Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Intro Exp Benzaldehyde of Benzylic Acid
Uploaded by
berjalankehadapanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Intro Exp Benzaldehyde of Benzylic Acid
Uploaded by
berjalankehadapanCopyright:
Available Formats
Intro exp benzaldehyde of benzylic acid
Multistep synthesis can be defined as the process of converting compounds that commercially
available into desired products by using known reactions. It involves more than one step which the
formation of intermediate is compulsory.
In this experiment, we were supposed to convert benzaldehyde to benzilic acid via a three step of
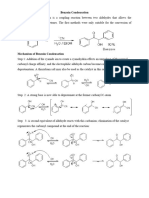
reactions. Firstly, two equivalents of benzaldehyde react to form benzoin by using thiamine-
catalyzed reaction. Thiamine is used as it acts as a coenzyme that enhances the reaction.Secondly,
benzoin undergoes oxidation to form benzil . Oxidation reaction occurs in order to utilize the mild
oxidizing agent which is nitric acid in pyridine.lastly, benzil rearranges to form benzilic acid by
reactions with KOH and then followed by H3o+. the rearrangement of benzil happens due to the
intramolecular oxidation and reduction forces of gaining and losing electrons. However, we were
failed during first step due to several factors which will be explained more details in the discussion
parts.
Thiamine hydrochloride is used as a “green” reagent as opposed to thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) to
catalyze the benzoin condensation. In the reaction, the proton at carbon two is removed with a
weak base to form the ylide, which acts as a nucleophile and adds to the carbonyl group of
benzaldehyde. Then another proton is removed with a base to form a double bond, which then
reacts with another equivalent of benzaldehyde to form another intermediate. The base then
removes another proton to yield benzoin and the ylide, which can hen react with more molecules of
benzaldehyde. Next, the benzoin produced in the first step is oxidized with nitric acid to prepare
benzil in the final reaction, the benzil produces is rearranged with potassium hydroxide and then an
acid reaction, the benzil produced is rearranged with potassium hydroxide and then an acid
(hydrochloric acid). The addition of potassium hydroxide to benzil yields a carboxylate salt,
potassium benzilate, which then reacts with an acid to produce the final product< benzilic acid.
Equation 1: Thiamine Catalysis of Benzoin
Equation 2:Oxidation of Benzil
Equation 3: Rearrangement of Benzil to Benzilic Acid
Infrared Spectroscopy (IR) is performed after each step to determine if the desired product is
formed. The 1H and 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR) of the final product is also
determined to ensure the correct product is created. These spectra can be found in the attached
appendix.
You might also like
- Lab 1 Dehydrogenation HydrogenationDocument3 pagesLab 1 Dehydrogenation HydrogenationJason Chen100% (1)
- Mechanism of Aldol Condensation ExplainedDocument30 pagesMechanism of Aldol Condensation ExplainedParameshwari kumar100% (1)
- Oxidation of Borneol To CamphorDocument17 pagesOxidation of Borneol To Camphorberjalankehadapan100% (4)
- Grade 10 Physical Sciences Platinum Navigation PackDocument63 pagesGrade 10 Physical Sciences Platinum Navigation PackLethabo PhilphNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY - Science Notes For End of Year 9 AssessmentDocument7 pagesCHEMISTRY - Science Notes For End of Year 9 AssessmentJenny Davidson50% (2)
- Pyrolysis and Chlorination of Small HydrocarbonsDocument24 pagesPyrolysis and Chlorination of Small HydrocarbonssylviealNo ratings yet
- CHM557 Lab Report on Aldol CondensationDocument17 pagesCHM557 Lab Report on Aldol CondensationsyafNo ratings yet
- Strategic Intervention Material in Chemical ReactionsDocument15 pagesStrategic Intervention Material in Chemical ReactionsLorna AggabaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 No 9Document8 pagesChapter 10 No 9Ain FzaNo ratings yet
