Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mathematical Language and Symbols
Uploaded by
JAVIER, KISSIE CZARINNEOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mathematical Language and Symbols
Uploaded by
JAVIER, KISSIE CZARINNECopyright:
Available Formats
Mathematical Language and
Symbols
Created @August 21, 2023 12:07 AM
Class MATHEMATICS IN MODERN WORLD
Type Lecture
Reviewed
Importance of the Language of Mathematics
To understand the expressed ideas
To communicate ideas to others
Characteristics of language of mathematics
1. Precise - able to make very fine distinctions
2. Concise - able to say things briefly
3. Powerful - able to express complex thoughts with relative ease
Mathematical Language and Symbols 1
Mathematical Language and Symbols 2
Expression in mathematics
a mathematical analogue of an English noun
Examples of expressions or mathematical objects:
numbers
Mathematical Language and Symbols 3
sets
functions
ordered pairs
matrices
vectors
SIMPLIFY
The most common type of problem involving an expression is to “SIMPLIFY”.
Simplify means to get a different name for the expression that in some way is simple.
SIMPLER
fewer symbols
fewer operations
Mathematical Language and Symbols 4
better suited for current use
preferred style/format
Example: fewer symbols
10 – 2 + 4 and 12 are both names of the same number but 12 uses fewer symbols
Example: fewer operations
10+10+10+10 and 4x10 are names of the same number but 4X10 uses fewer operations.
There are three additions in 10+10+10+10 while only one multiplication in 4x10.
Example: better suited for current use
(1 yard) / (3 feet) is another name for the number 1 for converting feet to yard
Example: preferred style or format
The number 5/10 and ½ they are both the same number but ½ is preferred because it is in
simplest form or reduced form.
EXPRESSIONS
have different names; the names we use depends on what we are doing with the expression
Mathematical Language and Symbols 5
Mathematical Sentence
analogue of an English sentence
a correct arrangement of mathematical symbols that states a complete thought
contains a verb
The grammar of mathematics
Some difficulties in math language
The word “is” could mean equality, inequality or membership in a set.
Different uses of a number; to express quantity (cardinal), to indicate the order (ordinal), and
as a label (nominal)
Mathematical objects may be represented in many ways, such as sets and functions
The words "and' & "or" means different from its English use
Mathematical Language and Symbols 6
Objects that we use in mathematics
Numbers (4 operations and properties)
Variables
Operations (unary & binary)
FOUR BASIC CONCEPTS:
1. Sets (relationships, operations, properties)
2. Relations (Equivalence relations)
3. Functions ( Injective, Surjective , Bijective)
4. Binary Operations
Mathematical language contains numbers and symbols. These mathematical symbols are used to
represent value, a mathematical object, an action on mathematical objects, a relation between
mathematical objects, or for structuring the other symbols that occur in a formula. If you can
recall some of your mathematics subjects in elementary and high school, then you can recall that
symbols allow us to "work with" parts in a theoretical manner like in your algebra, geometry,
calculus, statistics, etc.
Georg Ferdinand Ludwig Philipp Cantor
was a German mathematician. He created set theory, which has become a fundamental
theory in mathematics. Cantor established the importance of one-to-one correspondence
between the members of two sets, defined infinite and well-ordered sets, and proved that the
real numbers are more numerous than the natural numbers. In fact, Cantor's method of proof
of this theorem implies the existence of an infinity of infinities. He defined the cardinal and
ordinal numbers and their arithmetic.
Set
Mathematical Language and Symbols 7
is a well-defined collection of distinct objects. The objects that make up a set (also known as
the set's elements or members) can be anything: numbers, people, letters of the alphabet,
other sets, and so on.
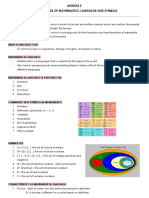
Venn diagram
also called primary diagram, set diagram or logic diagram, is a diagram that shows all
possible logical relations between a finite collection of different sets. These diagrams depict
elements as points in the plane, and sets as regions inside closed curves. A Venn diagram
consists of multiple overlapping closed curves, usually circles, each representing a set. The
points inside a curve labelled S represent elements of the set S, while points outside the
boundary represent elements not in the set S.
