Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alcohols Chemical Properties (Updated)
Uploaded by
akabalan24Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Alcohols Chemical Properties (Updated)
Uploaded by
akabalan24Copyright:
Available Formats
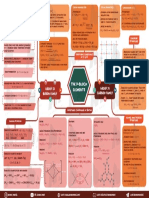
RO – H Cleavage:
Common Properties Esterification •
R’ = Cn’H2n’+1 and R = CnH2n+1 (Note: R and R’ might be the same).
(1°,2°& 3° alcohols) (athermic) •
Important:
→ → Reactivity of ROH: CH3OH > I° > II° > III°
→ → Reactivity of R’CO2H: HCOOH > RCH2COOH > R2CHCO2H > R3CCO2H
Chapter 9 – Alcohols – Chemical Reactions
• Increase yield by using one reactant in excess or removal of H 2O
• Remember that esterification: slow, athermic and reversible.
Fig. 9.7/pg 215
Catalytic Oxidation
(exothermic)
Fig. 9.8/pg 215
Catalytic Dehydrogenation
Mild Oxidation
Distinctive Properties
(endothermic)
(ALCOHOLS ARE
(1°& 2° alcohols ONLY) REDUCTANTS)
(I°):
• 1st, 3RCH2OH + Cr2O72- + 8H+ heat 3RCHO + 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
By Oxidants Cr3O72-,
RCOOH
• 2nd, 3RCHO + Cr2O72- + 8H+ replace 3RCHO + 2Cr3+ + 47H2O
MnO4-, etc.
2-
Excess Cr2O7 , acid major product; excess alcohol, aldehyde major product
(II°): 3R2CHOH + Cr2O72 + 8H+ 3R2CO + 2Cr3+ + 7H2O
(III°): no mild oxidation
Check figures 9.9, 9.10, 9.12, 9.12, 9.14, 9.15, 9.16, 9.17 / pg. 216-219
You might also like
- Annual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1971From EverandAnnual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1971John McMurryNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument1 pageAlcohols Phenols and EthersNitisha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Alkane and Alkyl Halides PP5Document9 pagesAlkane and Alkyl Halides PP5odubade opeyemiNo ratings yet
- Annual Reports in Organic Synthesis–1982: Annual Reports in Organic SynthesisFrom EverandAnnual Reports in Organic Synthesis–1982: Annual Reports in Organic SynthesisL. G. WadeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Alkanes Alkenes AlkynesDocument2 pagesAlkanes Alkenes AlkynesGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- STPM Chemistry Topic 18 Carbonyl Compound (Short Notes)Document1 pageSTPM Chemistry Topic 18 Carbonyl Compound (Short Notes)Chris Lau100% (2)
- Southwest Power Conference SCR Catalyst Management: Terry Mcternan, P.E 919 620-3023Document53 pagesSouthwest Power Conference SCR Catalyst Management: Terry Mcternan, P.E 919 620-3023JeeEianYannNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon To Amines Short NotesDocument31 pagesHydrocarbon To Amines Short NotesMd AmanNo ratings yet
- Bansal Classes Organic Part 2Document195 pagesBansal Classes Organic Part 2Brain MasterNo ratings yet
- CH 20-21 Answers (All)Document36 pagesCH 20-21 Answers (All)Thục NghiNo ratings yet
- Propoxylated EmulsifierDocument1 pagePropoxylated EmulsifierFadhli KusumaNo ratings yet
- JC1 Chemistry Organic Reagent Practice - HWDocument14 pagesJC1 Chemistry Organic Reagent Practice - HWTesar DzikrullohNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Notes ch11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument8 pages12 Chemistry Notes ch11 Alcohols Phenols and Ethersmv7602456No ratings yet
- CO2 Capture & CompressionDocument22 pagesCO2 Capture & Compressionchen junwenNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons: Hydrocarbons Are Two TypesDocument35 pagesHydrocarbons: Hydrocarbons Are Two Typesdebraj sethiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ReactionDocument3 pagesOrganic Chemistry ReactionGAMEPORIUMNo ratings yet
- Θεωρία Υβριδισμού Του Ατόμου Του Άνθρακα Του Δημήτρη ΣιάπκαDocument27 pagesΘεωρία Υβριδισμού Του Ατόμου Του Άνθρακα Του Δημήτρη Σιάπκαaggelisgeorge8546No ratings yet
- CBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-11: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Structure of AlcoholsDocument8 pagesCBSE Class-12 Chemistry Quick Revision Notes Chapter-11: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Structure of AlcoholsSAKET TYAGINo ratings yet
