Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stationary Waves
Stationary Waves
Uploaded by
willowchenchenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Stationary Waves
Stationary Waves
Uploaded by
willowchenchenCopyright:
Available Formats
Stationary waves are set up on a rope of length 1.0 m fixed at both ends.
1.
Which statement is not correct?
A The first harmonic has a wavelength of 2.0 m.
The midpoint of the rope is always stationary for
B
even-numbered harmonics.
C A harmonic of wavelength 0.4 m can be set up on the rope.
D There are five nodes on the rope for the fifth harmonic.
(Total 1 mark)
Which one of the following statements about stationary waves is true?
2.
A Particles between adjacent nodes all have the same amplitude.
B Particles between adjacent nodes are out of phase with each other.
C Particles immediately on either side of a node are moving in opposite directions.
D There is minimum disturbance of the medium at an antinode.
(Total 1 mark)
Which one of the following statements about stationary waves is true?
3.
A Particles between adjacent nodes all have the same amplitude.
B Particles between adjacent nodes are out of phase with each other.
C Particles immediately on either side of a node are moving in opposite directions.
D There is a minimum disturbance of the medium at an antinode.
(Total 1 mark)
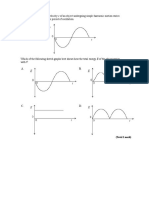
4.
frequency of vibration = 50 Hz
The diagram above shows a stationary wave on a stretched string at a time t = 0. Which one of
the diagrams, A to D, correctly shows the position of the string at a time t = 0.010 s?
Kings Oxford Page 2 of 9
A
D
(Total 1 mark)
Stationary waves are set up on a length of rope fixed at both ends. Which one of the following
5. statements is true?
A Between adjacent nodes, particles of the rope vibrate in phase with each other.
B The mid point of the rope is always stationary.
C Nodes need not necessarily be present at each end of the rope.
D Particles of the rope at adjacent antinodes always move in the same direction.
(Total 1 mark)
A uniform wire fixed at both ends is vibrating in its fundamental mode. Which one of the following
6. statements is not correct for all the vibrating particles?
A They vibrate in phase.
B They vibrate with the same amplitude.
C They vibrate with the same frequency.
D They vibrate at right angles to the wire.
(Total 1 mark)
Kings Oxford Page 3 of 9
A stationary wave is formed by two identical waves of frequency 300 Hz travelling in opposite
7. directions along the same line. If the distance between adjacent nodes is 0.60 m, what is the
speed of each wave?
A 180 m s−1
B 250 m s−1+
C 360 m s−1
D 500 m s−1
(Total 1 mark)
The frequency of the first harmonic of a wire fixed at both ends is 300 Hz.
8. The tension in the wire is now doubled.
What is the frequency of the first harmonic after this change?
A 150 Hz
B 210 Hz
C 420 Hz
D 600 Hz
(Total 1 mark)
Which line, A to D, in the table gives a correct difference between a progressive wave and a
9. stationary wave?
progressive wave stationary wave
all the particles vibrate some of the particles do not
A
vibrate
none of the particles vibrate all the particles vibrate with
B
with the same amplitude the same amplitude
all the particles vibrate in none of the particles vibrate in
C
phase with each other phase with each other
some of the particles do not all the particles vibrate in
D
vibrate phase with each other
(Total 1 mark)
Kings Oxford Page 4 of 9
The fundamental frequency f is the lowest frequency heard when a stretched string is vibrating.
10.
The string is now lightly touched one third of the way along its length.
What is the lowest frequency heard?
C f
D 3f
(Total 1 mark)
The frequency of the first harmonic of a standing wave on a wire is f. The length of the wire and
11.
tension in the wire are both doubled.
What is the frequency of the first harmonic as a result?
B f
D 2f
(Total 1 mark)
Kings Oxford Page 5 of 9
The diagram shows two pulses on a string travelling towards each other.
12.
Which of the following diagrams shows the shape of the string when the pulses have passed
through each other?
D
(Total 1 mark)
Which of the following is correct for a stationary wave?
13.
A Between two nodes the amplitude of the wave is constant.
B The two waves producing the stationary wave must always be 180° out of
phase.
C The separation of the nodes for the second harmonic is double the
separation of nodes for the first harmonic.
D Between two nodes all parts of the wave vibrate in phase.
(Total 1 mark)
Kings Oxford Page 6 of 9
Two radio transmitters emit waves at a frequency of 1.4 MHz. A stationary wave is set up
14. between the two transmitters due to the superposition of the radio waves.
What is the minimum distance between two nodes in the stationary wave?
A 107 m
B 214 m
C 428 m
D 857 m
(Total 1 mark)
A stationary wave is set up on a stretched string of length l and diameter d.
