Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ANXIOLYTICS Final
Uploaded by
Erika Blaire N. Olacao0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
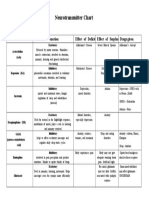
7 views5 pagesThis document provides information on several benzodiazepine drugs including alprazolam, clonazepam, and chlordiazepoxide. It lists their brand and generic names, pharmacologic class, general action, and mechanisms of action which commonly involve enhancing the effects of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA. Potential side effects are provided for several body systems including the central nervous system, cardiovascular, ear/nose/throat, gastrointestinal, and others. Drug-drug interactions are also noted that can alter metabolism and plasma levels of the benzodiazepines. Dosing guidelines are given at the end.
Original Description:
drug study
Original Title
ANXIOLYTICS-final
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information on several benzodiazepine drugs including alprazolam, clonazepam, and chlordiazepoxide. It lists their brand and generic names, pharmacologic class, general action, and mechanisms of action which commonly involve enhancing the effects of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA. Potential side effects are provided for several body systems including the central nervous system, cardiovascular, ear/nose/throat, gastrointestinal, and others. Drug-drug interactions are also noted that can alter metabolism and plasma levels of the benzodiazepines. Dosing guidelines are given at the end.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views5 pagesANXIOLYTICS Final
Uploaded by
Erika Blaire N. OlacaoThis document provides information on several benzodiazepine drugs including alprazolam, clonazepam, and chlordiazepoxide. It lists their brand and generic names, pharmacologic class, general action, and mechanisms of action which commonly involve enhancing the effects of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA. Potential side effects are provided for several body systems including the central nervous system, cardiovascular, ear/nose/throat, gastrointestinal, and others. Drug-drug interactions are also noted that can alter metabolism and plasma levels of the benzodiazepines. Dosing guidelines are given at the end.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
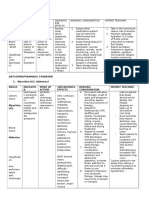
ANXIOLYTICS does not exhibit cross-tolerance w/ ALPRAZOLAM arm or leg pain, back pain, muscle rigidity,
sedative/hypnotics (e.g. benzodiazepine) muscle cramps, muscle twitch.
and will not block symptoms of their Respiratory: URI, dyspnea,
BUSPIRONE Brand Name: Alprazolam Intensol, Apo-
hyperventilation. Skin: pruritus, increased
withdrawal, gradually withdraw such agents Alpraz (CAN), Novo Alprazol (CAN),
Brand Name: Buspar sweating,
prior to initiation of buspirone. Xanax, Xanax TS (CAN), Xanax
Generic Name: Buspirone dermatitis. Other: influenza, injury,
Potentially Fatal: Increased BP when taken XR
General Action: Anxiolytic emergence of anxiety between doses,
w/ MAOIs. Generic Name: Alprazolam dependence,
Mechanism of Action: Buspirone, an Pharmacologic class: Benzodiazepine feeling warm, increased or decreased libido.
azaspirodecanedione, is an anxioselective General Action: Anxiolytic, antipanic
Time best given: May be taken with or
drug w/ only little sedative effect but w/o without food. Take consistently either Drug to Drug Interaction: amiodarone,
anticonvulsant and muscle relaxant Mechanism of Action: May increase cyclosporine, diltiazem, ergotamine,
always w/ or always w/o meals.
