-aromatic.
a
«
2fp 6
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5811)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Nationalism in Europe 2Document5 pagesNationalism in Europe 2tara.jojiNo ratings yet
- NB Question-1Document3 pagesNB Question-1tara.jojiNo ratings yet
- NotsDocument7 pagesNotstara.jojiNo ratings yet
- ch11 2Document90 pagesch11 2tara.jojiNo ratings yet
- Identity FomrationDocument3 pagesIdentity Fomrationtara.jojiNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2021-09-01 at 4.13.40 PMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2021-09-01 at 4.13.40 PMtara.jojiNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2021-09-01 at 7.04.13 PMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2021-09-01 at 7.04.13 PMtara.jojiNo ratings yet
- Datesheet 69726Document1 pageDatesheet 69726tara.jojiNo ratings yet
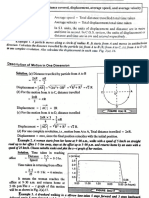
- Homework 2 PhysicsDocument1 pageHomework 2 Physicstara.jojiNo ratings yet
- Hindi Chapter 2Document4 pagesHindi Chapter 2tara.jojiNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jan 02, 2024Document20 pagesAdobe Scan Jan 02, 2024tara.jojiNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Dec 01, 2023Document24 pagesAdobe Scan Dec 01, 2023tara.jojiNo ratings yet