Professional Documents
Culture Documents
L1 Handout
L1 Handout
Uploaded by
librarianOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
L1 Handout
L1 Handout
Uploaded by
librarianCopyright:
Available Formats
Plot: Plot is the sequence of events that make up a story.
1. A plot can be used to create suspense and tension in a play. For example, in Romeo and Juliet, the
audience is kept in suspense as the two lovers try to escape their fate by eloping.
2. A plot can also be used to illustrate a moral lesson. For example, in The Crucible, the story of the Salem
Witch Trials is used to show the consequences of hysteria and false accusations.
Character: Character is a fictional person in a play or story.
1. Characters can be used to represent certain aspects of human nature. For example, in A Streetcar Named
Desire, Blanche Dubois is used to represent the fragility of the human psyche.
2. Characters can also be used to drive the plot forward. For example, in Hamlet, the audience follows
Hamlet on his quest for revenge against Claudius, which drives the plot of the play.
Dialogue: Dialogue is the words spoken by the characters in a play.
1. Dialogue can be used to reveal character traits and motivations. For example, in Macbeth, Lady
Macbeth’s dialogue reveals her ambition and her hunger for power.
2. Dialogue can also be used to reveal plot points. For example, in Othello, Iago’s dialogue reveals his plan
to manipulate Othello into believing that Desdemona is unfaithful.
Comedy: Comedy is a type of theatre that is intended to be humorous.
1. Comedy often uses satire to make its point. For example, in The Importance of Being Earnest, Oscar
Wilde uses satire to mock social conventions and hypocrisies. 2. Comedy also often uses physical humor
and exaggeration to create its effects. For example, in The Producers, the characters use physical humor to
poke fun at the characters and the plot.
Tragedy: Tragedy is a type of theatre that typically focuses on the downfall of a protagonist due to a
character flaw or a combination of external and internal forces.
1. Tragedy often uses heightened language to illustrate the characters’ emotions. For example, in King Lear,
Shakespeare uses poetic language to illustrate the characters’ pain and suffering.
2. Tragedy also often uses foreshadowing to hint at the eventual downfall of the protagonist. For example, in
Oedipus Rex, the audience is given clues throughout the play that hint at Oedipus’ fate.
Farce: Farce is a type of theatre that relies on physical humor and exaggerated situations for its
effects.
1. Farce often uses mistaken identities to create its humor. For example, in Twelfth Night, Viola disguises
herself as a man, which leads to confusion and comedy.
2. Farce also often relies on wordplay and puns to create its humor. For example, in The Comedy of Errors,
the characters use wordplay to create confusion and comedy.
Melodrama: Melodrama is a type of theatre that relies on exaggerated characters, situations, and
emotions for its effects.
1. Melodrama often uses characters that are larger than life and have extreme emotions. For example, in A
Tale of Two Cities, the characters are often melodramatic and have extreme reactions to the events of the
story.
2. Melodrama also often relies on coincidences and dramatic ironies to create its effects. For example, in Les
Misérables, the characters’ lives are all intertwined in unexpected ways.
You might also like
- Definitions and Characteristics of DramaDocument8 pagesDefinitions and Characteristics of DramaDinda Hasibuan 00595% (19)
- Elements of DramaDocument15 pagesElements of DramaJoemar Furigay100% (1)
- What's Reading A Play Like?Document7 pagesWhat's Reading A Play Like?Amina ShahNo ratings yet
- DramaDocument4 pagesDramaJem DizonNo ratings yet
- DramaDocument13 pagesDramaemirtas0411No ratings yet
- Understanding Drama: 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorldDocument24 pagesUnderstanding Drama: 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The WorlddaphnieNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document9 pagesLesson 5Mary Joy AliviadoNo ratings yet
- Elements of DramaDocument9 pagesElements of Dramakarin02No ratings yet
- Elements of Drama1Document10 pagesElements of Drama1njheboieNo ratings yet
- Analysing A PlayDocument9 pagesAnalysing A PlayCristina SerranoNo ratings yet
- Elements of DramaDocument11 pagesElements of DramaAnna Leah ApalesNo ratings yet
