Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Text 9723FF5B7B70 1
Uploaded by
ẞαɾαᴋ0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesImportant
Original Title
text-9723FF5B7B70-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentImportant
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesText 9723FF5B7B70 1
Uploaded by
ẞαɾαᴋImportant
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
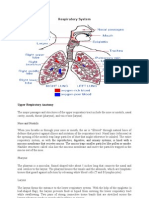
Gas Exchange - Humans
Gas exchange doesn't only happen in plants — it happens in humans too.
Oxygen goes into your bloodstream and you offload nasty 'orrible carbon dioxide...
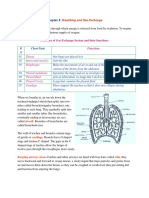
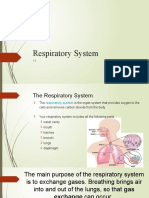
Alveoli Carry Out Gas Exchange in the Body
1)
The lungs contain millions and millions of little air sacs called alveoli where gas
exchange happens.
CO:
2) The blood passing next to the alveoli has just returned to the lungs from
alveolus
the rest of the body, so it contains lots of carbon dioxide and very little oxygen.
Oxygen diffuses out of the alveolus (high concentration) into the blood (low
concentration). Carbon dioxide diffuses out of the blood (high concentration) into
the alveolus (low concentration) to be breathed out.
blood capillary
body celle
3) When the blood reaches body cells, oxygen is released from the red blood cells
(where there's a high concentration) and diffuses into the body cells (where the
concentration is low).
4) At the same time, carbon dioxide diffuses out of the body cells (where there's a
high concentration) into the blood (where there's
blood capillary
a low concentration). It's then carried back to the lungs.
Alveoli are Specialised for Gas Exchange
1)
The huge number of microscopic alveoli gives the lungs an enormous surface area.
capillary, network
2)
There's a moist lining for gases to dissolve in.
3)
The alveoli have very thin walls — only one cell thick, so the gases don't have far
to diffuse.
4) They have a great blood supply to maintain a high concentration gradient.
5) The walls are permeable — so gases can diffuse across easily.
bronchiole
air in
small
-alveoli]
small vein
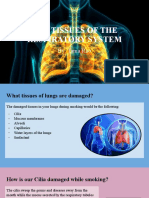
Smoking Tobacco Can Cause Quite a Few Problems
Smoking can severely affect your lungs and circulatory system. Here's how:
cilia
1) Smoking damages the walls inside the alveoli, reducing the surface area
mucus
for gas exchange and leading to diseases like emphysema.
Cell secreting mucus
The tar in cigarettes damages the cilia (little hairs) in your lungs and trachea.
These hairs, along with mucus, catch a load of dust and bacteria before they reach
the lungs. The cilia also help to keep the trachea clear by sweeping mucus back
towards the mouth. When these cilia are damaged, chest infections are more likely.
3) Tar also irritates the bronchi and bronchioles, encouraging mucus to be produced
which can't be cleared very well by damaged cilia — this causes smoker's cough and
chronic bronchitis.
4) The carbon monoxide in cigarette smoke reduces the amount of oxygen the blood
can carry.
To make up for this, heart rate increases - which leads to an increase in blood
pressure.
High blood pressure damages the artery walls, making the formation of blood clots
more likely.
This increases the risk of coronary heart disease (e.g. heart attacks).
5) Tobacco smoke also contains carcinogens - chemicals that can lead to cancer.
Alveoli - those guys are bags of fun...
The alveoli are super important in making sure that oxygen diffuses quickly enough
to supply all of our cells.
Q1
Give one way in which alveoli are specialised for gas exchange.