properties. It has high affinity for serotonin effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid isoniazid, macrolide
(5-HT1A and 5-HT2), moderate affinity for (GABA) and other inhibitory antibiotics (clarithromycin, erythromycin),
dopamine (D2), and no affinity for GABA neurotransmitters by binding to specific nicardipine, nifedipine, paroxetine,
receptors. benzodiazepine receptors in cortical and sertraline: Possible alteration in alprazolam
limbic areas of the CNS. GABA inhibits plasma levels antacids: Altered
Side Effects: CNS: dizziness, drowsiness, excitatory stimulation, which helps alprazolam absorption rate
headache, nervousness, insomnia, light- control emotional behavior. The limbic anticonvulsants; antidepressants;
headedness, system contains many benzodiazepine antihistamines; other benzodiazepines, CNS
fatigue, numbness, excitement, confusion, receptors, which may help explain drug’s depressants, and psychotropics: Possibly
depression, anger, decreased concentration, antianxiety effects. increased CNS depressant effects
paresthesia, incoordination, tremor, Side Effects: CNS: insomnia, irritability, carbamazepine: Decreased plasma level of
dizziness, headache, anxiety, confusion, alprazolam and potential decreased
hostility. CV: tachycardia, nonspecific chest
drowsiness, lightheadedness, sedation,
pain. effectiveness
somnolence, difficulty speaking, impaired
EENT: blurred vision. GI: dry mouth, cimetidine, fluoxetine, oral contraceptives,
coordination, memory
nausea, diarrhea, abdominal distress, impairment, fatigue, depression, suicide, propoxyphene: Decreased alprazolam
constipation, vomiting. Musculoskeletal: mental impairment, ataxia, paresthesia, elimination and increased effects
aches and pains. Skin: rash, sweating or dyskinesia, hypoesthesia, lethargy, vertigo,
clamminess. malaise, tremor, nervousness, restlessness, Time Best Given: Adults—At first, 0.5 to 1
agitation, nightmare, syncope, akathisia, milligram (mg) taken in the morning once a
Drug-Drug Interaction: Increased serum mania. CV: palpitations, chest pain, day. Your doctor may increase your dose as
concentration when used w/ CYP3A4 hypotension. EENT: blurred vision, tinnitus, needed. However, the dose is usually not
enzyme inhibitors (e.g. erythromycin, allergic rhinitis, nasal congestion. GI: more than 10 mg per day. Older adults—At
itraconazole, nefazodone, ritonavir, diarrhea, dry mouth, constipation, nausea, first, 0.5 mg taken in the morning once a
diltiazem, verapamil). Decreased increased or decreased appetite, anorexia, day.
vomiting, dyspepsia, abdominal pain,
metabolism and therapeutic effect when
increased or decreased salivation. GU:
used w/ CYP3A4 enzyme inducers (e.g.
dysmenorrhea, sexual dysfunction,
rifampicin). Enhanced sedative effect w/ premenstrual syndrome, difficulty urinating.
baclofen, lofexidine, nabilone, Metabolic: increased or decreased weight.
antihistamines. May increase serum Musculoskeletal: arthralgia, myalgia,
concentration of haloperidol. Buspirone
phenytoin RESP: Bronchitis, cough, respiratory
levodopa: Decreased efficacy of levodopa’s depression
CLONAZEPAM Other: Allergic reaction
CHLORDIAZEPOXIDE antiparkinsonian effects
Brand Name: Clonapam (CAN), Rivotril
opioids: Increased risk of significant
Brand Name: Librium (CAN) Drug to Drug Interaction:
respiratory depression
Generic Name: chlordiazepoxide Generic Name: clonazepam antianxiety drugs, antipyschotics
Pharmacologic class: Benzodiazepine Pharmacologic class: Benzodiazepine (butyrophenone and thioxanthene classes),
Time Best Given: Initial: 50 to 100 mg,
General Action: Anxiolytic General Action: Anticonvulsant, antipanic barbiturates, CNS depressants, MAO
usually given I.V. or I.M. Repeated in 2 to 4
hr inhibitors, narcotics, nonbarbiturate
Mechanism of Action: May potentiate the Mechanism of Action: Although unknown, hypnotics, other benzodiazepines,
followed by individualized oral dosage if
effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid drug is thought to prevent panic and phenothiazines, sedating antihistamines,
needed to control symptoms. I.V. given
(GABA) and other seizures by potentiating tricyclic antidepressants: Increased risk of
slowly no faster than 50 mg/min.
inhibitory neurotransmitters by binding to the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid CNS depression including significant
Maximum: 300 mg daily.
