Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Poc - Benzoin Condensation
Uploaded by
kavi bharathi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageOriginal Title
poc- benzoin condensation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pagePoc - Benzoin Condensation
Uploaded by
kavi bharathiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
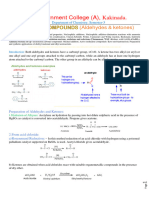
Benzoin Condensation
The Benzoin Condensation is a coupling reaction between two aldehydes that allows the
preparation of α-hydroxyketones. The first methods were only suitable for the conversion of
aromatic aldehydes.
Mechanism of Benzoin Condensation
Step 1: Addition of the cyanide ion to create a cyanohydrin effects an umpolung of the normal
carbonyl charge affinity, and the electrophilic aldehyde carbon becomes nucleophilic after
deprotonation: A thiazolium salt may also be used as the catalyst in this reaction
Step 2: A strong base is now able to deprotonate at the former carbonyl C-atom
Step 3: A second equivalent of aldehyde reacts with this carbanion; elimination of the catalyst
regenerates the carbonyl compound at the end of the reaction:
You might also like
- Benzoin CondensationDocument3 pagesBenzoin CondensationsazinaNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds TVVDocument13 pagesCarbonyl Compounds TVVjyothi sai sriNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Alkynes ReactionsDocument9 pagesOrganic Chemistry Alkynes ReactionsAnthony KwofieNo ratings yet
- Intro Exp Benzaldehyde of Benzylic AcidDocument2 pagesIntro Exp Benzaldehyde of Benzylic AcidberjalankehadapanNo ratings yet
- 8.2 Carbonyl Componds PropertiesDocument19 pages8.2 Carbonyl Componds PropertiesgoverotaropafadzwaNo ratings yet
- 1.aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument117 pages1.aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsKRISHNARJUNA NNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde and KetonesDocument45 pagesAldehyde and KetonesShivam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Named ReactionDocument21 pagesNamed ReactionVijaya RajuNo ratings yet
- Hydration of AlkynesDocument8 pagesHydration of AlkynesAnthony BasantaNo ratings yet
- MSC Chemistry Paper-III Unit-9Document24 pagesMSC Chemistry Paper-III Unit-9SIMARAN JAISWAL 41 M3SNo ratings yet
- Notes VIDocument4 pagesNotes VIAmahNo ratings yet
- Reaksi Kondensasi Senyawa KarbonilDocument62 pagesReaksi Kondensasi Senyawa KarbonilAdi Kurniawan EffendiNo ratings yet
- UNIT 12 Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsDocument40 pagesUNIT 12 Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsVarsha SundareswaranNo ratings yet
- Reaksi Kondensasi KarbonilDocument39 pagesReaksi Kondensasi KarbonilHesstii Sii ChemmicaLissttaaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry-All Reaction MechanismsDocument30 pagesOrganic Chemistry-All Reaction MechanismsParameshwari kumar100% (1)
- Wa0005.Document39 pagesWa0005.amaandeshmukh4No ratings yet
- Alkenes and AlkynesDocument22 pagesAlkenes and AlkynesAyodele AdeyonuNo ratings yet
- Aldol CondensationDocument71 pagesAldol CondensationJeyanthiNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 6C The Chemistry of Alkenes and Alkynes CME 2023Document37 pagesLECTURE 6C The Chemistry of Alkenes and Alkynes CME 2023LinearNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl compounds-II S-1Document5 pagesCarbonyl compounds-II S-1sciencewing rbiNo ratings yet
- Name Reaction 3569 PDFDocument38 pagesName Reaction 3569 PDFAshish AmbekarNo ratings yet
- Name Reaction 3569Document38 pagesName Reaction 3569Ashish AmbekarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22: Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution ReactionsDocument4 pagesChapter 22: Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactionsmikec86No ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon Chemistry CHE 225 Reactions of AlkynesDocument7 pagesHydrocarbon Chemistry CHE 225 Reactions of AlkynesNurul 'Uyun AhmadNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl CompoundsDocument29 pagesCarbonyl CompoundsKarthik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl CompoundsDocument29 pagesCarbonyl CompoundsKarthik SharmaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 12 Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsDocument50 pagesUNIT 12 Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acidssukaina fatima100% (1)
- CAIE Chemistry A-Level: 30: HydrocarbonsDocument4 pagesCAIE Chemistry A-Level: 30: HydrocarbonsahumanbeinginearthNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition ReactionsDocument64 pagesChapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactionsaggelisgeorge8546No ratings yet
- Chapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation ReactionsDocument36 pagesChapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation ReactionsAssyakurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Mechanism of Reaction: Aldol CondensationDocument17 pagesChapter 12 Mechanism of Reaction: Aldol CondensationTiya KapoorNo ratings yet
- Exp 4Document6 pagesExp 4zanjinyadzaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Chapter-12-Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsDocument26 pagesLecture Notes Chapter-12-Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsSHUBHAMNo ratings yet
- Organic Reactions and MechanismDocument51 pagesOrganic Reactions and MechanismAbhay Kumar Nayak75% (8)
- AlkenesDocument16 pagesAlkenesAbhijeetNo ratings yet
- 20.1 Electrophilic Substitution and Reduction Reactions PDFDocument21 pages20.1 Electrophilic Substitution and Reduction Reactions PDFJoshua VincentNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen OrganicDocument5 pagesNitrogen Organicsun riseNo ratings yet
- Poc Unit-5Document9 pagesPoc Unit-5Bintoo SharmaNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument37 pagesAldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acidsssheeladevi84100% (1)
- Carbanions ReactionsDocument6 pagesCarbanions ReactionsDr_GSNo ratings yet
- WADE7 Lecture 08Document69 pagesWADE7 Lecture 08panda_bearz95No ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids. Aldehydes and KetonesDocument42 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids. Aldehydes and KetonesVicky VigneshNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of AlcoholsDocument10 pagesSynthesis of AlcoholsMustaffa MansoorNo ratings yet
- Aldehida Dan KetonDocument88 pagesAldehida Dan KetonSITI FARAS RAHMAWATI 2021No ratings yet
- Reaction MechanismDocument5 pagesReaction MechanismKatniss Tathagata100% (1)
- Chapter 2.6 Aldehyde & KetoneDocument40 pagesChapter 2.6 Aldehyde & Ketone0JTINGNo ratings yet
- CHEM 4113 Organic Chemistry Ii Lecture Notes: Eq - 5 Eq - 7Document9 pagesCHEM 4113 Organic Chemistry Ii Lecture Notes: Eq - 5 Eq - 7Kuandi TanNo ratings yet
- Art Integrated Learning Project (Ritik Kumar)Document49 pagesArt Integrated Learning Project (Ritik Kumar)abhiabhishek6073No ratings yet
- Reactions of BenzeneDocument20 pagesReactions of BenzenehaniaNo ratings yet
- AldehydeDocument11 pagesAldehydeBabi Kumar KafleNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Reactive Intermediate FinalDocument38 pagesChemistry of Reactive Intermediate FinalTefera100% (1)
- Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones: Hydrogen Transfer Redox ReactionsDocument20 pagesReduction of Aldehydes and Ketones: Hydrogen Transfer Redox ReactionsDhewi LayNo ratings yet
- Reactions of MonosaccharideDocument13 pagesReactions of MonosaccharideKate Lyle ParfanNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic AcidsDocument39 pagesAldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic AcidsashathtNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1Document33 pagesChemistry 1Alvis MwangiNo ratings yet
- 18.0 Carbonyl CompoundsDocument9 pages18.0 Carbonyl CompoundsKudzayi Tusaumwe100% (1)
- Advances in Organometallic Chemistry and Catalysis: The Silver / Gold Jubilee International Conference on Organometallic Chemistry Celebratory BookFrom EverandAdvances in Organometallic Chemistry and Catalysis: The Silver / Gold Jubilee International Conference on Organometallic Chemistry Celebratory BookArmando J. L. PombeiroRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Alkane FunctionalizationFrom EverandAlkane FunctionalizationArmando J. L. PombeiroNo ratings yet
- Applied Homogeneous Catalysis with Organometallic Compounds: A Comprehensive Handbook in Four VolumesFrom EverandApplied Homogeneous Catalysis with Organometallic Compounds: A Comprehensive Handbook in Four VolumesBoy CornilsNo ratings yet