Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Infectious Diseases
Uploaded by
nasimzand780 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views15 pagesInfectious diseases - a level biology
Original Title
Infectious diseases
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentInfectious diseases - a level biology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views15 pagesInfectious Diseases
Uploaded by
nasimzand78Infectious diseases - a level biology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
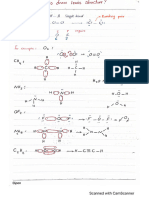
VVOVOORDOODURDVUUUUUBUETUUEUCEPPCCECEEE
Infectious disease
pate: Chapter 12 sup.
Trfectious discase » Ore caused by organism known as pathogens.
= Cause arm to. health of host
— Con be passed From one. arganism. 4a another:
hansmissable. vie, divect contact, exchange of Tluid
Conlaminalion, oir borne , vector.
Pathogens -» parasitic ( ci) disease Causing microorganisms.
—> Can be prokaryote / eukaryotes.
> 6g. backria, Virus, profoctists, fangil ge)
(Py Cea) (eu)
othe way which & pathogen passes from. one Person. to another 1. Called. the
transmission Cycle.
2 Diseases that are always in. population ove described. @3 endemic.
oan endemic Occurs when.there is.an increase in the muvnber oF Cases
a
(oy
+ the rate of death From diFberent cisceses ic relerred to c1 morlality
throughout a Continent ar across. the world.
Viruses
2 non-Cellalar Stractare.
2.0 plasma membrane, Oytoplasm, ribosomes.
° Only é
1) DNA or RNA
2) Protein coat = Capsid > protective Cont
may hove one or tito Coet.
3) many viruses may else have lipid envelope.
U4) Some proteins may be present. eg haemagglutinin, Newramindase.
Elipon
Scanned with CamScanner
Date: Sub:
eall parasitic.
*Can only reproduce by in feching living cehs
suse protein synthesising machinary of gel to repli Cecte.
host
Bacteria
what all backria do nothave? what au bacteria. have?
2 no. membrane - oud. Oganeles. 2 plasma membrone-
«no nucleus © Cylopiasm
Dwa ties free in cytoplasm © peptidoglycan cell wall
In the nuclesid region. > made..chains... crossed. linked.
by Amina. acids.
2 70s ribosames.
» Cirewlar, DIVA
2 PVA is naked -» nat associated
Types of pathogens (histore)eévith proteins.
Disease typeof Causative agent. name of Causotive agent.
Cholera Bacteria Vibrio cholerae
Malaria Protoctist Plasmodium fetciparum/ P. malariae
HIV/AIDS (Retvo) Virus hamen.immunadeficienty Virus
Tebercelosis Backria mycobacterium. tubercelosis 114. bovis
Smottpox Virus Variola.. Virus.
eo Endemic = a disease that exists permanently in a particular region. or
pepalation —» Malaria is Constant warry in parts of APrico.
Elipon
*
Scanned with CamScanner
QTARERADCAARAAAAAATA
oO
AA AA AM
aaa
VYOVIUOUYSSOUSOROEUUDUCHTUCEWCECRKCCCLEEE
Date: Sub:
« Epidemic = an dutbreak of diseases that. adfecks. many. peoples of
about the same bime and may spread Hirowgh one or. Several
Conmunilies a SARS. epidemic. in malaysia.
+ Pandemic= iuhen an epidemic... spreads thoughout the world.
Covid 19 was..a. world wide Pandertic.
Cholera. 4
2 Causilive organism : Vibrio. cholera. -.abacleria.
«Comma shaped « has. flagella, motile Se
(ty
transmission:
e lage numbers of vibrio. cholera Bund in faeces ( Gi) oF infected peop.
© infected people's faeces /sewage contaminates food and water.
o hausePlies land on faeas and contaminate food and water.
o aninbeckd person tat Contaminated Prod and. tye.ter.
hrod-borne (lerhe s27
Faecol- oral route Sw» Be po
wate. borne Fe ee
Symptoms and. effects :
4) if bacteria is not killed by Stomach cteid, bacteria reaches the smal
intestine Cou)
2) Backria Secrefes Chaleragen toxin.
3) toxin binds 2 complementary receptor on intestinat epithelial Cell
and enkrs Via. endocytosis
Elipon
Scanned with CamScanner
Date: ‘Sub:
4 Distrupts fonction of intestine epitheliam lining
ow ef a
ad, pit b ary CY Cer Tae
5) loss of Chloride ions and Sodivm.ions. From epitherial Cats .