Mathematical Language and Symbols 8
You might also like
- Defeat Cancer NaturallyDocument94 pagesDefeat Cancer NaturallyRknuviprasys Low100% (3)
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) and War-Related StressDocument56 pagesPosttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) and War-Related Stresshiggjp3No ratings yet
- Mathematical Languages and SymbolsDocument2 pagesMathematical Languages and SymbolsJoyce Salamat100% (6)
- Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument72 pagesMathematical Language and SymbolsJurren Valderama Pigao100% (1)
- Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument17 pagesMathematics in The Modern Worldabercrombie89% (18)
- Chapter 2 - Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument32 pagesChapter 2 - Mathematical Language and SymbolsAlthea Faye Rabanal100% (1)
- Op Amp AssignmentDocument10 pagesOp Amp AssignmentJuan-Wian CoetzerNo ratings yet
- Exam Materials ScienceDocument10 pagesExam Materials ScienceChimzoe CatalanNo ratings yet
- A554-15 Standard Specification For Welded Stainless Steel Mechanical TubingDocument8 pagesA554-15 Standard Specification For Welded Stainless Steel Mechanical TubingChuthaNo ratings yet
- Nestle SWOT AnalysisDocument3 pagesNestle SWOT AnalysisMubeen AbdulshakoorNo ratings yet
- Freedom As A Foundation of EthicsDocument3 pagesFreedom As A Foundation of EthicsGrant Jomar SiadorNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Week 3Document35 pagesLesson 1 Week 3leinardNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MMWDocument3 pagesChapter 2 MMWValerie Mae Librero AreñoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Language and SymbolsDocument52 pagesMathematics Language and SymbolsPrince Kerwin50% (2)
- The Ayurvedic Vegan Kitchen PDFDocument203 pagesThe Ayurvedic Vegan Kitchen PDFRuvaly MzNo ratings yet
- 2 Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument30 pages2 Mathematical Language and SymbolsEunice Bumanglag100% (6)
- Interference Measurement SOP v1.2 Sum PDFDocument26 pagesInterference Measurement SOP v1.2 Sum PDFTeofilo FloresNo ratings yet
- Bombardier Zefiro Technical Description enDocument15 pagesBombardier Zefiro Technical Description ennickerlesstezla100% (1)
- Mathematical Language 2Document27 pagesMathematical Language 2Althea Faye RabanalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MATHDocument36 pagesChapter 2 MATHllae92892No ratings yet
- MATHEMATICAL LAngDocument34 pagesMATHEMATICAL LAngJeianne Decerie MiguelNo ratings yet
- Mathematical LanguageDocument78 pagesMathematical LanguagenemieNo ratings yet
- Mathematics ReviewerDocument9 pagesMathematics ReviewerKier PanugaoNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Language AND Symbols: Armando C. ManzanoDocument26 pagesMathematical Language AND Symbols: Armando C. ManzanoAllen Kurt RamosNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2: Mathematical Language and Symbol (9 Hours)Document7 pagesUNIT 2: Mathematical Language and Symbol (9 Hours)Ell VNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lesson 2.1Document6 pagesChapter 2 Lesson 2.1Shereen MendizabalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Mathematecal LanguageDocument25 pagesChapter 2 Mathematecal LanguageririricelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document14 pagesChapter 2LIGAWAD, MELODY P.No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Day 1Document32 pagesUnit 2 - Day 1JCG XIIINo ratings yet
