Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inbound 8704190439505889998
Inbound 8704190439505889998
Uploaded by
Angelyn EndayaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Inbound 8704190439505889998
Inbound 8704190439505889998
Uploaded by
Angelyn EndayaCopyright:
Available Formats
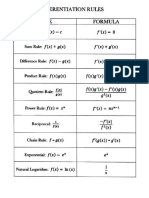
List of Derivative Rules
Below is a list of all the derivative rules we went over in class.
• Constant Rule: f (x) = c then f 0 (x) = 0
• Constant Multiple Rule: g(x) = c · f (x) then g 0 (x) = c · f 0 (x)
• Power Rule: f (x) = xn then f 0 (x) = nxn−1
• Sum and Difference Rule: h(x) = f (x)±g(x) then h0 (x) = f 0 (x)±g 0 (x)
• Product Rule: h(x) = f (x)g(x) then h0 (x) = f 0 (x)g(x) + f (x)g 0 (x)
f (x) f 0 (x)g(x) − f (x)g 0 (x)
• Quotient Rule: h(x) = then h0 (x) =
g(x) g(x)2
• Chain Rule: h(x) = f (g(x)) then h0 (x) = f 0 (g(x))g 0 (x)
• Trig Derivatives:
– f (x) = sin(x) then f 0 (x) = cos(x)
– f (x) = cos(x) then f 0 (x) = − sin(x)
– f (x) = tan(x) then f 0 (x) = sec2 (x)
– f (x) = sec(x) then f 0 (x) = sec(x) tan(x)
– f (x) = cot(x) then f 0 (x) = − csc2 (x)
– f (x) = csc(x) then f 0 (x) = − csc(x) cot(x)
• Exponential Derivatives
– f (x) = ax then f 0 (x) = ln(a)ax
– f (x) = ex then f 0 (x) = ex
– f (x) = ag(x) then f 0 (x) = ln(a)ag(x) g 0 (x)
– f (x) = eg(x) then f 0 (x) = eg(x) g 0 (x)
• Logarithm Derivatives
1
– f (x) = loga (x) then f 0 (x) =
ln(a)x
1
– f (x) = ln(x) then f 0 (x) =
x
g 0 (x)
– f (x) = loga (g(x)) then f 0 (x) =
ln(a)g(x)
0
g (x)
– f (x) = ln(g(x)) then f 0 (x) =
g(x)
You might also like
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedDocument3 pagesCalculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedShahnaz GazalNo ratings yet
- Maths ToolsDocument73 pagesMaths ToolsadobiNo ratings yet
- Nuovo Text DocumentDocument5 pagesNuovo Text Documentgiuseppe21112006No ratings yet
- Pravila Derivacije I IntegracijeDocument2 pagesPravila Derivacije I IntegracijeSasa UscumlicNo ratings yet
- Derivadas BasicasDocument1 pageDerivadas BasicasYamid PazNo ratings yet
- Limits: Calculus Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesLimits: Calculus Cheat SheetPratiksh PatelNo ratings yet
- Calculus TablesDocument5 pagesCalculus TablesLen ZymeriNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Cheat SheetDocument15 pagesDifferentiation Cheat SheetjieboNo ratings yet
- Limits and Derivatives FormulasDocument2 pagesLimits and Derivatives FormulasSwapnil GuptaNo ratings yet
- Formula Rio CNDocument5 pagesFormula Rio CNJoão OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Rumus Matematika Sma InterDocument19 pagesRumus Matematika Sma InterAde JayusNo ratings yet
- Polynomial Interpolation Piecewise Polynomial Interpolation: J J J J JDocument2 pagesPolynomial Interpolation Piecewise Polynomial Interpolation: J J J J JPH2303327No ratings yet
- Differentiation FormulaDocument2 pagesDifferentiation FormulahaqjmiNo ratings yet
- Formulario IntegraliDocument1 pageFormulario IntegraliAlessandro CaiazzoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12-b: Integral Calculus - ExtraDocument24 pagesChapter 12-b: Integral Calculus - ExtraShahnaz GazalNo ratings yet
- 0 DF DX 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 F (X) G (X) F (X) G (X) F (X) G (X) G (X) 1 G (X) G (X) G (X) 0 0Document4 pages0 DF DX 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 F (X) G (X) F (X) G (X) F (X) G (X) G (X) 1 G (X) G (X) G (X) 0 0Maher MestoNo ratings yet
- Math ReferenceDocument24 pagesMath ReferenceSujib BarmanNo ratings yet
- Some Basic DerivativesDocument2 pagesSome Basic DerivativesMuhammad Irfan KhanNo ratings yet
- Formula Rio CNDocument7 pagesFormula Rio CNJoana Alves QuitérioNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Maths Important Questions Limits and DerivativesDocument9 pagesClass 11 Maths Important Questions Limits and DerivativesRoy67% (6)
- Mathematics CalculusDocument11 pagesMathematics CalculusAnish NaniNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 13 Oct 2023Document2 pagesAdobe Scan 13 Oct 2023harshavardhankn05No ratings yet
- Prop DerivDocument1 pageProp DerivEloi Rubio GarciaNo ratings yet
- Formula RioDocument1 pageFormula RioMarioVerdicchioNo ratings yet