- Aldol Condensation Reaction: BenzalacetophenoneDocument12 pagesAldol Condensation Reaction: Benzalacetophenoneberjalankehadapan100% (1)
- CHEM35.1 E7 Cannizzaro ReactionDocument4 pagesCHEM35.1 E7 Cannizzaro ReactionGlenn Vincent Tumimbang100% (7)
- Experimental Organic Chemistry Post-Lab 7 Haloform ReactionDocument4 pagesExperimental Organic Chemistry Post-Lab 7 Haloform Reactionapi-235187189100% (2)
- Synthesis of Ibuprofen From BenzeneDocument11 pagesSynthesis of Ibuprofen From BenzeneEriika SaucdoNo ratings yet
- Benzoin CondensationDocument3 pagesBenzoin CondensationsazinaNo ratings yet
- Poc - Benzoin CondensationDocument1 pagePoc - Benzoin Condensationkavi bharathiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report on 4-Step Synthesis of HexaphenylbenzeneDocument3 pagesLab Report on 4-Step Synthesis of HexaphenylbenzeneMikey ZhitnitskyNo ratings yet
- Benzoin Exp7Document4 pagesBenzoin Exp7Liz Hackett0% (1)
- exp4Document6 pagesexp4zanjinyadzaNo ratings yet
- Benzoin Condensation.Document7 pagesBenzoin Condensation.Sam Bina92% (13)
- Chemistry 211 Experiment 10Document9 pagesChemistry 211 Experiment 10zFe 6No ratings yet
- Experiment 32Document14 pagesExperiment 32Morgan Elizabeth Lepley100% (6)
- Carbonyl Compounds TVVDocument13 pagesCarbonyl Compounds TVVjyothi sai sriNo ratings yet
- Methyl BenzoateDocument11 pagesMethyl BenzoaterasuhuruNo ratings yet
- (CHM234) Benzoin To Benzilic Acid Full ReportDocument1 page(CHM234) Benzoin To Benzilic Acid Full Reporthallred3450% (2)
- exp 4 FINALDocument11 pagesexp 4 FINALexpido tapologoNo ratings yet
- MSC II SEM 2023 - 24 Organic Reagents and Modern Synthetic ReactionsDocument51 pagesMSC II SEM 2023 - 24 Organic Reagents and Modern Synthetic Reactionsharirajans71No ratings yet
- 20.1 Electrophilic Substitution and Reduction Reactions PDFDocument21 pages20.1 Electrophilic Substitution and Reduction Reactions PDFJoshua VincentNo ratings yet
- Nitration of Methyl BenzoateDocument7 pagesNitration of Methyl BenzoateJanel Pauline G. Chua100% (1)
- Discussion of Benzoic Acid Identification TestDocument3 pagesDiscussion of Benzoic Acid Identification TestPrincess Loyola TapiaNo ratings yet
- Dewar BenzeneDocument7 pagesDewar BenzenechinuasfaNo ratings yet
- 18.07 Side-Chain Reactions of Benzene DerivativesDocument4 pages18.07 Side-Chain Reactions of Benzene Derivativesbahru demekeNo ratings yet
- Rohan Roy - pt314 - 3rdsemDocument13 pagesRohan Roy - pt314 - 3rdsem53 Rohan RoyNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Benomyl From 2-ButeneDocument14 pagesSynthesis of Benomyl From 2-ButeneSophia Chua MelotindoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: AROMATIC SIDE-CHAIN OXIDATION: PHTHALIC ACID FROM XYLENEDocument4 pagesExperiment 2: AROMATIC SIDE-CHAIN OXIDATION: PHTHALIC ACID FROM XYLENEPrincess Alyssa Abid0% (1)
- Adipic Acid PreparationDocument9 pagesAdipic Acid PreparationSmaeUB100% (1)
- Aldehydes & Ketones: Properties, Preparation and ReactionsDocument45 pagesAldehydes & Ketones: Properties, Preparation and ReactionsShivam GuptaNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Benzene from Benzoates Using Dry DistillationDocument9 pagesPreparation of Benzene from Benzoates Using Dry DistillationjolouisNo ratings yet
- Aldol Condensation and Synthesis of DibenzalacetoneDocument8 pagesAldol Condensation and Synthesis of DibenzalacetoneArturo CamañoNo ratings yet
- Hetero Cyclic CompoundsDocument22 pagesHetero Cyclic Compoundsdaus029445100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Lab ReportDocument11 pagesOrganic Chemistry Lab ReportVincentNo ratings yet
- Ionic Liquids Catalyzed Biginelli Reaction Under Solvent-Free ConditionsDocument3 pagesIonic Liquids Catalyzed Biginelli Reaction Under Solvent-Free ConditionsnileshsalunkheNo ratings yet
- Comptes Rendus Chimie: Full Paper/m EmoireDocument6 pagesComptes Rendus Chimie: Full Paper/m EmoireMuhammad Abdur RokhimNo ratings yet
