Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HERF Notes
Uploaded by
kreddy95054Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HERF Notes
Uploaded by
kreddy95054Copyright:
Available Formats
High Energy Rate Forming (HERF) Limitations
• Highly skilled personnel are required from design to execution.
• It can be used to form a wide variety of metals, difficult • Not suitable to highly brittle materials
to form materials like Titanium and Tungsten alloys, can • Source of energy (chemical explosive or electrical) must be
be deformed under high strain rates. handled carefully.
• Dies need to be much bigger to withstand high energy rates and
• applied a large amount of energy in a very short time shocks and to prevent cracking.
interval • Controlling the application of energy is critical as it may crack
• Large parts can be easily formed by this technique. the die or work.
Applications
• Accuracy of the objects is very high due to no elastic
• In ship building – to form large plates (up to 25 mm thick).
recovery
• Bending thick tubes/ pipes (up to 25 mm thick).
• Complex shapes/profiles can be made much easily, as • Elliptical domes used in space applications.
compared to conventional forming. • Cladding of two large plates of dissimilar metals
Explosive Forming • The work is firmly supported on the die and the die cavity is
evacuated.
• A definite quantity of explosive is placed suitably in water
medium at a definite stand off distance from the work.
• TNT and Dynamites for high energy and gun powder for low
energy is used
• On detonation of the explosive charge, a pressure pulse (or a
shock wave) of very high intensity is produced.
• When the pressure pulse impinges against the work (plate or
sheet) metal is deformed into the die with a high velocity of
around 120 m/s.
• Used for parts of thick materials.
Applications:
Aerospace, aircraft industries, Ship building, Elliptical domes in
space applications, etc.
• A sudden electrical discharge in the form of sparks is produced
Electro hydraulic Forming between electrodes and this discharge produces a shock wave in
the water medium.
• This shock wave deforms the work and collapses it into the die.
• The characteristics of this process are similar to those of
explosive forming.
• The major difference, however, is that a chemical explosive is
replaced by a capacitor bank, which stores the electrical energy.
• The capacitor is charged through a charging circuit.
• When the switch is closed, a spark is produced between
electrodes and a shock wave or pressure pulse is created.
• The energy released and peak pressure is much lesser than
explosive forming but easier and safer
Applications:
cone and other shapes and bulging operations in thinner and small
works.
• The electrical energy is stored in the capacitor bank
Electromagnetic forming
• The tubular work piece is mounted on a mandrel having the die
OR
cavity to produce shape on the tube.
Magnetic pulse forming
• A primary coil is placed around the tube and mandrel assembly.
• The coil produces a varying magnetic field around it.
• In the tube a secondary current is induced, which creates its own
magnetic field in the opposite direction.
• The directions of these two magnetic fields oppose one another and
hence the rigidly held coil repels the work into the die cavity.
• The process is most effective for relatively thin materials and
tubes(0.25 to 1.25 mm thick)
• Work piece must be electrically conductive but need not be
magnetic.
Applications:
Crimping of coils, tubes, wires Bending of tubes into complex shapes
Bulging of thin tubes.
Petro-Forging
OR • In this process, the stored chemical energy of a
Petro-Forge Forming hydrocarbon, like petrol or diesel is utilized to move
the dies at very high velocity
• The principle of working is just similar to I.C engine
• It is a piston cylinder- arrangement and a piston
drives a ram and a die.
• After air fuel mixture is ignited in the combustion
chamber pressure increases by 5 to 7 times which
brakes the seal and the high pressure gases act on
the top face of the piston
• The piston ram and die are accelerated at a very
rapid rate and strike up to 250 m/s
Assertion (A) : In magnetic pulse‐forming method,
magnetic field produced by eddy currents is used to
create force between coil and work piece.
Reason (R) : It is necessary for the work piece material
to have magnetic properties.
