Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Notes On Land Taxes in Kenya
Uploaded by
mugiyanjoroge0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesThis document discusses various land taxes in Kenya, including stamp duty, rental income tax, land rent, land rates, and capital gains tax. Stamp duty is paid on property purchases at rates of 4% in urban areas and 2% in rural areas. Rental income tax is paid by those with annual rental incomes between Kshs 144,000 to 10,000,000. Land rent is paid monthly to the ministry of lands based on 0.3% of the property value. Land rates are paid annually to county governments based on the unimproved site value. Capital gains tax of 5% is paid by sellers on properties acquired before 2015, with some exceptions.
Original Description:
Surveying
Original Title
Notes on Land Taxes in Kenya
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses various land taxes in Kenya, including stamp duty, rental income tax, land rent, land rates, and capital gains tax. Stamp duty is paid on property purchases at rates of 4% in urban areas and 2% in rural areas. Rental income tax is paid by those with annual rental incomes between Kshs 144,000 to 10,000,000. Land rent is paid monthly to the ministry of lands based on 0.3% of the property value. Land rates are paid annually to county governments based on the unimproved site value. Capital gains tax of 5% is paid by sellers on properties acquired before 2015, with some exceptions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesNotes On Land Taxes in Kenya
Uploaded by
mugiyanjorogeThis document discusses various land taxes in Kenya, including stamp duty, rental income tax, land rent, land rates, and capital gains tax. Stamp duty is paid on property purchases at rates of 4% in urban areas and 2% in rural areas. Rental income tax is paid by those with annual rental incomes between Kshs 144,000 to 10,000,000. Land rent is paid monthly to the ministry of lands based on 0.3% of the property value. Land rates are paid annually to county governments based on the unimproved site value. Capital gains tax of 5% is paid by sellers on properties acquired before 2015, with some exceptions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Notes on Land Taxes in Kenya
By
John Mugiya Njoroge
ESSQ/ 02664/2019
B.ENG (Geospatial)
Submitted to
George Konguka
2nd November, 2023
Introduction
Real estate business in Kenya is categorized into two, commercial and residential. KRA recently
launched its 8th Corporate Tax Plan with key focus being the implementation of the Tax Base
Expansion strategy which seeks to recruit new taxpayers. To achieve this, the KRA has
identified persons involved in the real estate sector as being integral to the achievement of its
goal. The following taxes are common to persons involved in buying and selling of land or real
property:
Stamp Duty
Rental Income Tax
Land Rent
Land Rates
Capital Gain Tax
1. Stamp Duty
This is the tax paid during the purchase of a property and is based on the sale price of the
property. Its rate is 4% in urban areas and 2% in rural areas. Stamp duty exemption can occur
under the following scenarios:
i. Transfer between spouses
ii. Transfer in favor of any body established for charitable purposes.
iii. Transferring between associated companies
iv. Transfer to a limited liability company held wholly by same family members.
It must be paid within 30 days after receiving the documents. Failure to pay this revenue will
result in the invalidity of the transaction and agreement signed by both parties. It will also result
into a fine that is assessed at 5% of the principal assessed Stamp Duty for every quarter of the
date of instrument. This revenue is paid to the KRA through iTax portal.
2. Rental Income Tax
i. Residential property and Mixed-Use Properties Rent Taxes
This tax is paid by people with rental incomes of Kshs 144000 to 10000000 per annum. It must
be filed every month on or before 20th without expenses, losses or capital deduction. Persons
with below Kshs 144000 or above 10000000 rental income per year is required to file annual tax
returns and declare the rental income with income from other sources. Failure to file before or on
20th attracts a penalty of 20000 or 5% of due tax, or whichever is higher, and subsequent interest
of 1% per month on the unpaid tax until payment is made in full.
ii. Commercial Property Rent Taxes
VAT is chargeable on commercial rental income and is charged to the tenant at a rate of 16 %.
However, the VAT on the sale of commercial property declared illegal for the sale of
commercial property. Other commercial income is required to file annual returns and declare
rental incomes.
3. Land Rent
Land rent is paid to the ministry of lands for leasehold titles. The land rent is usually stated on
the certificate of title and is usually revisable. Most land rents are revised during renewal and
extension of leases. The rent is paid at 0.3% of the property value per month. For instance, a land
worth 600000 will have a monthly land rent of 2000.