- Module 2 Mathematical Language and Symbols 1Document14 pagesModule 2 Mathematical Language and Symbols 1Ancheta LeahNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2-1. Mathematical LanguageDocument14 pagesLesson 2-1. Mathematical Languagedwaytikitan28No ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument31 pagesMathematics in The Modern WorldOnecho Angelo GabineteNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Mathematical LanguageDocument4 pagesModule 2 Mathematical LanguageErizza JavierNo ratings yet
- GEC 3 Module 2Document11 pagesGEC 3 Module 2samanthachua155No ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Language, Symbols and Conventions of MathematicsDocument12 pagesChapter 2: Language, Symbols and Conventions of MathematicsNi ValNo ratings yet
- MODULE-2-MATHEMATICAL-LANGUAGE-AND-SYMBOLS (Edited)Document20 pagesMODULE-2-MATHEMATICAL-LANGUAGE-AND-SYMBOLS (Edited)KRISTINACASSANDRA REGISNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document12 pagesLesson 2Erica ComendadorNo ratings yet
- 2 3. Mathematics As A LanguageDocument31 pages2 3. Mathematics As A LanguageAlex VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Colegio de San Gabriel Arcangel of Caloocan, Inc.: Module I: Mathematics As A LanguageDocument15 pagesColegio de San Gabriel Arcangel of Caloocan, Inc.: Module I: Mathematics As A LanguageKIRITO SALINASNo ratings yet
- Unit I - B (Part 1)Document13 pagesUnit I - B (Part 1)Angelo Rebayla OribiaNo ratings yet
- Math in The Modern World ReviewerDocument7 pagesMath in The Modern World Reviewerivy saludesNo ratings yet
- Math ReviewerDocument5 pagesMath Reviewermarcishere04No ratings yet
- M2LESSON1 Characteristics of Mathematics As A LanguageDocument1 pageM2LESSON1 Characteristics of Mathematics As A LanguageBilly James RamosNo ratings yet
- 4 Mathematics As A LanguageDocument30 pages4 Mathematics As A LanguageHiljane ConchasNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Mathematical Language and Symbols Week 3 To Week 4Document12 pagesMODULE 2 Mathematical Language and Symbols Week 3 To Week 4Ariane Leslie CambaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.1 Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument8 pagesChapter 2.1 Mathematical Language and SymbolsC J A SNo ratings yet
- LanguageDocument7 pagesLanguageallysajeandizon11No ratings yet
- Lesson 4.the Nature of Mathematics As A LanguageDocument3 pagesLesson 4.the Nature of Mathematics As A LanguagePlacido BucyayNo ratings yet
- MATH Nature of MathematicsDocument31 pagesMATH Nature of MathematicsajdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Part 1 MMWDocument13 pagesChapter 2 Part 1 MMWJob Dave ToledoNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Language and Symbols: Ms. Jessica Mae C. Salazar College InstructorDocument13 pagesMathematical Language and Symbols: Ms. Jessica Mae C. Salazar College InstructorJessica Mae SalazarNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument83 pagesMathematical Language and SymbolsTohruNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern World-Lesson4Document27 pagesMathematics in The Modern World-Lesson4LharvaeNo ratings yet
- 2-3. Mathematics As A LanguageDocument31 pages2-3. Mathematics As A LanguageMaridelle ManalastasNo ratings yet
- 1mathematics As A LanguageDocument2 pages1mathematics As A LanguageRonie mar Del rosarioNo ratings yet
- Pamantasan NG Cabuyao College of Education, Arts and SciencesDocument18 pagesPamantasan NG Cabuyao College of Education, Arts and Sciences-------No ratings yet
- Math Module 2Document3 pagesMath Module 2Yaz VergaraNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Mathematical Language and Symbols: What This Module Is AboutDocument7 pagesModule 2: Mathematical Language and Symbols: What This Module Is AboutJon Josh Mabunga MabiogNo ratings yet