specific benzodiazepine receptors in cortical (GABA), which is an inhibitory sedation and somnolence
5 to 10 mg P.O. three or four times daily
and limbic areas of the CNS. By binding to neurotransmitter. This action is also thought carbamazepine, lamotrigine, phenobarbital,
several days before surgery; 50
these receptors, chlordiazepoxide increases to suppress the spread of seizure activity phenytoin: Possibly decreased
to 100 mg I.M. 1 hr before surgery
GABA’s inhibitory effects and blocks caused by seizure-producing foci in the plasma clonazepam levels with potential for
cortical and limbic arousal, which helps cortex, limbic, and thalamus structures. interference with its effectiveness
control emotional behavior. It also helps fluconazole: Possibly impaired clonazepam
relieve symptoms of alcohol withdrawal by Side Effects: CNS: Abnormal dreams, metabolism with potential for
causing CNS depression. aggression, agitation, amnesia, anxiety,
exaggerated concentrations and effects
apathy, ataxia,
opioids: Increased risk of severe respiratory
Side Effects: CNS: Ataxia, confusion, attention disturbance, confusion,
depersonalization, depression, dizziness, depression
depression, drowsiness, suicidal ideation phenytoin: Possibly altered plasma
CV: ECG changes, hypotension, drowsiness, emotional lability, excessive
dreaming, fatigue, hallucinations, concentrations of phenytoin
GI: Elevated liver enzymes, hepatic
headache, hostility, hysteria, insomnia,
dysfunction, jaundice Time Best Given: Adults and children over
irritability, memory loss, nervousness,
HEME: Agranulocytosis nightmares, organic disinhibition, age 10. 1.5 mg daily in divided doses three
Other: Injection-site pain, redness, and psychosis, reduced intellectual ability, sleep times daily.
swelling disturbances, suicidal ideation Increased by 0.5 to 1 mg every 3 days, if
CV: Palpitations needed, until seizures are controlled.
Drug to Drug Interaction: antacids: EENT: Blurred vision, eyelid spasm,
Delayed absorption of chlordiazepoxide increased salivation, loss of taste,
cimetidine, disulfiram: Increased blood pharyngitis, rhinitis, sinusitis, yawning
chlordiazepoxide level GI: Abdominal pain, anorexia, constipation,
CNS depressants, opioids, other increased appetite
benzodiazepines, sedating antihistamines, GU: Altered libido, difficult ejaculation,
tricyclic antidepressants: Increased risk of dysmenorrhea, dysuria, enuresis,
impotence, nocturia, urine retention, UTI
sedation and somnolence and other
HEME: Anemia, eosinophilia, leukopenia,
CNS effects
thrombocytopenia
digoxin, phenytoin: Increased blood level MS: Dysarthria, myalgia
and risk of toxicity with digoxin and
psychological dependence. nausea, thirst, vomiting
DIAZEPAM GU: Libido changes
Drug- Drug Interaction: antacids: Altered HEME: Agranulocytosis, pancytopenia,
Brand Name: Diastat, Diazepam Intensol,
rate of diazepam absorption LORAZEPAM thrombocytopenia
Dizac, Valium
cimetidine, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, RESP: Apnea, respiratory depression,
Generic Name: diazepam Brand Name: Ativan, Lorazepam Intensol,
ketoconazole, omeprazole Decreased worsening of obstructive pulmonary
Pharmacologic class: Benzodiazepine Nu-Loraz (CAN)
diazepam metabolism, increased blood level disease or sleep apnea
General Action: Anticonvulsant, Generic Name: lorazepam
and risk of adverse effects including SKIN: Diaphoresis
anxiolytic, sedative-hypnotic, skeletal Pharmacologic class: Benzodiazepine
prolonged sedation Other: Anaphylaxis, injection-site pain
muscle relaxant General Action: Anxiolytic
CNS depressants including anesthetics, (I.M.) or phlebitis (I.V.), physical and
anticonvulsants, antipsychotics, psychological dependence, withdrawal
Mechanism of Action: May potentiate Mechanism of Action: May potentiate the
anxiolytics, barbiturates, hypnotics, MAO symptoms
effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid
(GABA) and other inhibitors, narcotics, phenothiazines, (GABA) and other
sedatives including sedative antihistamines, Drug- Drug Interaction: aminophylline,
inhibitory neurotransmitters by binding to inhibitory neurotransmitters by binding to
and other antidepressants: theophylline: Possibly reduced sedative
specific benzodiazepine receptors in cortical specific benzodiazepine receptors in cortical
Increased CNS depression and risk of falls effects of lorazepam
and limbic areas of CNS. GABA inhibits and limbic areas of CNS. GABA inhibits
and fractures clozapine: Increased risk of ataxia, delirium,
excitatory stimulation, which helps control excitatory stimulation, which
opioids: Increased risk of severe respiratory excessive salivation, hypotension,
emotional behavior. Limbic system contains helps control emotional behavior. Limbic
depression marked sedation, and respiratory arrest
a dense area of benzodiazepine receptors, system contains a highly dense area of
phenytoin: Decreased metabolic elimination CNS depressants: Additive CNS depression,
which may explain drug’s antianxiety benzodiazepine receptors, which may
of phenytoin, increased risk of potentially fatal respiratory
effects. explain drug’s antianxiety effects. Also,
adverse reactions depression
Diazepam suppresses spread of seizure lorazepam hyperpolarizes neuronal cells,
fentanyl: Possibly decreased therapeutic
activity caused by seizure-producing foci in thereby interfering with their ability to
Time Best Given: When using oral effects of fentanyl
cortex, limbic, and thalamus structures. generate seizures.