[1 mark]
Section 4 - Respiration and Gas Exchange
You might also like
- Quiz RespiratoryDocument123 pagesQuiz RespiratoryMedShare100% (23)
- Tetralogy of Fallot Case DiscussionDocument46 pagesTetralogy of Fallot Case DiscussionJoe Ha50% (2)
- Case Study COPDDocument16 pagesCase Study COPDRegine Cimafranca Macalaguing100% (5)
- Lung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandLung Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Gas Exchange PowerpointDocument53 pagesBreathing and Gas Exchange Powerpointapi-263357086100% (1)
- Physical Examination in PaediatricsDocument162 pagesPhysical Examination in PaediatricsUsman Ali100% (1)
- Learning Activity Worksheet Science 9 Q1 Weeks 1 2Document7 pagesLearning Activity Worksheet Science 9 Q1 Weeks 1 2ar0411No ratings yet
- L5 Surface Anatomy & DiaphragmDocument45 pagesL5 Surface Anatomy & DiaphragmatefmoussaNo ratings yet
- COPD Case ICUDocument19 pagesCOPD Case ICUKim Vizcarra100% (1)
- F3 Chapter 2 RespirationDocument13 pagesF3 Chapter 2 RespirationJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- Case Study CopdDocument7 pagesCase Study CopdIrveen Joy RamirezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology CopdDocument15 pagesAnatomy and Physiology CopdAssenav May100% (3)
- CIE A Level Biology - Gas ExchangeDocument14 pagesCIE A Level Biology - Gas ExchangeSaraNo ratings yet
- NCP For HepatitisDocument6 pagesNCP For Hepatitisorca0767% (3)
- Form 3 ScienceDocument10 pagesForm 3 ScienceCK100% (1)
- Script PDFDocument2 pagesScript PDFSiyul LEE [08R09]No ratings yet
- Respiration: 1.1 Human Breathing MechanismDocument3 pagesRespiration: 1.1 Human Breathing MechanismHalizah RamthanNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument4 pagesRespirationSiti NorhayatiNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Gas Exchange: RespirationDocument4 pagesBreathing and Gas Exchange: RespirationAbubakar Siddiq RaminNo ratings yet
- Breathing Is A Mechanical Process Where Oxygen Is Inhaled by Lungs andDocument9 pagesBreathing Is A Mechanical Process Where Oxygen Is Inhaled by Lungs andJamesShallowNo ratings yet
- The Human Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesThe Human Respiratory SystemChelsea EdwardsNo ratings yet
- LungsDocument3 pagesLungspinopinguinNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes - Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesBiology Notes - Respiratory SystemnoorbdeirNo ratings yet
- Smoking and Lung DamageDocument11 pagesSmoking and Lung DamageAbdulHadi IrfanNo ratings yet
- BreathingDocument5 pagesBreathingKekeletsoNo ratings yet
- Model of Lungs ExplainationDocument2 pagesModel of Lungs ExplainationAnthony HoseinNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesRespiratory SystemSudip NeupaneNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesThe Respiratory SystemmvslikavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Science Form 1Document19 pagesChapter 1 Science Form 1Che SalNo ratings yet
- Science Senior 2Document4 pagesScience Senior 2ajichristianbaniadamNo ratings yet
- Lec 17 Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesLec 17 Circulatory SystemEnmuskNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument8 pagesRespirationAwn Tarek AmmariNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DisorderDocument15 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disordercrabby_chicNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Science Chapter 1Document25 pagesForm 3 Science Chapter 1Mukilan MurugasanNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesThe Respiratory SystemChikuta ShingaliliNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System AssignmentDocument3 pagesRespiratory System AssignmentzainaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System AssignmentDocument3 pagesRespiratory System AssignmentzainaNo ratings yet
- Gas ExchangeDocument6 pagesGas Exchangerasha nadaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesRespiratory System Structure and FunctionRavi BhollahNo ratings yet
- 9 RespirationDocument3 pages9 RespirationKavin ManimaranNo ratings yet
- Harder: EasierDocument6 pagesHarder: Easieriffi_saeed123No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology CopdDocument15 pagesAnatomy and Physiology CopdAssenav MayNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesRespiratory SystemCraigNo ratings yet
- The Human Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesThe Human Respiratory SystemnekromadavidNo ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument4 pagesRespiration NotesJana AldourNo ratings yet
- The Tissues of The Respiratory System: By: Tania RaoDocument7 pagesThe Tissues of The Respiratory System: By: Tania RaoTania RaoNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DisorderDocument11 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DisorderOlivelhynn BernaldoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Respiration: 1.1 Human Breathing MechanismDocument7 pagesChapter 1: Respiration: 1.1 Human Breathing Mechanismsufi_sobariah8044No ratings yet