15.
Another stationary wave is also set up on a second string made from the same material and with
the same tension as the first.
What length and diameter are required for the second string so that both strings have the same
first-harmonic frequency?
Length of second string Diameter of second string
A 2l 2d
B l 2d
C 2d
D l
(Total 1 mark)
Kings Oxford Page 7 of 9
A uniform wire, fixed at both ends, is plucked in the middle so that it vibrates at the first harmonic
16. as shown.
What is the phase difference between the oscillations of the particles at P and Q?
A zero
(Total 1 mark)
Kings Oxford Page 8 of 9
Mark schemes
D
1.
[1]
C
2.
[1]
C
3.
[1]
C
4.
[1]
A
5.
[1]
B
6.
[1]
C
7.
[1]
C
8.
[1]
A
9.
[1]
D
10.
[1]
A
11.
[1]
C
12.
[1]
D
13.
[1]
A
14.
[1]
C
15.
[1]
A
16.
[1]
Kings Oxford Page 9 of 9
You might also like
- итоговое заданиеDocument2 pagesитоговое заданиеOlga Kukhtina100% (1)
- GOV 1010 - Survey Research Methods Syllabus HarvardDocument11 pagesGOV 1010 - Survey Research Methods Syllabus HarvardkienneuNo ratings yet
- Case 3 Analysis AdtrackmediaDocument2 pagesCase 3 Analysis Adtrackmediaapi-526105414No ratings yet
- ExerciseDocument1 pageExerciseRaka Barcelonista100% (1)
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsFrom EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chapter 4 2010 (SL and HL)Document8 pagesChapter 4 2010 (SL and HL)Harry HaghanyNo ratings yet
- Sound Test 1Document22 pagesSound Test 1Matheesha RajapakseNo ratings yet
- M Q R B: (Total 1 Mark)Document24 pagesM Q R B: (Total 1 Mark)da_reaper_dasNo ratings yet
- Wave Practice 2Document24 pagesWave Practice 2Soyoko U.No ratings yet
- Chapter No. 8 - WavesDocument3 pagesChapter No. 8 - Wavesnazarin.nordinNo ratings yet
- Standing WavesDocument17 pagesStanding WavesSkruzdelyte MielaNo ratings yet
- Waves - Worksheet1706502930061Document1 pageWaves - Worksheet1706502930061uvwx611No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Worksheet 5 Aurora High SchoolDocument3 pagesUnit 2 Worksheet 5 Aurora High SchoolシューゴNo ratings yet
- Waves IIDocument19 pagesWaves IIJIGGONINo ratings yet
- StandingWaves P1Document10 pagesStandingWaves P1Orisa THANAJARONo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 - Group 1Document4 pagesAP Physics 1 - Group 1Maja BolesnikovNo ratings yet
- CH 15 C 11 Marks 1 and 2 QuesDocument7 pagesCH 15 C 11 Marks 1 and 2 QuesVikrant Shivajirao SambheraoNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 - Quiz 2 - Group 1 - END - VERTIKALNA TABELADocument6 pagesAP Physics 1 - Quiz 2 - Group 1 - END - VERTIKALNA TABELAMaja BolesnikovNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 - 2010-2015 (May 2013 Missing) 2Document149 pagesChapter - 4 - 2010-2015 (May 2013 Missing) 2saba falahNo ratings yet
- Abp Waves Multiple Choice 2013-07-12Document5 pagesAbp Waves Multiple Choice 2013-07-12cjNo ratings yet
- A2 SHMDocument44 pagesA2 SHMAmraa aNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 MCQ March 2022: (38 Marks)Document18 pagesTopic 4 MCQ March 2022: (38 Marks)Zi StyleNo ratings yet
- 4.5 Standing WavesDocument28 pages4.5 Standing WavesXavierNo ratings yet
- Superposition Tutorial Solutions 2022Document41 pagesSuperposition Tutorial Solutions 2022Woh Jon LaiNo ratings yet
- Teacher's SAT (Waves) (Nitin) : PART A: Single Choice CorrectDocument7 pagesTeacher's SAT (Waves) (Nitin) : PART A: Single Choice CorrectAmulya SreeNo ratings yet
- CH21-3 - Standing Waves: Important IdeasDocument4 pagesCH21-3 - Standing Waves: Important Ideasمحمد رزقNo ratings yet
- R2019 49P1MSDocument29 pagesR2019 49P1MSSkruzdelyte MielaNo ratings yet
- Superposition + Stationary WavesDocument35 pagesSuperposition + Stationary Waves5000epcbbNo ratings yet
- Basara Gnana Saraswathi Campus Kakatiya Hills: y 5 MM Sin T y 5 MM Sin T / 6 SDocument8 pagesBasara Gnana Saraswathi Campus Kakatiya Hills: y 5 MM Sin T y 5 MM Sin T / 6 SKARRA ASHISH REDDYNo ratings yet
- Ch15c11marks1and2ques SolutionDocument16 pagesCh15c11marks1and2ques SolutionVikrant Shivajirao SambheraoNo ratings yet