- Oxidations: JACS 1951, 73, 65Document25 pagesOxidations: JACS 1951, 73, 65aggelisgeorge8546No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry PosterDocument1 pageOrganic Chemistry Poster텅텅No ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Catalytic ReactionsDocument33 pagesChapter 7. Catalytic ReactionsAbhinav AnandNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon: Reagent - Function: NotesDocument46 pagesHydrocarbon: Reagent - Function: NotesSowmya AnandNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart - HydrocarbonsDocument77 pagesFlow Chart - HydrocarbonsKalyan Reddt100% (2)
- Kirk Orthmer UreaDocument19 pagesKirk Orthmer UreaGiovanni JonathanNo ratings yet
- Sol Gel TechnologyDocument7 pagesSol Gel TechnologySrisha MudavathNo ratings yet
- Sol-Gel Technology: Aytan MuradovaDocument7 pagesSol-Gel Technology: Aytan MuradovaIRAIS CARDENAS AYALANo ratings yet
- Aqua RegiaDocument6 pagesAqua RegiaGanesh DixitNo ratings yet
- ReductionDocument7 pagesReductionPranayNo ratings yet
- Dehydol LT 6 TI ENDocument6 pagesDehydol LT 6 TI ENErhan KüçükNo ratings yet
- 11 - Inhibitors 2007Document13 pages11 - Inhibitors 2007MattNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl CompoundsDocument10 pagesCarbonyl CompoundsMahendra ChouhanNo ratings yet
- FaziraRazak - HydrogenDocument50 pagesFaziraRazak - HydrogenaieyinHengNo ratings yet
- Dimethyl EtherDocument2 pagesDimethyl EtheraisyahNo ratings yet
- Alcohol and Ether CompleteDocument2 pagesAlcohol and Ether CompleteAdvik GuptaNo ratings yet
- Guerbet Chemistry: Journal of Surfactants and Detergents July 2001Document17 pagesGuerbet Chemistry: Journal of Surfactants and Detergents July 2001Sanggari MogarajaNo ratings yet
- Reduction, Oxidation - Hydrolysis Theory PDFDocument14 pagesReduction, Oxidation - Hydrolysis Theory PDFGOURISH AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- S-Block For Jee AdvanceDocument38 pagesS-Block For Jee AdvanceSitabai JadhavNo ratings yet
- SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF GRAPHENE OXIDE - PowerpointDocument23 pagesSYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF GRAPHENE OXIDE - Powerpointjoyson229No ratings yet
- STPM Chemistry Topic 17 Hydroxyl Compound (Short Notes)Document1 pageSTPM Chemistry Topic 17 Hydroxyl Compound (Short Notes)Chris Lau100% (1)
- Sodium Borohydride: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument27 pagesSodium Borohydride: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchChaeyoung SonNo ratings yet
- Acetic Acid Industrial ChemistryDocument12 pagesAcetic Acid Industrial ChemistryPragadeeshNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidDocument28 pagesCarboxylic AcidManthan HaritashNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - Ony PDFDocument5 pagesFormula Sheet - Ony PDFSana ImamNo ratings yet
- CH Mka With AnnotationsDocument76 pagesCH Mka With AnnotationsgvygtvcNo ratings yet
- Calcium Nitrate (Wiki)Document2 pagesCalcium Nitrate (Wiki)xcvNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 SlidesDocument63 pagesChapter 8 SlidespoojaNo ratings yet
- Organic Synthesis. ReductionsDocument64 pagesOrganic Synthesis. ReductionsKartik RanaNo ratings yet
- Dehydol LS 6 TI en 2013Document4 pagesDehydol LS 6 TI en 2013Erhan KüçükNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes + Ketones - Lecture IDocument41 pagesAldehydes + Ketones - Lecture IVanessa Osafo MensahNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid 13-02-2019Document29 pagesCarboxylic Acid 13-02-2019Sania KhanNo ratings yet
- 11 - The P-Block ElementsDocument1 page11 - The P-Block ElementsPuppika DogNo ratings yet
- Tema 10 IGDocument20 pagesTema 10 IGPanda Mi ÍDOLONo ratings yet
- Maestri Hot TopicDocument56 pagesMaestri Hot TopicRaamses DíazNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic & DerivtDocument7 pagesCarboxylic & DerivtNanda NaimahNo ratings yet
