Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How Does A Hard Drive Work
Uploaded by
NataliaRzonsowskaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How Does A Hard Drive Work
Uploaded by
NataliaRzonsowskaCopyright:
Available Formats
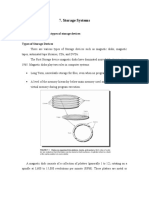
How does a hard drive work?
Hard drive is a device used to store data. Data is recorded on high-speed spinning discs. Each disc is
coated with a film of microscopic magnetised metal grains. All group of grains also known as a bit
used to store data in the form of ones and zeros. Magnetive reader converts strings of bits into useful
informations for computer. The electromagnet is used to record data on the disk transmitted by the
computer. Strings of ones and zeros are used by our computer to interpret information. For example
string of eight ones and zeros (eight bits) represents a letter of the alphabet. But things like a photos
require an average of eight millions bits. Modern hard drive has about 600 gigabits per square inch (1
gigabite is equal to 8 billion bits). It is estimated that this number will rise to twenty terabytes per
square inch in the coming times.
You might also like
- Computers: Hardware and Software: ComputerDocument27 pagesComputers: Hardware and Software: ComputerDaniya AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Moore's Law: Encyclopædia Britannica, IncDocument22 pagesMoore's Law: Encyclopædia Britannica, IncAugastine NdetiNo ratings yet
- English Project 1Document6 pagesEnglish Project 1Ion BotnaruNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Surface Storage DevicesDocument8 pagesMagnetic Surface Storage DevicesvidyawarrierNo ratings yet
- COA AssignmentDocument8 pagesCOA AssignmentVijay SankarNo ratings yet
- Secondary Storage and MediaDocument33 pagesSecondary Storage and MediaBharti PahujaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - 2Document5 pagesChapter 2 - 2randyNo ratings yet
- BBC NEWS - Technology - Drive Advance Fuels Terabyte EraDocument2 pagesBBC NEWS - Technology - Drive Advance Fuels Terabyte EraSrinivas SaiNo ratings yet
- How Do Hard Drives Work - Kanawat Senanan - enDocument4 pagesHow Do Hard Drives Work - Kanawat Senanan - enkholilNo ratings yet
- CH3 Storage Devices and MediaDocument16 pagesCH3 Storage Devices and MediaSeif MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Data StorageDocument20 pagesData StorageSameer HussainNo ratings yet
- Hard disk drive overview and historyDocument19 pagesHard disk drive overview and historyNewScribdMemberNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument4 pagesProjectimantjasperNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Moores Law and MoreDocument33 pagesCH 6 Moores Law and Morethomas alvarezNo ratings yet
- Hard Disk: Guided By:-Mrs. Vandana Kate & Priyanka Madam Submitted By: - Prachi TelangDocument17 pagesHard Disk: Guided By:-Mrs. Vandana Kate & Priyanka Madam Submitted By: - Prachi TelangsachinmandleNo ratings yet
- 5 Generations of Computers Checklist: From Vacuum Tubes to AIDocument40 pages5 Generations of Computers Checklist: From Vacuum Tubes to AIAmitNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa Inggris HardiskDocument3 pagesMakalah Bahasa Inggris Hardiskuang intNo ratings yet
- Hard Disk Drive: Cassette TapeDocument12 pagesHard Disk Drive: Cassette Tapeapi-3760834No ratings yet
- CPE 101-Chapter3 Updated2022Document25 pagesCPE 101-Chapter3 Updated2022The boy thats lost in the woodsNo ratings yet
- Types of Hardware DevicesDocument13 pagesTypes of Hardware Devicesanon_678973145No ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer: Md. Mumtahin Habib Ullah MazumderDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Computer: Md. Mumtahin Habib Ullah MazumderShokanta RoyNo ratings yet
- Standards Organization & InternetDocument14 pagesStandards Organization & InternetArooj ArifNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Hard Disks: By-Satyam JhawarDocument23 pagesPresentation On Hard Disks: By-Satyam JhawarSatyam JhawarNo ratings yet
- Secondary Storage DevicesDocument17 pagesSecondary Storage DevicesWamiq ReyazNo ratings yet
- Secondary Storage DevicesDocument3 pagesSecondary Storage DevicesHaider Habib RanaNo ratings yet
- Experiment CP 1Document7 pagesExperiment CP 1rajdecoratorsNo ratings yet
- Guide to common input and storage devices under 40 charactersDocument4 pagesGuide to common input and storage devices under 40 charactersvaishaliNo ratings yet