solution, dilute dose just before giving with probenecid, valproate: Possibly increased
liquid or semisolid food, therapeutic and adverse effects of lorazepam
Side Effects: CNS: drowsiness, dysarthria, Side Effects: CNS: Amnesia, anxiety, other benzodiazepines, sedating
such as water, juices, soda or sodalike
slurred speech, tremor, transient amnesia, ataxia, coma, confusion, delusions, antihistamines, opioids, tricyclic
beverages, applesauce, or pudding.
fatigue, ataxia, depression, antidepressants: Increased risk of profound
Adults: Depending on severity, 2 to 10 mg
headache, insomnia, paradoxical anxiety, dizziness, drowsiness, euphoria, respiratory depression, sedation, and
PO b.i.d. to q.i.d. Or, 2 to 10 mg IM or IV.
hallucinations, minor changes in EEG extrapyramidal symptoms, fatigue, somnolence
May repeat in 3 to 4 hours if needed.
patterns, pain, vertigo, confusion, headache,
Children age 6 months and older: 1 to 2.5
depression. CV: CV collapse, bradycardia, hypokinesia, irritability, malaise, Time Best Given: 2 to 4 mg at bedtime
mg PO t.i.d. or q.i.d., increased gradually, as
hypotension. EENT: diplopia, blurred nervousness, seizures, slurred speech,
needed and tolerated.
vision, nystagmus. GI: nausea, constipation, suicidal
diarrhea with rectal form, dry mouth. GU: ideation, tremor, unsteadiness, vertigo
incontinence, urine retention. Hematologic: CV: Chest pain, palpitations, tachycardia
neutropenia. Hepatic: jaundice. Respiratory: EENT: Blurred vision, diplopia, dry mouth,
respiratory depression, apnea, increased salivation, photophobia
hiccups. Skin: rash, phlebitis at injection ENDO: Syndrome of inappropriate ADH
site. Other: altered libido, physical or GI: Abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea,
elevated liver enzymes, jaundice,
Potentially Fatal: Increased sleep duration
Time Best Given: Hypnotic and CNS depression w/ Na oxybate.
Adult: 65-200 mg via IM inj (should not
exceed 5 mL at any single site) or IV inj Time Best Given: Phenobarbital is given by
AMOBARBITAL (should not exceed 50 mg/min) at bedtime. mouth in the form of a tablet, capsule, liquid
Max: 1,000 mg as a single dose. May be PENTOBARBITAL solution, paste, or chewable. It may be
Brand Name: Amytal Sodium or Tuinal
taken with or without food. Brand Name: Nembutal. given with or without food.
Generic Name: Amobarbital
Generic Name: Pentobarbital
Pharmacologic class: Barbiturates
Pharmacologic class: Barbiturate Oral
General Action:
General Action: sedative-hypnotics Hypnotic
Adult: 100-200 mg at bedtime.
Mechanism of Action: Amobarbital
Mechanism of Action: Pentobarbital is a
interferes w/ the transmission of impulses
barbiturate mainly used as a sedative and Sedation
from the thalamus to the cortex of the brain
hypnotic. It has been suggested that its Adult: 20-40 mg 2-4 times daily.
which develops an imbalance in central
pharmacologic effect is due to its property Child: 2-6 mg/kg daily in 3 divided doses.
inhibitory and facilitatory mechanisms.
to enhance the activity of GABA by altering Max: 100 mg.