• Both A and R are individually true and R is the
correct explanation of A
• Both A and R are individually true but R is NOT the
correct explanation of A
• A is true but R is false
• A is false but R is true
You might also like
- HERFDocument11 pagesHERFflyingz2810No ratings yet
- HERFDocument6 pagesHERFRupesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Subtopic 6 High Velocity NotesDocument22 pagesSubtopic 6 High Velocity NotesKipkirui YegoNo ratings yet
- High Energy Rate Forming ProcessesDocument47 pagesHigh Energy Rate Forming ProcessesArun SrivastanNo ratings yet
- Unconventional FormingDocument16 pagesUnconventional FormingBrijesh VermaNo ratings yet
- HERFDocument16 pagesHERFYateesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- PC-ME701 Class2 15092021 EBMDocument23 pagesPC-ME701 Class2 15092021 EBMDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- ADVANCED MATERIALS PROCESSING TECHNIQUES Unit-4Document74 pagesADVANCED MATERIALS PROCESSING TECHNIQUES Unit-4Ishaan ThakerNo ratings yet
- Module #0: Reading ListDocument27 pagesModule #0: Reading Listkamel touilebNo ratings yet
- 6 - Breakdown in Solid and Liquid DielectricDocument53 pages6 - Breakdown in Solid and Liquid Dielectricatik jawadNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Class 1Document9 pagesModule 3 Class 1Nikhil SekharanNo ratings yet
- Mri MidtermsDocument13 pagesMri MidtermsJerick JusayNo ratings yet
- AMP (MIN572) Lecture 3 FormingDocument46 pagesAMP (MIN572) Lecture 3 FormingNAMAN AGARWALLANo ratings yet
- CurrentDocument10 pagesCurrentSalikNo ratings yet
- Welding Problems and Defects - Causes and Remedies: Deformation Arc Blow SpatterDocument3 pagesWelding Problems and Defects - Causes and Remedies: Deformation Arc Blow Spatterdselvakuu50% (2)
- Damping System in BuildingsDocument17 pagesDamping System in BuildingsASHISH MAHERIYANo ratings yet
- FuseelcbDocument24 pagesFuseelcbMahbub KhanNo ratings yet
- UEEEL0025 LPP 1 TX TQGC v1Document165 pagesUEEEL0025 LPP 1 TX TQGC v1hx5kwznmhqNo ratings yet
- Electroslag Welding: Operating PrincipleDocument5 pagesElectroslag Welding: Operating Principlesomashutosh7671No ratings yet
- High EnergyDocument14 pagesHigh EnergyGautam KocherNo ratings yet
- J. T. Mahajan Polytechnic, Faizpur: Electric Discharge Machining (EDM)Document19 pagesJ. T. Mahajan Polytechnic, Faizpur: Electric Discharge Machining (EDM)ShubhamNo ratings yet
- Advanced Structural Dynamic: Subject of PresentationDocument27 pagesAdvanced Structural Dynamic: Subject of PresentationSaurabh PednekarNo ratings yet
- Transformer: Construction, Principle of Operation, EMF EquationDocument10 pagesTransformer: Construction, Principle of Operation, EMF EquationKrishnaNo ratings yet
- DC GeneratorsDocument6 pagesDC GeneratorsLord8 MatiraNo ratings yet
- Production of Magnetic FieldDocument7 pagesProduction of Magnetic FieldSeenipandian RaviNo ratings yet
- Plasma Arc Machining - Lect 2Document17 pagesPlasma Arc Machining - Lect 2sachhpNo ratings yet
- ECEG 4123 Electrical Machines: ConstructionDocument15 pagesECEG 4123 Electrical Machines: ConstructionmebrahtenNo ratings yet
- YoucanDocument31 pagesYoucanananda narayananNo ratings yet
- Understanding Lightning ProtectionDocument67 pagesUnderstanding Lightning Protectionsatish reddyNo ratings yet
- Mri Instrumentation: Roshinee R TripathiDocument35 pagesMri Instrumentation: Roshinee R TripathiTHE GR8 HUBNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document11 pagesModule 5Jan Renn ArleNo ratings yet
- Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) : By: 1602-031 022 024 032 046 048 Submitted to:Dr.S.B.MISHRADocument35 pagesElectrical Discharge Machining (EDM) : By: 1602-031 022 024 032 046 048 Submitted to:Dr.S.B.MISHRAmanish kumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document18 pagesLecture 4Ap kowshikNo ratings yet
- MF F222 Joining ProcessesDocument104 pagesMF F222 Joining ProcessesKislay TiwaryNo ratings yet
- Blu-Ray Disc: Submitted by Vaibhav Tripathi SEM Mechanical Submitted To Mr. DharamDocument16 pagesBlu-Ray Disc: Submitted by Vaibhav Tripathi SEM Mechanical Submitted To Mr. Dharamvbhv_tripathi14No ratings yet
- Lecture 09 Impact and FractureDocument20 pagesLecture 09 Impact and Fractureantoine demeireNo ratings yet
- EET DC Machines 05sDocument8 pagesEET DC Machines 05sSachin RohillaNo ratings yet
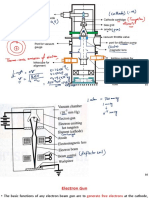
- Tungsten Filament Which Is Heated, Freeing Electrons.: - The Electron Beam Gun Has ADocument13 pagesTungsten Filament Which Is Heated, Freeing Electrons.: - The Electron Beam Gun Has APrashant PuriNo ratings yet
- Machine SetupDocument3 pagesMachine SetupBiswadeep Roy ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Electric Discharge Machining (Edm) BY: Dr. Manas Das Assistant ProfessorDocument40 pagesElectric Discharge Machining (Edm) BY: Dr. Manas Das Assistant ProfessorSrinivasanNo ratings yet
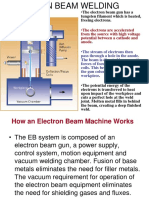
- Electron Beam Machining - Lect 5Document23 pagesElectron Beam Machining - Lect 5sachhpNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation: Roshinee R TripathiDocument33 pagesInstrumentation: Roshinee R TripathiTHE GR8 HUBNo ratings yet
- High Energy Rate Forming (HERF) : Muhammed LabeebDocument15 pagesHigh Energy Rate Forming (HERF) : Muhammed LabeebAmbarish MajiNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic WeldingDocument4 pagesUltrasonic WeldingDarryl007No ratings yet
- Lead Extrusion DamperDocument1 pageLead Extrusion Damperoscargon19No ratings yet
- Advanced Machining Processes - Module 3 Part 1Document33 pagesAdvanced Machining Processes - Module 3 Part 1Kenneth C.LinojNo ratings yet
- Edm PDFDocument32 pagesEdm PDFPrashantJangidNo ratings yet
- Ignition System FinalDocument11 pagesIgnition System Finalmanesamarpit2No ratings yet
- Transformer IntenshipDocument26 pagesTransformer IntenshipVivek SinghNo ratings yet
- "Lightning Arrester": Seminar Report ONDocument14 pages"Lightning Arrester": Seminar Report ONDev KumarNo ratings yet
- EDMDocument60 pagesEDMHarjot SinghNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document29 pagesLecture 5FarwaNo ratings yet
- EBM - (Electron Beam Machining)Document11 pagesEBM - (Electron Beam Machining)prankur giriNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection and Switchgear: Fundamentals of Protective Relaying VDocument17 pagesPower System Protection and Switchgear: Fundamentals of Protective Relaying VSampath AnbuNo ratings yet
- Advanced Manufacturing Technology (PC-ME701)Document23 pagesAdvanced Manufacturing Technology (PC-ME701)Deepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam Machining - Lect 4Document28 pagesElectron Beam Machining - Lect 4sachhpNo ratings yet
- Edm ReportDocument47 pagesEdm ReportMr PotatoNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Discharges - Magnetohydrodynamics - X-Rays - UltrasonicsFrom EverandCapacitor Discharges - Magnetohydrodynamics - X-Rays - UltrasonicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Insulation Co-ordination in High-voltage Electric Power SystemsFrom EverandInsulation Co-ordination in High-voltage Electric Power SystemsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
