Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sociology'''
Uploaded by
Cresty Eid0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pagesThe document is a sociology worksheet that defines and provides examples of key sociological concepts related to culture. It discusses the differences between material culture and non-material culture, defines culture as consisting of values, norms, knowledge and ideas, and provides examples of beliefs and how they can be true or false. It also defines and gives examples of ideal culture versus real culture, and explains how and why cultures can change over time through discovery, invention, and diffusion.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document is a sociology worksheet that defines and provides examples of key sociological concepts related to culture. It discusses the differences between material culture and non-material culture, defines culture as consisting of values, norms, knowledge and ideas, and provides examples of beliefs and how they can be true or false. It also defines and gives examples of ideal culture versus real culture, and explains how and why cultures can change over time through discovery, invention, and diffusion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pagesSociology'''
Uploaded by
Cresty EidThe document is a sociology worksheet that defines and provides examples of key sociological concepts related to culture. It discusses the differences between material culture and non-material culture, defines culture as consisting of values, norms, knowledge and ideas, and provides examples of beliefs and how they can be true or false. It also defines and gives examples of ideal culture versus real culture, and explains how and why cultures can change over time through discovery, invention, and diffusion.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Sociology Worksheet
1. What does the non-material culture involve?
It involves beliefs, ideas, and knowledge.
2. What does the “material culture” mean?
It means the relation of the physical objects to culture.
3. What is culture made up of?
Culture is made up of values, norms, knowledge, and ideas.
4. What do we mean by beliefs?
beliefs are ideas about the nature of reality. They can be true or false.
5. Give example to a false belief related to The Romans.
The Romans believed Caesar Augustus to be a god, and this is a false
belief.
6. Give example to a false belief about the Tribe of Madagascar.
They believed that the souls of their kings passed into snakes.
7. Why are beliefs important?
Beliefs are important because people base their behavior on what they
believe in.
8. What do we mean by the “ Ideal culture”
The ideal culture is cultural guidelines embraced by members of a society.
9. What do we mean by “ Real Culture”?
Real culture is the actual behavior patterns which could conflict with
these guidelines of the ideal culture.
10.Give example of real culture and ideal culture related to America.
Americans say that their ideal culture is honesty, yet in real culture
honesty is not really practiced, as some businessmen engage in dishonest
practices.
11.Does the fact that we sometimes ignore some cultural guidelines make the
ideal culture meaningless?
No, that is not true. The ideal culture is important whether people
followed it or didn’t.
12.The ideal culture provides which standards?
It provides high standards of behavior and communication
13.What does the ideal culture prevent?
It prevents deviant ( or abnormal) behavior.
14. Does culture change?
Yes, culture could change over the years. For example, middle class
women at a time of history were not encouraged to work, while now this
idea changed.
15.What are the reasons for the change of any culture?
1. Discovery ( you discover something that already exists)
2.Invention or creation of something new
3. Diffusion
16.Are teenage troubles only hormonal?
No, they are cultural as well.
17. Why could we find “ cultural diversity”
Cultural diversity is a result of social categories.
18.Who are the “ subculturers”?
Subculturers are groups that have some ways of thinking, feeling, and
behaving that set them apart from the broad culture of the society.
19.Where could we find “ subculturers ”
Subcultural groups could be found in large or complex societies.
20.What do we mean by “ subculture ”
A subculture is part of the dominant culture but differs in some aspects.
21. What do we mean by a “ counter culture”?
Counterculture is a subculture that deliberately and consciously opposed
to certain beliefs or attitudes of the dominant culture.
22. What do we mean by “ Ethnocentrism”?
Ethnocentrism means to become strongly committed to your culture and
not able to imagine any other way of life. You may even judge others in
terms of your own standards.
23. What do we mean by “ cultural universals”?
Cultural universals are traits that exist in all cultures. They include marriage,
sports, cooking, education, funerals, and medicine.
24. How are cultural universals expressed?
Education, marriage, medicine, and sports, and funerals are not always
carried out in the same way. Different cultures have developed different
ways of expressing or dealing with these universals.
25. Why do cultural universals exist?
Because there are biological similarities shared by all human beings, and
because societies face many of the same social problems.
