Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Important Polymer Properties
Important Polymer Properties
Uploaded by
Umashankar S0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views11 pagesThe document discusses important properties of polymers, including that they can be crystalline or amorphous. Crystalline polymers have properties like sharp melting points and high chemical resistance, while amorphous polymers have broad softening ranges and are usually transparent. The document also discusses glass transition temperature, which is an important property that distinguishes the brittle glassy state from the rubbery or pliable state of amorphous polymers. Molecular weight and its distribution as well as the viscoelastic nature of polymers are also covered.
Original Description:
bits pdf
Original Title
L3_
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses important properties of polymers, including that they can be crystalline or amorphous. Crystalline polymers have properties like sharp melting points and high chemical resistance, while amorphous polymers have broad softening ranges and are usually transparent. The document also discusses glass transition temperature, which is an important property that distinguishes the brittle glassy state from the rubbery or pliable state of amorphous polymers. Molecular weight and its distribution as well as the viscoelastic nature of polymers are also covered.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views11 pagesImportant Polymer Properties
Important Polymer Properties
Uploaded by
Umashankar SThe document discusses important properties of polymers, including that they can be crystalline or amorphous. Crystalline polymers have properties like sharp melting points and high chemical resistance, while amorphous polymers have broad softening ranges and are usually transparent. The document also discusses glass transition temperature, which is an important property that distinguishes the brittle glassy state from the rubbery or pliable state of amorphous polymers. Molecular weight and its distribution as well as the viscoelastic nature of polymers are also covered.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
Important Polymer Properties
• Crystalline and Amorphous Polymers
• Molecular Weight and its Distribution
• Glass Transition Temperature
• Visco-elastic Nature of Polymers
BITS Pilani, K K Birla Goa Campus
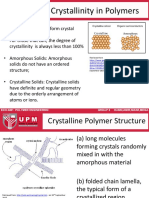
Crystalline and Amorphous Polymers
Crystalline Amorphous
BITS Pilani, K K Birla Goa Campus
Properties of Crystalline Polymers
• Sharp Melting point
• Usually Opaque
• High Shrinkage
• High Chemical resistance
• Good fatigue resistance
• Good wear resistance
BITS Pilani, K K Birla Goa Campus
Properties of Amorphous Polymers
• Broad Softening range
• Usually Transparent
• Low Shrinkage
• Low chemical resistance
• Poor fatigue resistance
• Poor wear resistance
BITS Pilani, K K Birla Goa Campus
Crystalline Polymers
• Polyethylene (PE)
• Polypropylene (PP)
• Polyamide (PA)
• Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) -a Polyester
BITS Pilani, K K Birla Goa Campus
Factors Affecting Crystallinity
• Rate of Cooling
• Shape of Polymer repeat unit (e.g. PP Vs PC)
• Molecular Structure of Polymer ( Linear, branched,
crosslinked or networked).
• Random and graft copolymers ( less chances of
crystallinity)
• Presence of bulky side group atoms
( e.g. Styrene)
• Moulding conditions ( e.g. Mechanical stretching in blow
moulding induces crystallization)
BITS Pilani, K K Birla Goa Campus
Crystallinity and Cooling rate
BITS Pilani, K K Birla Goa Campus
Semicrystalline Polymer
( Fringed Micelle Model)
BITS Pilani, K K Birla Goa Campus
Amorphous Polymers
• Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
• Polystyrene (PS)
• Polycarbonate
• Acrylic
• Acrylonitrile Butadine-Styrene (ABS)
BITS Pilani, K K Birla Goa Campus
Glass Transition Temperature (Tg)
BITS Pilani, K K Birla Goa Campus
Glass Transition and Melting temperature