- Benzene RxnsDocument1 pageBenzene Rxnsapi-465421809No ratings yet
- STPM Chemistry Topic 14 Carbon Chemistry (Short Notes)Document1 pageSTPM Chemistry Topic 14 Carbon Chemistry (Short Notes)Chris Lau100% (1)
- PDF Glassmaking PDFDocument5 pagesPDF Glassmaking PDFAli AliNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - May 2016Document1 pageChemistry - May 2016Rahique ShuaibNo ratings yet
- Poster NAM Reyna-2Document1 pagePoster NAM Reyna-2omarNo ratings yet
- AC Hipots 15-200kVDocument4 pagesAC Hipots 15-200kVfelipe.aounNo ratings yet
- Revised Implementing Rules and Regulations Ra 10575Document79 pagesRevised Implementing Rules and Regulations Ra 10575Rodel D. LuyaoNo ratings yet
- Clavija L5-30P Ref 2611Document3 pagesClavija L5-30P Ref 2611CristianDuarteSandovalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cavitation in Pumps and Their TypesDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Cavitation in Pumps and Their TypesMujadid Khawaja100% (1)
- Maruti FinalDocument23 pagesMaruti FinalYash MangeNo ratings yet
- Chain Rule 3LNDocument2 pagesChain Rule 3LNsaad khNo ratings yet
- Akebono NVH White PaperDocument4 pagesAkebono NVH White Paperapi-3702571100% (1)
- 2015.15009.fundamental Principles of Physical Chemistry - Text PDFDocument782 pages2015.15009.fundamental Principles of Physical Chemistry - Text PDFAnoif Naputo Aidnam100% (1)
- Harmonica IntroDocument5 pagesHarmonica Introapi-26593142100% (1)
- AI LabDocument17 pagesAI LabTripti JainNo ratings yet
- Sri Anjaneya Cotton Mills LimitedDocument63 pagesSri Anjaneya Cotton Mills LimitedPrashanth PB50% (2)
- Drinking Water Treatment Unit Scheme Ver 2Document31 pagesDrinking Water Treatment Unit Scheme Ver 2josephsedNo ratings yet
- TQ Science10 Q3 ST4Document2 pagesTQ Science10 Q3 ST4mae cudal100% (1)
- Isabela State University: Republic of The Philippines Roxas, IsabelaDocument17 pagesIsabela State University: Republic of The Philippines Roxas, IsabelaMarinette MedranoNo ratings yet
- Comprehension: The Boy Is Playing With A Fire TruckDocument79 pagesComprehension: The Boy Is Playing With A Fire Truckbhupendra singh sengarNo ratings yet
- Ev Conversion PDFDocument2 pagesEv Conversion PDFShannonNo ratings yet
- RK3066 Mid PDFDocument17 pagesRK3066 Mid PDFSharon MurphyNo ratings yet
- Adherence Tradeoff To Multiple Preventive Therapies and All-Cause Mortality After Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument12 pagesAdherence Tradeoff To Multiple Preventive Therapies and All-Cause Mortality After Acute Myocardial InfarctionRoberto López MataNo ratings yet
- Focus: Optimised Efficiency For The Paper IndustryDocument24 pagesFocus: Optimised Efficiency For The Paper IndustryZoran BadurinaNo ratings yet
- Swot Ananlysis of Fintech CompaniesDocument7 pagesSwot Ananlysis of Fintech CompaniesUyen Le VuNo ratings yet
- Dpco 151223080520 PDFDocument23 pagesDpco 151223080520 PDFSiva PrasadNo ratings yet
- Migloo's Day Info SheetDocument4 pagesMigloo's Day Info SheetCandlewick PressNo ratings yet
- Study - Id23039 - Travel and Tourism in India Statista Dossier PDFDocument60 pagesStudy - Id23039 - Travel and Tourism in India Statista Dossier PDFaashmeen25No ratings yet
- Pressuremeter TestDocument33 pagesPressuremeter TestHo100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics and Machinery Laboratory Manual: by Dr. N. Kumara SwamyDocument4 pagesFluid Mechanics and Machinery Laboratory Manual: by Dr. N. Kumara SwamyMD Mahmudul Hasan Masud100% (1)
- World War 1 NotesDocument2 pagesWorld War 1 NotesSoarSZNNo ratings yet
- Product Data Sheet: Type: P25-34/0DDocument1 pageProduct Data Sheet: Type: P25-34/0DAlejandro RustrianNo ratings yet
- The USP AdvantageDocument30 pagesThe USP AdvantageGabriel A. RamírezNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry DPP-1Document2 pagesElectrochemistry DPP-1tarunNo ratings yet
- SCI Annual Report 2017Document32 pagesSCI Annual Report 2017The Seamen's Church Institute100% (2)