- Practical No 5Document9 pagesPractical No 5shyam rana100% (1)
- IGCSE Computer Studies Notes On Data Storage (Zafar Ali Khan)Document14 pagesIGCSE Computer Studies Notes On Data Storage (Zafar Ali Khan)EthanielNo ratings yet
- Computer ApplicationsDocument21 pagesComputer ApplicationsdudungNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Computers: I. Computer Architecture (Ca)Document4 pagesFundamentals of Computers: I. Computer Architecture (Ca)sumanctsNo ratings yet
- Storage Systems: 1. Explain Various Types of Storage DevicesDocument24 pagesStorage Systems: 1. Explain Various Types of Storage DevicesVijiya LakshmiNo ratings yet
- ImproveDocument1 pageImproveSwathy JoshyNo ratings yet
- Chapter: 1.1 Data Representation: Computer Science 2210 (Notes)Document12 pagesChapter: 1.1 Data Representation: Computer Science 2210 (Notes)Athuai DoorNo ratings yet
- Rules of Thumb in Data EngineeringDocument10 pagesRules of Thumb in Data EngineeringNavneet GuptaNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing Data: ElectronicDocument2 pagesReading and Writing Data: ElectronicDebashish RoyNo ratings yet
- Module VI - Secondary StorageDocument24 pagesModule VI - Secondary StorageMajety S LskshmiNo ratings yet
- Notes Unit 5 OSDocument16 pagesNotes Unit 5 OSSahil PahwaNo ratings yet
- Importance of Physics in Computer Science and Spinning DiskDocument14 pagesImportance of Physics in Computer Science and Spinning DiskMuhammad shahwaizNo ratings yet
- Hard Disk: A Report OnDocument13 pagesHard Disk: A Report OnJoshna KumareNo ratings yet
- 3D XPointDocument7 pages3D XPointRajkumar0% (1)
- Ict 1Document15 pagesIct 1Noor AliNo ratings yet
- 1.1.3 Data StorageDocument12 pages1.1.3 Data StorageTrynosNo ratings yet
- Construction: Hamdard University Dep. of Computing Name: M. Nafees BS (CS) - I Introduction To ComputingDocument6 pagesConstruction: Hamdard University Dep. of Computing Name: M. Nafees BS (CS) - I Introduction To Computingمحمد نفیسNo ratings yet
- Magnetic MemoryDocument3 pagesMagnetic MemoryMeenakshi SuryavanshiNo ratings yet
- IT study guide for systems and componentsDocument3 pagesIT study guide for systems and componentsToniann LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Secondary Memory: Hard Disk Drives and TypesDocument9 pagesSecondary Memory: Hard Disk Drives and TypesAmarnath SahNo ratings yet
- How Big is a Petabyte, Exabyte, Zettabyte or YottabyteDocument2 pagesHow Big is a Petabyte, Exabyte, Zettabyte or Yottabyteuomomedicina.itNo ratings yet
- Computer For IBPSDocument61 pagesComputer For IBPSRajiv KumarNo ratings yet
- Pixie DustDocument25 pagesPixie Dustid.arun5260100% (4)
- HARD DRIVE AND GRAPHICS CARD GUIDEDocument4 pagesHARD DRIVE AND GRAPHICS CARD GUIDERia RoyNo ratings yet
- A. RAM - Random Access Memory: Main Types of RAMDocument14 pagesA. RAM - Random Access Memory: Main Types of RAMPutera HeriyantoNo ratings yet
- Secondary Storage DevicesDocument5 pagesSecondary Storage DevicesTauseef ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Media 2Document3 pagesMedia 2Wahab Z DarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer TechnologyDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Computer TechnologyHanz Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Digital Assignment-1: Venkata Ajay Kumar Vutty 17BIS0076Document10 pagesDigital Assignment-1: Venkata Ajay Kumar Vutty 17BIS0076Aj KNo ratings yet
- Lec 4. Secondary StorageDocument7 pagesLec 4. Secondary StorageMaaz shahidNo ratings yet
- Ntroduction: Computer Memory Based On The Protein Bacterio-RhodopsinDocument19 pagesNtroduction: Computer Memory Based On The Protein Bacterio-Rhodopsinapi-19937584No ratings yet
- Mega Drive Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #3From EverandMega Drive Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #3No ratings yet
- User InterfacesDocument4 pagesUser InterfacesNataliaRzonsowskaNo ratings yet
- Computer EthicsDocument4 pagesComputer EthicsNataliaRzonsowskaNo ratings yet
- Computer EthicsDocument4 pagesComputer EthicsNataliaRzonsowskaNo ratings yet
- Practice Test January 2024 LogisticsDocument11 pagesPractice Test January 2024 LogisticsNataliaRzonsowskaNo ratings yet
- Practice Test November 2023 LogisticsDocument12 pagesPractice Test November 2023 LogisticsNataliaRzonsowskaNo ratings yet