of Polymer
BITS Pilani, K K Birla Goa Campus
You might also like
- Pet Pre Form Pet Resin Pet Recycling Technology Book PDFDocument11 pagesPet Pre Form Pet Resin Pet Recycling Technology Book PDFazamsoomro0% (1)
- Advanced Concrete Technology-3Document358 pagesAdvanced Concrete Technology-3c kumarNo ratings yet
- IPP05 Material Selection PDFDocument51 pagesIPP05 Material Selection PDFsebastianNo ratings yet
- Industrial CatalystDocument26 pagesIndustrial CatalystAritra SenNo ratings yet
- Lect Slides - Catalytic ReformingDocument20 pagesLect Slides - Catalytic ReformingPRAJWAL RASTOGINo ratings yet
- Polytone: ABR Series/Thermoplastic Acrylic ResinsDocument7 pagesPolytone: ABR Series/Thermoplastic Acrylic ResinsAdhvik PuriNo ratings yet
- Mef452 Composite Materials and Design/Mst G 522 Advanced Compositesl5Document18 pagesMef452 Composite Materials and Design/Mst G 522 Advanced Compositesl5Umashankar SNo ratings yet
- CMD Merged MidsemDocument365 pagesCMD Merged Midsemnitingautam1907No ratings yet
- Factors Affecting TM and TG: BITS Pilani, K K Birla Goa CampusDocument11 pagesFactors Affecting TM and TG: BITS Pilani, K K Birla Goa CampusUmashankar SNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices 07-08-2014: BITS Pilani, K K Birla Goa CampusDocument27 pagesElectronic Devices 07-08-2014: BITS Pilani, K K Birla Goa CampusJeswin EldhoNo ratings yet
- Mef452 Composite Materials and Design/Mst G 522 Advanced Compositesl1Document18 pagesMef452 Composite Materials and Design/Mst G 522 Advanced Compositesl1Umashankar SNo ratings yet
- CH - 01 Introduction PDFDocument36 pagesCH - 01 Introduction PDFNiyatiNo ratings yet
- CrystallinityDocument14 pagesCrystallinityShweta BagdiNo ratings yet
- Plastic Properties Crystalline PolymerDocument7 pagesPlastic Properties Crystalline PolymerMuhammad Noman MehboobNo ratings yet
- Plastic MouldingDocument22 pagesPlastic Moulding4064 Harshitha RampellyNo ratings yet
- Polymer Processing: Module - 5Document41 pagesPolymer Processing: Module - 5Abhishek KarpeNo ratings yet
- PolymersDocument57 pagesPolymersAkram MohithNo ratings yet
- Product Detailing - Before Class Stest-1Document81 pagesProduct Detailing - Before Class Stest-1iramkNo ratings yet
- L5 QcarDocument7 pagesL5 QcarDarsh MenonNo ratings yet
- Polybutadiene: Yasir AbbasDocument27 pagesPolybutadiene: Yasir AbbasYasir AbbasNo ratings yet
- Polycarbonate (PC) : Dr. Pradeepa.K.G Assistant Professor Dept. of Polymer Science & TechnologyDocument28 pagesPolycarbonate (PC) : Dr. Pradeepa.K.G Assistant Professor Dept. of Polymer Science & TechnologyApoorva MNNo ratings yet
- Plastics Material For DPT Iv SemDocument49 pagesPlastics Material For DPT Iv SemMohsin Alam100% (2)
- Thermoplastic Materials Engineering PlasticsDocument62 pagesThermoplastic Materials Engineering PlasticsFranzMig100% (1)
- Polymer PropertiesDocument23 pagesPolymer PropertiesNugroho Faris SudrajatNo ratings yet
- Polimers PDFDocument71 pagesPolimers PDFomer faruqeNo ratings yet
- The 3designers: Our 3D Printed Components From Carbon and Silicon CarbideDocument16 pagesThe 3designers: Our 3D Printed Components From Carbon and Silicon CarbideGanda PrajaNo ratings yet
- Chain FlexibilityDocument38 pagesChain FlexibilityNilesh Patil100% (1)
- Aggregates 5Document33 pagesAggregates 5SHALINI SOLANKENo ratings yet
- Review On CarbotaniumDocument20 pagesReview On CarbotaniumSahil DalalNo ratings yet
- A1120897415 23418 4 2018 PolymersDocument43 pagesA1120897415 23418 4 2018 PolymersKushNo ratings yet
- Casting L18Document10 pagesCasting L18Pranav KochetaNo ratings yet
- 2 Engineering Plastics - PPTDocument28 pages2 Engineering Plastics - PPTApoorva MNNo ratings yet
- An Engineers Guide To Specify The Right ThermoplasticDocument63 pagesAn Engineers Guide To Specify The Right ThermoplasticChithiran CullenNo ratings yet
- Scientific Study On Tension Reel Poly Urethane Sleeve2Document10 pagesScientific Study On Tension Reel Poly Urethane Sleeve2Anonymous pC7MGONo ratings yet