- MMW Third LectureDocument41 pagesMMW Third LectureJanine CrisoloNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document14 pagesModule 2basanjelica018No ratings yet
- Mathematical Language and Symbols: Math in The Modern WorldDocument23 pagesMathematical Language and Symbols: Math in The Modern WorldKreal VileNo ratings yet
- Language of Mathematics - Mathematicl TranslationDocument37 pagesLanguage of Mathematics - Mathematicl TranslationMark Julius Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 (Prelim) - Language of MathematicsDocument50 pagesLesson 3 (Prelim) - Language of MathematicsAndro BisnarNo ratings yet
- Dear God,: IF I Am Wrong, Correct Me. IF I Am Lost, Guide Me. IF I Start To Give Up, Keep Me GoingDocument33 pagesDear God,: IF I Am Wrong, Correct Me. IF I Am Lost, Guide Me. IF I Start To Give Up, Keep Me GoingopawbunaNo ratings yet
- 2 Language of Mathematics LectureDocument32 pages2 Language of Mathematics Lecturegweychol100% (1)
- Ge 104 - Module 2 (Chapter 2)Document24 pagesGe 104 - Module 2 (Chapter 2)Nightmare GamingNo ratings yet
- Gec4 Lesson2Document5 pagesGec4 Lesson2Queen Ann QuibanNo ratings yet
- Ge 104 Module 2Document23 pagesGe 104 Module 2Nica De JuanNo ratings yet
- Modern Math Module 2-4Document7 pagesModern Math Module 2-4Jerald LinogonNo ratings yet
- 2021 Lifting Points Main Catalogue V1 - V - RUDDocument120 pages2021 Lifting Points Main Catalogue V1 - V - RUDmengyu hanNo ratings yet
- Customer - Reprint DhoniDocument1 pageCustomer - Reprint DhoniBaljit SinghNo ratings yet
- Homework 3rd SteelDocument4 pagesHomework 3rd SteelPiseth HengNo ratings yet
- MiniNova GuideDocument41 pagesMiniNova GuideBob FredNo ratings yet
- Jeppview For Windows: List of Pages in This Trip KitDocument12 pagesJeppview For Windows: List of Pages in This Trip KitNguyen MinhNo ratings yet
- HOconsDocument14 pagesHOconsMax PradoNo ratings yet
- Q4 Lesson 3 Hinge Theorem and Its ConverseDocument36 pagesQ4 Lesson 3 Hinge Theorem and Its ConverseZenn Tee100% (1)
- Hemiplegia LectureDocument37 pagesHemiplegia LectureRancesh FamoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Tanker Familiarization (CTF) : Companies Can Opt For Block BookingDocument1 pageChemical Tanker Familiarization (CTF) : Companies Can Opt For Block BookingSamiulNo ratings yet
- GalvInfoNote 1 4Document4 pagesGalvInfoNote 1 4rplata63No ratings yet
- Modding For Ysflight - Scenery EditorDocument92 pagesModding For Ysflight - Scenery Editordecaff_42No ratings yet
- Fortified Rice FssaiDocument8 pagesFortified Rice FssaisaikumarNo ratings yet
- The Beginningof The Church.R.E.brownDocument4 pagesThe Beginningof The Church.R.E.brownnoquierodarinforNo ratings yet
- Our School Broke Up For The Winter VacationsDocument7 pagesOur School Broke Up For The Winter VacationsprinceNo ratings yet
- Designing New Vanillin Schiff Bases and Their Antibacterial StudiesDocument4 pagesDesigning New Vanillin Schiff Bases and Their Antibacterial StudiesAvinash PurohitNo ratings yet
- Bhsa Inggris'Document5 pagesBhsa Inggris'Dwi NovianaNo ratings yet
- Chm130 Test Batch-2Document3 pagesChm130 Test Batch-2misakisuki7No ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument6 pagesUntitled DocumentrameezshyamaleeNo ratings yet
- Astm D6321-98-2004Document3 pagesAstm D6321-98-2004Thyagu LingamurthyNo ratings yet
- 2022 Specimen Paper 1 Mark Scheme 1Document4 pages2022 Specimen Paper 1 Mark Scheme 1Herman HermanNo ratings yet