GABA receptor-mediated inhibitory
Side Effects: Bradycardia, syncope,
synaptic transmissions
hypotension; apnoea, atelectasis (post-op),
hypoventilation; agitation, anxiety, ataxia,
Side Effects: Drowsiness, somnolence,
confusion, CNS depression, dizziness,
dizziness, anxiety, insomnia; hypotension,
fever, hallucinations, headache, insomnia,
apnoea, resp depression, bronchospasm,
nightmares, nervousness, psychiatric
laryngospasm, bradycardia, CNS
disturbances, somnolence, abnormal
depression, physical and psychological
thinking; hyperkinesias; nausea, vomiting,
dependence, psychiatric disturbance,
constipation; liver damage; megaloblastic
confusion, hallucinations, nightmares,
anaemia (following chronic phenobarbital
thinking abnormality, syncope,
use); angioedema, rash; inj site reaction.
hyperkinesias, ataxia, agitation,
nervousness, nausea, vomiting, constipation,
Drug- Drug Interaction: May reduce plasma
pain at inj site.
levels of oral anticoagulants (e.g. warfarin,
Potentially Fatal: Stevens-Johnson
dicoumarol, acenocoumarol,
syndrome.
phenprocoumon), corticosteroids,
griseofulvin, doxycycline, Na valproate and
Drug- Drug Interaction: Additive effect w/
valproic acid. Constant monitoring of blood
other CNS depressants. Increased plasma
levels when concomitantly used w/
concentrations w/ MAO inhibitors. May
phenytoin. May increase CNS depressant
decrease serum levels of phenytoin,
effect w/ antihistamines, sedative/hypnotics,
carbamazepine, valproic acid. May increase
tranquilisers. May prolong the effect w/
metabolism of anticoagulants,
MAOIs. May reduce the effect of estradiol,
corticosteroids, griseofulvin, doxycycline
progesterone, estrone and other steroidal
and hormonal contraceptives.
hormones.
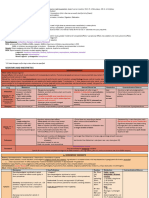
Hepatobiliary disorders: Hepatitis, amprenavir, darunavir, lopinavir, indinavir,
cholestasis. nelfinavir, saquinavir), clonazepam,
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue aprepitant, β-blockers (e.g. metoprolol,
disorders: Dupuytren's contracture, timolol), Ca channel blockers (e.g.
PHENOBARBITAL arthralgia, frozen shoulder, osteomalacia, felodipine, diltiazem, verapamil,
rickets; osteopenia, osteoporosis (prolonged nifedipine), digoxin, ciclosporin, tacrolimus,
Brand Name: Luminal Sodium®,
use). corticosteroids, etoposide, irinotecan,
Solfoton®, Tedral®
Nervous system disorders: Drowsiness, eplerenone, haloperidol, gestrinone,
Generic Name: Phenobarbital
ataxia, nystagmus. toremifene, methadone, montelukast,
Pharmacologic class: Barbiturates
Psychiatric disorders: Mental depression, theophylline, sodium oxybate, thyroid
General Action: Anticonvulsants /
hallucination; confusion, restlessness (in hormones, tibolone, tropisetron, vitamin D.
Hypnotics & Sedatives
elderly); memory and cognitive impairment; May reduce the effect of oral contraceptives
behavioural disturbances (in children). containing estrogen and/or progestogen.
Mechanism of Action: Phenobarbital is a
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: May increase the metabolism of
long-acting barbiturate that has hypnotic,
Maculopapular, morbilliform or paracetamol which may lead to reduced
sedative, and anticonvulsant activities. The
scarlatiniform rashes. effect and increased risk of hepatotoxicity.
exact mechanism of action is unknown, but
Vascular disorders: Hypotension, syncope.
it may be related to its ability to enhance
Time Best Given:
and/or mimic the synaptic action of GABA.