- WS WavesDocument1 pageWS WavesPhysics IBNo ratings yet
- IB Phys GNTP C.4 Standing Waves and ResonanceDocument9 pagesIB Phys GNTP C.4 Standing Waves and Resonancea20142174No ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document92 pagesChapter 8omimahaniyaNo ratings yet
- EM Radiation & Quantum Phenomena (Multiple Choice) QPDocument12 pagesEM Radiation & Quantum Phenomena (Multiple Choice) QPimfineNo ratings yet
- Waves p1Document7 pagesWaves p1shaziaNo ratings yet
- SuperpositionDocument32 pagesSuperpositionReece RemediosNo ratings yet
- Particles (Multiple Choice) QPDocument13 pagesParticles (Multiple Choice) QPimfineNo ratings yet
- 1591355973-Sample Paper 10Document6 pages1591355973-Sample Paper 10sithur2305No ratings yet
- A2 SHMDocument45 pagesA2 SHMMalik Rashid Ali LangrialNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument6 pagesWavesShrinay ChandraNo ratings yet
- 60 MarksDocument22 pages60 MarksSkruzdelyte MielaNo ratings yet
- NK C SI R: Exercise-02 MCQ (One or More Choice Correct)Document4 pagesNK C SI R: Exercise-02 MCQ (One or More Choice Correct)Rushwin VaishnavNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument9 pagesMultiple Choice QuestionsAniruddh RaoNo ratings yet
- Topic402 (Interference - Standing Waves)Document13 pagesTopic402 (Interference - Standing Waves)Jeffry RamonidaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Wave-Sheet: 5: Level - IDocument7 pagesMechanical Wave-Sheet: 5: Level - Ivivek mishraNo ratings yet
- General Instructions:: Sample Question Paper - 20 Physics (042) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22Document6 pagesGeneral Instructions:: Sample Question Paper - 20 Physics (042) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22bruno we dont talk aboutNo ratings yet
- Interference and Diffraction (MCQ Only)Document7 pagesInterference and Diffraction (MCQ Only)naithanisharadNo ratings yet
- PlijDocument6 pagesPlijDarsheel AmbasthaNo ratings yet
- CH 0Document16 pagesCH 0abdoag1691998No ratings yet
- Waves GCDocument23 pagesWaves GClumine0755No ratings yet
- 4.4 Waves - Wave Motion QPDocument52 pages4.4 Waves - Wave Motion QPwill hayNo ratings yet
- 15 Wave Motion & Waves On A StringDocument26 pages15 Wave Motion & Waves On A StringSamsul BahriNo ratings yet
- Current & Resistance: - Current and Current Density - Ohm's Law - Resistivity - ResistanceDocument17 pagesCurrent & Resistance: - Current and Current Density - Ohm's Law - Resistivity - ResistancePedroNo ratings yet
- Ib SL Waves Exercize x1b CompressDocument10 pagesIb SL Waves Exercize x1b Compressjujube.dynastie-0vNo ratings yet
- MECHANICAL WAVE-SHEET: 6 (Lecture - 6) Level - I: Page 1 of 4 CPP - Sankalp - Mw-6-Ph-IvDocument4 pagesMECHANICAL WAVE-SHEET: 6 (Lecture - 6) Level - I: Page 1 of 4 CPP - Sankalp - Mw-6-Ph-Ivvivek mishraNo ratings yet
- Wave SuperpositionDocument29 pagesWave SuperpositionAndrei Allen GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Country's Best Online Test PlatformDocument7 pagesCountry's Best Online Test PlatformTejas DhandaNo ratings yet
- Chap14 LGDocument11 pagesChap14 LGEdgar PhiriNo ratings yet
- Class Xii - Assignment - 1 (Obj) # Moving Charges and Magnetism - 18.11.2016Document8 pagesClass Xii - Assignment - 1 (Obj) # Moving Charges and Magnetism - 18.11.2016Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Waves-Quantum and Nuclear-Resolution-Atomic and NuclearDocument45 pagesWaves-Quantum and Nuclear-Resolution-Atomic and NuclearMartinNo ratings yet
- QP - PreBoard - 1 - PhysicsDocument9 pagesQP - PreBoard - 1 - PhysicsABHIK THE GHOULNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Review WAVE 1528318407509 TCDocument27 pagesFinal Exam Review WAVE 1528318407509 TCJoyce CarilloNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Practice Test 3Document18 pagesSolutions To Practice Test 3Trey CrossNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Energy, Power and Resistance - EMF and PD QPDocument14 pages4.2 Energy, Power and Resistance - EMF and PD QPwillowchenchenNo ratings yet