4. Land Rates
Land rates are paid to the county government on an annual base for both leasehold and freehold
properties. The land rates are governed by the Rating act. The fees are based on the unimproved
site value of the property which are based on the Valuation Roll, which is revised every now and
then for updating.
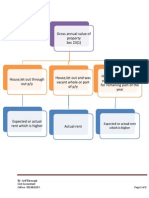
5. Capital Gain Tax
This tax is levied on the transfer of property situated in Kenya, acquired on or before 2015. It is
paid by the seller. It is a final tax and is subject to further taxation after the payment of the 5%
net gain tax. The following are exceptions on Capital Gain Tax:
Income that is taxed elsewhere as in the case of property dealers.
Issuance by a company of its own shares and debentures
Disposal of property for the purpose of administering the estate of a deceased
person.
Transfer of property between spouses as a part of a divorce settlement.
A private residence if the individual owner has occupied the residence
continuously for the three-year period immediately prior to transfer.
Agricultural property having an area of fewer than 100 acres where that property
is situated outside a municipality or urban area.
You might also like
- Series 65 Practice Exam For Available Courses PageDocument8 pagesSeries 65 Practice Exam For Available Courses PagePatrick Crutcher100% (3)
- Tax Sales for Rookies: A Beginner’s Guide to Understanding Property Tax SalesFrom EverandTax Sales for Rookies: A Beginner’s Guide to Understanding Property Tax SalesNo ratings yet
- Co-Ownership, Estate and TrustDocument6 pagesCo-Ownership, Estate and TrustRyan Christian Balanquit100% (2)
- Taxation of IndividualsDocument49 pagesTaxation of IndividualsAnastasha Grey100% (1)
- Real Estate TaxesDocument5 pagesReal Estate TaxesJorgeNo ratings yet
- Guideline in The Transfer of Titles of Real PropertyDocument4 pagesGuideline in The Transfer of Titles of Real PropertyLeolaida AragonNo ratings yet
- Taxation Virgilio D Reyes 2 PDFDocument273 pagesTaxation Virgilio D Reyes 2 PDFitsmenatoyNo ratings yet
- The Taxes Involved in A Sale of Real Estate PropertyDocument7 pagesThe Taxes Involved in A Sale of Real Estate PropertyJessa CaberteNo ratings yet
- P6ATX Revision Question Bank SelectedQuestions PDFDocument46 pagesP6ATX Revision Question Bank SelectedQuestions PDFMubashar HussainNo ratings yet
- Lease of Properties: ExemptDocument12 pagesLease of Properties: Exemptmariyha PalangganaNo ratings yet
- Taxes On Commercial LeaseDocument8 pagesTaxes On Commercial Leasebelbel08No ratings yet
- Taxation Law 2007 Bar Question and AnswerDocument12 pagesTaxation Law 2007 Bar Question and AnswerHenry M. Macatuno Jr.No ratings yet
- 6,6 Taxation of Income of PersonsDocument29 pages6,6 Taxation of Income of Personsjoseph mbuguaNo ratings yet
- 2 Corporation-RevisedDocument8 pages2 Corporation-RevisedSamantha Nicole Hoy100% (2)
- Salient Points of TRAIN LawDocument21 pagesSalient Points of TRAIN LawNani kore100% (1)
- 3P Turbo - Cross Border Investment in BrazilDocument10 pages3P Turbo - Cross Border Investment in BrazilRahul KashyapNo ratings yet
- Module 07 - Introduction To Regular Income TaxDocument25 pagesModule 07 - Introduction To Regular Income TaxJANELLE NUEZNo ratings yet
- Estate Tax and Donors TaxDocument19 pagesEstate Tax and Donors Taxtalla aldover100% (1)
- MITERM Reviewer (Chap 1-4)Document17 pagesMITERM Reviewer (Chap 1-4)Necy Adeline GenogalingNo ratings yet
- Printout of Sbi Mutual FundDocument57 pagesPrintout of Sbi Mutual Fundknox21villeNo ratings yet
- Develop Understanding of TaxationDocument19 pagesDevelop Understanding of TaxationHenok Eosi83% (6)
- Gains in Dealings of Properties: BAM 127: Income Taxation For BA Module #11Document11 pagesGains in Dealings of Properties: BAM 127: Income Taxation For BA Module #11Mylene SantiagoNo ratings yet