You might also like
- Chapter 5 CultureDocument28 pagesChapter 5 CultureCristinaNo ratings yet
- Chaper 1 & 2Document22 pagesChaper 1 & 2Nisa IstafadNo ratings yet
- 8 +Cultural+RelativismDocument56 pages8 +Cultural+RelativismReylan Javillo100% (1)
- What Is Culture?: Social StructureDocument3 pagesWhat Is Culture?: Social StructureBhienz BendorioNo ratings yet
- CultureDocument4 pagesCultureLady Lee CabiganNo ratings yet
- PageMaker Short NotesDocument37 pagesPageMaker Short NotesSur Velan100% (1)
- Definition, Characteristics and Important Functions of Culture (Jaena&Parba)Document28 pagesDefinition, Characteristics and Important Functions of Culture (Jaena&Parba)Vergie Lyn Pioquinto JaenaNo ratings yet
- Cultural Relativism PPT 1st Sem 2022 2023Document21 pagesCultural Relativism PPT 1st Sem 2022 2023Juls PanchoNo ratings yet
- UNESCO - Community Radio Handbook 2001Document105 pagesUNESCO - Community Radio Handbook 2001breegones100% (3)
- Chapter IV Culture and Moral BehaviourDocument15 pagesChapter IV Culture and Moral BehaviourRika MaeNo ratings yet
- Cultural RelativismDocument8 pagesCultural Relativismruth honradoNo ratings yet
- Tomas Claudio Colleges: EDUC 201 - Foundations of Education EDUC 201 - Foundations of EducationDocument47 pagesTomas Claudio Colleges: EDUC 201 - Foundations of Education EDUC 201 - Foundations of EducationKimberly ToquirreNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Heat Transfer LabDocument92 pagesLab Manual Heat Transfer Labعلى طرق السفرNo ratings yet
- Tablet by Anand KumarDocument15 pagesTablet by Anand KumarAnand Kumar100% (1)
- The Cultural Context: Chapter ObjectivesDocument8 pagesThe Cultural Context: Chapter ObjectivesTilaVathyNo ratings yet
- CULTUREDocument15 pagesCULTUREAyesha Khalid100% (1)
- Chapter 1 To 3 - Understanding The SelfDocument8 pagesChapter 1 To 3 - Understanding The SelfAbby Umali-Hernandez100% (2)
- Culture Shapes Moral BehaviorDocument14 pagesCulture Shapes Moral BehaviorCorrine AbucejoNo ratings yet
- EthicsDocument4 pagesEthicsChristine Joy SistosoNo ratings yet
- Cultural Relativism - Week4 - GRP 2 - Ethics 0008-49Document24 pagesCultural Relativism - Week4 - GRP 2 - Ethics 0008-49Bryan Castro TumazarNo ratings yet
- Ethics - Topic 1 - Culture, Cultural Relativism, Filipino Way and Universal ValuesDocument14 pagesEthics - Topic 1 - Culture, Cultural Relativism, Filipino Way and Universal ValuesgabgohobNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: The Culture of Human SocietyDocument7 pagesLesson 3: The Culture of Human SocietyNicole Roxanne RubioNo ratings yet
- CULTUREDocument6 pagesCULTUREBIBINo ratings yet
- Popular CultureDocument2 pagesPopular CultureKlare TyNo ratings yet
- II. CultureDocument40 pagesII. CultureLyvelyn Gallentes Ferrer100% (1)
- The Dynamics of Social Behaviour: I. Why Is Culture So Important?Document3 pagesThe Dynamics of Social Behaviour: I. Why Is Culture So Important?Deni DarmawanNo ratings yet
- 7 Cultural RelativismDocument4 pages7 Cultural RelativismChristine Joy VillasisNo ratings yet
- Sosio Chapter 3 (Edit)Document3 pagesSosio Chapter 3 (Edit)Deni DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 The Challenge of Cultural RelativismDocument4 pagesChapter 8 The Challenge of Cultural Relativismmaye labitoriaNo ratings yet
- AnthropologyDocument13 pagesAnthropologyqaaniNo ratings yet
- Effects of Education On Cultural Development: Unit StructureDocument14 pagesEffects of Education On Cultural Development: Unit StructureAbdulAhadNo ratings yet