- UNIT 12 Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsDocument40 pagesUNIT 12 Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsVarsha SundareswaranNo ratings yet
- Uses of The CompoundsDocument10 pagesUses of The CompoundsXin PurpleNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument8 pagesManualSweta Suman100% (1)
- Rearrangement of Benzopinacol To Benzopinacolone TheoryDocument2 pagesRearrangement of Benzopinacol To Benzopinacolone TheoryElif YeşilyaprakNo ratings yet
- Applied Chemistry - I: AssignmentDocument5 pagesApplied Chemistry - I: AssignmentMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Reactions of MonosaccharideDocument13 pagesReactions of MonosaccharideKate Lyle ParfanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Benzoic AcidDocument6 pagesLecture 8 Benzoic AcidIgnacio Real BuffelliNo ratings yet
- ExerciseDocument16 pagesExercisecse.220840131017No ratings yet
- 14 Diphenyl 13 ButadieneDocument7 pages14 Diphenyl 13 ButadienesaiNo ratings yet
- Named ReactionDocument21 pagesNamed ReactionVijaya RajuNo ratings yet
- molecules: Cesium Carbonate-Catalyzed α-Phenylchalcogenation of Carbonyl Compounds with Diphenyl DichalcogenideDocument9 pagesmolecules: Cesium Carbonate-Catalyzed α-Phenylchalcogenation of Carbonyl Compounds with Diphenyl DichalcogenidejeielyferreirNo ratings yet
- Modified Vilsmeier-Haack Reactions of A-Methylene Ketones: Chapter ThreeDocument48 pagesModified Vilsmeier-Haack Reactions of A-Methylene Ketones: Chapter Threeumesh123patilNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 3 03Document39 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 3 03Ng Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Cyclohexanone Oxime Synthesis NotesDocument4 pagesCyclohexanone Oxime Synthesis NotesSherlock Wesley ConanNo ratings yet
- Aldol Condensation: Synthesis of DibenzaldehydeDocument7 pagesAldol Condensation: Synthesis of DibenzaldehydeLevy Medina TrayaNo ratings yet
- Test For Proteins - Exp 12Document3 pagesTest For Proteins - Exp 12Mara MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl CompoundsDocument29 pagesCarbonyl CompoundsKarthik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl CompoundsDocument29 pagesCarbonyl CompoundsKarthik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Aromatic, Benzenoid and Heterocyclic ChemistryDocument24 pagesAromatic, Benzenoid and Heterocyclic Chemistryrosemoses305No ratings yet
- Poc Unit-5Document9 pagesPoc Unit-5Bintoo SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sample Formal Report in Organic ChemistryDocument10 pagesSample Formal Report in Organic ChemistryAudrey CobankiatNo ratings yet
- H2o2 Radical BrominationDocument3 pagesH2o2 Radical BrominationJuan PerezNo ratings yet
- Advanced OrganicDocument190 pagesAdvanced Organicnisar khanNo ratings yet
- Physical Organic Chemistry — 3: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Third IUPAC Conference on Physical Organic Chemistry, Montpellier, France, 6 - 10 September, 1976From EverandPhysical Organic Chemistry — 3: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Third IUPAC Conference on Physical Organic Chemistry, Montpellier, France, 6 - 10 September, 1976A. FruchierNo ratings yet
- Spray Drying MethodDocument2 pagesSpray Drying MethodberjalankehadapanNo ratings yet
- Used Cooking Oil Environmental ImpactsDocument4 pagesUsed Cooking Oil Environmental ImpactsberjalankehadapanNo ratings yet
- Calamine Lotion DiscussionDocument6 pagesCalamine Lotion Discussionberjalankehadapan0% (1)
- IntroductionDocument5 pagesIntroductionberjalankehadapanNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument5 pagesIntroductionberjalankehadapanNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument5 pagesIntroductionberjalankehadapanNo ratings yet
- Rates Conversions of Alcohols To Alkyl Bromide Organic Lab ReportDocument12 pagesRates Conversions of Alcohols To Alkyl Bromide Organic Lab Reportberjalankehadapan100% (1)