- Plastic Materials For Lenses: Noeh O. Fernandez JR., OD, MATSDocument44 pagesPlastic Materials For Lenses: Noeh O. Fernandez JR., OD, MATSDeitherAlforqueNo ratings yet
- Glass Reinforced Plastic PPTXDocument43 pagesGlass Reinforced Plastic PPTXTRISTAR TEKZONENo ratings yet
- Different Industrial PolymersDocument22 pagesDifferent Industrial PolymersSHYAMNo ratings yet
- Amorphous and Semi-Crystalline Engineering Thermoplastics: Materials, Properties and ApplicationsDocument30 pagesAmorphous and Semi-Crystalline Engineering Thermoplastics: Materials, Properties and Applicationsjesus MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Biobased Materials For Paper Coating: Charles P. Klass Klass Associates Inc. Redington Beach, FLDocument32 pagesBiobased Materials For Paper Coating: Charles P. Klass Klass Associates Inc. Redington Beach, FLlucy.hughesNo ratings yet
- Concrete: CE F230 Civil Engineering MaterialsDocument22 pagesConcrete: CE F230 Civil Engineering Materialsvasu khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Glass Reinforced Plastic PPTXDocument43 pagesGlass Reinforced Plastic PPTXSatyam LakheraNo ratings yet
- Pavement Materials: Module 3, Lecture 5 Physical Properties of Bitumen (Part 3)Document21 pagesPavement Materials: Module 3, Lecture 5 Physical Properties of Bitumen (Part 3)Siva Rama Krishna UppuluriNo ratings yet
- 3 - Equations of Change For Isothermal SystemsDocument29 pages3 - Equations of Change For Isothermal SystemsAdheep DasNo ratings yet
- Amorphous and Semi-Crystalline Engineering Thermoplastics: Materials, Properties and ApplicationsDocument29 pagesAmorphous and Semi-Crystalline Engineering Thermoplastics: Materials, Properties and ApplicationsabhidssNo ratings yet
- Alkylation, Isomerization and Polymerization: BITS PilaniDocument25 pagesAlkylation, Isomerization and Polymerization: BITS PilaniHritik LalNo ratings yet
- Mse 470 S20 L10-11 PDFDocument24 pagesMse 470 S20 L10-11 PDFAndre VictorNo ratings yet
- Design For Plastic Processing: Group 1 Faisal Bin Abd. Nasir Gan Yin Ting Habibah Binti Abd. MutallibDocument24 pagesDesign For Plastic Processing: Group 1 Faisal Bin Abd. Nasir Gan Yin Ting Habibah Binti Abd. MutallibKelly GanNo ratings yet
- LPLCDocument19 pagesLPLCTahira AzamNo ratings yet
- Thermoplastics: Submitted By:)Document15 pagesThermoplastics: Submitted By:)Nikhil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Los Polymeros en El Control de La CorrosionDocument11 pagesLos Polymeros en El Control de La Corrosionhenry307No ratings yet
- 9 Types of PolymersDocument28 pages9 Types of PolymersLahiru JananjayaNo ratings yet
- Repair Materials: Systems and MethodsDocument40 pagesRepair Materials: Systems and Methodsapoorv mishraNo ratings yet
- High Performance Thermoplastics: Materials, Properties and ApplicationsDocument40 pagesHigh Performance Thermoplastics: Materials, Properties and ApplicationsbrotherNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices 05-08-2014: BITS Pilani, K K Birla Goa CampusDocument23 pagesElectronic Devices 05-08-2014: BITS Pilani, K K Birla Goa CampusJeswin EldhoNo ratings yet
- Amorphous and Semi-Crystalline Commodity Thermoplastics: Materials, Properties and ApplicationsDocument35 pagesAmorphous and Semi-Crystalline Commodity Thermoplastics: Materials, Properties and ApplicationsrajkalmekarNo ratings yet
- Polymer EngineeringDocument16 pagesPolymer EngineeringMegaraj ReddyNo ratings yet
- Lecture On FC VLiso Trieste 2020Document39 pagesLecture On FC VLiso Trieste 2020Umashankar SNo ratings yet
- 3 Poetry - AK RamanujanDocument5 pages3 Poetry - AK RamanujanUmashankar SNo ratings yet
- Observations: BITS Pilani, K K Birla Goa CampusDocument10 pagesObservations: BITS Pilani, K K Birla Goa CampusUmashankar SNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting TM and TG: BITS Pilani, K K Birla Goa CampusDocument11 pagesFactors Affecting TM and TG: BITS Pilani, K K Birla Goa CampusUmashankar SNo ratings yet