- 07 Income From Property (50 59)Document11 pages07 Income From Property (50 59)jafferyasim100% (2)
- 2023 Jurists Last Minute Tips On Taxation LawDocument17 pages2023 Jurists Last Minute Tips On Taxation LawCM EustaquioNo ratings yet
- ESSAY Suggested AnswersDocument5 pagesESSAY Suggested AnswersAe-cha Nae GukNo ratings yet
- Land Admn and Management Property TaxationDocument4 pagesLand Admn and Management Property TaxationsammiemeshNo ratings yet
- Understanding Real Estate TaxationDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Real Estate TaxationCashmoney AlaskaNo ratings yet
- 06 Estate Tax PayableDocument12 pages06 Estate Tax PayableJabonJohnKennethNo ratings yet
- Tax 2 Module1 Estate TaxationDocument28 pagesTax 2 Module1 Estate TaxationXyza JabiliNo ratings yet
- Activi: Taxation 219Document14 pagesActivi: Taxation 219Block escapeNo ratings yet
- Real Estate Investment in PortugalDocument3 pagesReal Estate Investment in Portugalyoman777No ratings yet
- Property Registration in GurgaonDocument4 pagesProperty Registration in GurgaonSSKohliNo ratings yet
- Nigeria Property Tax in Federal Capital TerritoryDocument3 pagesNigeria Property Tax in Federal Capital TerritoryMark allenNo ratings yet
- TaxationDocument25 pagesTaxationkherbalcapsulNo ratings yet
- VND Openxmlformats-Officedocument WordprocessingmlDocument25 pagesVND Openxmlformats-Officedocument WordprocessingmlHimanshu RajputNo ratings yet
- Presentation 3 Real Property Gains TaxDocument29 pagesPresentation 3 Real Property Gains TaxAimi AzemiNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Principles Governing Real Property TaxationDocument5 pagesFundamental Principles Governing Real Property TaxationgraceNo ratings yet
- T 4 - Co-Ownership Estate TrustDocument21 pagesT 4 - Co-Ownership Estate TrustKristine Aubrey AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Estate Tax PropertyDocument3 pagesEstate Tax Propertymoveena abdullahNo ratings yet
- Withholding Tax On RentalDocument2 pagesWithholding Tax On Rentalsabir.mail28576No ratings yet
- 2 - Income From PropertyDocument5 pages2 - Income From PropertyALI HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- The Taxperts GroupDocument2 pagesThe Taxperts GrouptaxpertsNo ratings yet
- Other Income Tax AccountingDocument19 pagesOther Income Tax AccountingHabtamu Hailemariam AsfawNo ratings yet
- Taxation of CompaniesDocument3 pagesTaxation of CompaniesJEBET RUTH KIPLAGATNo ratings yet
- Tax Code Notations Part IDocument31 pagesTax Code Notations Part IJonaliza O. BellezaNo ratings yet
- Direct TaxDocument6 pagesDirect TaxAKSHAY KATARENo ratings yet
- 2012 08 NIRC Remedies TablesDocument8 pages2012 08 NIRC Remedies TablesJaime Dadbod NolascoNo ratings yet
- Group 10Document41 pagesGroup 10mau nbsbNo ratings yet
- Tax On Corporate Transactions in PhilippinesDocument21 pagesTax On Corporate Transactions in PhilippinesD GNo ratings yet
- Quick Sell Repossessed Properties FNB: WWW - Quicksell.co - ZaDocument9 pagesQuick Sell Repossessed Properties FNB: WWW - Quicksell.co - ZaChristian MakandeNo ratings yet
- FAQ Property Tax 10 02 2017Document7 pagesFAQ Property Tax 10 02 2017Diya PandeNo ratings yet
- House Property TaxationDocument13 pagesHouse Property TaxationAnupam BaliNo ratings yet
- Taxation: 1. Capital Gains TaxDocument9 pagesTaxation: 1. Capital Gains TaxChelsy SantosNo ratings yet
- 10 Real Property Tax in The Philippines - Things To Know - AllPropertiesDocument4 pages10 Real Property Tax in The Philippines - Things To Know - AllPropertiesjrstockholmNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7, 8, 12Document41 pagesChapter 7, 8, 12assadrafaqNo ratings yet
- Real Esate Going Global: VietnamDocument11 pagesReal Esate Going Global: VietnamNguyen Quang MinhNo ratings yet