- Understanding The Uses of Radioactivity: SubtopicDocument22 pagesUnderstanding The Uses of Radioactivity: SubtopicberjalankehadapanNo ratings yet
- Balmer' Lab Report Physical ChemistryDocument8 pagesBalmer' Lab Report Physical ChemistryberjalankehadapanNo ratings yet
- What Is Photocell Lights Up Your DayDocument12 pagesWhat Is Photocell Lights Up Your DayberjalankehadapanNo ratings yet
- BiomassGasificationFoam: OpenFOAM solver for biomass gasificationDocument29 pagesBiomassGasificationFoam: OpenFOAM solver for biomass gasificationbinho58No ratings yet
- Carbonyl Condensation ReactionsDocument39 pagesCarbonyl Condensation ReactionsHesstii Sii ChemmicaLissttaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Alcohols, Phenols, and ThiolsDocument19 pagesChapter 7. Alcohols, Phenols, and Thiolshanna liuNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometric relationships and calculationsDocument99 pagesStoichiometric relationships and calculationsAziz Samet ZorluNo ratings yet
- Bioinorganic Chemistry of Oxygen - Ei-Ichiro OchiaiDocument7 pagesBioinorganic Chemistry of Oxygen - Ei-Ichiro OchiaiPhúc NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bromination of Phenol Red by Hydrogen Peroxide Is Possible in The Absence of HaloperoxidasesDocument8 pagesChemical Bromination of Phenol Red by Hydrogen Peroxide Is Possible in The Absence of HaloperoxidasesVictor Hugo Guadalupe IllescasNo ratings yet
- Presented To:: Dr. Manisha Bhardwaj Presented By: Prerna (M.SC Biochemistry)Document15 pagesPresented To:: Dr. Manisha Bhardwaj Presented By: Prerna (M.SC Biochemistry)Anubhuti JhaNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Practice Test 1Document17 pagesEquilibrium Practice Test 1Carlos HfNo ratings yet
- Answer Key-Catalyst Activation - Special ProceduresDocument4 pagesAnswer Key-Catalyst Activation - Special ProceduresJinadNo ratings yet
- Sir Gerobel Narrative Report in ChemistryDocument19 pagesSir Gerobel Narrative Report in Chemistryangelo aquinoNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Problem SetDocument16 pagesOrganic Chemistry Problem SetAgot Barbero NorillaNo ratings yet
- Reversible Reactions and EquilibriumDocument8 pagesReversible Reactions and Equilibriummahika gaurNo ratings yet
- A Study On Making of Compact Manual Paper Recycling Plant For Domestic PurposeDocument22 pagesA Study On Making of Compact Manual Paper Recycling Plant For Domestic PurposeEinjhel RamosNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equations Made EasyDocument6 pagesChemical Equations Made EasydongwonNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids: SolutionDocument9 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids: SolutionPanchi palNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper Organic Chemistry-2nd SemDocument4 pagesModel Question Paper Organic Chemistry-2nd SemPragyan ChutiaNo ratings yet
- Models - Chem.hi Batch ReactorDocument12 pagesModels - Chem.hi Batch ReactorAnonymous wt2BA7uNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument20 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDinesh Samantha DissanayakeNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Reaction Engineering CHE 505Document42 pagesBiochemical Reaction Engineering CHE 505Haru MasaNo ratings yet
- ACF DesignDocument5 pagesACF DesignRonald ManyamaNo ratings yet
- Org Chem Module ADocument21 pagesOrg Chem Module ATootsie YeollieNo ratings yet
- No. of Patents US4013428 - Lurgi Gasification ProcessDocument8 pagesNo. of Patents US4013428 - Lurgi Gasification ProcessChristian ImanuelNo ratings yet
- Advance Chemistry Q4 M1Document19 pagesAdvance Chemistry Q4 M1Trexia SingsonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class 10 Meatals and NonmetalsDocument9 pagesChemistry Class 10 Meatals and NonmetalsGokulNo ratings yet
- CHMB41 Fall 2019 SyllabusDocument9 pagesCHMB41 Fall 2019 SyllabusdaramdasNo ratings yet