- ELEMENTS of DRAMA Part 1Document8 pagesELEMENTS of DRAMA Part 1Maeann Malaquilla NaviaNo ratings yet
- Drama: Drama Is A Literary Composition Involving ConflictDocument6 pagesDrama: Drama Is A Literary Composition Involving ConflictElvin Nobleza PalaoNo ratings yet
- 4.1 History of DramaDocument4 pages4.1 History of Dramarahultripathi7447No ratings yet
- What Is DramaDocument6 pagesWhat Is DramaAurora LobigasNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of DramaDocument9 pagesCharacteristics of Dramaniluka welagedaraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Writing DramaDocument10 pagesLesson 6 - Writing DramaMargielane AcalNo ratings yet
- The Elements of DramaDocument36 pagesThe Elements of DramaPutro Bagus Wahida50% (2)
- English DramaDocument11 pagesEnglish DramaBood CloveNo ratings yet
- MAKALAH OF DRAMA by RizqyDocument18 pagesMAKALAH OF DRAMA by RizqyRizqy Eko PramonoNo ratings yet
- Literary D Evices & F Ig U Rative Lang U Ag e - Rom Eo & Juliet Exa MP LesDocument4 pagesLiterary D Evices & F Ig U Rative Lang U Ag e - Rom Eo & Juliet Exa MP LesRose CristalNo ratings yet
- DRAMADocument43 pagesDRAMAdian luthfiyati100% (2)
- HUM101-Finals (DRAMA)Document4 pagesHUM101-Finals (DRAMA)Rosemarie RinNo ratings yet
- DramaDocument21 pagesDramaRica CapaNo ratings yet
- Types of PlayDocument5 pagesTypes of PlayShielah Marie RequizNo ratings yet
- Types of PlayDocument5 pagesTypes of PlayShielah Marie RequizNo ratings yet
- Drama Is A Type of Literature Telling A Story, Which Is Intended To Be Performed To An AudienceDocument5 pagesDrama Is A Type of Literature Telling A Story, Which Is Intended To Be Performed To An AudienceJohanna Dapuyen MacaybaNo ratings yet
- ReplitDocument4 pagesReplitVic-Aljari RazonNo ratings yet
- DRAMADocument5 pagesDRAMAdollymay.palasanNo ratings yet
- Notes in Creative Writing FinalsDocument4 pagesNotes in Creative Writing FinalsJ4NV3N G4M1NGNo ratings yet
- What Is DramaDocument10 pagesWhat Is DramaAndrie PrabowoNo ratings yet
- Common Literary Elements PDFDocument6 pagesCommon Literary Elements PDFSajib DasNo ratings yet
- Text 2Document6 pagesText 2anisabunjaku48No ratings yet
- Dramatic TechniquesDocument12 pagesDramatic TechniquesJotika Rattan100% (1)
- Poly Aaisngmentffff PDFDocument20 pagesPoly Aaisngmentffff PDFMd Saidul IslamNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Lit. Reviewer MidtermDocument4 pages21st Century Lit. Reviewer MidtermMaria Ana Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- English DramaDocument26 pagesEnglish DramakrishaNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Dramatic ReadingDocument9 pagesGlossary of Dramatic ReadingSidra Nasir KhanNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter - Lesson 8 - Understanding DramaDocument12 pages4th Quarter - Lesson 8 - Understanding DramaJubilee May ZaragozaNo ratings yet
- 21st CENTURY LITERATURE MODULE 5Document9 pages21st CENTURY LITERATURE MODULE 5Reyman Andrade LosanoNo ratings yet
- Drama: Features of A PlayDocument4 pagesDrama: Features of A Playmahesh 0669No ratings yet
- World Literature About A PlayDocument3 pagesWorld Literature About A PlayNASNo ratings yet
- Elements of DramaDocument9 pagesElements of DramaFelicity Grace DalitNo ratings yet
- Drama: Drama Is A Literary Composition Involving Conflict, Action Crisis andDocument5 pagesDrama: Drama Is A Literary Composition Involving Conflict, Action Crisis andkalkayaqaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 DramaDocument5 pagesChapter 9 DramaCH ARL IENo ratings yet
- DramaDocument11 pagesDramaHasan AljburiNo ratings yet
- Outline in 21stDocument5 pagesOutline in 21stFrancis EricNo ratings yet
- GED11 - 14. DramaDocument6 pagesGED11 - 14. DramaKyle CepilloNo ratings yet
- DramaDocument10 pagesDramaMeshu QadirNo ratings yet
- 16th Century DramaDocument17 pages16th Century Dramashaymaa ZuhairNo ratings yet
- Romeo JulietDocument30 pagesRomeo Julietapi-252344608No ratings yet
- Introduction of Literature "Drama"Document6 pagesIntroduction of Literature "Drama"Anonymous yXYr6LkNo ratings yet
- Ujian Gendre Fundamental DramaDocument8 pagesUjian Gendre Fundamental DramaMylestari OfficialNo ratings yet
- TheaterDocument24 pagesTheaterShekinah FuentesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Contemporary LiteratureDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Contemporary LiteratureMarjorie M. Magcanta100% (1)