- Types of TaxesDocument27 pagesTypes of TaxesJosh DumalagNo ratings yet
- Income From Property IIUI Spring Semester 22Document13 pagesIncome From Property IIUI Spring Semester 22Wahaj AhmedNo ratings yet
- Fair RentDocument19 pagesFair RentProf. Vandana Tiwari SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 6 - Annual Value of House PropertyDocument2 pages6 - Annual Value of House PropertyAnupam BaliNo ratings yet
- Tax LecturesDocument14 pagesTax LecturesHiro SherNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Estate TaxDocument14 pagesModule 2 - Estate TaxHaidee Flavier SabidoNo ratings yet
- Registration ResearchesDocument2 pagesRegistration ResearchesAnonymous rVFG5CNo ratings yet
- Villanueva V City of IloiloDocument48 pagesVillanueva V City of Iloiloamun dinNo ratings yet
- TRAIN (Changes) ???? Pages 2, 6, 10, 14, 15 PDFDocument5 pagesTRAIN (Changes) ???? Pages 2, 6, 10, 14, 15 PDFblackmail1No ratings yet
- Withholding Tax On Rental Services: Guide 01Document2 pagesWithholding Tax On Rental Services: Guide 01Abdul NafiNo ratings yet
- Highlights-FinanceAct2022-23 TANVEER LAW ASSOCIATESDocument45 pagesHighlights-FinanceAct2022-23 TANVEER LAW ASSOCIATESAhmed RazaNo ratings yet
- HUMTUM15 TH AugDocument2 pagesHUMTUM15 TH AugSushil_Pandey_4297No ratings yet
- Riph - Module 6Document7 pagesRiph - Module 6Reigne Yzabelle T. PALOMONo ratings yet
- Individual Income TaxDocument19 pagesIndividual Income TaxShopee PhilippinesNo ratings yet
- Tax1 Assigned CasesDocument5 pagesTax1 Assigned CasesflorencemanulatNo ratings yet
- Scalable Capital ISA GuideDocument15 pagesScalable Capital ISA Guidenitind_kNo ratings yet
- Tax System in IndiaDocument18 pagesTax System in IndiaDEV HUGENNo ratings yet
- CA Final Direct Tax Suggested Answer Nov 2020 OldDocument25 pagesCA Final Direct Tax Suggested Answer Nov 2020 OldBhumeeka GargNo ratings yet
- SBN-0270: Capital Gains Tax and Documentary Stamp Tax Exemption For Expropriated LandsDocument4 pagesSBN-0270: Capital Gains Tax and Documentary Stamp Tax Exemption For Expropriated LandsRalph RectoNo ratings yet
- DTC Agreement Between Egypt and ItalyDocument16 pagesDTC Agreement Between Egypt and ItalyOECD: Organisation for Economic Co-operation and DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- Income Taxation For IndividualsDocument60 pagesIncome Taxation For IndividualsFrancis Elaine FortunNo ratings yet
- Review TaxDocument2 pagesReview TaxRose May AdanNo ratings yet
- CIR v. Estate of Benigno Toda, 438 SCRA 290, 2004Document8 pagesCIR v. Estate of Benigno Toda, 438 SCRA 290, 2004JMae MagatNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Income Taxation Individual TaxpayersDocument58 pagesWeek 3 Income Taxation Individual TaxpayersJulienne Untalasco100% (1)
- Bir Form 1701 Primer: Page 1 of 22Document22 pagesBir Form 1701 Primer: Page 1 of 22Alexander Cooley0% (1)
- CARL of 1998 Sec 62-67Document2 pagesCARL of 1998 Sec 62-67Elisa Dela FuenteNo ratings yet
- (Corporate Secretaryship) Degree Course SyllabusDocument34 pages(Corporate Secretaryship) Degree Course Syllabussan291076No ratings yet
- Reverse Mortgage in IDBI BANKDocument66 pagesReverse Mortgage in IDBI BANKMohmmad SameemNo ratings yet
- Theory Capital GainDocument6 pagesTheory Capital GainRuthvik RevanthNo ratings yet
- ETA Star Infopark - WatermarkDocument73 pagesETA Star Infopark - WatermarkRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Yes, Since The Leased Portion Is Not ActuallyDocument2 pagesYes, Since The Leased Portion Is Not ActuallyResty VillaroelNo ratings yet
- QP - TaxDocument4 pagesQP - Taxcommercetrek21No ratings yet
- How Much Does It Cost To Transfer A Land Title in The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesHow Much Does It Cost To Transfer A Land Title in The PhilippinesDebra BraciaNo ratings yet