6) walker potential decrase , Waly meves Out from bloods,
down woer pottaliol gradient by osmosis though parhally permesble
membrane. rae
WY Guuse Severe diarrhoea + dehydration Geers A Stet
More Symptoms:
« Diarrhoew «loss of watey and Sals- low blood pressure
* Dehydration weakness and fatigue. + weight loss -
. Vomitting
Diagnosis: 5 microscopical analysis of faeces.
Treatment :
+ Oral rehydration therapy.
+ ase oral rehydration solution (ORS) that has glucose | salts.
« Ensare thet flaid intake = fluid loss in urine 2 fa7cace.
= maintain osmotic balance af blood and tissue Muids.
_> almost all treated patient are survive.
Prevention
2 proper sewage treatment to break dransmission eycie.
eChlarinate weer to Kin bacteria be lore drinking.
2 Drink bolted water.
Elipon
Scanned with CamScanner
PRPRFTFREFRKEFTCTFRUARCADUAAADARAAARAATA
VORVYdDVDOOROHOUUYUHGTHUHUVLOHUUE EE
Date: Sub:
es yaccinalion only offers short-term protection (no.tonger recommended)
Malaria.
Causitive organisms Plasmodium a Protoctist (eukaryote), parasite
2 in human, malaria is Caused by +
Plasmodium Fatciparam (752).4.P- malariae « P.Ovele« P. vivax C207)
e its appearance changes depends. on.tife cycle. stages. ©
Vector / transmission: G
2 Vector = Organism that Carries adisease from a
person to. another / fom animal. to. humen.
© Insect vectors Female. anopheles. mosquitoes.
> only Female take blood meals bo supply eggs with nastrents
«alse thmugh bleed transhsion,use of unskente. needles, and Can pass
acess. placenta from mother.
mos takes blood meal fom inkected person and then. takes a blood meal
From uninfected person.
Life cycle of Plasmodium:
1 prasmodium’s gametes fuse, multiples in and fre infective... stages
in mosquitoes.
2. when mos takes a blood meal, parasite enters hast with mas’s
Gakicoagulant and. Saliva
& inkective Stages of parasite enters bioodsheam and then liver Cells
4. parasite mature mln Cll, then enkrs KBCs
Elipon
4
Scanned with CamScanner
Date: Sub:
© 5. parasites mattiply ia RBCs, Causing RECs to lpe
6. parasites are released and infect other RBCs
F. parasites picked up by another mos in a blood meal.
protocite _plasmodiam
Vector > the Femaie anapheles mosquilves.
Malaria Sites of actions fiver. red [blood Cell, brain
The life of piasmodium ¢
RATCAAADARAAAADAEAE
mosquito takes 2H W_ male and fealty gamedles iz
infected blood meal oF parasite fuse in mos’ stomach days
4
t
mmacureslioh and. production oP parasites’ Gali division. produces
mate and] female (gametes) thousands of immature @
| 4-42 maleriot, parasites €
Parosites ‘ieave liver cells ? @
A
and enix RBCs infective stages of parasite imede @&
1 masqueites Salivary. glands e
infected siages of parasites J @
enkey blood sheom and then liver <= inected mosquito takes blood meal @
els 7
ce G
Symptoms : © Headache «Fever» muscular pain and fatigue @
e Back pain «Skin chins and Sweating » Dry Cough G
+ enlarged Spleen + Nausea + Vomiting» Anaemia a
dee es oF we °
a
Elipon
Scanned with CamScanner
VVPVYSVVOSOUUSORBUUELDEYUHVECMTCECEEEE
Date: Sub:
Diagnosis : + microscopical analysis of blood
+ Dip stick tes! Sr malaria antigens ie’ blood
Treatment :
«anti. malarial drags
2 @.g: Quinine, Choloroquine« arlemisin
2 Chlorequine . inhibits protein synthesis and prevent parasite fom
spreading within the body.
¢ Proguanin. inhibits sexual reproduction oF the mos.
2 Combination therapy = where maltiple drugs are used af the Same
time — used to. prevent diug- resistance.