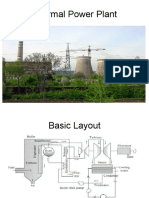
- Thermal Power PlantDocument29 pagesThermal Power Plantshamna AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Activated Sludge - Kinetic ModelDocument19 pagesActivated Sludge - Kinetic ModelDevendra SharmaNo ratings yet
- Module - 3 and 4Document72 pagesModule - 3 and 4Karthik A KulalNo ratings yet
- Central Mine Planning and Design Institute LimitedDocument6 pagesCentral Mine Planning and Design Institute LimitedTriptiNo ratings yet
- Colorimeter NewDocument22 pagesColorimeter NewKarthik RajaNo ratings yet
- Tile Adhesive Standards and Their Relevance For Tile InstallationDocument6 pagesTile Adhesive Standards and Their Relevance For Tile InstallationAhmadAlsekaweNo ratings yet
- 93234700-4702 Monolec PDFDocument6 pages93234700-4702 Monolec PDFDeltalube TangerangNo ratings yet
- Formulae and Oxidation NumbersDocument14 pagesFormulae and Oxidation NumbersDoc_CrocNo ratings yet
- EPCSC02 Staff Wegnerj Current Classes Int. Chem-Phys ICP Labs-Activities 11.6 Buoyancy PhET Lab AnswersDocument2 pagesEPCSC02 Staff Wegnerj Current Classes Int. Chem-Phys ICP Labs-Activities 11.6 Buoyancy PhET Lab AnswersAsa Ka50% (2)
- 6th Semester Project PosterDocument1 page6th Semester Project PosterJoydeep NaskarNo ratings yet
- KSSM Science Form 4 Chapter 9 9.1Document47 pagesKSSM Science Form 4 Chapter 9 9.1TSE100% (1)
- Sds Caustic SodaDocument8 pagesSds Caustic Sodaabil khausarNo ratings yet
- Infrared Technologies For Defence Systems - DRDO DSJDocument2 pagesInfrared Technologies For Defence Systems - DRDO DSJmercy calloNo ratings yet
- RADIOIMMUNOASSAYDocument4 pagesRADIOIMMUNOASSAYJansen MunioNo ratings yet
- Acoustics 4Document24 pagesAcoustics 4That GuyNo ratings yet
- Heat FlowDocument22 pagesHeat FlowIshita MongaNo ratings yet
- Fluid I - Lec 3 and 4 - ProductionDocument34 pagesFluid I - Lec 3 and 4 - Productionamr mohamedNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument10 pagesFormula SheetHuraiza AsifNo ratings yet
- BoQ-Beam Retrofitting Works LandTDocument2 pagesBoQ-Beam Retrofitting Works LandTAbhijit KarpeNo ratings yet
- The Charge of The ElectronDocument3 pagesThe Charge of The ElectronSaeed AlMheiriNo ratings yet
- B 6a Aircraft Materials and Corrosion SRDocument156 pagesB 6a Aircraft Materials and Corrosion SRSumit SamanyaNo ratings yet
- Interphase Mass TransferDocument55 pagesInterphase Mass TransferRishab SrivatsaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 1: Volumetric Properties of Pure FluidsDocument24 pagesThermodynamics 1: Volumetric Properties of Pure FluidsHabib Faisal Yahya100% (1)
- Sample Exit EXAM Perpared by Abel MDocument6 pagesSample Exit EXAM Perpared by Abel MTadesse MegersaNo ratings yet
- Laminar Premixed FlamesDocument84 pagesLaminar Premixed FlamesKoharudin SyahNo ratings yet
- Right Hand RuleDocument14 pagesRight Hand RuleTyra Christine Victorio FloresNo ratings yet
- Tinogard Q TdsDocument4 pagesTinogard Q TdsMarlon2370100% (1)
- Physics 715 HW 3Document18 pagesPhysics 715 HW 3Juan Manuel Orozco HenaoNo ratings yet
- Seven Stars Solar 20181107Document23 pagesSeven Stars Solar 20181107msagaliwaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/42Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/42septinNo ratings yet