- Charge and Current 1 MSDocument4 pagesCharge and Current 1 MSwillowchenchenNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Waves - Superposition MSDocument20 pages4.4 Waves - Superposition MSwillowchenchenNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Waves - Superposition QPDocument33 pages4.4 Waves - Superposition QPwillowchenchenNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Waves - Electromagnetic Waves QPDocument30 pages4.4 Waves - Electromagnetic Waves QPwillowchenchenNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Waves - Electromagnetic Waves MSDocument19 pages4.4 Waves - Electromagnetic Waves MSwillowchenchenNo ratings yet
- 09 Magnets and CurrentsDocument119 pages09 Magnets and CurrentswillowchenchenNo ratings yet
- Heat Engines For Basic Mechanical EngineeringDocument28 pagesHeat Engines For Basic Mechanical EngineeringJigar Mevada100% (2)
- Fillers Adaptations On Traditional and CDocument10 pagesFillers Adaptations On Traditional and CMaja SMNo ratings yet
- ch4 Standard DeviationDocument14 pagesch4 Standard DeviationAkbar SuhendiNo ratings yet
- DZ 200 CdiDocument2 pagesDZ 200 CdipowerveeNo ratings yet
- Tale of Two SievesDocument13 pagesTale of Two SievesMark MarkesonNo ratings yet
- Consultant ListDocument9 pagesConsultant ListFitsum DojuNo ratings yet
- 12 - WaywardDocument119 pages12 - WaywardAndy WilliamsNo ratings yet
- MELODY 5.3 Treatment Methods Theoretical - V2.0 - 211122Document19 pagesMELODY 5.3 Treatment Methods Theoretical - V2.0 - 211122MelodyNo ratings yet
- 8 - Schlumberger - Alberto Stevens Well Integrity Evaluation With Wireline LogsDocument16 pages8 - Schlumberger - Alberto Stevens Well Integrity Evaluation With Wireline LogsHendrik FoxNo ratings yet
- NoteMapper User GuideDocument25 pagesNoteMapper User GuideJuan PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Opamp DesignDocument60 pagesOpamp DesignSiva KumarNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0278612521000601 MainDocument16 pages1 s2.0 S0278612521000601 MainPrarthanaNo ratings yet
- Assignments MOSDocument4 pagesAssignments MOSRajeev RanaNo ratings yet
- Active Learning Guide 1St Edition Heuvelen Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesActive Learning Guide 1St Edition Heuvelen Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFtamara.hendrick989100% (17)
- API DocumentDocument5,210 pagesAPI DocumentfjlNo ratings yet
- Assay Ob Borax PDFDocument14 pagesAssay Ob Borax PDFAbram Louies Hanna100% (1)
- Report 219 (Final)Document18 pagesReport 219 (Final)TalHa IFtiKharNo ratings yet
- Some Observable Classroom BehaviorDocument33 pagesSome Observable Classroom BehaviorMaNerissa Peñamora SanchezNo ratings yet
- ArmorDocument7 pagesArmorRecep VatanseverNo ratings yet
- Datum, Positioning Dan Photo Udara: B. Sulistijo, PHD Email:Budis@Mining - Itb.Ac - Id Private:0812 202 1017Document50 pagesDatum, Positioning Dan Photo Udara: B. Sulistijo, PHD Email:Budis@Mining - Itb.Ac - Id Private:0812 202 1017Hary laksanaNo ratings yet
- Ch.2 English & Its StagesDocument35 pagesCh.2 English & Its StagesMatilda100% (1)
- Site Development Plan Vicinity Map: Sheet IndexDocument1 pageSite Development Plan Vicinity Map: Sheet IndexRachel PetersNo ratings yet
- Statistics in The Crem As of October 2020Document11 pagesStatistics in The Crem As of October 2020kamijou08No ratings yet
- Slack Briefing NoteDocument2 pagesSlack Briefing NotePedro Inácio FumoNo ratings yet
- Generator ProtectionDocument10 pagesGenerator ProtectionSriram rams100% (1)
- Homegoing - A Literary Reflection of American Racism and Its Disproportionate Effects On Black WomenDocument2 pagesHomegoing - A Literary Reflection of American Racism and Its Disproportionate Effects On Black WomenTutlalee WinesNo ratings yet
- RDC - Thesis and Dissertation IMRAD Format 1Document151 pagesRDC - Thesis and Dissertation IMRAD Format 1DENVER ALIGANo ratings yet