0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views2 pagesUnderstanding Physical and Chemical Properties
This document discusses key concepts in general chemistry including:
- Physical and chemical properties as well as physical and chemical changes
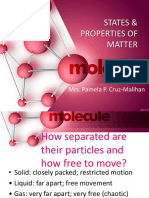
- The three states of matter: solids, liquids, and gases and their characteristics
- Mixtures and pure substances
- Common separation techniques used in chemistry like evaporation, distillation, and filtration
- Classification of matter as pure substances or mixtures that can be either homogeneous or heterogeneous
- Significant figures rules for determining precision of measurements
Uploaded by
Davis PasuquinCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views2 pagesUnderstanding Physical and Chemical Properties
This document discusses key concepts in general chemistry including:
- Physical and chemical properties as well as physical and chemical changes
- The three states of matter: solids, liquids, and gases and their characteristics
- Mixtures and pure substances
- Common separation techniques used in chemistry like evaporation, distillation, and filtration
- Classification of matter as pure substances or mixtures that can be either homogeneous or heterogeneous
- Significant figures rules for determining precision of measurements
Uploaded by
Davis PasuquinCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd