67% found this document useful (3 votes)
4K views3 pagesAsa Class
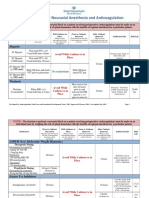
The document describes the ASA physical status classification system, which provides a common language to describe a patient's physiological status prior to surgery. The 6-level classification system considers a patient's age, functional capacity, and medical comorbidities to determine their ASA status, ranging from ASA I (a normal healthy patient) to ASA VI (a brain-dead patient). Examples are given of common medical conditions and their corresponding ASA physical status based on disease severity and control.
Uploaded by
Priska Gusti WulandariCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
67% found this document useful (3 votes)
4K views3 pagesAsa Class
The document describes the ASA physical status classification system, which provides a common language to describe a patient's physiological status prior to surgery. The 6-level classification system considers a patient's age, functional capacity, and medical comorbidities to determine their ASA status, ranging from ASA I (a normal healthy patient) to ASA VI (a brain-dead patient). Examples are given of common medical conditions and their corresponding ASA physical status based on disease severity and control.
Uploaded by
Priska Gusti WulandariCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- ASA Physical Status Classification Overview: Introduces the ASA physical status classification and general categories ranging from 'healthy' to 'declared brain dead'.
- Examples of ASA Physical Status Classification - Part 1: Provides examples for ASA physical status classification focusing on physiological status including CVS, RS, and CNS.
- Examples of ASA Physical Status Classification - Part 2: Continues examples of ASA classification with focus on endocrine, GI, hematology, renal, and other systems.