Drug- Drug Interaction: Concurrent use Phenobarbital is given by mouth in the form
It depresses the sensory cortex, reduces
with MAOIs, SSRIs, and TCAs may of a tablet, capsule, liquid solution, paste, or
motor activity, changes cerebellar function,
antagonise antiepileptic activity of chewable. It may be given with or without
and produces drowsiness, sedation, and
phenobarbital by reducing the convulsive food.
hypnosis. Its anticonvulsant property is
threshold. May result in additive CNS Sedation
exhibited at high doses.
depressant effects when used concomitantly Adult: 30-120 mg daily in 2-3 divided doses
with other CNS depressants (e.g. via deep IM inj or slow IV inj at a rate of no
Side Effects: ignificant: Respiratory
antihistamines, narcotics, tranquilisers). more than 60 mg/min. Max: 400 mg daily.
depression (particularly IV use), suicidal
Increased plasma concentration with
ideation and behaviour; paradoxical
oxcarbazepine, phenytoin, methylphenidate, Oral
responses (including agitation,
chloramphenicol, valproic acid or Na Sedation
hyperactivity); drug dependence, decreased
valproate. May decrease plasma Adult: 30-120 mg daily in 2-3 divided
BMD, increased risk of fractures (prolonged
concentration with vigabatrin or folic acid. doses. Max: 400 mg daily.
use).
May decrease efficacy with memantine.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders:
May reduce the plasma concentrations of
Agranulocytosis, megaloblastic anaemia,
disopyramide, quinidine, chloramphenicol,
thrombocytopenia.
doxycycline, metronidazole, rifampicin,
Cardiac disorders: Bradycardia.
anticoagulants (e.g. dicoumarol),
Gastrointestinal disorders: Nausea,
chlorpromazine, paroxetine, mianserin,
vomiting.
TCAs, carbamazepine, lamotrigine,
General disorders and administration site
tiagabine, zonisamide, primidone,
conditions: Lethargy, hangover effect; inj
ethosuximide, antifungals (e.g. itraconazole,
site reactions (IV/IM).
posaconazole, griseofulvin, voriconazole),
aripiprazole, antivirals (e.g. abacavir,
You might also like
- Neurotransmitter ChartDocument1 pageNeurotransmitter Chartmonster40lbs100% (2)
- Psych Drugs Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesPsych Drugs Cheat SheetHJ G100% (3)
- Drugs Acting On CNSDocument19 pagesDrugs Acting On CNSAditya sagarNo ratings yet
- Psych Drugs Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesPsych Drugs Cheat SheetSuha Abdullah100% (4)
- Introduction To PharmacologyDocument50 pagesIntroduction To PharmacologyAbdishakour Hassa.100% (1)
- Anxiolytic, Sedative-Hypnotic DrugsDocument39 pagesAnxiolytic, Sedative-Hypnotic DrugsNina100% (1)
- Benzodiazepines Drug StudyDocument4 pagesBenzodiazepines Drug Studyaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology (1) - 104-122Document19 pagesPharmacology (1) - 104-122Dental LecturesMMQNo ratings yet
- All Other ClassificationsDocument6 pagesAll Other ClassificationsCorey100% (1)
- Demerol DrugDocument2 pagesDemerol DrugMsOrange100% (1)
- Beating the Benzo Blues: Getting off BenzodiazapinesFrom EverandBeating the Benzo Blues: Getting off BenzodiazapinesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Drug Study (Anesthesia)Document4 pagesDrug Study (Anesthesia)Jane Arian Berzabal100% (4)
- Prescription AnalysisDocument16 pagesPrescription AnalysisMohd Azfar HafizNo ratings yet
- NCM 106Document23 pagesNCM 106DALE DELA CRUZ100% (1)
- Ativan (Lorazepam) Drug StudyDocument3 pagesAtivan (Lorazepam) Drug StudyCHERISE CORDOVA100% (2)
- DiazepamDocument1 pageDiazepamGracia Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- TRIAZOLAMDocument4 pagesTRIAZOLAMEzequiel RosalesNo ratings yet
- Alprazolam BiperidinDocument6 pagesAlprazolam BiperidinFionah RetuyaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Reviewer For Final Exam: Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesPharmacology: Reviewer For Final Exam: Nervous Systempatty janeNo ratings yet