- Ringkasan DramaDocument6 pagesRingkasan DramaSilvi PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Study Guide for Decoding Romeo and Juliet: With Typical Questions and AnswersFrom EverandStudy Guide for Decoding Romeo and Juliet: With Typical Questions and AnswersNo ratings yet
- Study Guide for Decoding Hamlet: With Typical Questions and AnswersFrom EverandStudy Guide for Decoding Hamlet: With Typical Questions and AnswersNo ratings yet
- First Term Holiday Classes Timetable-1Document1 pageFirst Term Holiday Classes Timetable-1librarianNo ratings yet
- School Resources Special Offer FormDocument18 pagesSchool Resources Special Offer FormlibrarianNo ratings yet
- I Am A LeaderDocument6 pagesI Am A LeaderlibrarianNo ratings yet
- Biz A&M WS09022024Document3 pagesBiz A&M WS09022024librarianNo ratings yet
- Summary Note Business Documents Year 8 BusinessDocument1 pageSummary Note Business Documents Year 8 BusinesslibrarianNo ratings yet
- Stock Management Module 4Document5 pagesStock Management Module 4librarianNo ratings yet
- Chinh Thuc 2009-2010Document2 pagesChinh Thuc 2009-2010KetMaiNo ratings yet
- PCK 4Document5 pagesPCK 4Christine Lomeda VillaNo ratings yet
- 6 Ynu 7 U 7Document4 pages6 Ynu 7 U 7Packers49ersNo ratings yet
- Rules For Accentual PatternsDocument5 pagesRules For Accentual PatternsPearl100% (1)
- King Lear Thesis Statement BlindnessDocument8 pagesKing Lear Thesis Statement Blindnessbkx3abyc100% (2)
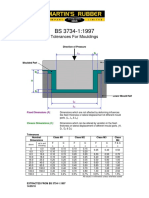
- Tolerances For MouldingsDocument1 pageTolerances For MouldingsAhmet HamamcıoğluNo ratings yet
- PEAC Module English8 Q1 PDFDocument82 pagesPEAC Module English8 Q1 PDFCamille Sison-Almirol100% (4)
- 10 Grammar, Vocabulary, and Pronunciation B: Grammar 1 Complete The Sentences Using The Present or Past PassiveDocument6 pages10 Grammar, Vocabulary, and Pronunciation B: Grammar 1 Complete The Sentences Using The Present or Past PassiveАнгелина Сущенко50% (2)
- Sample Lesson Exemplar - The Composition of The EarthDocument3 pagesSample Lesson Exemplar - The Composition of The EarthRommel DaysonNo ratings yet
- Ficha2 - Unidad 1 - Jer - 1°Document2 pagesFicha2 - Unidad 1 - Jer - 1°carlosfranciaavilaNo ratings yet
- SAP CRM Service - Tech Component RequirementsDocument33 pagesSAP CRM Service - Tech Component RequirementsSuresh MalisettyNo ratings yet
- MSP430™ Programming With The JTAG Interface: User's GuideDocument98 pagesMSP430™ Programming With The JTAG Interface: User's Guideagsan.algabh2718No ratings yet
- Bohr & Wheeler Fission Theory Calculation 4 March 2009: Z A 2 A ADocument22 pagesBohr & Wheeler Fission Theory Calculation 4 March 2009: Z A 2 A AAlexandre PereiraNo ratings yet
- Fun For Movers - UNIT 22Document40 pagesFun For Movers - UNIT 22anhnhu doanNo ratings yet
- Delta Publishing Games True or LieDocument1 pageDelta Publishing Games True or LiemcrisbvNo ratings yet
- JK LakshmiDocument1 pageJK Lakshmipatel vimalNo ratings yet
- Mohamad Sulaiman CVDocument2 pagesMohamad Sulaiman CVAlaa JamoosNo ratings yet
- Horn GRADE 7Document2 pagesHorn GRADE 7xaviergeorgeNo ratings yet
- Zoetmulder 1971 Indonesia Wayang As Philosophical ThemeDocument13 pagesZoetmulder 1971 Indonesia Wayang As Philosophical ThemeCatherine Bourdonneau TranNo ratings yet
- Principles of Macroeconomics 5th Edition Frank Test BankDocument25 pagesPrinciples of Macroeconomics 5th Edition Frank Test BankJeremySmithwrok100% (46)
- The Elite Among The Faster Khusus Al Khusus Sawm 2022Document15 pagesThe Elite Among The Faster Khusus Al Khusus Sawm 2022Salahuddin MuhammadNo ratings yet
- GCA Error MessagesDocument270 pagesGCA Error Messagesokokokst6kNo ratings yet
- DIN 4017 Equation For Bearing CapacityDocument86 pagesDIN 4017 Equation For Bearing CapacityamolhkNo ratings yet
- Bibliografie LiturgicaDocument27 pagesBibliografie LiturgicateologusNo ratings yet
- Teaching English in Algerian Middle School Coordinators Meeting Sept 29 2015Document4 pagesTeaching English in Algerian Middle School Coordinators Meeting Sept 29 2015Samir Bounab92% (25)
- Chapter 3 Screen DesignDocument29 pagesChapter 3 Screen DesignroNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Process SchedulingDocument100 pagesCH 5 Process SchedulingblablaNo ratings yet
- (Lecture - 7) Conditional SentencesDocument21 pages(Lecture - 7) Conditional SentencesN. W. FlannelNo ratings yet
- Rhapsody of Realities 11 May 2010Document2 pagesRhapsody of Realities 11 May 2010Sunny Umukoro50% (2)
- Unbiased LanguageDocument1,295 pagesUnbiased LanguageRameeza OmairNo ratings yet