Prevention:
eno vocene fer. malaria
1) use prophy lactic / preventive drags (@g. Chloroquine)
2) Reduce. of mosquitves
3) prevention of being bitten by infected mosquitoes.
athe vector, the napheles masquibes survives ond breeds in hot
and hamid. areas
Elipon
4
Scanned with CamScanner
Date: Sub:
HIV / AIDS
Causitive organism: humman immunodefieney virus CHEV). aviras
o ibis a RNA Virus. / retrovirus
* Contain single- Stranded RUA as genetic material
+ Has protein Cant / Capsid made of capsomeres.
= Has Outer Viral envelope made of a. lipid. bilayer and proteins
Cmesty delivered. from host)
¢ Has. viral gigco proteins on the Ovber. envelope
o Has 2 enzymes
i) Reverse transcriptase —, uses RWA as femplake + produce wa
in host Cell.
2) Protease ~» cleave ¢2ul% / process new viral proteins.
The life cycle of HIV S
4. the viral RNA ond reverse transcriptase (RT) enters T helper
Iym phocytes
2. RT Converts RNA to Ona,
3. The viral ONA is incorporaked into the! hos t DAA
4. the Cells’ mochinary is Used to expiess Viral proteins (though
transcription and transletion)
5, Viral proteins are assembled info many Viruses.
Elipon
Scanned with CamScanner
PDOPROAHDARSFARARAAARADAARAAAAAAETC
oad
VPVVVSYVSKROSOUULUEYUGTYUECUHCCECLEEE
Dote: ‘Sub:
Transmission
+ through direct exchange oF laody. Fluids.
oyirus is unable to survive oatoF human. body:
Semen. Vaginal Fluids during Sexual intercourse.
+ Blood transmission vie infecled bleod
2 mother fo baby transmission across placenta / breast milk.
e having maltiple sex parfners allows . virus 4o spread more widely.
« @nal intercourse increases risk of transmission.
Symptoms and. effects:
2 Slow. infection Virus Con stay .dormant Fer. years.
+ Changes surface protein to bide. from. immune. system.
o HIV infects. cells oF the immune system, Caled. helper T Cells
© this deshoys helper T Cells and reduce their proportion.
2 Body is unable te defend ifset against infection.
Symptoms of HIV infection:
o Flu. like symptoms and then. Symptomless
Gsince virus Can stay dormant for years)
© Opportunistic infer ction Con Occur as result oF a compromised
immune sys hen
« Collection of opportuniotic diseases associated with immunodehency
Gaused by HIV = AIDS
Elipon
Scanned with CamScanner
Date: ‘Sub:
Tabercutosis iw
Causitive organism: mycobaclriam tubercubsis, M- bovis ~ bacteria
© Mycobacterium tuberewbsis > Causes TB in human.
o my cobetctericam bovis a in Cows haman,.and
other mammals
“Transmission ¢
Mycobacterium tuber Cubsir +
+ By aerosol infection.
«Pathogens isin airbarne droplets.
+ infected person Coughs | Sneezes.
+ Uninfecled person breathes in droplets.
Mycobacterium bovis:
ofiom inkeckd Cows (Cattle
- eat undercooked Contaminated meot
+ Drink anpastearised milk Containing bacteria.
Site of infection:
« primary = lungs
+ Secondary = in lymph nodes, bones, and gut
Elipon
Scanned with CamScanner
OPPDOTFARTBATAAAAAAAAARAES
200
92
VVVOSYSOREEBLEUEEVIU EASY ULLEE
Date: ‘Sub:
Antibiotics
e-anhbiotics ave drags used.
2 Usuatty delivered Fam miicroorganisms.
ote kill /inhbit. growth of bacteria.
» whitoat harming. the infected organism.
o Bacteriocidal. antibiotics — kill bacleria
2 Bacteriostatic. antibiotics. - inhibit bacterial growth.
«prevent speed of bacteria twithin body.
oe harmless to human Cels-
o Have No a hect on viruses.
How do antibiotics work ?
o inhibit bacterial Cell cual. synthesis
« inhibit. activily of specihc membrone protein / glyco protein -» biock
binding 40 celts
2 Block specitic enzyme action,
a Inhibit piotiin synthesis and nackic acid synthesis target encyme
that bacteria have, but humans. dont
+ many, different antibiotics each have. different mechanisms
alpen
Scanned with CamScanner
Date: Sub:
Penicillin
© inthe absence of penicillin
«Bacleiat cell walt is made of peptidoglycans.
+ When bacteria Cell grou, it Secretes autolysins
» autolysins makes tiny holes to allow the Cell wall to stretch.