- Air We BreathDocument2 pagesAir We BreathLorraineNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Case StudyDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Case StudyRj MagpayoNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange and SmokingDocument6 pagesGas Exchange and Smokingarrowphoto10670340nasimurNo ratings yet
- COPD May Include Diseases That Cause Airflow Obstruction (E.g., Emphysema, ChronicDocument13 pagesCOPD May Include Diseases That Cause Airflow Obstruction (E.g., Emphysema, Chronicmaxmay07No ratings yet
- Gas Exchange Presentation4 Ambot1Document13 pagesGas Exchange Presentation4 Ambot1Archel GalorportNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration - Glucose + Oxygen Water + EnergyDocument3 pagesAerobic Respiration - Glucose + Oxygen Water + EnergyEsteban OrtegaNo ratings yet
- 3.6 Respiratory SystemDocument11 pages3.6 Respiratory SystemJhonnyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Nose and NostrilsDocument8 pagesRespiratory System: Nose and NostrilsKabang MoaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Scs f3Document15 pagesChapter 1 Scs f3putridequenoNo ratings yet
- Causes: How Your Lungs Are AffectedDocument3 pagesCauses: How Your Lungs Are AffectedKalet GamayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Respiration 1.1 The Human Breathing MechanismDocument4 pagesChapter 1: Respiration 1.1 The Human Breathing MechanismWindy SanNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory System: When InhalingDocument4 pagesHuman Respiratory System: When InhalingMohanasundari MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Biology - Respiration & The Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesBiology - Respiration & The Respiratory SystemMegan TaylorNo ratings yet
- SMOKINGDocument15 pagesSMOKINGhamlet pinakleNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System 9Document23 pagesRespiratory System 9scaythereignNo ratings yet
- BreathingDocument5 pagesBreathingvictory IsaacNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange in The Mammalian Lungs: by Vytautas KontrimasDocument10 pagesGaseous Exchange in The Mammalian Lungs: by Vytautas KontrimascluendoNo ratings yet
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASESDocument7 pagesChapter 17 - BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASESprernatiwary508No ratings yet
- Biology 5 - Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesBiology 5 - Anatomy and PhysiologyCristal Jean BalucanNo ratings yet
- General ExaminationDocument5 pagesGeneral Examinationகௌசிக் வெNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of Gases Class 11 Study Notes 1Document8 pagesBreathing and Exchange of Gases Class 11 Study Notes 1Raj priyam UpadhyayaNo ratings yet
- Body Systems ReviewDocument19 pagesBody Systems ReviewJ15No ratings yet
- 10th Biology Solved MCQS (Bismillah) EditDocument19 pages10th Biology Solved MCQS (Bismillah) EditSohail Afzal100% (1)
- Module I - Lesson 2 - Respiratory System - PPT NotesDocument9 pagesModule I - Lesson 2 - Respiratory System - PPT NotesRobson ScozNo ratings yet
- Term 2 P7 Science WorkDocument61 pagesTerm 2 P7 Science WorkSamson KisenseNo ratings yet
- 4Hs 4TsDocument5 pages4Hs 4TsChui Yee WongNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 Learning Activity Sheet 5Document4 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Learning Activity Sheet 5Arjay CarolinoNo ratings yet
- Slide Referat Dr. EKoDocument16 pagesSlide Referat Dr. EKoekomujiNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilator: Nur Aina Athiraa Binti Azman Wan Sabrina Binti Wan Safuan Azkiyyah Wahida Binti DzulkifliDocument35 pagesMechanical Ventilator: Nur Aina Athiraa Binti Azman Wan Sabrina Binti Wan Safuan Azkiyyah Wahida Binti DzulkifliJia HuiNo ratings yet
- 9.1 BloodDocument29 pages9.1 Bloodangxl1c fl0w3rsNo ratings yet
- 41 Ev VTP CQZNXJKVK AH9 IDocument7 pages41 Ev VTP CQZNXJKVK AH9 INothingNo ratings yet
- 34 CirculationDocument27 pages34 Circulationapi-233777623No ratings yet
- Book 3Document373 pagesBook 3Vidhu YadavNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka-Wps OfficeDocument2 pagesDaftar Pustaka-Wps OfficeRezha July prakosoNo ratings yet
- 3 Surgery - Mediastinum and PleuraDocument6 pages3 Surgery - Mediastinum and PleuraCassey Koi FarmNo ratings yet
- Case Study Asthma Group 2Document17 pagesCase Study Asthma Group 2Kennedy PelicoNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument8 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasessuryababaNo ratings yet
- DR - Wahid Helmi Ped Rev PDFDocument2,088 pagesDR - Wahid Helmi Ped Rev PDFNatalia NatNo ratings yet
- Pathology For The Health Professions 5Th Edition Damjanov Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesPathology For The Health Professions 5Th Edition Damjanov Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFcrastzfeiej100% (8)
- Class X Science Pre Board Sample PaperDocument23 pagesClass X Science Pre Board Sample PaperNasla ShiyasNo ratings yet
- Ingles StudyDocument23 pagesIngles StudyMatiasUrraNo ratings yet