- Ailene F. Quinto BSMA-lllDocument3 pagesAilene F. Quinto BSMA-llljennie kimNo ratings yet
- Culture and Subculture Lo3Document13 pagesCulture and Subculture Lo3fento2011No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Gel 423 Introduction To Popular Culture..Document6 pagesLesson 1 Gel 423 Introduction To Popular Culture..KAYE B. NECESARIONo ratings yet
- General Elective 1 PrelimsDocument5 pagesGeneral Elective 1 PrelimsJessica BernalNo ratings yet
- Ucsp Q3 M3Document10 pagesUcsp Q3 M3camposojoshua8No ratings yet
- EthicsDocument11 pagesEthicsKernalyn AkmadNo ratings yet
- The Challenge of Cultural Relativism and Global Citizen Values.Document4 pagesThe Challenge of Cultural Relativism and Global Citizen Values.Jhezell OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Other Sub-Concepts Related To CultureDocument6 pagesOther Sub-Concepts Related To CultureErika BaloloyNo ratings yet
- CULTUREDocument7 pagesCULTUREAnas idrees100% (1)
- Culture, Elements, TypesDocument28 pagesCulture, Elements, TypesZoraiz Ali100% (1)
- Aspects of Culture, Ethnocentrism, Cultural RelativismDocument57 pagesAspects of Culture, Ethnocentrism, Cultural RelativismRain BucadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Culture The Concept of CultureDocument3 pagesChapter 2: Culture The Concept of CultureJimenez JohnNo ratings yet
- BSN1 B Grp.5 Cultural RelativismDocument4 pagesBSN1 B Grp.5 Cultural RelativismRuben BascoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: The Nature and Elements of CultureDocument5 pagesLesson 1: The Nature and Elements of CultureLalaine De JesusNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of CultureDocument20 pagesCharacteristics of CulturelutfiNo ratings yet
- A.) Culture and Its Role in Moral BehaviourDocument6 pagesA.) Culture and Its Role in Moral BehaviourAnnahNo ratings yet
- Psycology For Engineers 2021: Cultural Impact On Human BehaviorDocument8 pagesPsycology For Engineers 2021: Cultural Impact On Human BehaviorArosha RohanapuraNo ratings yet
- Ucsp PortfolioDocument33 pagesUcsp PortfolioCasey keith Garcia0% (1)
- EthicsDocument13 pagesEthicsVinnese Rile Balataria SecuyaNo ratings yet
- GEC8 - Culture and MoralityDocument54 pagesGEC8 - Culture and MoralityNica RomeroNo ratings yet
- Ethics Module 4Document4 pagesEthics Module 4Jamaica Lyra AndradeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document42 pagesChapter 1lagalkanjeralynNo ratings yet
- Self Module 4Document5 pagesSelf Module 4Riya LalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 The Culture Challenge in International Business ModuleDocument10 pagesLesson 2 The Culture Challenge in International Business ModuleKuya ANo ratings yet
- Forms of Tangible and Intangible Heritage - 0Document24 pagesForms of Tangible and Intangible Heritage - 0anjelynlusterioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Cultural Relativism - Part 1 (Reaction Paper)Document2 pagesLesson 2 Cultural Relativism - Part 1 (Reaction Paper)Bai Zaida Abid100% (1)
- Lesson Element Different Types of Culture and Cultural HybridityDocument9 pagesLesson Element Different Types of Culture and Cultural HybridityHannah Abigail BaceaNo ratings yet
- Part III: Ethical Frameworks and Principles: Course Learning OutcomesDocument25 pagesPart III: Ethical Frameworks and Principles: Course Learning OutcomesRIZ ANN JOSENo ratings yet
- 2014 6 5midwifery BridgingcultureandpracticeNFCheungDocument5 pages2014 6 5midwifery BridgingcultureandpracticeNFCheungkeluargasulawesi18No ratings yet