- PsychiatryDocument5 pagesPsychiatryJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Atypical AntipsychoticsDocument4 pagesAtypical AntipsychoticsErika Blaire N. OlacaoNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Anxiety and InsomniaDocument10 pagesDrugs For Anxiety and InsomniaApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 4Document9 pagesDrug Study 4bobo gamingNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System: A Sedative Can Become A Hypnotic If It Is Given in Large Enough DosesDocument6 pagesCentral Nervous System: A Sedative Can Become A Hypnotic If It Is Given in Large Enough Doseschubbygunny_29776413No ratings yet
- Drowsiness, Sedation, LightDocument2 pagesDrowsiness, Sedation, LightGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Medications ChartDocument2 pagesAnxiety Medications ChartNashNo ratings yet
- DRUG StudyDocument3 pagesDRUG StudyArfe BaquinquitoNo ratings yet
- DS GadDocument2 pagesDS Gadbianca musicNo ratings yet
- Risperidone: Generic Name: ClassificationsDocument9 pagesRisperidone: Generic Name: ClassificationsColeen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyVenus April LimonNo ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonsDocument4 pagesAnti ParkinsonsMichaela BernadasNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGY Assisgnment 01Document5 pagesPHARMACOLOGY Assisgnment 01muhammadhamza muhammadiqbalNo ratings yet
- Antiepilepsi & AntikonvulsiDocument8 pagesAntiepilepsi & Antikonvulsishofa nur rahmannisaNo ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonsDocument4 pagesAnti ParkinsonsMichaela BernadasNo ratings yet
- AnxietyDocument6 pagesAnxietyMasa MasaNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitters AnxietyDocument7 pagesNeurotransmitters AnxietyMatthew SyNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action Prozac Anti-DepressantsDocument13 pagesMechanism of Action Prozac Anti-DepressantsJose Luis HernandezNo ratings yet
- Medicines and Falls - Guidance On Causes and Risks: (Version 1 - July 2015)Document4 pagesMedicines and Falls - Guidance On Causes and Risks: (Version 1 - July 2015)Dr. Asif RahmanNo ratings yet
- 2018-2019 Cns DepressantsDocument5 pages2018-2019 Cns DepressantsMary AgorillaNo ratings yet
- Pesquera, Jon Jaspher MangulabnanDocument1 pagePesquera, Jon Jaspher MangulabnanAERONH JOHN PURIFICANDONo ratings yet
- Anti-Depressants 1. Sertraline (Zoloft)Document5 pagesAnti-Depressants 1. Sertraline (Zoloft)Ronilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Lui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionDocument1 pageLui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionMagdayao Romamea100% (1)
- Psychotherapeutic AgentsDocument2 pagesPsychotherapeutic AgentsjustinahorroNo ratings yet
- CNS PNS Pharma NotesDocument21 pagesCNS PNS Pharma NotesClaire GUMAPACNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyAlex Silvano0% (1)
- Obat2 Yang Bekerja Pada Ganguan Kesadaran: Elly Usman Bagian Farmakologi Dan Terapi, Fakultas Kedokteran, UnandDocument29 pagesObat2 Yang Bekerja Pada Ganguan Kesadaran: Elly Usman Bagian Farmakologi Dan Terapi, Fakultas Kedokteran, UnandKhairani HakimNo ratings yet
- Adult: IV/IM 5-10 MG, Drowsiness, Fatigue, Ataxia,: Injectable Form: ShockDocument1 pageAdult: IV/IM 5-10 MG, Drowsiness, Fatigue, Ataxia,: Injectable Form: ShockinfectionmanNo ratings yet
- PHARM250 Nervous System Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument15 pagesPHARM250 Nervous System Cheat Sheet: by ViaThư PhạmNo ratings yet
- Valproic Acid: Pharmacologic Class: CarboxylicDocument2 pagesValproic Acid: Pharmacologic Class: CarboxylicBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Psychopharmacology Article StyleDocument9 pagesPsychopharmacology Article StyleLizethNo ratings yet
- CT Week 7 PharmaDocument15 pagesCT Week 7 PharmaJoelynMacalintalNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia Drugs Cheat SheetDocument10 pagesAnesthesia Drugs Cheat Sheetapolan2No ratings yet
- Depression PDFDocument10 pagesDepression PDFLyadelou FortuNo ratings yet
- Mental HealthDocument6 pagesMental HealtholadapoNo ratings yet
- Camba-Course Task 9Document19 pagesCamba-Course Task 9Rachelle CambaNo ratings yet