2 New peptidoglycans. formed.
+ peptidase enzyme. Form cross-links between peptidoglycans chains.
+ to Perm Celt veut.
2 in the presence of penicilin =
¢ Peniviliin inhibits pepidase eneyme.
2 stop formation oP Gross. links between peplidagly cans Paty mrs
in the Cell evatl.
2» autolysins make tiny holes. to allow the Cell wall to Stretch
o new pepdoglycans Grmed but cannot link ue:
» the cell wall is weaker:
+ Cell walls Gnable to withstand turgor pressure.
zwhen wel moves in by osmosis, bacteria lyees and dies.
a Different antibiotics ae eFPective againt diferent backrie-
Elipon
Scanned with CamScanner
PPHOHRHRFFFPASHKTKTRETCAARAADARAAAUTAAA
VROVOOOVRBORBEUBYLEUDYEUVHVECWCCCCEKESE
Date: ‘Sub:
AnWibiolic dies Can be placed in pelri dish with grocsing bacteria.
The diameke of the zone of inhibition shoes how eflechive the antibioti
is :
Why antibiotics do not affect viruses?
e viruses dont have peplidegiycan Cell evel, instead have protein Coct)
+ Viruses dont have their awn metabolism ,rely on host Cells
e Viruses have no cell. Strackore / very Few Organelies - very fers siles
for antibiotic te act an.
@ Viruses five inside host cel Out oP reach of onlibiolics.
° Antivivats exist usiaty target viral glyco pisteins on viral enveiape.
Antibiotic Resistance when alibiotics are nolonger efFective against
baclevie.
«if Con be spread. from. backeria te. bactevia.
€.g. many bacteria have pericillis”emeynes which can break it down.
« Become resistance to Penicctn
» Caused by:
+ Spontoneous / random mutection in bacleria,
» malolion couse change in Prokein/ prockchion oF new.prottin
thet Can not be targeted by antibiotics.
Elipon
4
Scanned with CamScanner
Date: Sub:
© Neural selechon enables resistance genes te be spread.
+ Antibiotics is the selection Pressure.
© antibiaties only Kills bacteria thed are not- resistance.
= resistance bactria Survie and reproduce.
e antibiotic resistance gene is spread to the nextgen and another bac.
© they are (genes) usually found in plasmids.
Bacteria Can spread Gntibiotic resistance genes Using
<> Vertical transmission» pass plasmids down to. deaghter ces by
binary fission.
~5 Horizontal. transmission —» Poss plasmids to other bacteria by
Conjugodion.
TEVUCAAUDAVDAACACAATAF
Antibistic Resistance Couse:
2 Due to patient not Completing Course oF antibiotics given» trectment Ge
may not be Completed 50 Some Susceptible. backeria. servites.
> Bacteria veplicales and have Increased Chence of mutedion | becomig Ga
resistant.
Consequences:
A) bacteria con Carry several esti biotic resistence genes
@) Develop multiple resistance
#) Become a Super bug.
exg- methicillin- resistant Staphylococeus aveus CAARSA)
> Wounds dont heal and ae Continaally inkected with bacteria,
EiPON 4 Can not be killed Jinhibited by Common antibiotics.
Scanned with CamScanner
PHSSVEVERVYERDEVUEYEUHH ECC CLES
Date: ‘Sub:
Gas
Vertical transmission Horizontal. Trans mission
sistant Coll non-resistant
Bacterial vests Call.
Chromosomes 0 resistont
‘and Parent
Plasmid cell 1
replicate |
Cent i A
fon) Conjuag ating bacteria.
Duaghter Cells each recie a
copy of the plasmid and ave A single DA strand of the plasmid
resistor is transferred. Eeach. bacteriam then
Synthesises a Complementary Strand.
Both Cells are now resistant
Elion,
Z
Scanned with CamScanner
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Lewis, Polarity, Molecular ShapeDocument12 pagesLewis, Polarity, Molecular Shapenasimzand78No ratings yet
- Cell Membrane and TransportDocument12 pagesCell Membrane and Transportnasimzand78No ratings yet
- Biological Molecules & EnzymeDocument14 pagesBiological Molecules & Enzymenasimzand78No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument21 pagesCardiovascular Systemnasimzand78No ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid and Protein SynthesisDocument14 pagesNucleic Acid and Protein Synthesisnasimzand78No ratings yet
- Cell Structures & Organelles FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Structures & Organelles Functionsnasimzand78100% (1)