- Understanding The SelfDocument8 pagesUnderstanding The SelfDannahNo ratings yet
- Sociology Class 2Document45 pagesSociology Class 2Ganis WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- On Consumer Behaviour: Environmental and Group InfluencesDocument49 pagesOn Consumer Behaviour: Environmental and Group InfluencesGwendeline Bruce DulceNo ratings yet
- Concept Notes Ethnocentrism and Cultural Relativism 1Document10 pagesConcept Notes Ethnocentrism and Cultural Relativism 1Carlo Joseph CarzaNo ratings yet
- OTL Contingent Worker Functionality Purchasing Timecard LayoutDocument22 pagesOTL Contingent Worker Functionality Purchasing Timecard LayoutAnil AbrahamNo ratings yet
- URIT-3000 Operation Manual (2.00V2.25)Document65 pagesURIT-3000 Operation Manual (2.00V2.25)Phạm Ngọc Tài100% (1)
- Facebook, Twitter and Google Data Analysis Using Hadoop PDFDocument6 pagesFacebook, Twitter and Google Data Analysis Using Hadoop PDFAbdifatah OsmanNo ratings yet
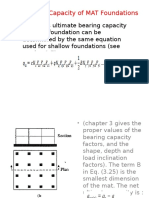
- 5.3. Bearing Capacity of MAT FoundationsDocument15 pages5.3. Bearing Capacity of MAT Foundationsnurul100% (1)
- Term 1 Grade 6 Integrated PT With English Health ArtDocument5 pagesTerm 1 Grade 6 Integrated PT With English Health ArtGC kasohoNo ratings yet
- Karmachari Sancahie KoshDocument9 pagesKarmachari Sancahie KoshSabeen budhathokiNo ratings yet
- An1131 Layout GuideDocument42 pagesAn1131 Layout GuideJaviCuellorNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument29 pagesNervous SystemMuhammed Aslam NVNo ratings yet
- 10th UHS Scientific Program - 16-01-23Document6 pages10th UHS Scientific Program - 16-01-23SabNo ratings yet
- FOC Mock Prelim 2022-23Document2 pagesFOC Mock Prelim 2022-23Saaril ShahNo ratings yet
- Guideline Configuratoin Dslam 5605Document6 pagesGuideline Configuratoin Dslam 5605Moacir de CaldasNo ratings yet
- Mosaic Uk 2009 Brochure Jun10Document24 pagesMosaic Uk 2009 Brochure Jun10stooge1983No ratings yet
- Ammonium Nitrate SpecDocument1 pageAmmonium Nitrate Specomega555No ratings yet
- 2022 Physical Verification FormatDocument1 page2022 Physical Verification FormatGhs PahrooNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulant Anti Platelet Fibrinolytic Drugs08 Black and WhiteDocument28 pagesAnticoagulant Anti Platelet Fibrinolytic Drugs08 Black and WhiteJagdesh SajnaniNo ratings yet
- Avenger 220 DespieceDocument77 pagesAvenger 220 DespieceJavier ValerioNo ratings yet
- How To Gather Information About ServerDocument3 pagesHow To Gather Information About ServerSyedNo ratings yet
- DATA ANTOINE Crude Oil BunyuDocument12 pagesDATA ANTOINE Crude Oil BunyuwynneralphNo ratings yet
- 08 Grp11 Hybrid EcmDocument67 pages08 Grp11 Hybrid Ecmeurospeed2No ratings yet
- Abdul Hamid Al Habib - Model Puff - STMKGDocument16 pagesAbdul Hamid Al Habib - Model Puff - STMKGAbdul Hamid Al HabibNo ratings yet
- Five Years in Jail For Spreading Infections UAE's Geocachers Treasure The ThrillsDocument1 pageFive Years in Jail For Spreading Infections UAE's Geocachers Treasure The Thrillsapi-251943787No ratings yet
- What Is A Problem?: PPS OverviewDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Problem?: PPS OverviewErmanda DishaNo ratings yet
- Control Engineering April 2016Document96 pagesControl Engineering April 2016saeedahmad901No ratings yet
- EnfuncDocument102 pagesEnfuncRafael OlaveNo ratings yet
- Crash Test For Chapter 5 To 7Document5 pagesCrash Test For Chapter 5 To 7Kamran AliNo ratings yet