- BuspironeDocument2 pagesBuspironeFatima Diane S. MondejarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 Sedative-Hypnotic and Anti-Anxiety AgentsDocument32 pagesLecture 11 Sedative-Hypnotic and Anti-Anxiety AgentsHafsa ShakilNo ratings yet
- Course Task - Week 7Document34 pagesCourse Task - Week 7JoelynMacalintalNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Module 4Document6 pagesDrug Study Module 4Hannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetic Drug Interactions: Syed Imran Prof. Mrs. Vidya. P. SableDocument20 pagesPharmacokinetic Drug Interactions: Syed Imran Prof. Mrs. Vidya. P. SableDALI SAPARI 2021No ratings yet
- The Medicinal Chemistry of Development of Imatinib PDFDocument2 pagesThe Medicinal Chemistry of Development of Imatinib PDFhaker10100101No ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics ReviewerDocument3 pagesPharmacokinetics ReviewerJennifer HerediaNo ratings yet
- Tocilizumab Distributors List - KarnatakaDocument1 pageTocilizumab Distributors List - KarnatakaDeepak Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- CimetidineDocument3 pagesCimetidineRodolfo Lone UlvenNo ratings yet
- Lopinavir 9Document9 pagesLopinavir 9นิวนิ่วนิ้ว ศิษย์ปตทNo ratings yet
- Day 2Document9 pagesDay 2Anil SoniNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature-Guideline USPDocument31 pagesNomenclature-Guideline USPDenise EulalioNo ratings yet
- Prasad Sir DataDocument6 pagesPrasad Sir Datajagdish prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Dialog Bahasa InggirsDocument2 pagesDialog Bahasa InggirsKeRtha NeghaRaNo ratings yet
- Form Gdoc Febuari 2024Document29 pagesForm Gdoc Febuari 2024baktipratamamedikacirebonNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacokinetics and PharmacodynamicsDocument20 pagesClinical Pharmacokinetics and PharmacodynamicsAndre MouraNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms, Drug Delivery Systems and Medical Devices Pharm 201L Name:Tallod, Emerson John L. Group:11 Year/Section:Q2A Final RatingDocument7 pagesPharmaceutical Dosage Forms, Drug Delivery Systems and Medical Devices Pharm 201L Name:Tallod, Emerson John L. Group:11 Year/Section:Q2A Final RatingJames AzurinNo ratings yet
- General Pharmacology MCQ: 1. The Science Which Deals With The Drug and Their Action On Human Body Is CalledDocument274 pagesGeneral Pharmacology MCQ: 1. The Science Which Deals With The Drug and Their Action On Human Body Is CalledAmritesh singh thakurNo ratings yet
- Review Jurnal Interaksi Obat Antihipertensi - Radhwa Fauztina (20190350050)Document13 pagesReview Jurnal Interaksi Obat Antihipertensi - Radhwa Fauztina (20190350050)Radhwa FauztinaNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Institutional Pharmacy Practice Chapter 2Document14 pagesHandbook of Institutional Pharmacy Practice Chapter 2Joe FX TraderNo ratings yet
- Phenytoin Prescribing and Monitoring GuidlineDocument12 pagesPhenytoin Prescribing and Monitoring GuidlineSeptaniaDiniArvianiNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Sem4Document21 pagesSyllabus Sem4Sudhir royNo ratings yet
- Medicine ListDocument40 pagesMedicine ListCricket ThingsNo ratings yet
- Biopharmaceutics Uos Past PapersDocument9 pagesBiopharmaceutics Uos Past PapersMr nobodyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Chemistry in Everyday LifeDocument10 pagesChapter 16 - Chemistry in Everyday LiferamNo ratings yet
- Multi-Layer TabletsDocument14 pagesMulti-Layer Tabletsprasad_ram8850% (2)
- Stok All Cabang1Document1,318 pagesStok All Cabang1Akhmad “Billy Rafi” HambaliNo ratings yet
- Opioid Conversion ChartDocument4 pagesOpioid Conversion ChartVanessa NicoleNo ratings yet
- 13.4. Obat-Obatan 13.4.1. Obat Generik NO Kemasan Harga 1 3 4 Nama Obat 2Document18 pages13.4. Obat-Obatan 13.4.1. Obat Generik NO Kemasan Harga 1 3 4 Nama Obat 2nanarizkiNo ratings yet
- Lista Medicamente 01.01.2014Document143 pagesLista Medicamente 01.01.2014Teodora Costea CoropcariuNo ratings yet
- Midterm DraftDocument32 pagesMidterm DraftUn knownnnNo ratings yet