- Formulas EdDocument4 pagesFormulas EdCarlos Loler NavarroNo ratings yet
- Formulaire de Derivation PDFDocument1 pageFormulaire de Derivation PDFAshraeNo ratings yet
- 1 Arcsin 1 1 Arc Sec 1Document1 page1 Arcsin 1 1 Arc Sec 1kapsicumNo ratings yet
- Tab LiceDocument2 pagesTab LiceМилован МиљковићNo ratings yet
- Calculus BookletDocument6 pagesCalculus Bookletangie81No ratings yet
- BasicsDocument2 pagesBasicsmadcow_scribdNo ratings yet
- Basic (1) MathDocument2 pagesBasic (1) MathIan KrebsNo ratings yet
- Derivative RulesDocument2 pagesDerivative RulessuperchawaNo ratings yet
- Basic Calculus FormulaeDocument4 pagesBasic Calculus FormulaeAkshay Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- Math Formulas: Common Derivatives: Basic Properties of DerivativesDocument2 pagesMath Formulas: Common Derivatives: Basic Properties of DerivativesPranav SaihgalNo ratings yet
- Calculus FormulaDocument2 pagesCalculus FormulaleeshiNo ratings yet
- SummaryDocument2 pagesSummaryZainariah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Video Segment: ControlDocument14 pagesVideo Segment: ControliavramovNo ratings yet
- Exam - 2011 10 28Document5 pagesExam - 2011 10 28lieth-4No ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus, 2007-10-26. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Document5 pagesMultivariable Calculus, 2007-10-26. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4No ratings yet
- Look-Up Table: Solving Differential EquationsDocument10 pagesLook-Up Table: Solving Differential Equationsgaurav_juneja_4No ratings yet
- 4 Standard Derivatives: JJ II J IDocument2 pages4 Standard Derivatives: JJ II J IJulián GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Math 221 Solution To ProblemsDocument16 pagesMath 221 Solution To ProblemsRyan Kristoffer NuñezNo ratings yet
- Derivatives Formula Sheet CondensedDocument1 pageDerivatives Formula Sheet CondensedintegralCALCNo ratings yet
- Tabel DerivateDocument1 pageTabel DerivateMarinescu FlaviuNo ratings yet
- MAT060 12 Differential Notation and Trigonometric FunctionsDocument52 pagesMAT060 12 Differential Notation and Trigonometric FunctionsShine Ibarra AlabaNo ratings yet
- X X X X Ecx Ecx: Tan - Sec Sec Cot - Cos CosDocument4 pagesX X X X Ecx Ecx: Tan - Sec Sec Cot - Cos Cossharanmit2039No ratings yet
- Numerical Integration TechniquesDocument60 pagesNumerical Integration TechniquesImran ParvezNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Differentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDifferentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)From EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)No ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Hyperbolic Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandHyperbolic Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Process UITMDocument12 pagesLab Report Process UITMEiman UzmiNo ratings yet
- Unknown 2Document23 pagesUnknown 2Eiman UzmiNo ratings yet
- Apparatus Material BaruDocument4 pagesApparatus Material BaruEiman UzmiNo ratings yet
- Anthony Brooks OLLDocument1 pageAnthony Brooks OLLEiman UzmiNo ratings yet
- Component in Milk GoatDocument1 pageComponent in Milk GoatEiman UzmiNo ratings yet
- CHE555 Assignment 2Document2 pagesCHE555 Assignment 2Eiman UzmiNo ratings yet
- Che 231 Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesChe 231 Lesson PlanEiman UzmiNo ratings yet
- C K T C N Time, T Substrate Concentration, M 10 4.65 20 3.75 30 2.54 40 1.57 50 0.73 60 0.42Document1 pageC K T C N Time, T Substrate Concentration, M 10 4.65 20 3.75 30 2.54 40 1.57 50 0.73 60 0.42Eiman UzmiNo ratings yet
- CHE244 Project GuidelinesDocument5 pagesCHE244 Project GuidelinesEiman UzmiNo ratings yet
- Chem RXN EquilDocument44 pagesChem RXN EquilEiman UzmiNo ratings yet
- Solution ThermoDocument31 pagesSolution ThermoEiman UzmiNo ratings yet
- Marcet BoilereditDocument25 pagesMarcet BoilereditEiman Uzmi0% (1)
- Sample Article ArgumentativeDocument3 pagesSample Article ArgumentativeEiman UzmiNo ratings yet
- E 2 HcrxnsDocument8 pagesE 2 HcrxnsEiman UzmiNo ratings yet
- Fluidized Bed Reactor: Prepared By: 1. Saiful 2. Afiq 3. Zoulfikri 4. Eiman 5. ZyaidDocument10 pagesFluidized Bed Reactor: Prepared By: 1. Saiful 2. Afiq 3. Zoulfikri 4. Eiman 5. ZyaidEiman UzmiNo ratings yet